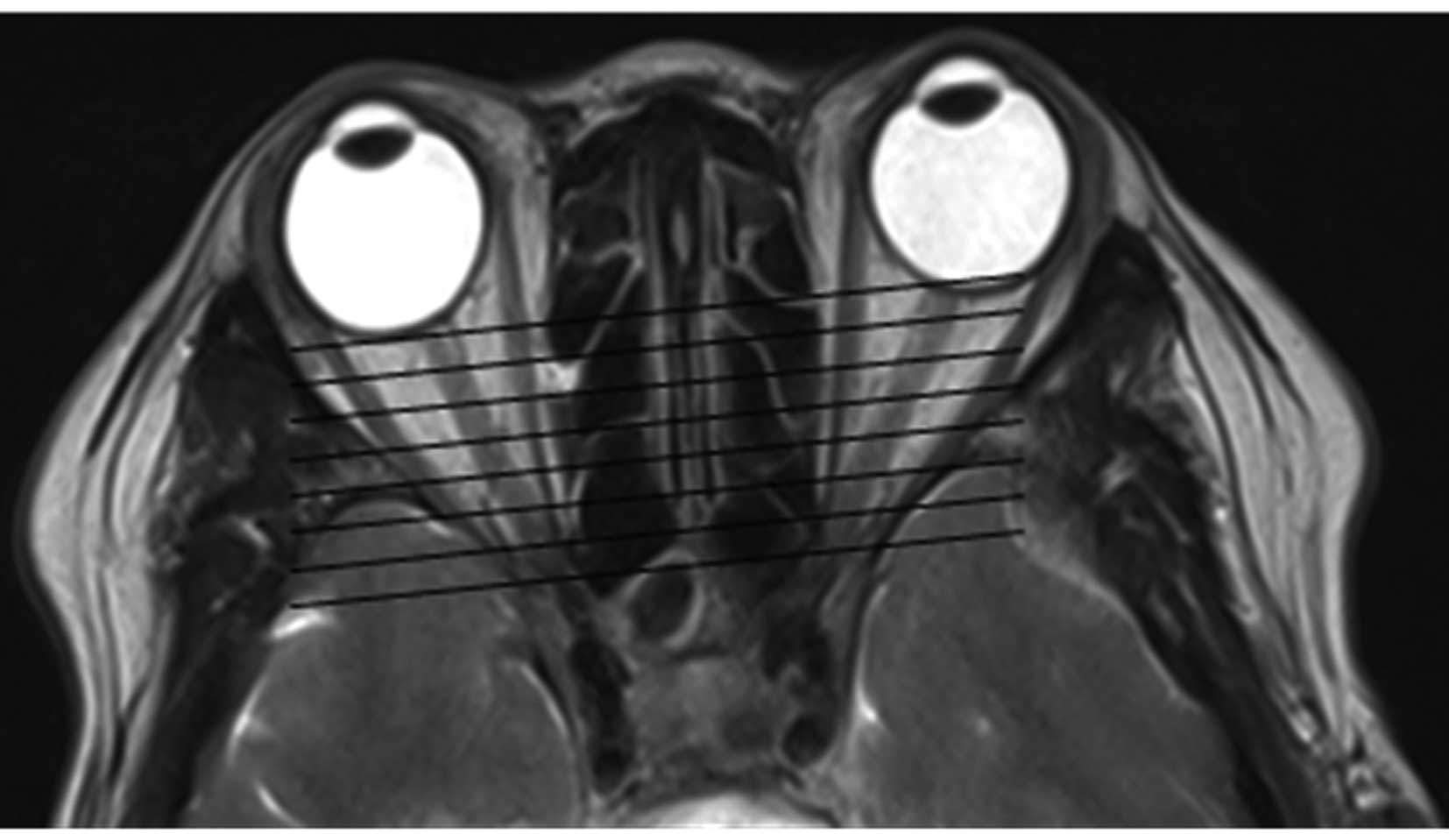
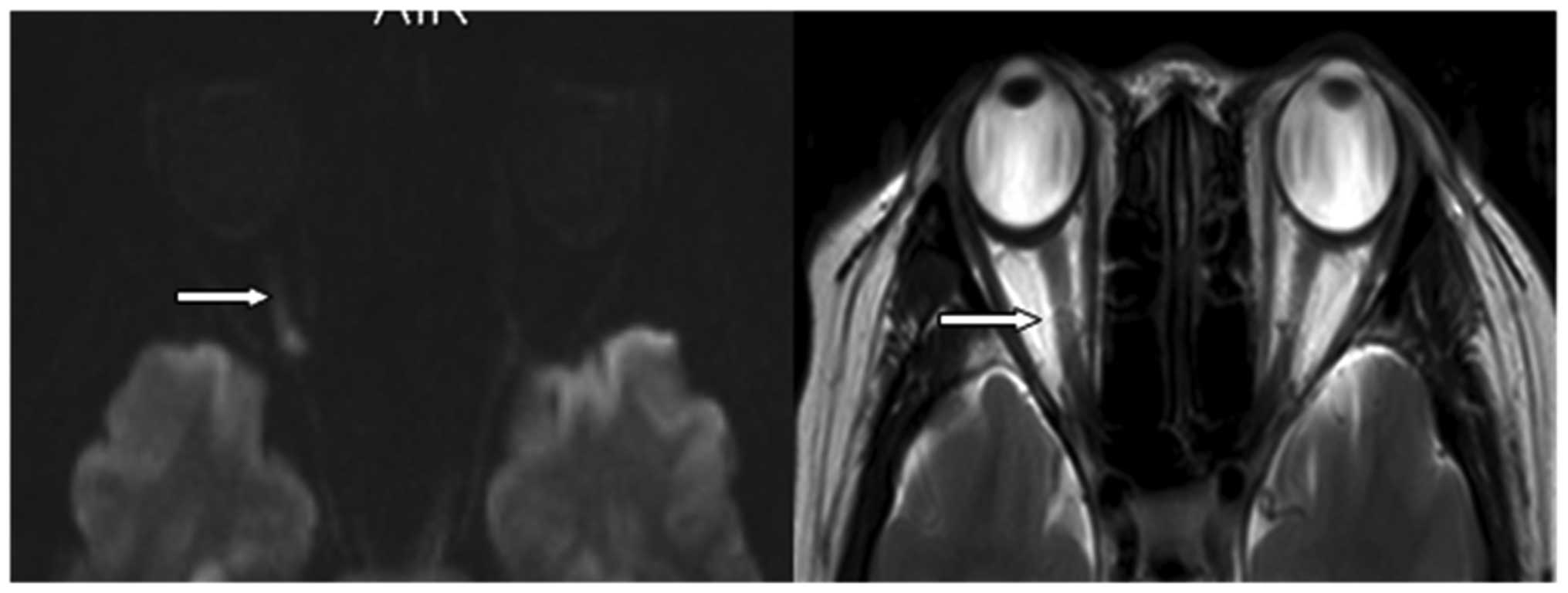
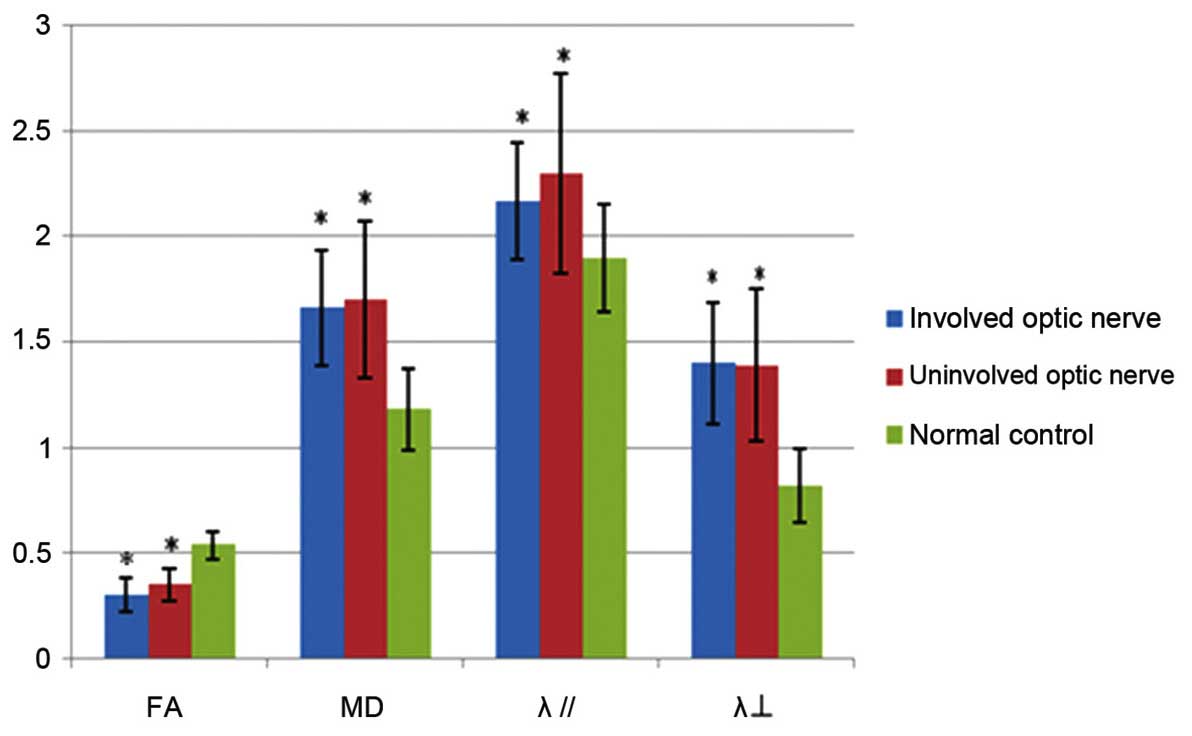
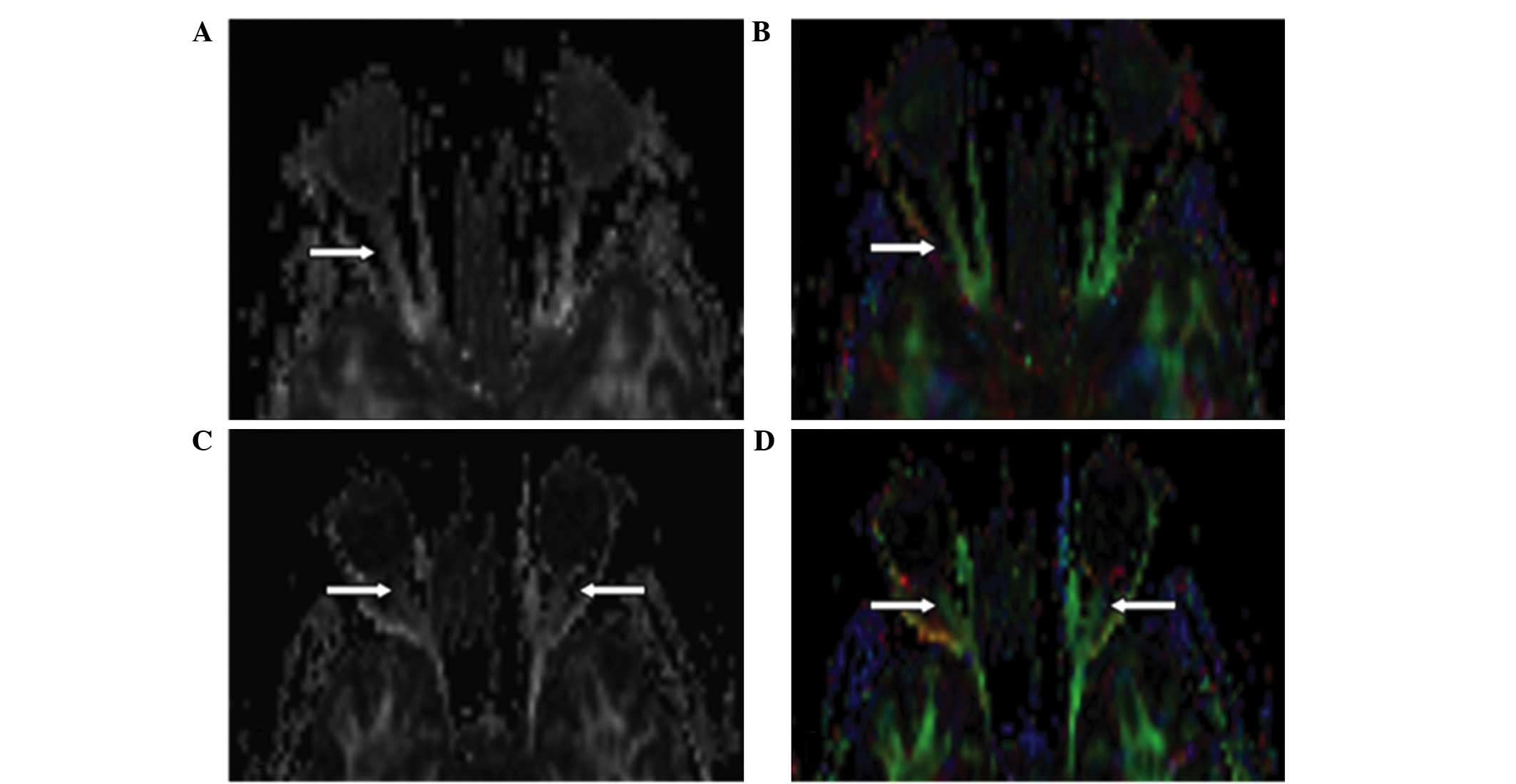
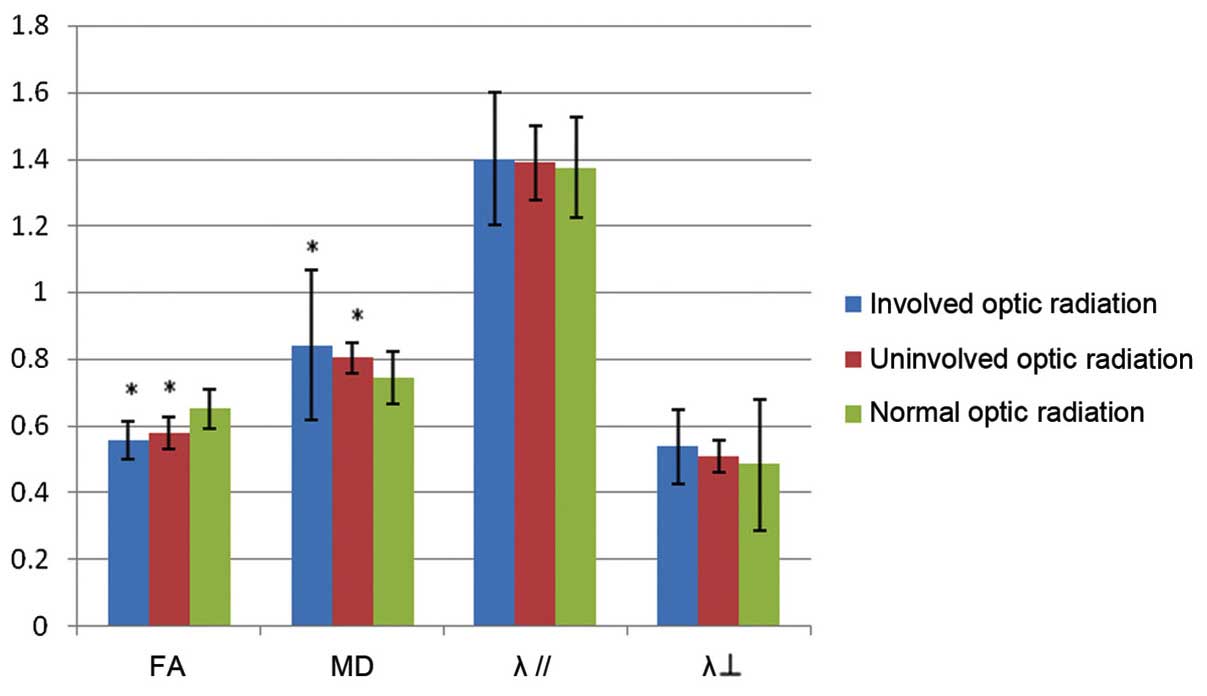
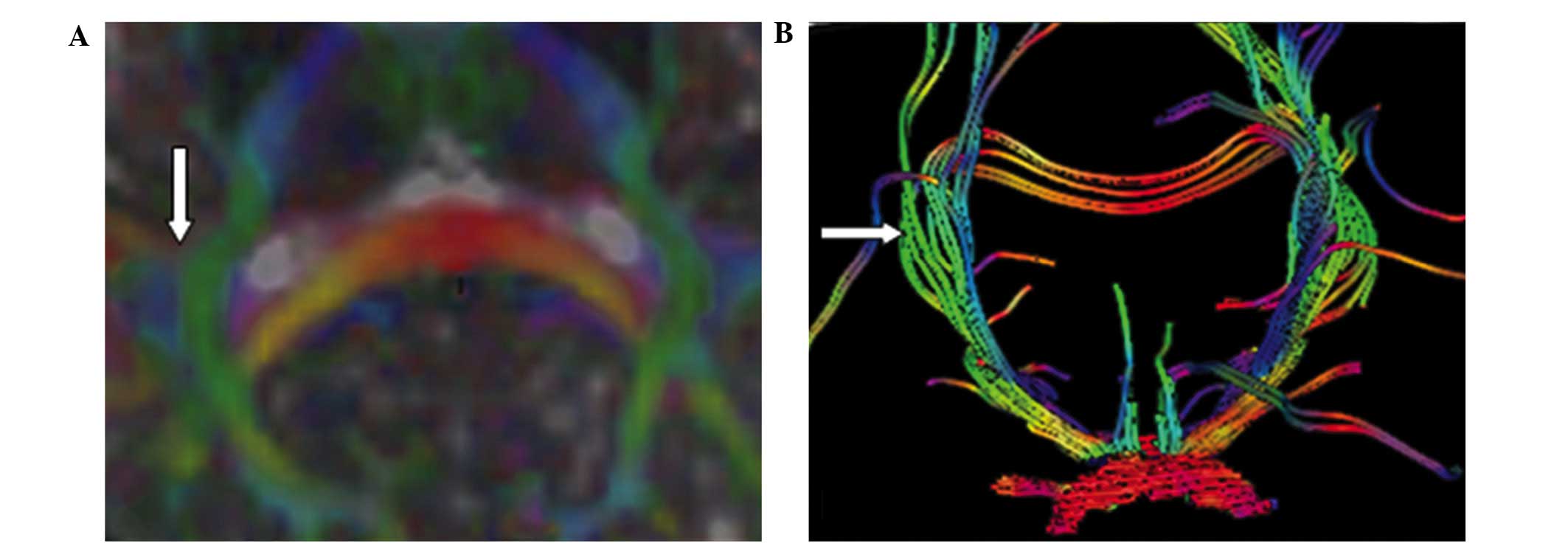
|
1
|
Alonso A and Hernán MA: Temporal trends in
the incidence of multiple sclerosis: A systematic review.
Neurology. 71:129–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al-Afasy HH, Al-Obaidan MA, Al-Ansari YA,
Al-Yatama SA, Al-Rukaibi MS, Makki NI, Suresh A and Akhtar S: Risk
factors for multiple sclerosis in Kuwait: A population-based
case-control study. Neuroepidemiology. 40:30–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berer K and Krishnamoorthy G: Microbial
view of central nervous system autoimmunity. FEBS Lett.
588:4207–4213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Simon JH: MRI outcomes in the diagnosis
and disease course of multiple sclerosis. Handb Clin Neurol.
122:405–425. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barkhof F: The clinico-radiological
paradox in multiple sclerosis revisited. Curr Opin Neurol.
15:239–245. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ge Y, Law M, Johnson G, Herbert J, Babb
JS, Mannon LJ and Grossman RI: Preferential occult injury of corpus
callosum in multiple sclerosis measured by diffusion tensor
imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 20:1–7. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gallo A, Rovaris M, Riva R, Ghezzi A,
Benedetti B, Martinelli V, Falini A, Comi G and Filippi M:
Diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging detects
normal-appearing white matter damage unrelated to short-term
disease activity in patients at the earliest clinical stage of
multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol. 62:803–808. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gratsias G, Kapsalaki E, Kogia S,
Dardiotis E, Tsimourtou V, Lavdas E, Kousi E, Pelekanou A,
Hadjigeorgiou GM and Fezoulidis I: A quantitative evaluation of
damage in normal appearing white matter in patients with multiple
sclerosis using diffusion tensor MR imaging at 3 T. Acta Neurol
Belg. 115:111–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beaulieu C: The basis of anisotropic water
diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR Biomed.
15:435–455. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reich DS, Smith SA, Gordon-Lipkin EM,
Ozturk A, Caffo BS, Balcer LJ and Calabresi PA: Damage to the optic
radiation in multiple sclerosis is associated with retinal injury
and visual disability. Arch Neurol. 66:998–1006. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sinnecker T, Oberwahrenbrock T, Metz I,
Zimmermann H, Pfueller CF, Harms L, Ruprecht K, Ramien C, Hahn K,
Brück W, et al: Optic radiation damage in multiple sclerosis is
associated with visual dysfunction and retinal thinning - an
ultrahigh-field MR pilot study. Eur Radiol. 25:122–131. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klawiter EC, Xu J, Naismith RT, Benzinger
TL, Shimony JS, Lancia S, Snyder AZ, Trinkaus K, Song SK and Cross
AH: Increased radial diffusivity in spinal cord lesions in
neuromyelitis optica compared with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler.
18:1259–1268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song SK, Sun SW, Ju WK, Lin SJ, Cross AH
and Neufeld AH: Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates
axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal
ischemia. Neuroimage. 20:1714–1722. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Klistorner A, Sriram P, Vootakuru N, Wang
C, Barnett MH, Garrick R, Parratt J, Levin N, Raz N, van der Walt
A, et al: Axonal loss of retinal neurons in multiple sclerosis
associated with optic radiation lesions. Neurology. 82:2165–2172.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roosendaal SD, Geurts JJ, Vrenken H, Hulst
HE, Cover KS, Castelijns JA, Pouwels PJ and Barkhof F: Regional DTI
differences in multiple sclerosis patients. Neuroimage.
44:1397–1403. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Naismith RT, Xu J, Tutlam NT, Trinkaus K,
Cross AH and Song SK: Radial diffusivity in remote optic neuritis
discriminates visual outcomes. Neurology. 74:1702–1710. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kolbe S, Bajraszewski C, Chapman C, Nguyen
T, Mitchell P, Paine M, Butzkueven H, Johnston L, Kilpatrick T and
Egan G: Diffusion tensor imaging of the optic radiations after
optic neuritis. Hum Brain Mapp. 33:2047–2061. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hofling AA, Kim JH, Fantz CR, Sands MS and
Song SK: Diffusion tensor imaging detects axonal injury and
demyelination in the spinal cord and cranial nerves of a murine
model of globoid cell leukodystrophy. NMR Biomed. 22:1100–1106.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Trip SA, Wheeler-Kingshott C, Jones SJ, Li
WY, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, Plant GT and Miller DH: Optic nerve
diffusion tensor imaging in optic neuritis. Neuroimage. 30:498–505.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
MacDonald CL, Dikranian K, Bayly P,
Holtzman D and Brody D: Diffusion tensor imaging reliably detects
experimental traumatic axonal injury and indicates approximate time
of injury. J Neurosci. 27:11869–11876. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Smith SA, Williams ZR, Ratchford JN,
Newsome SD, Farrell SK, Farrell JA, Gifford A, Miller NR, van Zijl
PC, Calabresi PA and Reich DS: Diffusion tensor imaging of the
optic nerve in multiple sclerosis: Association with retinal damage
and visual disability. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 32:1662–1668. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chard DT, Brex PA, Ciccarelli O, Griffin
CM, Parker GJ, Dalton C, Altmann DR, Thompson AJ and Miller DH: The
longitudinal relation between brain lesion load and atrophy in
multiple sclerosis: A 14 year follow up study. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 74:1551–1554. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brex PA, Ciccarelli O, O'Riordan JI,
Sailer M, Thompson AJ and Miller DH: A longitudinal study of
abnormalities on MRI and disability from multiple sclerosis. N Engl
J Med. 346:158–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wieshmann UC, Symms MR, Clark CA, Lemieux
L, Franconi F, Parker GJ, Barker GJ and Shorvon SD: Wallerian
degeneration in the optic radiation after temporal lobectomy
demonstrated in vivo with diffusion tensor imaging. Epilepsia.
40:1155–1158. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|