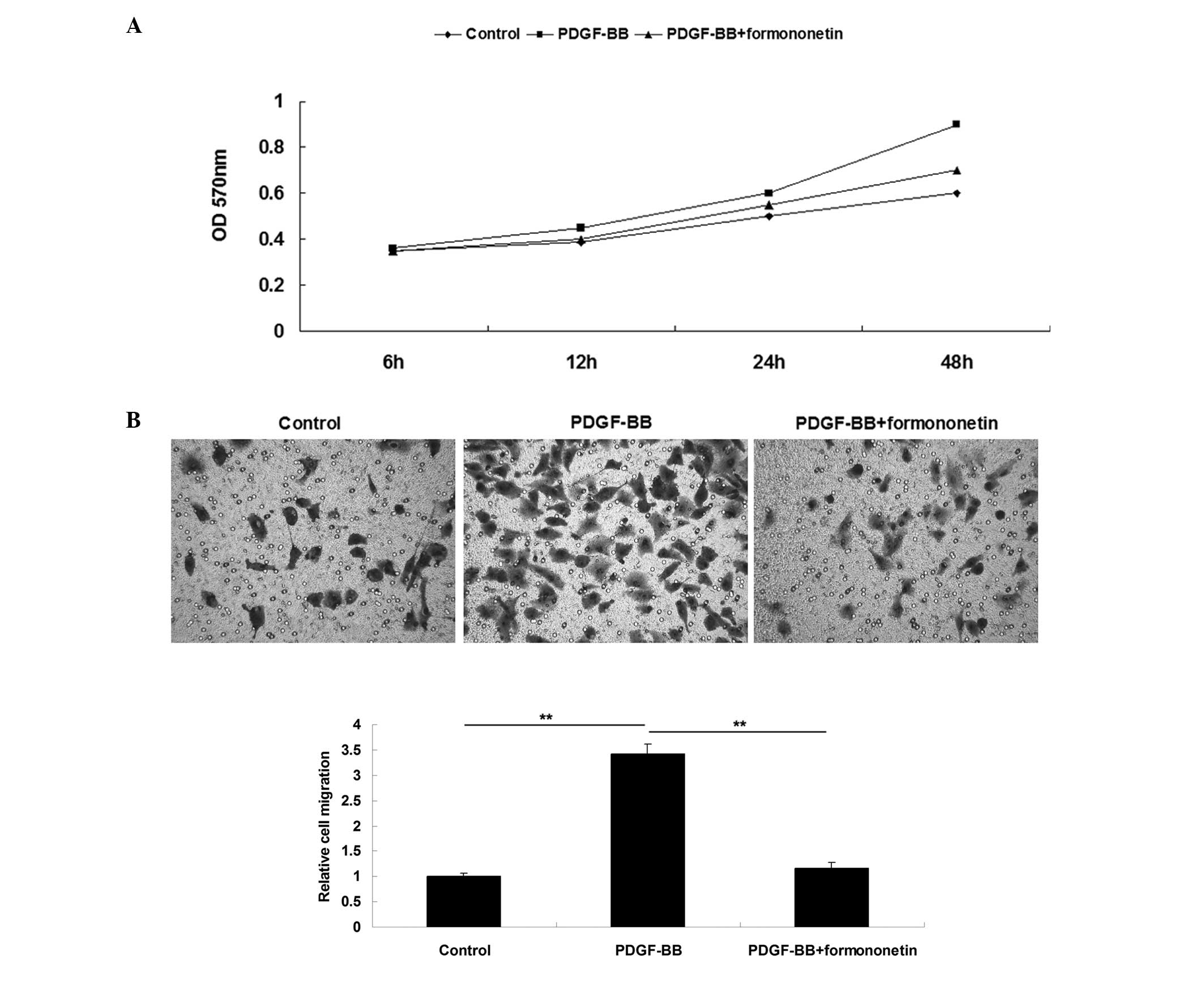
|
1
|
Rodríguez AI, Csányi G, Ranayhossaini DJ,
Feck DM, Blose KJ, Assatourian L, Vorp DA and Pagano PJ: MEF2B-Nox1
signaling is critical for stretch-induced phenotypic modulation of
vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
35:430–438. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chiong M, Cartes-Saavedra B,
Norambuena-Soto I, Mondaca-Ruff D, Morales PE, García-Miguel M and
Mellado R: Mitochondrial metabolism and the control of vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2:722014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choe N, Kwon JS, Kim JR, Eom GH, Kim Y,
Nam KI, Ahn Y, Kee HJ and Kook H: The microRNA miR-132 targets
Lrrfip1 to block vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
neointimal hyperplasia. Atherosclerosis. 229:348–355. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin M, Zhao K, Huang Q and Shang P:
Structural features and biological activities of the
polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Int J Biol
Macromol. 64:257–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agyemang K, Han L, Liu E, Zhang Y, Wang T
and Gao X: Recent Advances in Astragalus membranaceus
anti-diabetic research: Pharmacological effects of its
phytochemical constituents. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:6546432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Xie X, Li C and Fu P: Systematic
review of the renal protective effect of Astragalus
membranaceus (root) on diabetic nephropathy in animal models. J
Ethnopharmacol. 126:189–196. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu F and Chen X: A review of
pharmacological study on Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.)
Bge. Zhong Yao Cai. 27:232–234. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li T, Zhao X, Mo Z, Huang W, Yan H, Ling Z
and Ye Y: Formononetin promotes cell cycle arrest via
downregulation of Akt/Cyclin D1/CDK4 in human prostate cancer
cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1351–1358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou R, Xu L, Ye M, Liao M, Du H and Chen
H: Formononetin inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 and
4T1 breast cancer cells by suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9 through
PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Horm Metab Res. 46:753–760. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Bi L, Ye Y and Chen J:
Formononetin induces apoptosis in PC-3 prostate cancer cells
through enhancing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratios and regulating the p38/Akt
pathway. Nutr Cancer. 66:656–661. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jia WC, Liu G, Zhang CD and Zhang SP:
Formononetin attenuates hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced apoptosis
and NF-κB activation in RGC-5 cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:2191–2197. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang K, Ye Y, Wang Y, Zhang J and Li C:
Formononetin mediates neuroprotection against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in rats via downregulation of the Bax/Bcl-2
ratio and upregulation PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Neurol Sci.
344:100–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huh JE, Nam DW, Baek YH, Kang JW, Park DS,
Choi DY and Lee JD: Formononetin accelerates wound repair by the
regulation of early growth response factor-1 transcription factor
through the phosphorylation of the ERK and p38 MAPK pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:46–54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu H, Zou L, Tian J, Lin F, He J and Hou
J: Protective effects of sulphonated formononetin in a rat model of
cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Planta Med. 80:262–268.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee MH, Kwon BJ, Seo HJ, Yoo KE, Kim MS,
Koo MA and Park JC: Resveratrol inhibits phenotype modulation by
platelet derived growth factor-bb in rat aortic smooth muscle
cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:5724302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Cai Y, Zhang W, Liu X and Liu S:
Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet-derived growth
factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth
muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling. Exp Ther
Med. 8:1253–1258. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guan BZ, Yan RL, Huang JW, Li FL, Zhong
YX, Chen Y, Liu FN, Hu B, Huang SB and Yin LH: Activation of G
Protein coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) promotes the migration of
renal cell carcinoma via the PI3K/AKT/MMP-9 signals. Cell Adh Migr
0. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Salabei JK and Hill BG: Autophagic
regulation of smooth muscle cell biology. Redox Biol. 4:97–103.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu J, Zheng Y, Hu J, Liao D, Gregersen H,
Deng X, Fan Y and Wang G: Biomechanical regulation of vascular
smooth muscle cell functions: From in vitro to in vivo
understanding. J R Soc Interface. 11:201308522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li H, Luo K and Hou J: Inhibitory effect
of Puerariae radix flavones on platelet-derived growth
factor-BB-induced proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells via
PI3K and ERK pathways. Exp Ther Med. 9:257–261. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guan S, Tang Q, Liu W, Zhu R and Li B:
Nobiletin Inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and migration and attenuates neointimal hyperplasia
in a rat carotid artery injury model. Drug Dev Res. 75:489–496.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tolva V, Mazzola S, Zerbi P, Casana R,
Albertini M, Calvillo L, Selmin F and Cilurzo F: A successful
experimental model for intimal hyperplasia prevention using a
resveratrol-delivering balloon. J Vasc Surgp. ii:S0741–S5214.
2014.
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, He J, Chen X, Li J, Shen M, Yu W,
Yang Y and Xiao Z: The proapoptotic effect of formononetin in human
osteosarcoma cells: Involvement of inactivation of ERK and Akt
pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:637–645. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang X, Jin Y, Zhou D, Xu G, Huang J and
Shen L: IQGAP1 promotes the phenotypic switch of vascular smooth
muscle by myocardin pathway: A potential target for varicose vein.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:6475–6485. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song Y, Long L, Zhang N and Liu Y:
Inhibitory effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A on PDGF-BB-induced
proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via
mediating Akt signaling. Mol Med Rep. 10:1555–1560. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song MC, Park J and Kim TJ:
Diethylstilbestrol induces arrest of rat vascular smooth muscle
cell cycle progression through downregulation of cyclin D1 and
cyclin E. Mol Cell Biochem. 360:103–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding Q, Chai H, Mahmood N, Tsao J,
Mochly-Rosen D and Zhou W: Matrix metalloproteinases modulated by
protein kinase Cε mediate resistin-induced migration of human
coronary artery smooth muscle cells. J Vasc Surg. 53:1044–1051.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo L, Ning W, Tan Z, Gong Z and Li X:
Mechanism of matrix metalloproteinase axis-induced neointimal
growth. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 66:116–125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Toker A: Achieving specificity in Akt
signaling in cancer. Adv Biol Regul. 52:78–87. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vasudevan KM and Garraway LA: AKT
signaling in physiology and disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
347:105–133. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu D, Liu J, Lin B, Liu S, Hou R, Hao Y,
Liu Q, Zhang S and Iwamori M: Lewis y regulate cell cycle related
factors in ovarian carcinoma cell RMG-I in vitro via ERK and Akt
signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 13:828–839. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park ES, Kang SI, Yoo KD, Lee MY, Yoo HS,
Hong JT, Shin HS, Kim B and Yun YP: Camptothecin inhibits
platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced proliferation of rat
aortic vascular smooth muscle cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 319:982–991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iida M, Tanabe K, Kozawa O and Iida H:
Differential effects of intravenous anesthetics on PDGF-BB-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Cell Physiol Biochem.
33:1827–1837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Son JE, Jeong H, Kim H, Kim YA, Lee E, Lee
HJ and Lee KW: Pelargonidin attenuates PDGF-BB-induced aortic
smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by direct inhibition
of focal adhesion kinase. Biochem Pharmacol. 89:236–245. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|