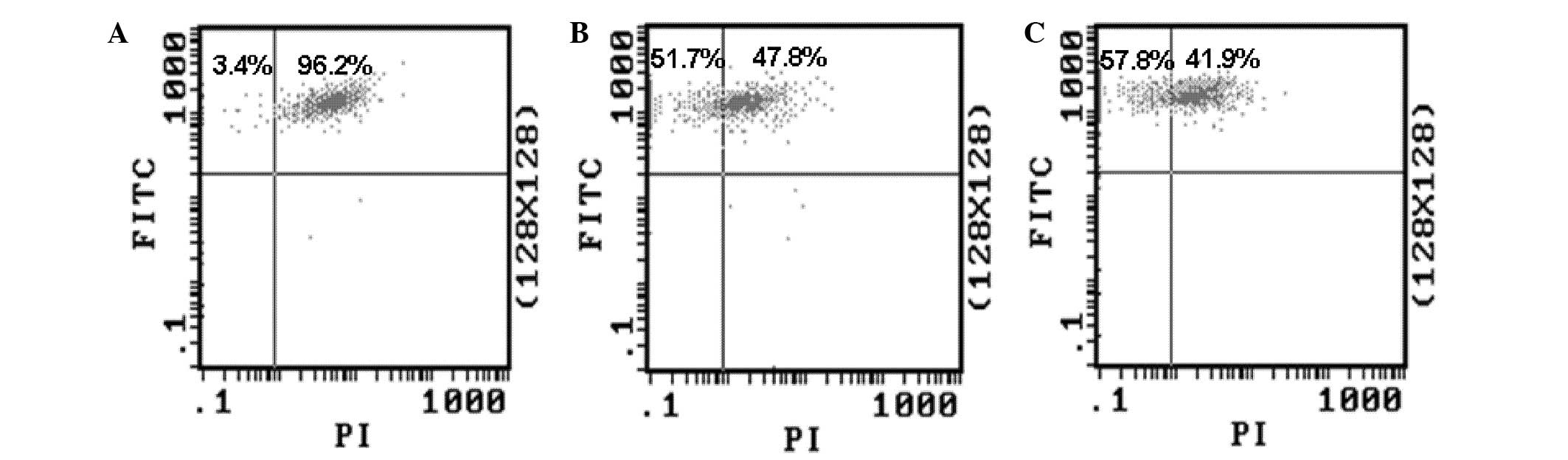
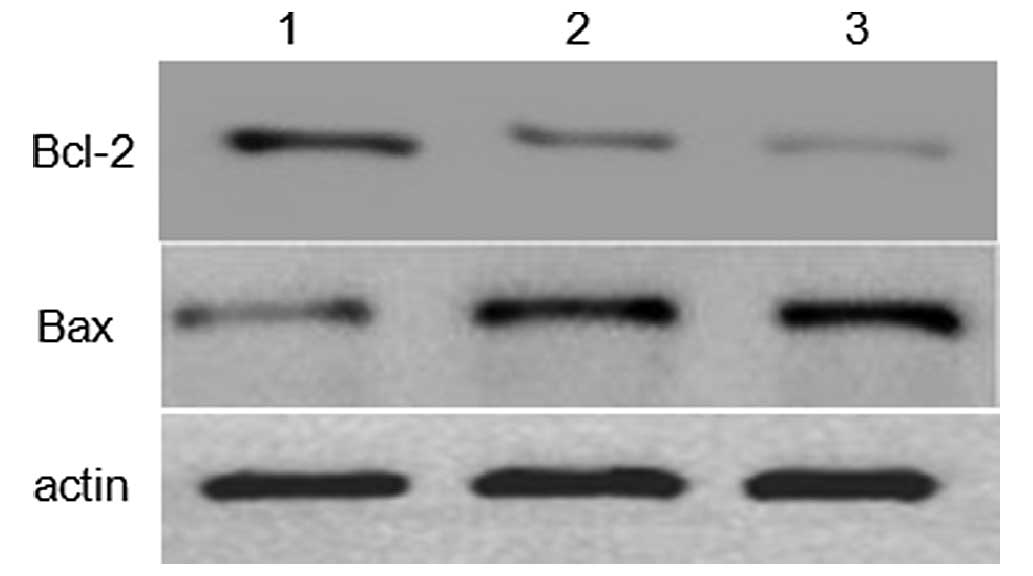
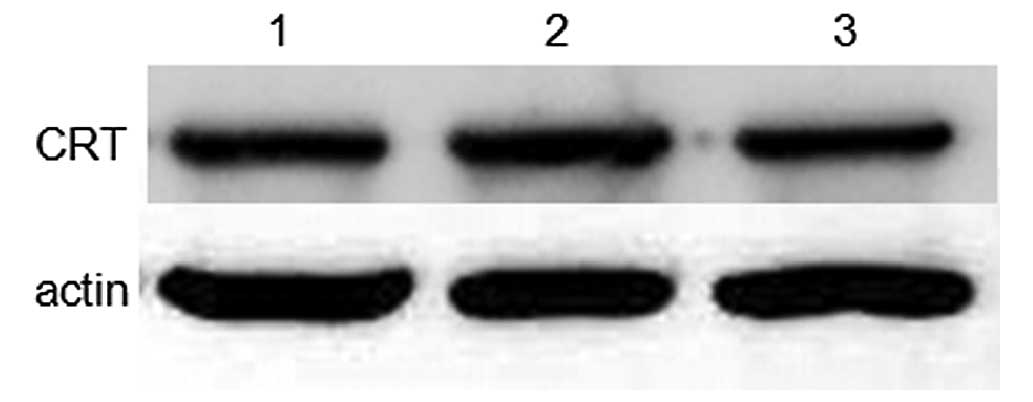
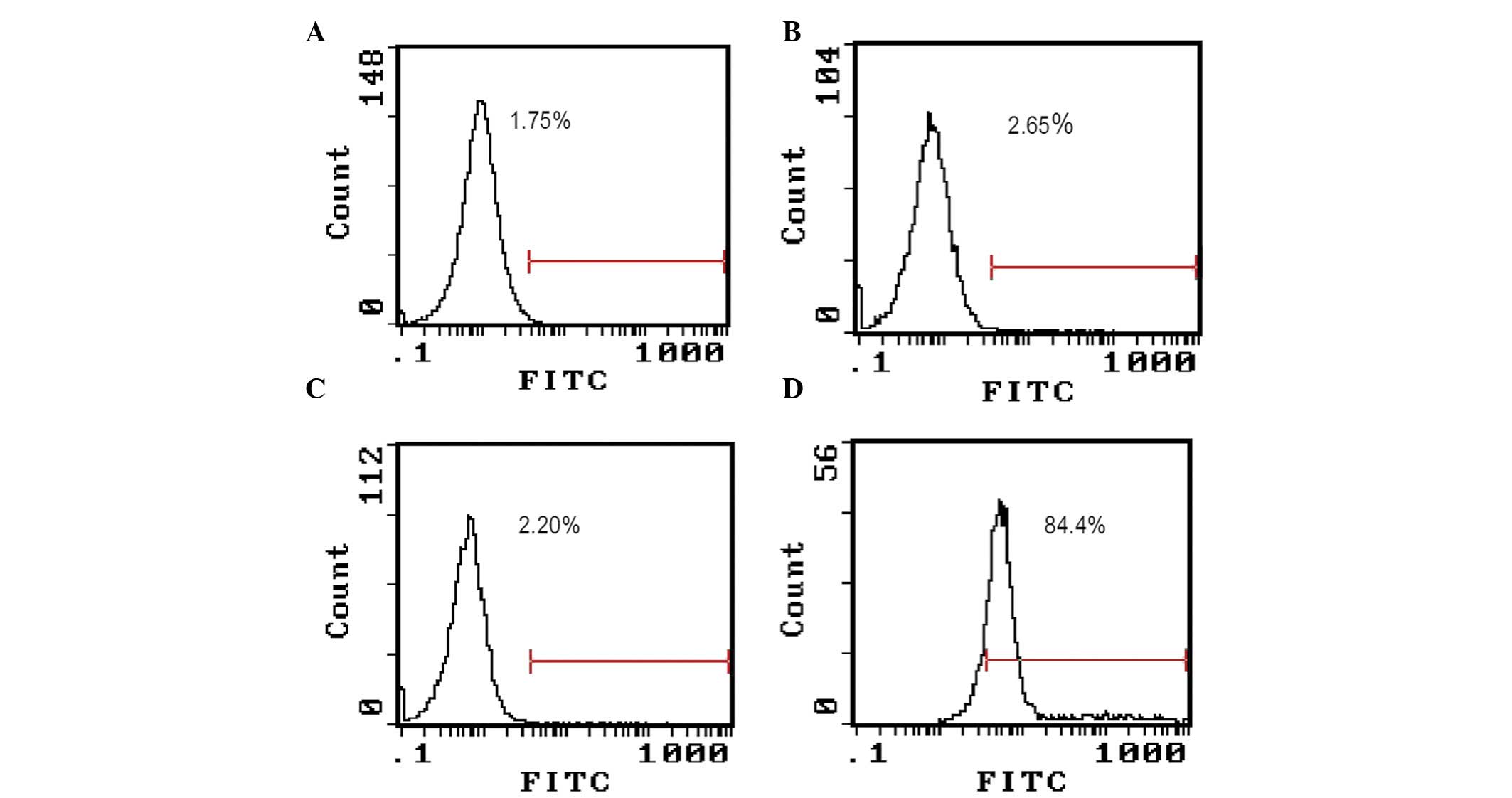
|
1
|
Messerschmitt PJ, Garcia RM, Abdul-Karim
FW, Greenfield EM and Getty PJ: Osteosarcoma. J Am Acad Orthop
Surg. 17:515–527. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Anderson ME: Update on Survival in
Osteosarcoma. Orthop Clin North Am. 47:283–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chou AJ, Geller DS and Gorlick R: Therapy
for osteosarcoma: Where do we go from here? Paediatr Drugs.
10:315–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siclari VA and Qin L: Targeting the
osteosarcoma cancer stem cell. J Orthop Surg Res. 5:782010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kuijjer ML, Hogendoorn PC and
Cleton-Jansen AM: Genome-wide analyses on high-grade osteosarcoma:
Making sense of a genomically most unstable tumor. Int J Cancer.
133:2512–2521. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anninga JK, Gelderblom H, Fiocco M, Kroep
JR, Taminiau AH, Hogendoorn PC and Egeler RM: Chemotherapeutic
adjuvant treatment for osteosarcoma: Where do we stand? Eur J
Cancer. 47:2431–2445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O and Zitvogel
L: Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol.
31:51–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O,
Agostinis P and Vandenabeele P: Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in
cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:860–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A,
Ghiringhelli F, Roux S, Chaput N, Schmitt E, Hamai A, Hervas-Stubbs
S, Obeid M, et al: Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of
doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med. 202:1691–1701.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia
GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Mignot G, Panaretakis T,
Casares N, et al: Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity
of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 13:54–61. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pol J, Vacchelli E, Aranda F, Castoldi F,
Eggermont A, Cremer I, Sautès-Fridman C, Fucikova J, Galon J,
Spisek R, et al: Trial Watch: Immunogenic cell death inducers for
anticancer chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 4:e10088662015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Beltran J, Ghosh AK and Basu S:
Immunotherapy of tumors with neuroimmune ligand capsaicin. J
Immunol. 178:3260–3264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
D'Eliseo D, Manzi L and Velotti F:
Capsaicin as an inducer of damage-associated molecular patterns
(DAMPs) of immunogenic cell death (ICD) in human bladder cancer
cells. Cell Stress Chaperones. 18:801–808. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Savill J and Fadok V: Corpse clearance
defines the meaning of cell death. Nature. 407:784–788. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matzinger P: The danger model: A renewed
sense of self. Science. 296:301–305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri S, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, et al: Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death
2009: Classification of cell death: Recommendations of the
Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ.
16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zou W: Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity
and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:295–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zitvogel L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F,
André F, Tesniere A and Kroemer G: The anticancer immune response:
Indispensable for therapeutic success? J Clin Invest.
118:1991–2001. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han HS, Shim YK, Kim JE, Jeon HJ, Lim SN,
Oh TK, Lee KH and Kim ST: A pilot study of adrenal suppression
after dexamethasone therapy as an antiemetic in cancer patients.
Support Care Cancer. 20:1565–1572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garg AD and Agostinis P: Editorial:
Immunogenic Cell Death in Cancer: From Benchside Research to
Bedside Reality. Front Immunol. 7:1102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song KH, Jung SY, Kang SM, Kim MH, Ahn J,
Hwang SG, Lee JH, Lim DS, Nam SY and Song JY: Induction of
immunogenic cell death by radiation-upregulated karyopherin alpha 2
in vitro. Eur J Cell Biol. Apr 11–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fučíková J, Bartůňková J and Špíšek R: The
Concept of Immunogenic Cell Death in Antitumor Immunity. Klin
Onkol. 4:4S48–4S55. 2015.(In Czech). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Krause KH and Michalak M: Calreticulin.
Cell. 88:439–443. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson S, Michalak M, Opas M and Eggleton
P: The ins and outs of calreticulin: From the ER lumen to the
extracellular space. Trends Cell Biol. 11:122–129. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bedard K, Szabo E, Michalak M and Opas M:
Cellular functions of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones
calreticulin, calnexin, and ERp57. Int Rev Cytol. 245:91–121. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gold LI, Eggleton P, Sweetwyne MT, Van
Duyn LB, Greives MR, Naylor SM, Michalak M and Murphy-Ullrich JE:
Calreticulin: Non-endoplasmic reticulum functions in physiology and
disease. FASEB J. 24:665–683. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu H, Han Y, Qin Y, Cao C, Xia Y, Liu C
and Wang Y: Whole-cell vaccine coated with recombinant calreticulin
enhances activation of dendritic cells and inducestumour-specific
immune responses. Oncol Rep. 2:529–534. 2013.
|
|
28
|
Tesniere A, Panaretakis T, Kepp O, Apetoh
L, Ghiringhelli F, Zitvogel L and Kroemer G: Molecular
characteristics of immunogenic cancer cell death. Cell Death
Differ. 1:3–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Son KJ, Choi KR, Lee SJ and Lee H:
Immunogenic Cell Death Induced by Ginsenoside Rg3: Significance in
Dendritic Cell-based Anti-tumor Immunotherapy. Immune Netw.
1:75–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chao MP, Jaiswal S, Weissman-Tsukamoto R,
Alizadeh AA, Gentles AJ, Volkmer J, Weiskopf K, Willingham SB,
Raveh T, Park CY, Majeti R and Weissman IL: Calreticulin is the
dominant pro-phagocytic signal on multiple human cancers and is
counterbalanced by CD47. Sci Transl Med. 2:63ra942010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|