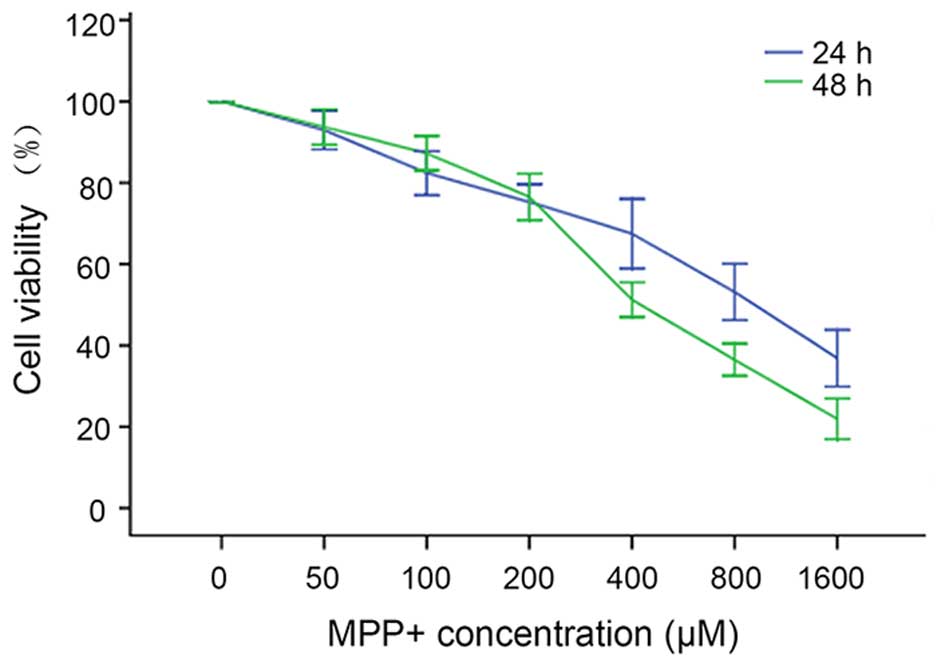
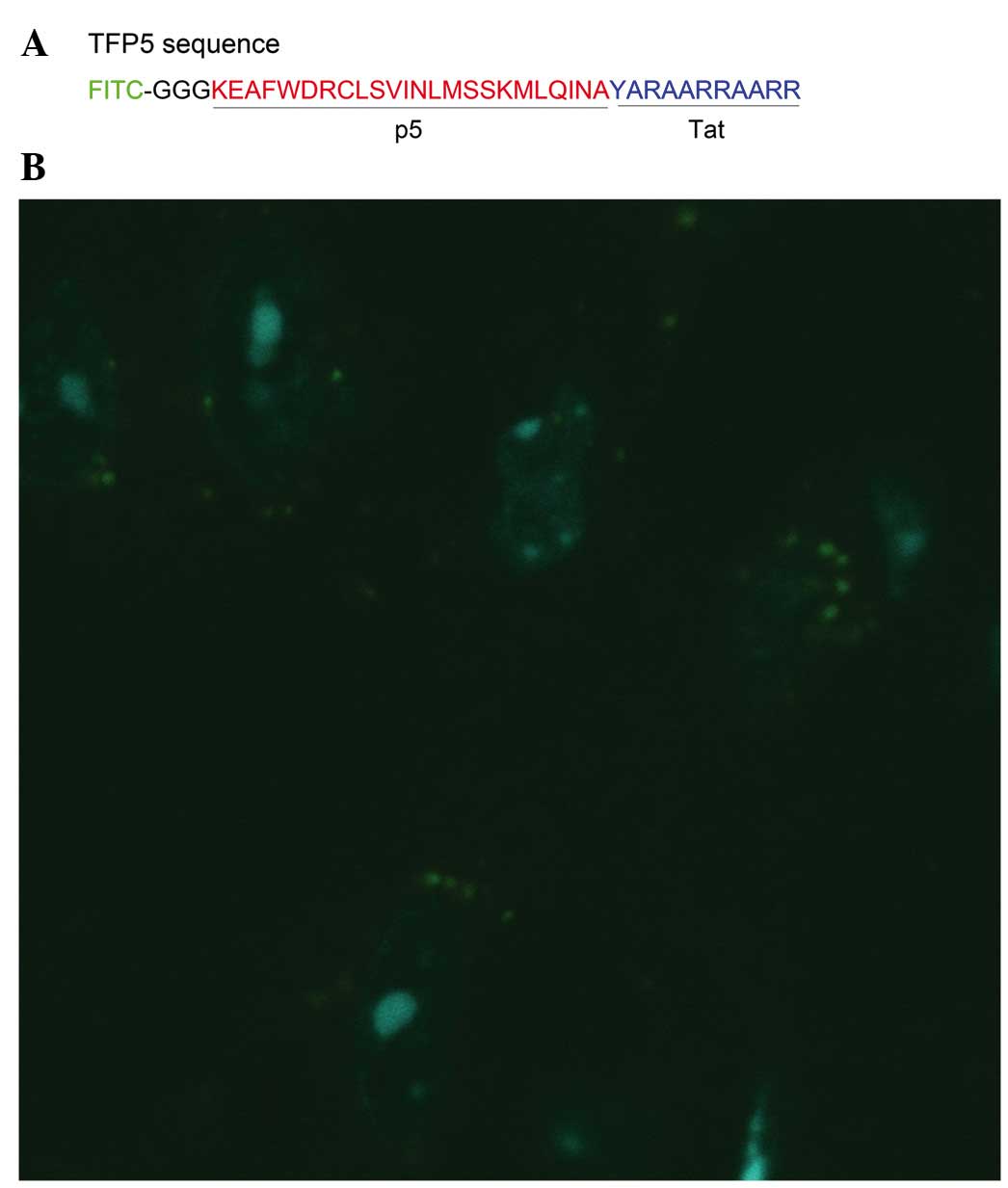
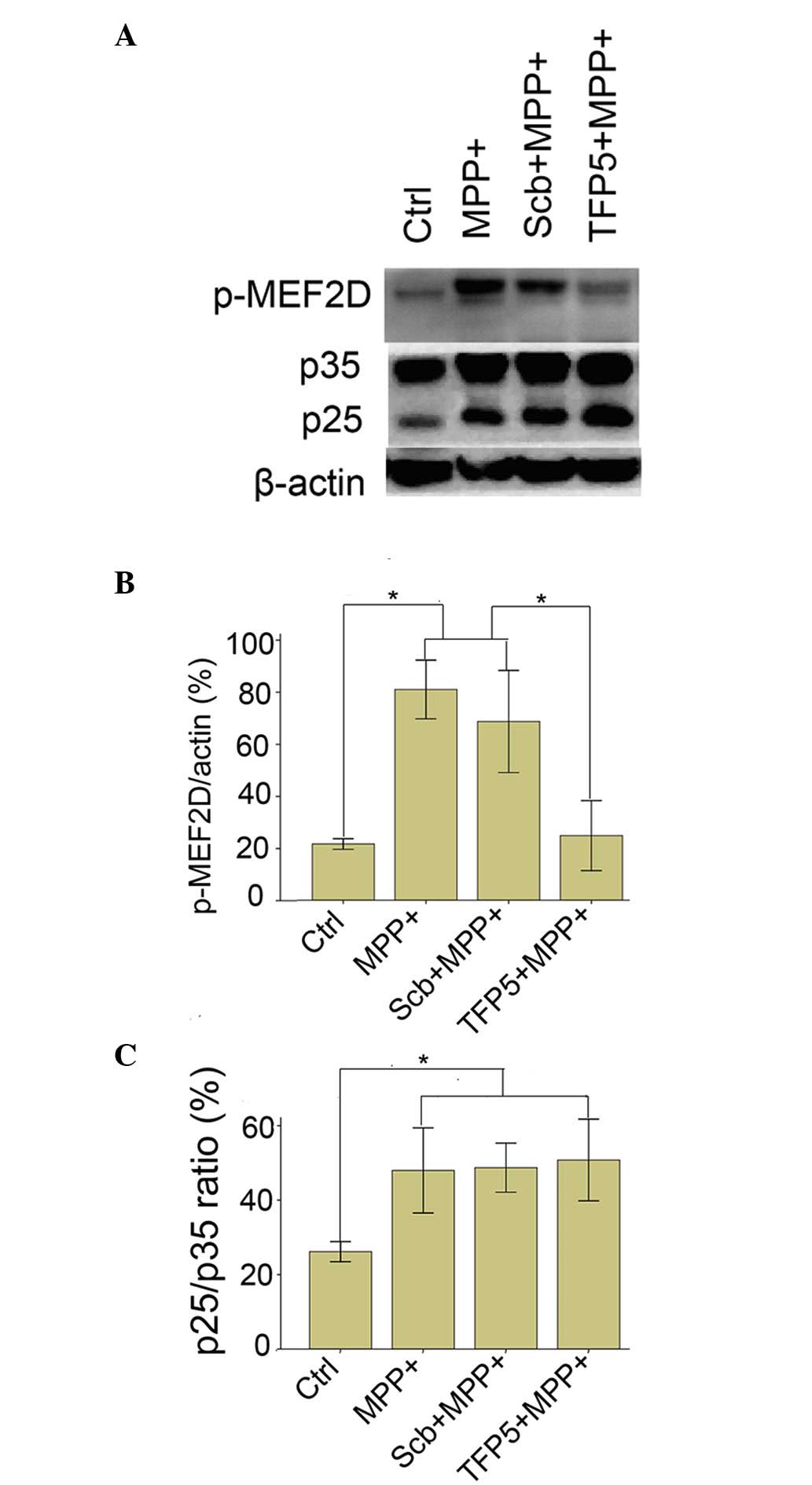
|
1
|
Rascol O: Drugs and drug delivery in PD:
Optimizing control of symptoms with pramipexole prolonged-release.
Eur J Neurol. 18 Suppl 1:S3–S10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Salat D and Tolosa E: Levodopa in the
treatment of Parkinson's disease: Current status and new
developments. J Parkinsons Dis. 3:255–269. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wood-Kaczmar A, Gandhi S and Wood NW:
Understanding the molecular causes of Parkinson's disease. Trends
Mol Med. 12:521–528. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Su SC and Tsai LH: Cyclin-dependent
kinases in brain development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
27:465–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander
RM and Tsai LH: Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by
calpain. Nature. 405:360–364. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alvira D, Ferrer I, Gutierrez-Cuesta J,
Garcia-Castro B, Pallàs M and Camins A: Activation of the
calpain/cdk5/p25 pathway in the girus cinguli in Parkinson's
disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 14:309–313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hattori N and Mizuno Y: Pathogenetic
mechanisms of parkin in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 364:722–724.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith PD, Crocker SJ, Jackson-Lewis V,
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Hayley S, Mount MP, O'Hare MJ, Callaghan S,
Slack RS, Przedborski S, et al: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a
mediator of dopaminergic neuron loss in a mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:13650–16655. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wong AS, Lee RH, Cheung AY, Yeung PK,
Chung SK, Cheung ZH and Ip NY: Cdk5-mediated phosphorylation of
endophilin B1 is required for induced autophagy in models of
Parkinson's disease. Nat Cell Biol. 13:568–579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Avraham E, Rott R, Liani E, Szargel R and
Engelender S: Phosphorylation of Parkin by the cyclin-dependent
kinase 5 at the linker region modulates its ubiquitin-ligase
activity and aggregation. J Biol Chem. 282:12842–12850. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Smith PD, Mount MP, Shree R, Callaghan S,
Slack RS, Anisman H, Vincent I, Wang X, Mao Z and Park DS:
Calpain-regulated p35/cdk5 plays a central role in dopaminergic
neuron death through modulation of the transcription factor myocyte
enhancer factor 2. J Neurosci. 26:440–447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Camins A, Verdaguer E, Folch J, Canudas AM
and Pallàs M: The role of CDK5/P25 formation/inhibition in
neurodegeneration. Drug News Perspect. 19:453–460. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Liu W, Szumlinski KK and Lew J:
p10, the N-terminal domain of p35, protects against
CDK5/p25-induced neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:20041–20046. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rosales JL and Lee KY: Extraneuronal roles
of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Bioessays. 28:1023–1034. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lopes JP and Agostinho P: Cdk5:
Multitasking between physiological and pathological conditions.
Prog Neurobiol. 94:49–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Piedrahita D, Hernández I, López-Tobón A,
Fedorov D, Obara B, Manjunath BS, Boudreau RL, Davidson B, Laferla
F, Gallego-Gómez JC, et al: Silencing of CDK5 reduces
neurofibrillary tangles in transgenic alzheimer's mice. J Neurosci.
30:13966–13976. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shukla V, Zheng YL, Mishra SK, Amin ND,
Steiner J, Grant P, Kesavapany S and Pant HC: A truncated peptide
from p35, a Cdk5 activator, prevents Alzheimer's disease phenotypes
in model mice. FASEB J. 27:174–186. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gong CX and Iqbal K: Hyperphosphorylation
of microtubule-associated protein tau: A promising therapeutic
target for Alzheimer disease. Curr Med Chem. 15:2321–2328. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu SY, Wu YM, Ji Z, Gao XY and Pan SY: A
modified technique for culturing primary fetal rat cortical
neurons. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:8039302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shukla V, Skuntz S and Pant HC:
Deregulated Cdk5 activity is involved in inducing Alzheimer's
disease. Arch Med Res. 43:655–662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wen Z, Shu Y, Gao C, Wang X, Qi G, Zhang
P, Li M, Shi J and Tian B: CDK5-mediated phosphorylation and
autophagy of RKIP regulate neuronal death in Parkinson's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 35:2870–2880. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng YL, Amin ND, Hu YF, Rudrabhatla P,
Shukla V, Kanungo J, Kesavapany S, Grant P, Albers W and Pant HC: A
24-residue peptide (p5), derived from p35, the Cdk5 neuronal
activator, specifically inhibits Cdk5-p25 hyperactivity and tau
hyperphosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 285:34202–34212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Namura I, Douillet P, Sun CJ, Pert A,
Cohen RM and Chiueh CC: MPP+ (1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine)
is a neurotoxin to dopamine-, norepinephrine- and
serotonin-containing neurons. Eur J Pharmacol. 136:31–37. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie HR, Hu LS and Li GY: SH-SY5Y human
neuroblastoma cell line: In vitro cell model of dopaminergic
neurons in Parkinson's disease. Chin Med J (Engl). 123:1086–1092.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Binukumar BK, Zheng YL, Shukla V, Amin ND,
Grant P and Pant HC: TFP5, a peptide derived from p35, a Cdk5
neuronal activator, rescues cortical neurons from glucose toxicity.
J Alzheimers Dis. 39:899–909. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|