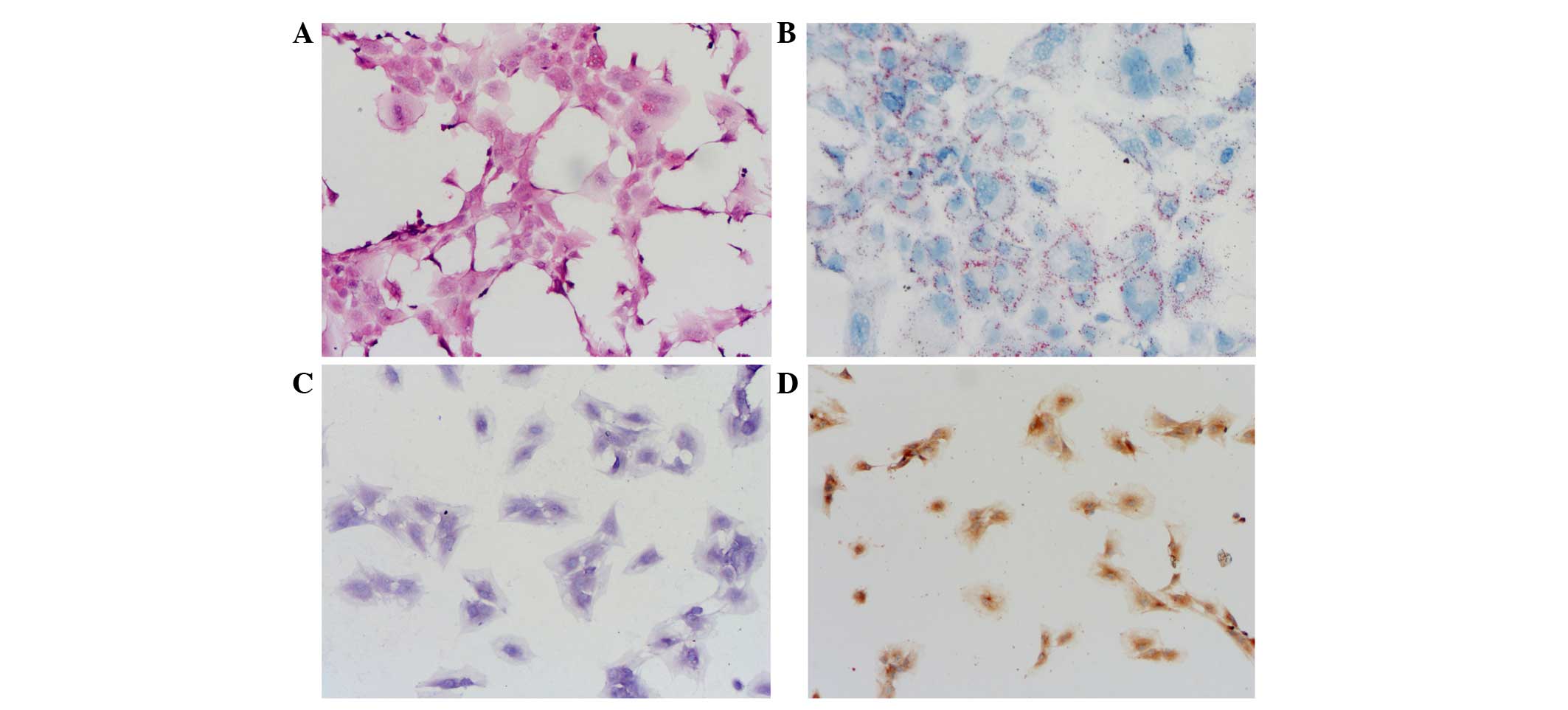
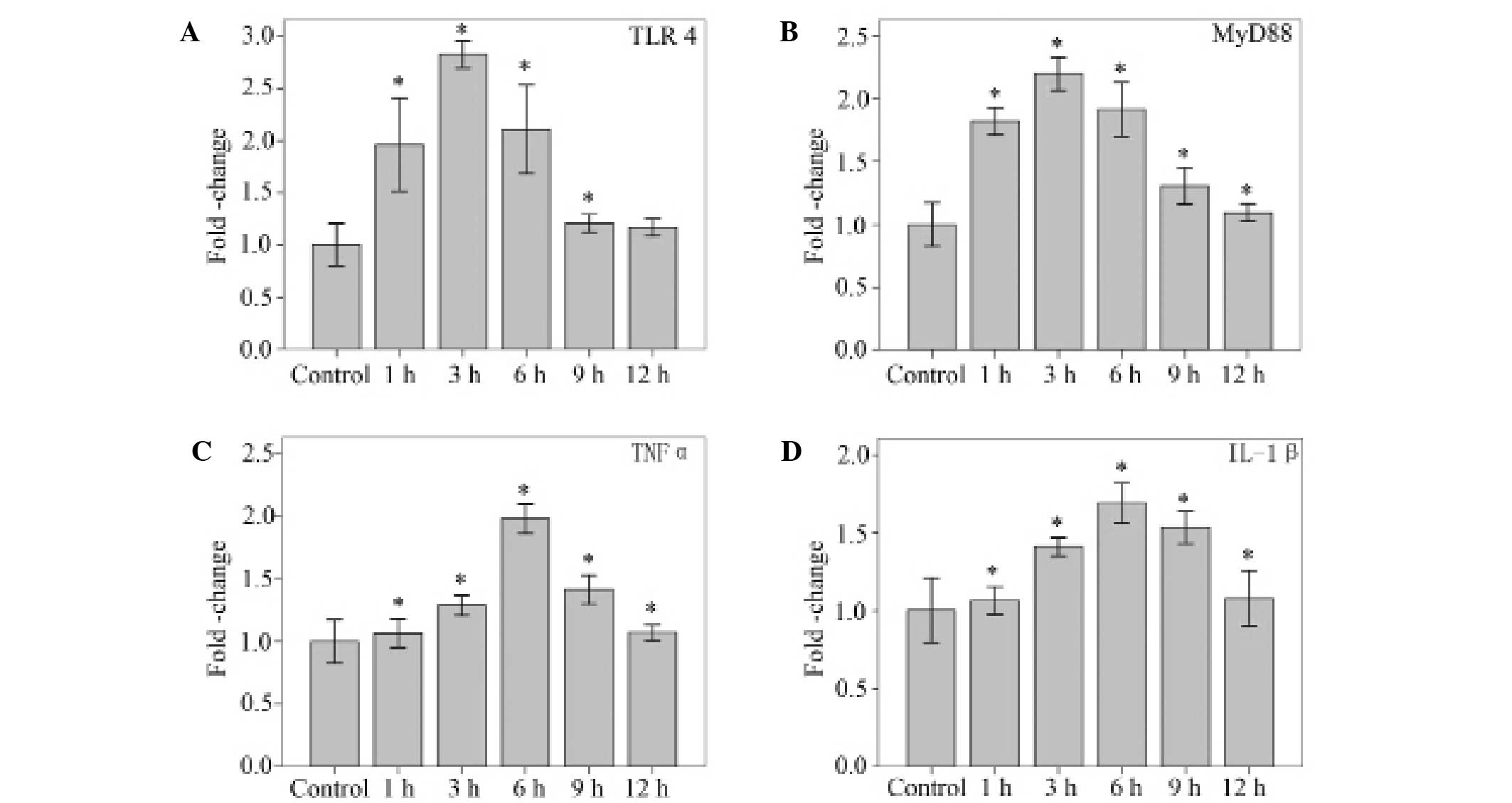
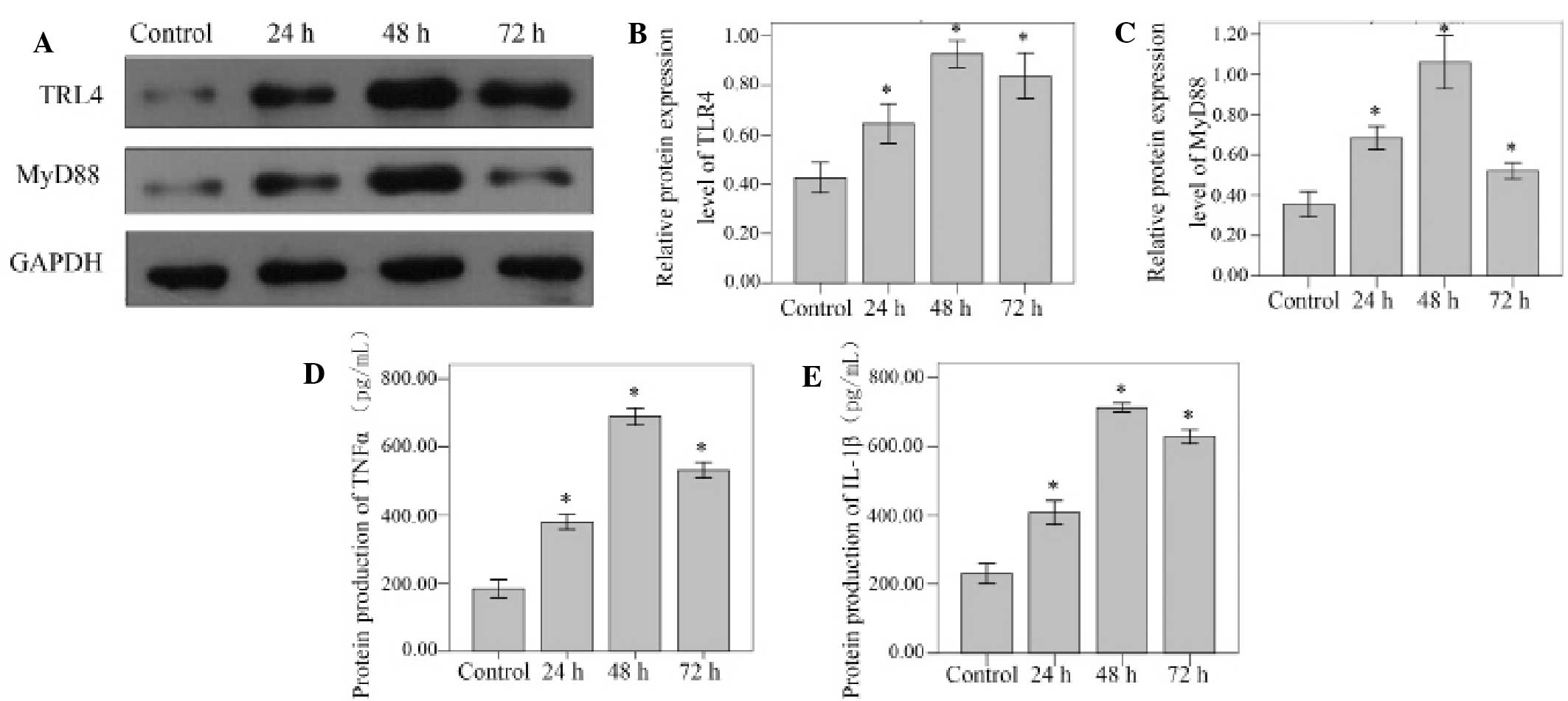
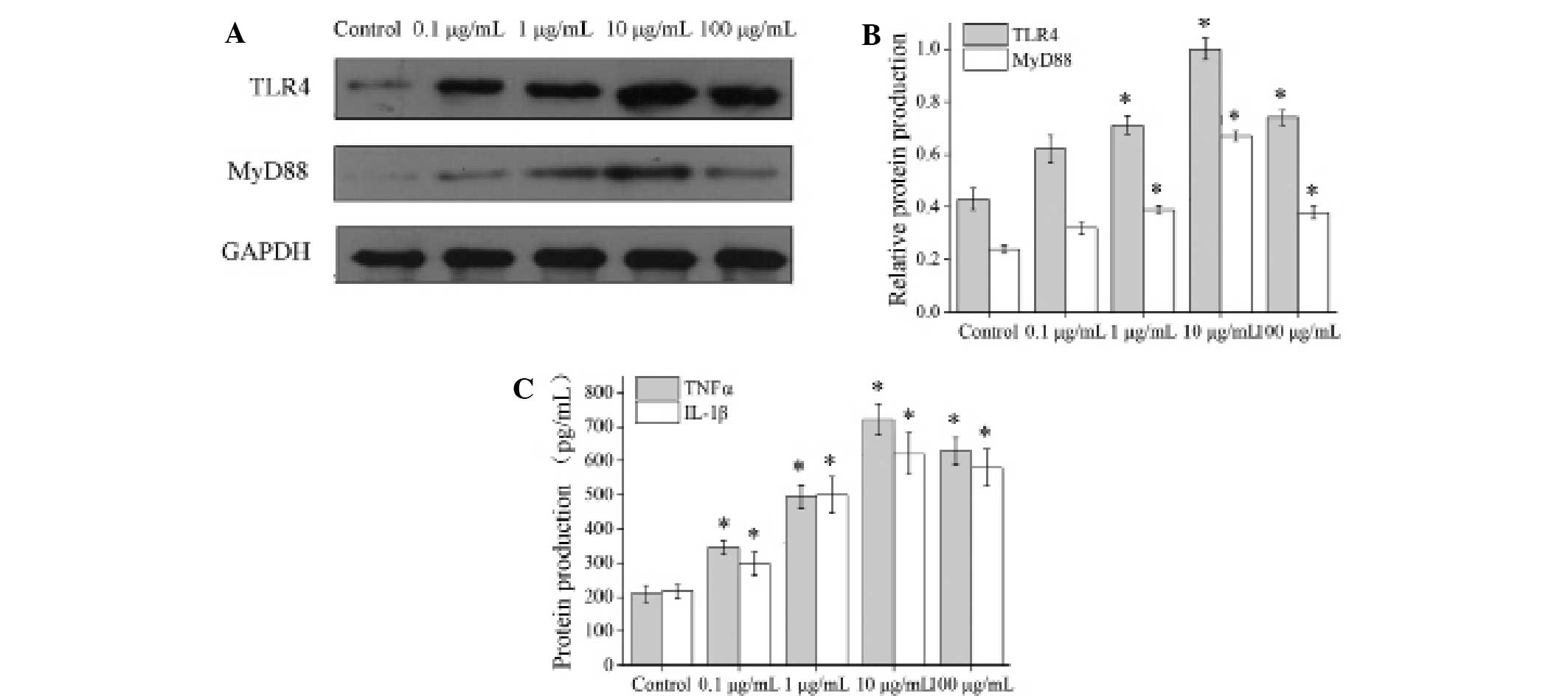
|
1
|
Deyo RA, Cherkin D, Conrad D and Volinn E:
Cost, controversy, crisis: Low back pain and the health of the
public. Annu Rev Public Health. 12:141–156. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kabbara A and Hayek SM: Intradiscal
electrothermal therapy (IDET) for the treatment of discogenic pain.
Tech Reg Anesth Pain Manag. 13:102–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cheung KM, Karppinen J, Chan D, Ho DW,
Song YQ, Sham P, Cheah KS, Leong JC and Luk KD: Prevalence and
pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a
population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 34:934–940. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ireland D: Molecular mechanisms involved
in intervertebral disc degeneration and potential new treatment
strategies. Biosci Horiz. 2:83–89. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Maidhof R, Alipui DO, Rafiuddin A, Levine
M, Grande DA and Chahine NO: Emerging trends in biological therapy
for intervertebral disc degeneration. Discov Med. 14:401–411.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rajan NE, Bloom O, Maidhof R, Stetson N,
Sherry B, Levine M and Chahine NO: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)
expression and stimulation in a model of intervertebral disc
inflammation and degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:1343–1351.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Antoniou J, Steffen T, Nelson F,
Winterbottom N, Hollander AP, Poole RA, Aebi M and Alini M: The
human lumbar intervertebral disc: Evidence for changes in the
biosynthesis and denaturation of the extracellular matrix with
growth, maturation, ageing, and degeneration. J Clin Invest.
98:996–1003. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roughley PJ, Alini M and Antoniou J: The
role of proteoglycans in aging, degeneration and repair of the
intervertebral disc. Biochem Soc Trans. 30:869–874. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Le Maitre CL, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA:
Localization of degradative enzymes and their inhibitors in the
degenerate human intervertebral disc. J Pathol. 204:47–54. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pockert AJ, Richardson SM, Le Maitre CL,
Lyon M, Deakin JA, Buttle DJ, Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA: Modified
expression of the ADAMTS enzymes and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinases 3 during human intervertebral disc degeneration.
Arthritis Rheum. 60:482–491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Goldring MB: The role of the chondrocyte
in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 43:1916–1926. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee S, Moon CS, Sul D, Lee J, Bae M, Hong
Y, Lee M, Choi S, Derby R, Kim BJ, et al: Comparison of growth
factor and cytokine expression in patients with degenerated disc
disease and herniated nucleus pulposus. Clin Biochem. 42:1504–1511.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Masuda K, Imai Y, Okuma M, Muehleman C,
Nakagawa K, Akeda K, Thonar E, Andersson G and An HS: Osteogenic
protein-1 injection into a degenerated disc induces the restoration
of disc height and structural changes in the rabbit anular puncture
model. Spine. 31:742–754. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ellman MB, Kim JS, An HS, Chen D, KC R, An
J, Dittakavi T, van Wijnen AJ, Cs-Szabo G, Li X, et al: Toll-like
receptor adaptor signaling molecule MyD88 on intervertebral disk
homeostasis: in vitro, ex vivo studies. Gene. 505:283–290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE and
Boos N: Expression and distribution of tumor necrosis factor alpha
in human lumbar intervertebral discs: A study in surgical specimen
and autopsy controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:44–53; discussion
54. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Le Maitre CL, Hoyland JA and Freemont AJ:
Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human
intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile.
Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R772007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tukhvatulin AI, Logunov DY, Shcherbinin
DN, Shmarov MM, Naroditsky BS, Gudkov AV and Gintsburg AL:
Toll-like receptors and their adapter molecules. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 75:1098–1114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Janeway CJ and Medzhitov R: Innate immune
recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 20:197–216. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee HK and Iwasaki A: Innate control of
adaptive immunity: Dendritic cells and beyond. Semin Immunol.
19:48–55. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takeda K, Kaisho T and Akira S: Toll-like
receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 21:335–376. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beutler B: Inferences, questions and
possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature.
430:257–263. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Youn HS, Lee JY, Fitzgerald KA, Young HA,
Akira S and Hwang DH: Specific inhibition of MyD88-independent
signaling pathways of TLR3 and TLR4 by resveratrol: Molecular
targets are TBK1 and RIP1 in TRIF complex. J Immunol.
175:3339–3346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akira S, Takeda K and Kaisho T: Toll-like
receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity.
Nat Immunol. 2:675–680. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hiyama A, Sakai D, Risbud MV, Tanaka M,
Arai F, Abe K and Mochida J: Enhancement of intervertebral disc
cell senescence by WNT/β-catenin signaling-induced matrix
metalloproteinase expression. Arthritis Rheum. 62:3036–3047. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang F, Wu XT, Zhuang SY, Wang YT, Hong X,
Zhu L and Bao JP: Ex vivo observation of human nucleus pulposus
chondrocytes isolated from degenerated intervertebral discs. Asian
Spine J. 5:73–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mao M, Lei H, Liu Q, Chen Y, Zhao L, Li Q,
Luo S, Zuo Z, He Q, Huang W, et al: Effects of miR-33a-5P on
ABCA1/G1-mediated cholesterol efflux under inflammatory stress in
THP-1 macrophages. PLoS One. 9:e1097222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McGirt MJ, Ambrossi GL, Datoo G, Sciubba
DM, Witham TF, Wolinsky JP, Gokaslan ZL and Bydon A: Recurrent disc
herniation and long-term back pain after primary lumbar discectomy:
Review of outcomes reported for limited versus aggressive disc
removal. Neurosurgery. 64:338–344; discussion 344–345. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Glassman SD, Carreon LY, Djurasovic M,
Dimar JR, Johnson JR, Puno RM and Campbell MJ: Lumbar fusion
outcomes stratified by specific diagnostic indication. Spine J.
9:13–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mirza SK and Deyo RA: Systematic review of
randomized trials comparing lumbar fusion surgery to nonoperative
care for treatment of chronic back pain. Spine. 32:816–823. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Galbusera F, Bellini CM, Zweig T, Ferguson
S, Raimondi MT, Lamartina C, Brayda-Bruno M and Fornari M: Design
concepts in lumbar total disc arthroplasty. Eur Spine J.
17:1635–1650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bothmann M, Kast E, Boldt GJ and Oberle J:
Dynesys fixation for lumbar spine degeneration. Neurosurg Rev.
31:189–196. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Barton GM and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptor signaling pathways. Science. 300:1524–1525. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
O'Neill LA: Targeting signal transduction
as a strategy to treat inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
5:549–563. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kanzler H, Barrat FJ, Hessel EM and
Coffman RL: Therapeutic targeting of innate immunity with Toll-like
receptor agonists and antagonists. Nat Med. 13:552–559. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Netea MG, van Deuren M, Kullberg BJ,
Cavaillon JM and Van der Meer JW: Does the shape of lipid A
determine the interaction of LPS with Toll-like receptors? Trends
Immunol. 23:135–139. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Beutler B: Tlr4: Central component of the
sole mammalian LPS sensor. Curr Opin Immunol. 12:20–26. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Masuda K, Aota Y, Muehleman C, Imai Y,
Okuma M, Thonar EJ, Andersson GB and An HS: A novel rabbit model of
mild, reproducible disc degeneration by an anulus needle puncture:
Correlation between the degree of disc injury and radiological and
histological appearances of disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 30:5–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sobajima S, Kompel JF, Kim JS, Wallach CJ,
Robertson DD, Vogt MT, Kang JD and Gilbertson LG: A slowly
progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc
degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray and histology. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 30:15–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim KS, Yoon ST, Li J, Park JS and Hutton
WC: Disc degeneration in the rabbit: A biochemical and radiological
comparison between four disc injury models. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
30:33–37. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rousseau MA, Ulrich JA, Bass EC, Rodriguez
AG, Liu JJ and Lotz JC: Stab incision for inducing intervertebral
disc degeneration in the rat. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:17–24.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sobajima S, Shimer AL, Chadderdon RC,
Kompel JF, Kim JS, Gilbertson LG and Kang JD: Quantitative analysis
of gene expression in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc
degeneration by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Spine J.
5:14–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ulrich JA, Liebenberg EC, Thuillier DU and
Lotz JC: ISSLS prize winner: Repeated disc injury causes persistent
inflammation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:2812–2819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|