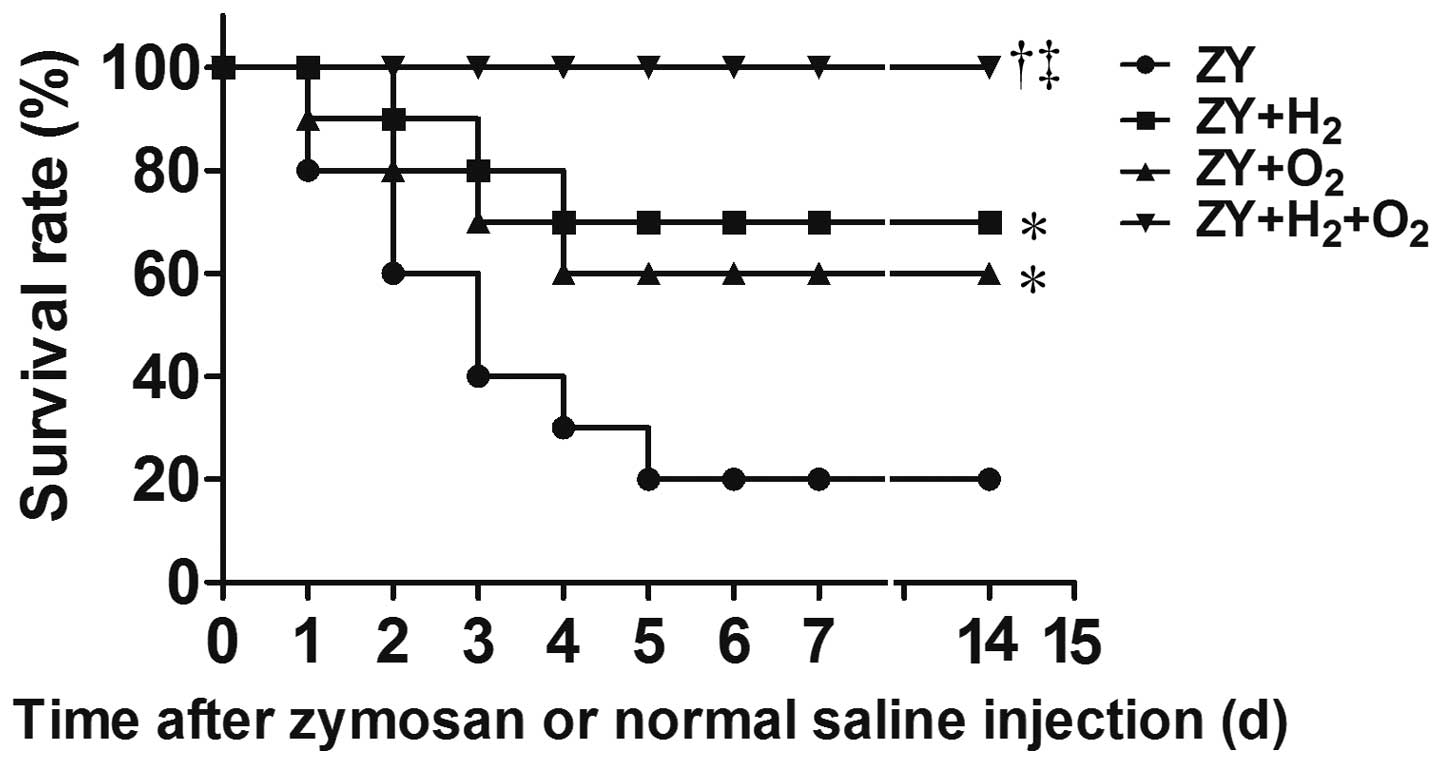
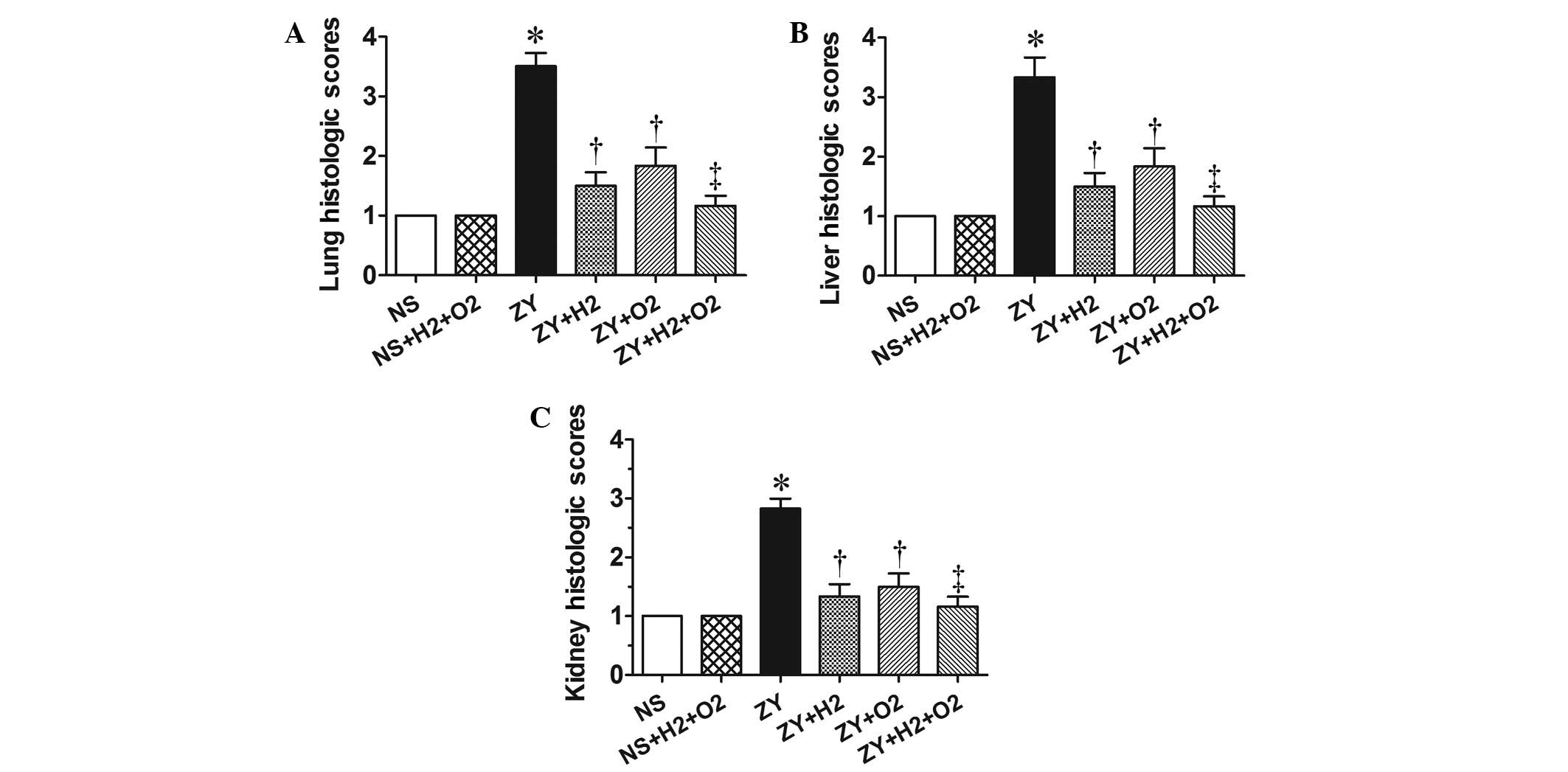
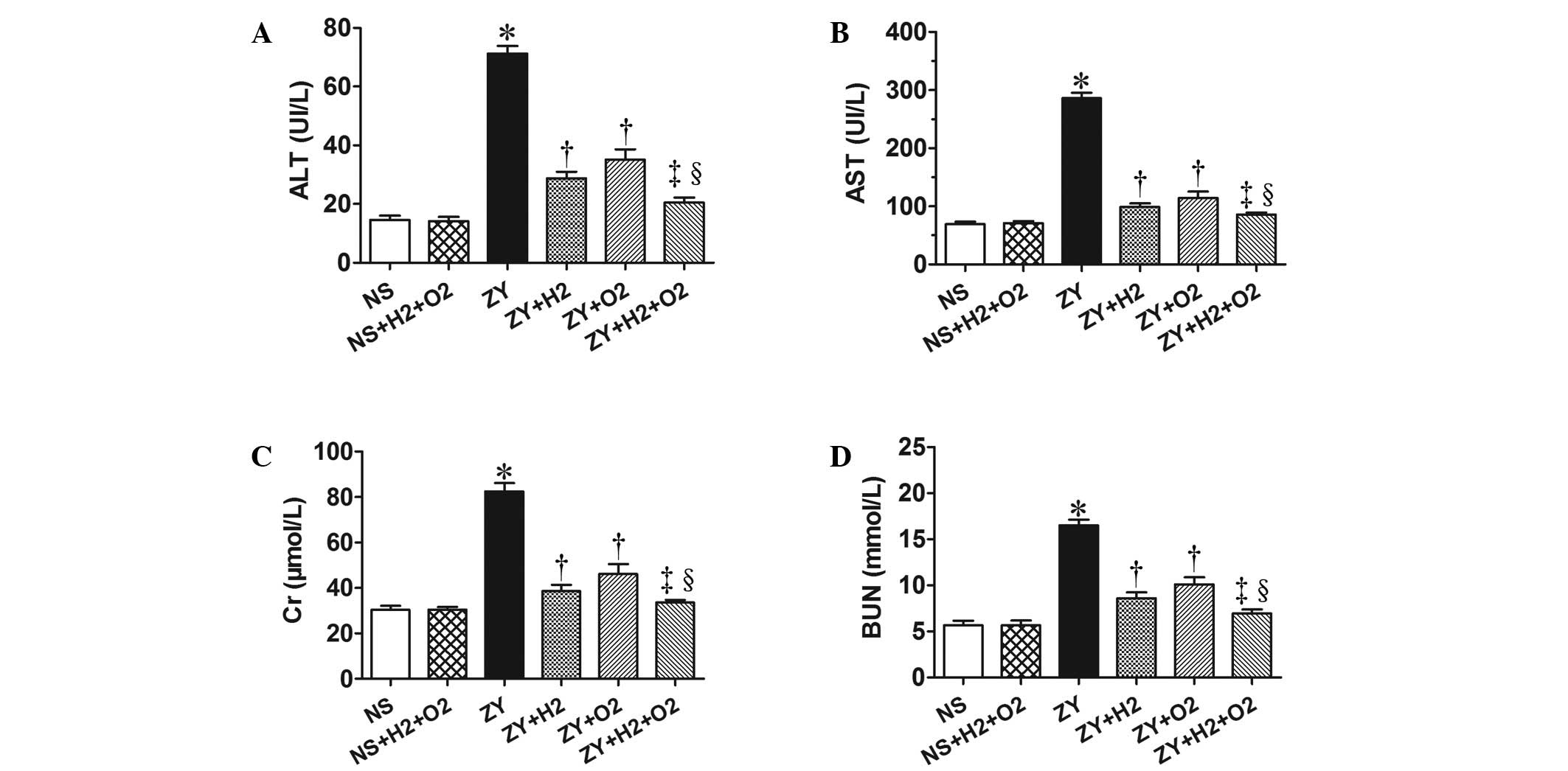
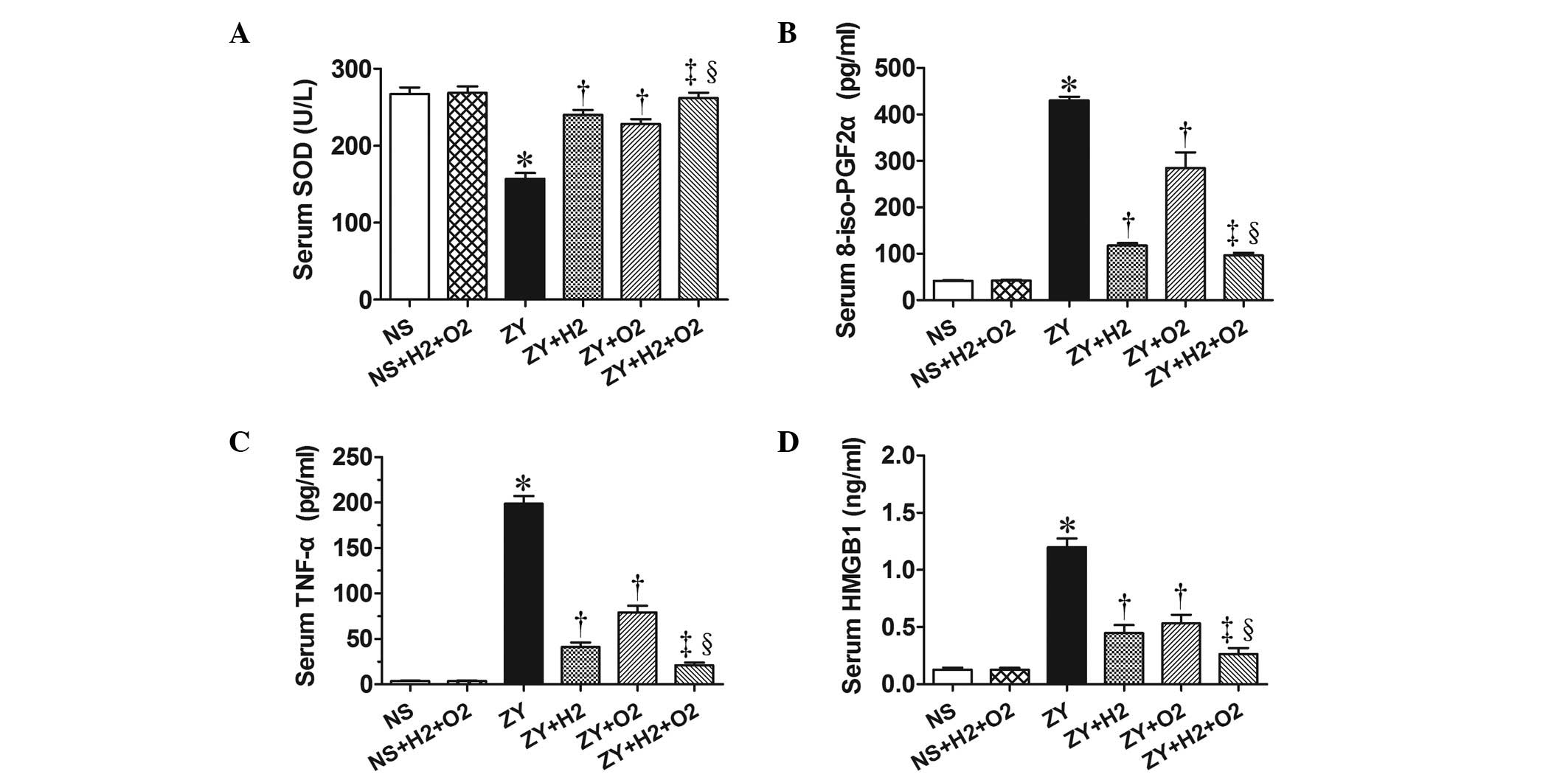
|
1
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. N Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shayevitz JR, Miller C, Johnson KJ and
Rodriguez JL: Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: End organ and
systemic inflammatory response in a mouse model of nonseptic
origin. Shock. 4:389–396. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hotchkiss RS and Karl IE: The
pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 348:138–150.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Asfar P, Calzia E, Huber-Lang M, Ignatius
A and Radermacher P: Hyperoxia during septic shock-Dr. Jekyll or
Mr. Hyde? Shock. 37:122–123. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Waisman D, Brod V, Rahat MA, Amit-Cohen
BC, Lahat N, Rimar D, Menn-Josephy H, David M, Lavon O, Cavari Y
and Bitterman H: Dose-related effects of hyperoxia on the lung
inflammatory response in septic rats. Shock. 37:35–102. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hauser B, Barth E, Bassi G, Simon F,
Gröger M, Oter S, Speit G, Ploner F, Möller P, Wachter U, et al:
Hemodynamic, metabolic and organ function effects of pure oxygen
ventilation during established fecal peritonitis-induced septic
shock. Crit Care Med. 37:2465–2469. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barth E, Bassi G, Maybauer DM, Simon F,
Gröger M, Oter S, Speit G, Nguyen CD, Hasel C, Möller P, et al:
Effects of ventilation with 100% oxygen during early hyperdynamic
porcine fecal peritonitis. Crit Care Med. 36:495–503. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hou L, Xie K, Li N, Qin M, Lu Y, Ma S, Ji
G and Xiong L: 100% oxygen inhalation protects against
zymosan-induced sterile sepsis in mice: The roles of inflammatory
cytokines and antioxidant enzymes. Shock. 32:451–461. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Folz RJ, Abushamaa AM and Suliman HB:
Extracellular superoxide dismutase in the airways of transgenic
mice reduces inflammation and attenuates lung toxicity following
hyperoxia. J Clin Invest. 103:1055–1066. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Altemeier WA and Sinclair SE: Hyperoxia in
the intensive care unit: Why more is not always better. Curr Opin
Crit Care. 13:73–78. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K,
Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S
and Ohta S: Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by
selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med.
13:688–694. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ohta S: Hydrogen gas and hydrogen water
act as a therapeutic and preventive antioxidant with a novel
concept. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 45:355–362. 2008.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fukuda K, Asoh S, Ishikawa M, Yamamoto Y,
Ohsawa I and Ohta S: Inhalation of hydrogen gas suppresses hepatic
injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion through reducing oxidative
stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 361:670–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cai J, Kang Z, Liu WW, Luo X, Qiang S,
Zhang JH, Ohta S, Sun X, Xu W, Tao H and Li R: Hydrogen therapy
reduces apoptosis in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model. Neurosci
Lett. 441:167–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang CS, Kawamura T, Toyoda Y and Nakao
A: Recent advances in hydrogen research as a therapeutic medical
gas. Free Radic Res. 44:971–982. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie K, Fu W, Xing W, Li A, Chen H, Han H,
Yu Y and Wang G: Combination therapy with molecular hydrogen and
hyperoxia in a murine model of polymicrobial sepsis. Shock.
38:656–663. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cuzzocrea S, Costantino G, Mazzon E and
Caputi AP: Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine on multiple organ
failure induced by zymosan in the rat. Crit Care Med. 27:1524–1532.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Volman TJ, Hendriks T and Goris RJ:
Zymosan-induced generalized inflammation: Experimental studies into
mechanisms leading to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Shock.
23:291–297. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Humphreys K, Weingardt KR and Harris AH:
Influence of subject eligibility criteria on compliance with
National Institutes of Health guidelines for inclusion of women,
minorities, and children in treatment research. Alcohol Clin Exp
Res. 31:988–995. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie K, Yu Y, Pei Y, Hou L, Chen S, Xiong L
and Wang G: Protective effects of hydrogen gas on murine
polymicrobial sepsis via reducing oxidative stress and HMGB1
release. Shock. 34:90–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie K, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Liu W, Pei Y, Xiong
L, Hou L and Wang G: Hydrogen gas improves survival rate and organ
damage in zymosan-induced generalized inflammation model. Shock.
34:495–501. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hou L, Xie K, Qin M, Peng D, Ma S, Shang
L, Li N, Li S, Ji G, Lu Y and Xiong L: Effects of reactive oxygen
species scavenger on the protective action of 100% oxygen treatment
against sterile inflammation in mice. Shock. 33:646–654. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dworski R, Roberts LJ II, Murray JJ,
Morrow JD, Hartert TV and Sheller JR: Assessment of oxidant stress
in allergic asthma by measurement of the major urinary metabolite
of F2-isoprostane, 15-F2t-IsoP (8-iso-PGF2alpha). Clin Exp Allergy.
31:387–390. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Martin DS and Grocott MP: Oxygen therapy
in critical illness: Precise control of arterial oxygenation and
permissive hypoxemia. Crit Care Med. 41:423–432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J,
Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E and Tomlanovich M: Early
Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group: Early goal-directed
therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl
J Med. 345:1368–1377. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meier J, Kemming GI, Kisch-Wedel H, Blum
J, Pape A and Habler OP: Hyperoxic ventilation reduces six-hour
mortality after partial fluid resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock.
Shock. 22:240–247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sukhotnik I, Krausz MM, Brod V, Balan M,
Turkieh A, Siplovich L and Bitterman H: Divergent effects of oxygen
therapy in four models of uncontrolled hemorrhagic shock. Shock.
18:277–284. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kayar SR and Fahlman A: Decompression
sickness risk reduced by native intestinal flora in pigs after H2
dives. Undersea Hyperb Med. 28:89–97. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM,
Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, et
al: HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice.
Science. 285:248–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hou LC, Qin MZ, Zheng LN, Lu Y, Wang Q,
Peng DR, Yu XP, Xin YC, Ji GL and Xiong LZ: Severity of sepsis
correlated with the elevation of serum high-mobility group box 1 in
rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 122:449–454. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|