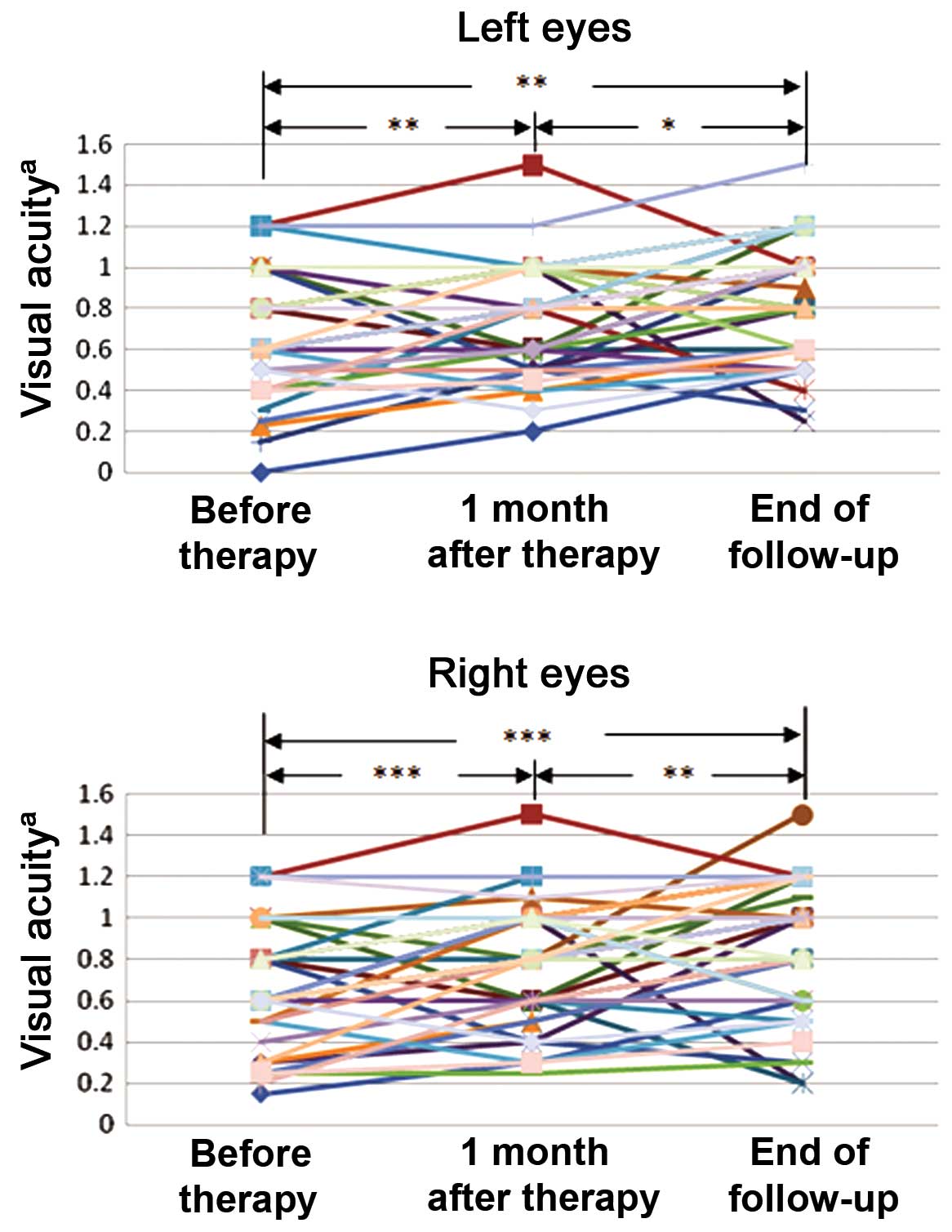
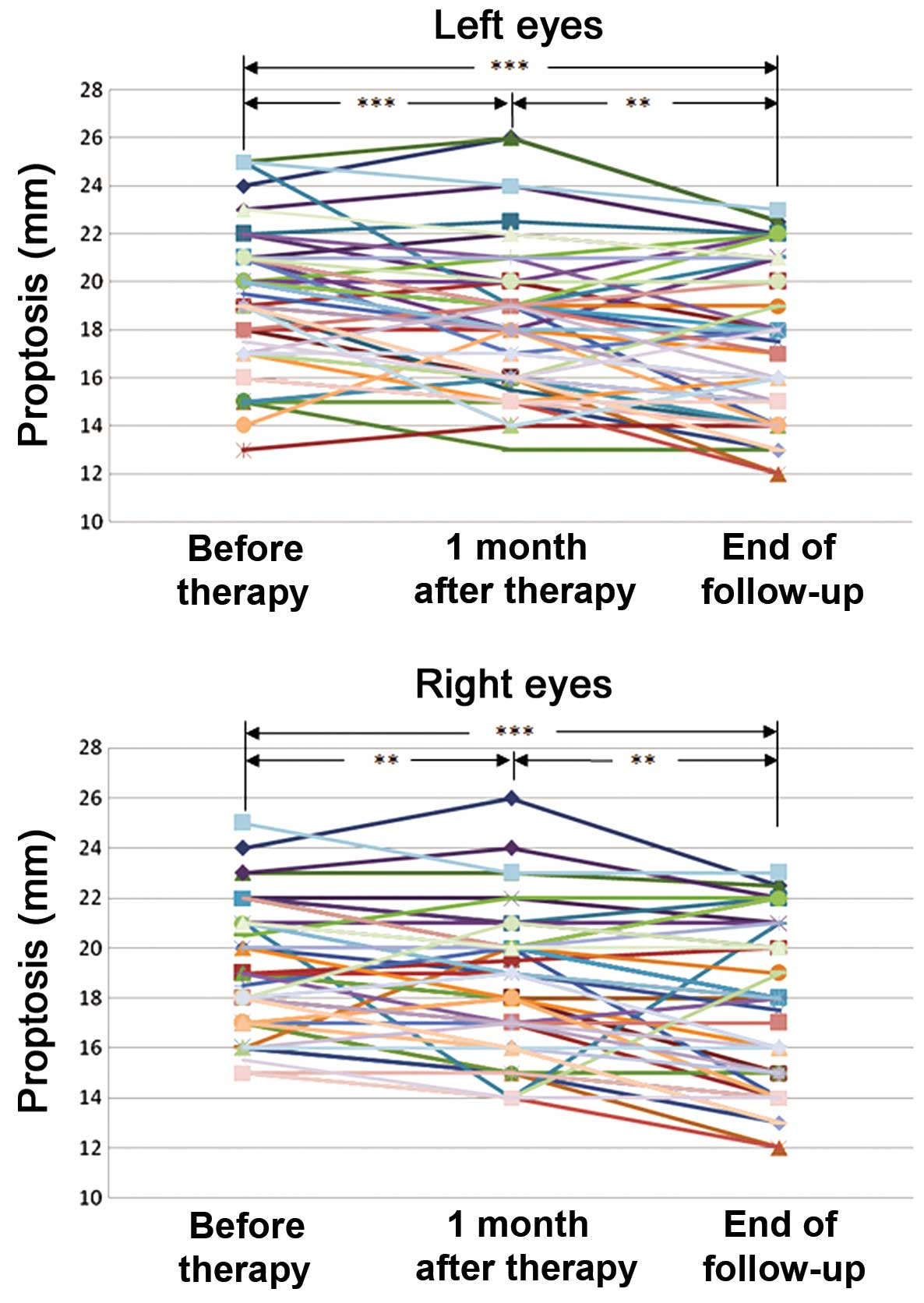
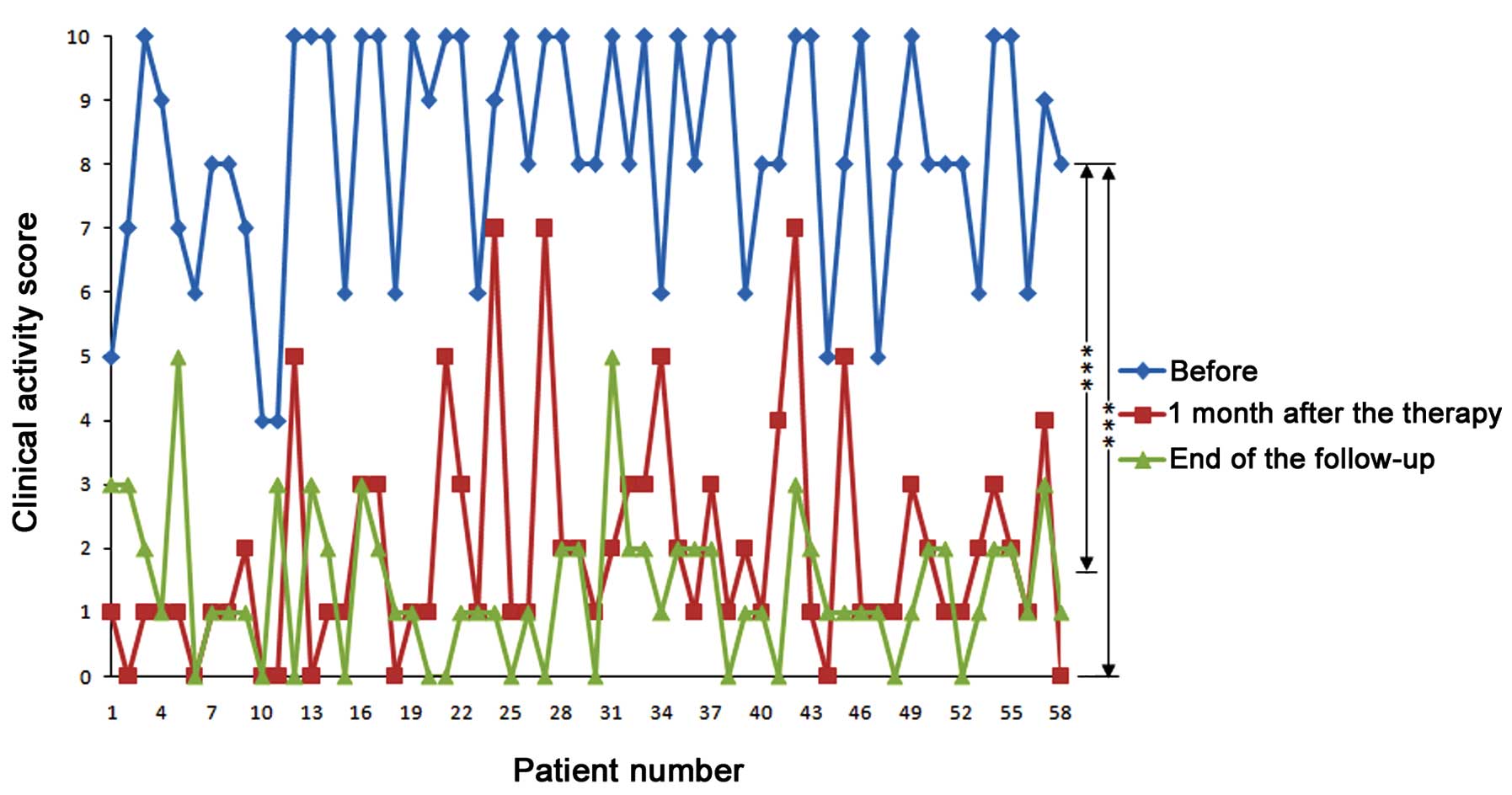
|
1
|
Wall JR and Lahooti H: Pathogenesis of
thyroid eye disease - does autoimmunity against the TSH receptor
explain all cases? Endokrynol Pol. 61:222–227. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartley GB: The epidemiologic
characteristics and clinical course of ophthalmopathy associated
with autoimmune thyroid disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Trans
Am Ophthalmol Soc. 92:477–588. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brent GA: Clinical practice. Graves'
disease. N Engl J Med. 358:2594–2605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kinsell LW, Partridge JW and Foreman N:
The use of ACTH and cortisone in the treatment and in the
differential diagnosis of malignant exophthalmos. Ann Intern Med.
38:913–917. 1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartalena L and Tanda ML: Clinical
practice. Graves' ophthalmopathy. N Engl J Med. 360:994–1001. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartalena L, Baldeschi L, Dickinson A,
Eckstein A, Kendall-Taylor P, Marcocci C, Mourits M, Perros P,
Boboridis K, Boschi A, Currò N, Daumerie C, Kahaly GJ, Krassas GE,
Lane CM, Lazarus JH, Marinò M, Nardi M, Neoh C, Orgiazzi J, Pearce
S, Pinchera A, Pitz S, Salvi M, Sivelli P, Stahl M, von Arx G and
Wiersinga WM: European Group on Graves' Orbitopathy (EUGOGO).
Consensus statement of the European Group on Graves' orbitopathy
(EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur J Endocrinol. 158:273–285. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khoo DH, Eng PH, Ho SC, Tai ES,
Morgenthaler NG, Seah LL, Fong KS, Chee SP, Choo CT and Aw SE:
Graves' ophthalmopathy in the absence of elevated free thyroxine
and triiodothyronine levels: Prevalence, natural history and
thyrotropin receptor antibody levels. Thyroid. 10:1093–1100. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khoo DH, Ho SC, Seah LL, Fong KS, Tai ES,
Chee SP, Eng PH, Aw SE and Fok AC: The combination of absent
thyroid peroxidase antibodies and high thyroid-stimulating
immunoglobulin levels in Graves' disease identifies a group at
markedly increased risk of ophthalmopathy. Thyroid. 9:1175–1180.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
De Bellis A, Di Martino S, Fiordelisi F,
Muccitelli VI, Sinisi AA, Abbate GF, Gargano D, Bellastella A and
Bizzarro A: Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1)
concentrations in Graves' disease patients followed up for
development of ophthalmopathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
83:1222–1225. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heufelder AE and Bahn RS: Soluble
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) in sera of patients
with Graves' ophthalmopathy and thyroid diseases. Clin Exp Immunol.
92:296–302. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dickinson AJ and Perros P: Controversies
in the clinical evaluation of active thyroid-associated
orbitopathy: Use of a detailed protocol with comparative
photographs for objective assessment. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf).
55:283–303. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mourits MP, Koornneef L, Wiersinga WM,
Prummel MF, Berghout A and van der Gaag R: Clinical criteria for
the assessment of disease activity in Graves' ophthalmopathy: A
novel approach. Br J Ophthalmol. 73:639–644. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang DD, Gonzalez MO and Durairaj VD:
Medical management of thyroid eye disease. Saudi J Ophthalmol.
25:3–13. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wakelkamp IM, Baldeschi L, Saeed P,
Mourits MP, Prummel MF and Wiersinga WM: Surgical or medical
decompression as a first-line treatment of optic neuropathy in
Graves' ophthalmopathy? A randomized controlled trial. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 63:323–328. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tambe K, Bhargava J, Tripathi A, Gregory
M, Burns J and Sampath R: The role of intravenous
methylprednisolone immunosuppression in the management of active
thyroid eye disease. Orbit. 29:227–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartalena L, Baldeschi L, Dickinson A,
Eckstein A, Kendall-Taylor P, Marcocci C, Mourits M, Perros P,
Boboridis K, Boschi A, et al: Consensus statement of the European
Group on Graves' orbitopathy (EUGOGO) on management of GO. Eur J
Endocrinol. 158:273–285. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zang S, Ponto KA and Kahaly GJ: Clinical
review: Intravenous glucocorticoids for Graves' orbitopathy:
Efficacy and morbidity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:320–332. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang TC, Kao SC, Hsiao YL, Lu CP, Huang
KM and Tzeng SS: Therapeutic responses to corticosteroids in
Graves' ophthalmopathy. J Formos Med Assoc. 95:833–838.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohtsuka K, Sato A, Kawaguchi S, Hashimoto
M and Suzuki Y: Effect of steroid pulse therapy with and without
orbital radiotherapy on Graves' ophthalmopathy. Am J Ophthalmol.
135:285–290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sánchez-Orgaz M, Grabowska A, Royo-Oreja
A, Asencio-Durán M, Romero-Martín R and Arbizu-Duralde A: Optic
neuropathy following orbital irradiation for Graves'
ophthalmopathy: A case report and literature review. Orbit.
31:30–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
European Group of Graves' Orbitopathy.
Perros P, Baldeschi L, Boboridis K, Dickinson AJ, Hullo A, Kahaly
GJ, Kendall-Taylor P, Krassas GE, Lane CM, Lazarus JH, et al: A
questionnaire survey on the management of Graves' orbitopathy in
Europe. Eur J Endocrinol. 155:207–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ramos HE, Diehl LA, Camacho CP, Perros P
and Graf H: Latin American Thyroid Society: Management of Graves'
orbitopathy in Latin America: An international questionnaire study
compared with Europe. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 69:951–956. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stiebel-Kalish H, Robenshtok E,
Hasanreisoglu M, Ezrachi D, Shimon I and Leibovici L: Treatment
modalities for Graves' ophthalmopathy: Systematic review and
metaanalysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:2708–2716. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gillespie EF, Smith TJ and Douglas RS:
Thyroid eye disease: Towards an evidence base for treatment in the
21st century. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 12:318–324. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hägg E and Asplund K: Is endocrine
ophthalmopathy related to smoking? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed).
295:634–635. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bartalena L, Martino E, Marcocci C,
Bogazzi F, Panicucci M, Velluzzi F, Loviselli A and Pinchera A:
More on smoking habits and Graves' ophthalmopathy. J Endocrinol
Invest. 12:733–737. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bahn RS: Graves' ophthalmopathy. N Engl J
Med. 362:726–738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prummel MF and Wiersinga WM: Smoking and
risk of Graves' disease. JAMA. 269:479–482. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen YL, Chang TC and Chen CJ: Influence
of smoking on Graves' disease with or without ophthalmopathy and
nontoxic nodular goiter in Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 93:40–44.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Briassoulis G, Papassotiriou I, Mavrikiou
M, Lazaropoulou C and Margeli A: Longitudinal course and clinical
significance of TGF-beta1, sL- and sE-Selectins and sICAM-1 levels
during severe acute stress in children. Clin Biochem. 40:299–304.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou SL, Chen YL, Peng XZ, Zhao YX, Xie
PZ, Ling L, Chen XW and Dai KM: Expression of serum sICAM-1 in
patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship
with liver fibrosis. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
28:181–182. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Pablo R, Monserrat J, Reyes E, Díaz D,
Rodríguez-Zapata M, de la Hera A, Prieto A and Álvarez-Mon M:
Circulating sICAM-1 and sE-Selectin as biomarker of infection and
prognosis in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
Eur J Intern Med. 24:132–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cha JJ, Hyun YY, Jee YH, Lee MJ, Han KH,
Kang YS, Han SY and Cha DR: Plasma concentration of soluble
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) is elevated in type 2
diabetic patients, and sICAM-1 synthesis is associated with
leptin-induced activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase
(MAPK) pathway. Inflammation. 36:878–887. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dymicka-Piekarska V, Guzinska-Ustymowicz
K, Kuklinski A and Kemona H: Prognostic significance of adhesion
molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1) and VEGF in colorectal cancer
patients. Thromb Res. 129:e47–e50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|