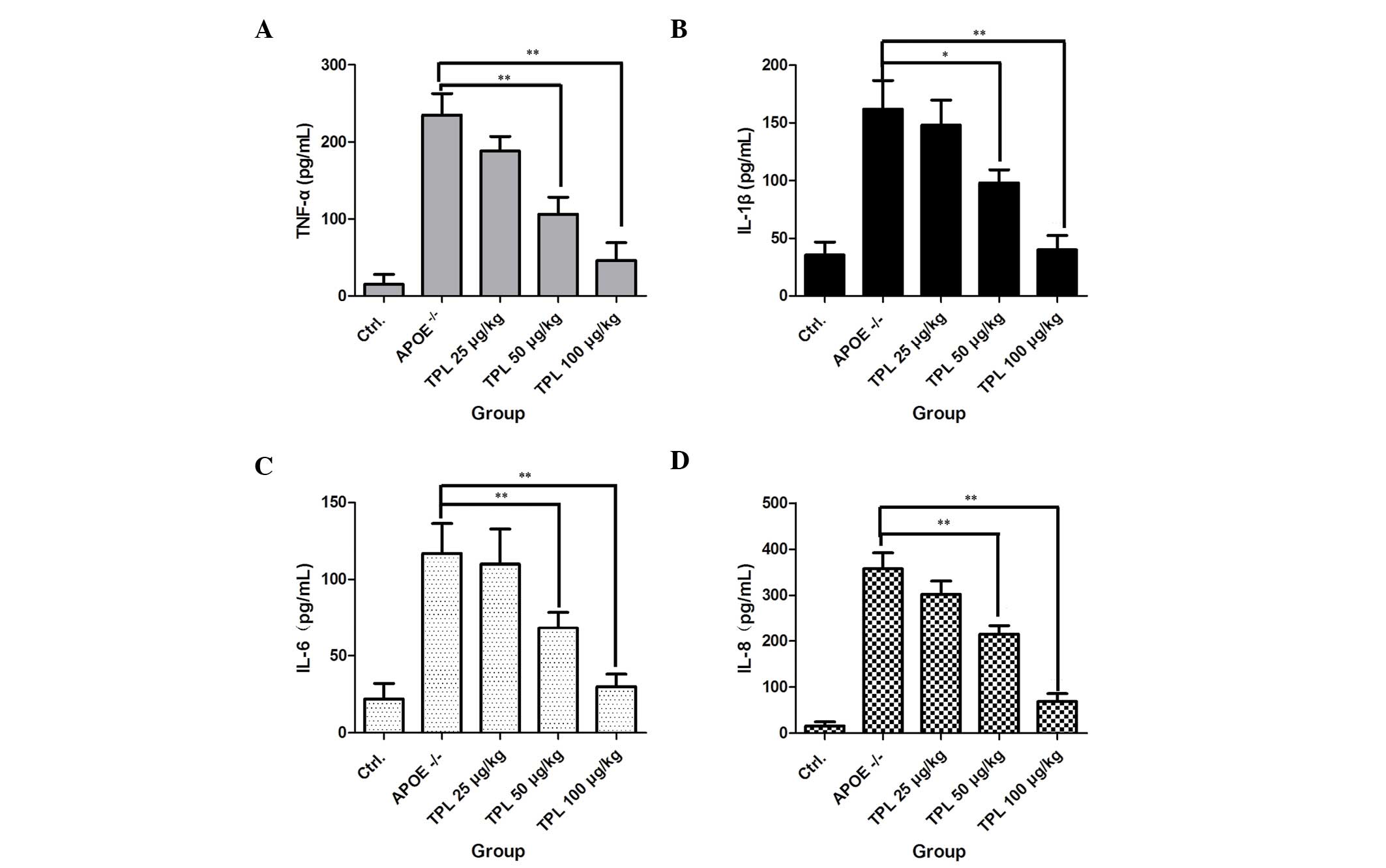
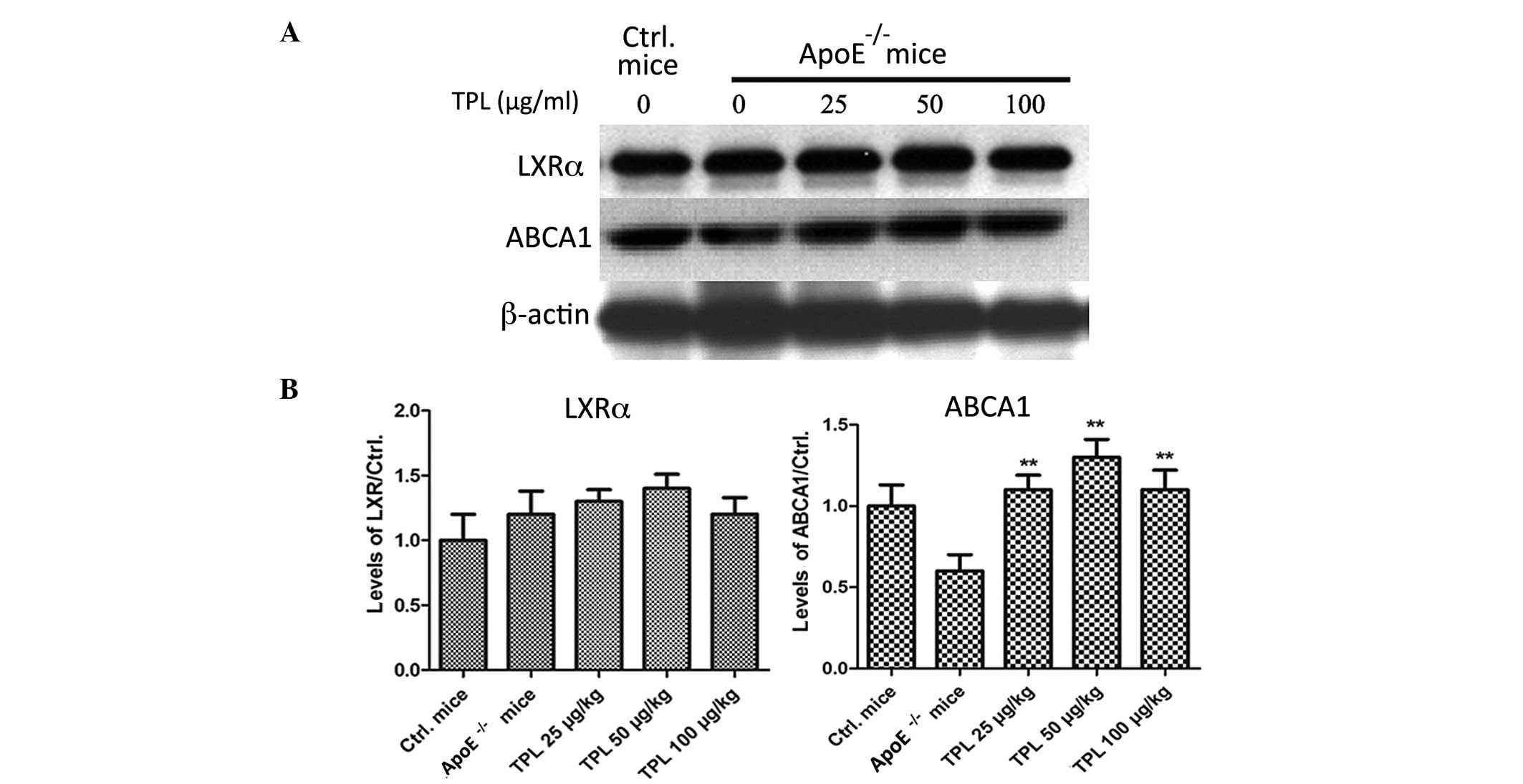
|
1
|
Watanabe T, Sato K, Itoh F, Iso Y,
Nagashima M, Hirano T and Shichiri M: The roles of salusins in
atherosclerosis and related cardiovascular diseases. J Am Soc
Hypertens. 5:359–365. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeng Y, Song JX and Shen XC: Herbal
remedies supply a novel prospect for the treatment of
atherosclerosis: A review of current mechanism studies. Phytother
Res. 26:159–167. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suzuki M, Minami A, Nakanishi A, Kobayashi
K, Matsuda S, Ogura Y and Kitagishi Y: Atherosclerosis and tumor
suppressor molecules (review). Int J Mol Med. 34:934–940.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hulthe J, Wikstrand J, Mattsson-Hulten L
and Fagerberg B: Circulating ICAM-1 (intercellular cell-adhesion
molecule 1) is associated with early stages of atherosclerosis
development and with inflammatory cytokines in healthy 58 year-old
men: The atherosclerosis and insulin resistance (AIR) study. Clin
Sci (Lond). 103:123–129. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maranhão RC and Leite AC Jr: Development
of anti-atherosclerosis therapy based on the inflammatory and
proliferative aspects of the disease. Curr Pharm Des. 21:1196–1204.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shing CM, Fassett RG, Peake JM and Coombes
JS: Voluntary exercise decreases atherosclerosis in nephrectomised
ApoE knockout mice. PloS One. 10:e01202872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
González-Gay MA, González-Juanatey C,
Llorca J and Castañeda S: The influence of inflammation in the
development of subclinical atherosclerosis in psoriatic arthritis:
Comment on ‘Cardiovascular comorbidities in patients with psoriatic
arthritis: A systematic review’ by Jamnistki etal. Ann Rheum Dis.
73:e272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hansson GK: Immune and inflammatory
mechanisms in the development of atherosclerosis. Br Heart J.
69:(Suppl). S38–S41. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pizzi J, Silva LR, Moser D and Leite N:
Relationship between subclinical atherosclerosis, blood pressure
and lipid profile in obese children and adolescents: A systematic
review. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol. 57:1–6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kreisberg RA and Oberman A: Clinical
review 141: Lipids and atherosclerosis: Lessons learned from
randomized controlled trials of lipid lowering and other relevant
studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:423–437. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang L and Yang L: Anti-inflammatory
effects of vinpocetine in atherosclerosis and ischemic stroke: A
review of the literature. Molecules. 20:335–347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory
disease. Am Heart J. 138:S419–S420. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis - an inflammatory
disease. N Engl J Med. 340:115–126. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schlag B, Winkler L, Plonné D, Dürer U and
Dargel R: Preparation of apoE-free rat low density lipoprotein for
catabolic studies. J Lipid Res. 28:1521–1524. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Martinez-Oliván J, Arias-Moreno X,
Velazquez-Campoy A, Millet O and Sancho J: LDL receptor/lipoprotein
recognition: Endosomal weakening of ApoB and ApoE binding to the
convex face of the LR5 repeat. FEBS J. 281:1534–1546. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kostogrys RB, Franczyk-żarów M, Maślak E,
Gajda M, Mateuszuk L, Jackson CL and Chłopicki S: Low carbohydrate,
high protein diet promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein
E/low-density lipoprotein receptor double knockout mice
(apoE/LDLR−/−). Atherosclerosis. 223:327–331.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shimano H, Yamada N, Katsuki M, Yamamoto
K, Gotoda T, Harada K, Shimada M and Yazaki Y: Plasma lipoprotein
metabolism in transgenic mice overexpressing apolipoprotein E.
Accelerated clearance of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B.
J Clin Invest. 90:2084–2091. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shimano H, Yamada N, Katsuki M, Shimada M,
Gotoda T, Harada K, Murase T, Fukazawa C, Takaku F and Yazaki Y:
Overexpression of apolipoprotein E in transgenic mice: Marked
reduction in plasma lipoproteins except high density lipoprotein
and resistance against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 89:1750–1754. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dallongeville J, Lussier-Cacan S and
Davignon J: Modulation of plasma triglyceride levels by apoE
phenotype: A meta-analysis. J Lipid Res. 33:447–454.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Piedrahita JA and
Maeda N: Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in
mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 258:468–471. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Weingärtner O, Ulrich C, Lütjohann D,
Ismail K, Schirmer SH, Vanmierlo T, Böhm M and Laufs U:
Differential effects on inhibition of cholesterol absorption by
plant stanol and plant sterol esters in
apoE−/− mice. Cardiovasc Res. 90:484–492.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sato M, Yamada Y, Matsuoka H, Nakashima S,
Kamiya T, Ikeguchi M and Imaizumi K: Dietary pine bark extract
reduces atherosclerotic lesion development in male ApoE-deficient
mice by lowering the serum cholesterol level. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 73:1314–1317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gopal K, Kumar K, Nandini R, Jahan P and
Kumar MJ: High fat diet containing cholesterol induce aortic
aneurysm through recruitment and proliferation of circulating
agranulocytes in apoE knock out mice model. J Thromb Thrombolysis.
30:154–163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zou Y, Du H, Yin M, Zhang L, Mao L, Xiao
N, Ren G, Zhang C and Pan J: Effects of high dietary fat and
cholesterol on expression of PPAR alpha, LXR alpha and their
responsive genes in the liver of apoE and LDLR double deficient
mice. Mol Cell Biochem. 323:195–205. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Zhang L, Duan W, Liu B, Gong P,
Ding Y and Wu X: Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide by
inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway in LPS-induced acute lung
injury in a murine model. Mol Med Rep. 10:447–452. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen BJ: Triptolide, a novel
immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory agent purified from a
Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Leuk Lymphoma.
42:253–265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Calabresi L, Gomaraschi M, Simonelli S,
Bernini F and Franceschini G: HDL and atherosclerosis: Insights
from inherited HDL disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1851:13–18.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rao X, Zhong J, Maiseyeu A, Gopalakrishnan
B, Villamena FA, Chen LC, Harkema JR, Sun Q and Rajagopalan S:
CD36-dependent 7-ketocholesterol accumulation in macrophages
mediates progression of atherosclerosis in response to chronic air
pollution exposure. Circulation Res. 115:770–780. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Woollard KJ: Immunological aspects of
atherosclerosis. Clinical Sci. 125:221–235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen JH, Wang CJ, Wang CP, Sheu JY, Lin CL
and Lin HH: Hibiscus sabdariffa leaf polyphenolic extract inhibits
LDL oxidation and foam cell formation involving up-regulation of
LXRalpha/ABCA1 pathway. Food Chem. 141:397–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Lee Y and Lee CH: Review: The
physiological and computational approaches for atherosclerosis
treatment. Int J Cardiol. 167:1664–1676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rodondi N, Auer R, de Bosset Sulzer V,
Ghali WA and Cornuz J: Atherosclerosis screening by noninvasive
imaging for cardiovascular prevention: A systematic review. J Gen
Intern Med. 27:220–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hartman J and Frishman WH: Inflammation
and atherosclerosis: A review of the role of interleukin-6 in the
development of atherosclerosis and the potential for targeted drug
therapy. Cardiol Rev. 22:147–151. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ziaei S and Halaby R: Immunosuppressive,
anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties of triptolide: A mini
review. Avicenna J Phytomed. 6:149–164. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hoeke G, Kooijman S, Boon MR, Rensen PC
and Berbee JF: Role of brown fat in lipoprotein metabolism and
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:173–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smith BW, Miller RJ, Wilund KR, O'Brien WD
Jr and Erdman JW Jr: Effects of tomato and soy germ on lipid
bioaccumulation and atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. J Food Sci.
80:H1918–1925. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee HF, Lee TS and Kou YR:
Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of triptolide on
traumatic brain injury in rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 182:1–8.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han R, Rostami-Yazdi M, Gerdes S and
Mrowietz U: Triptolide in the treatment of psoriasis and other
immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
74:424–436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matta R, Wang X, Ge H, Ray W, Nelin LD and
Liu Y: Triptolide induces anti-inflammatory cellular responses. Am
J Transl Res. 1:267–282. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|