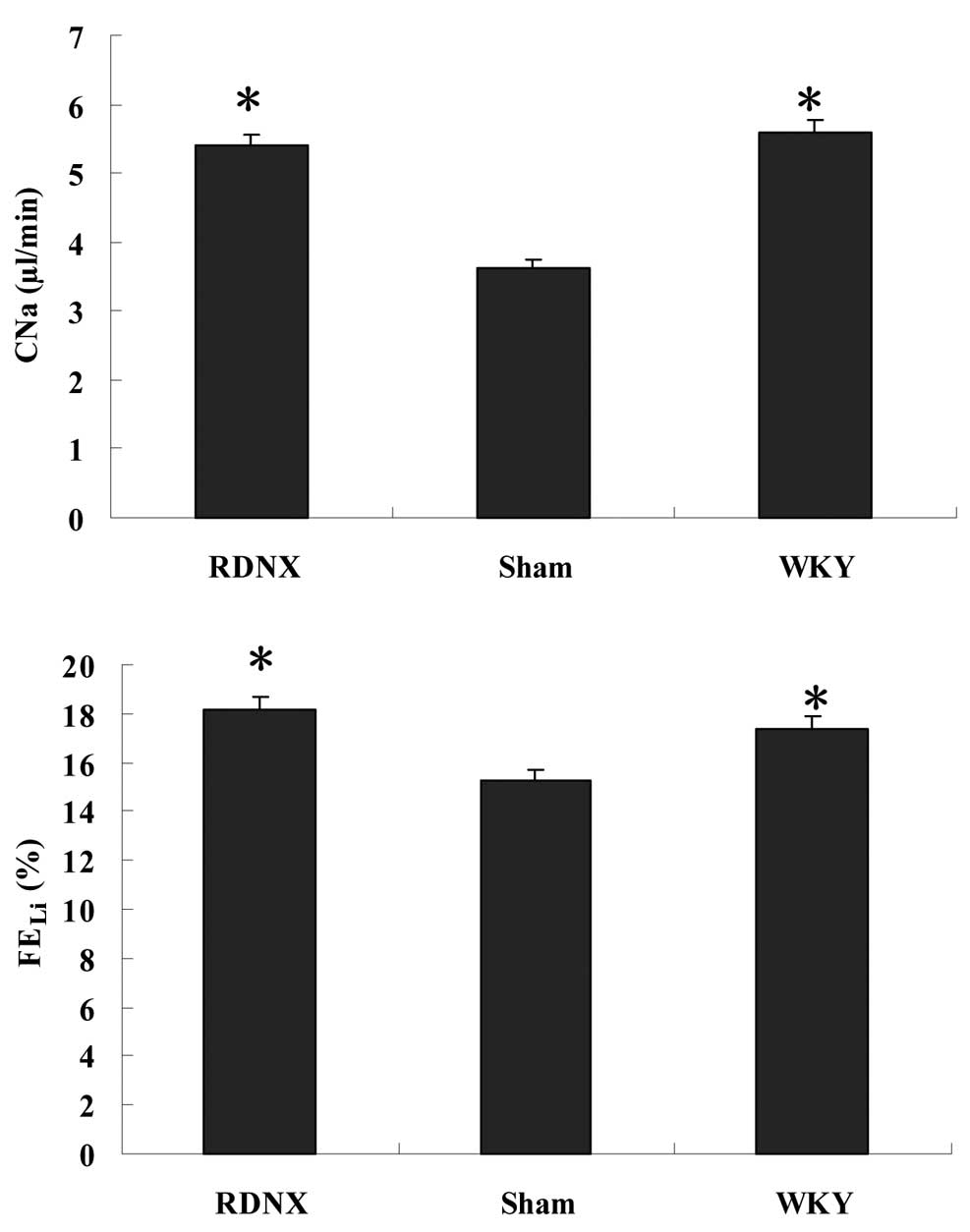
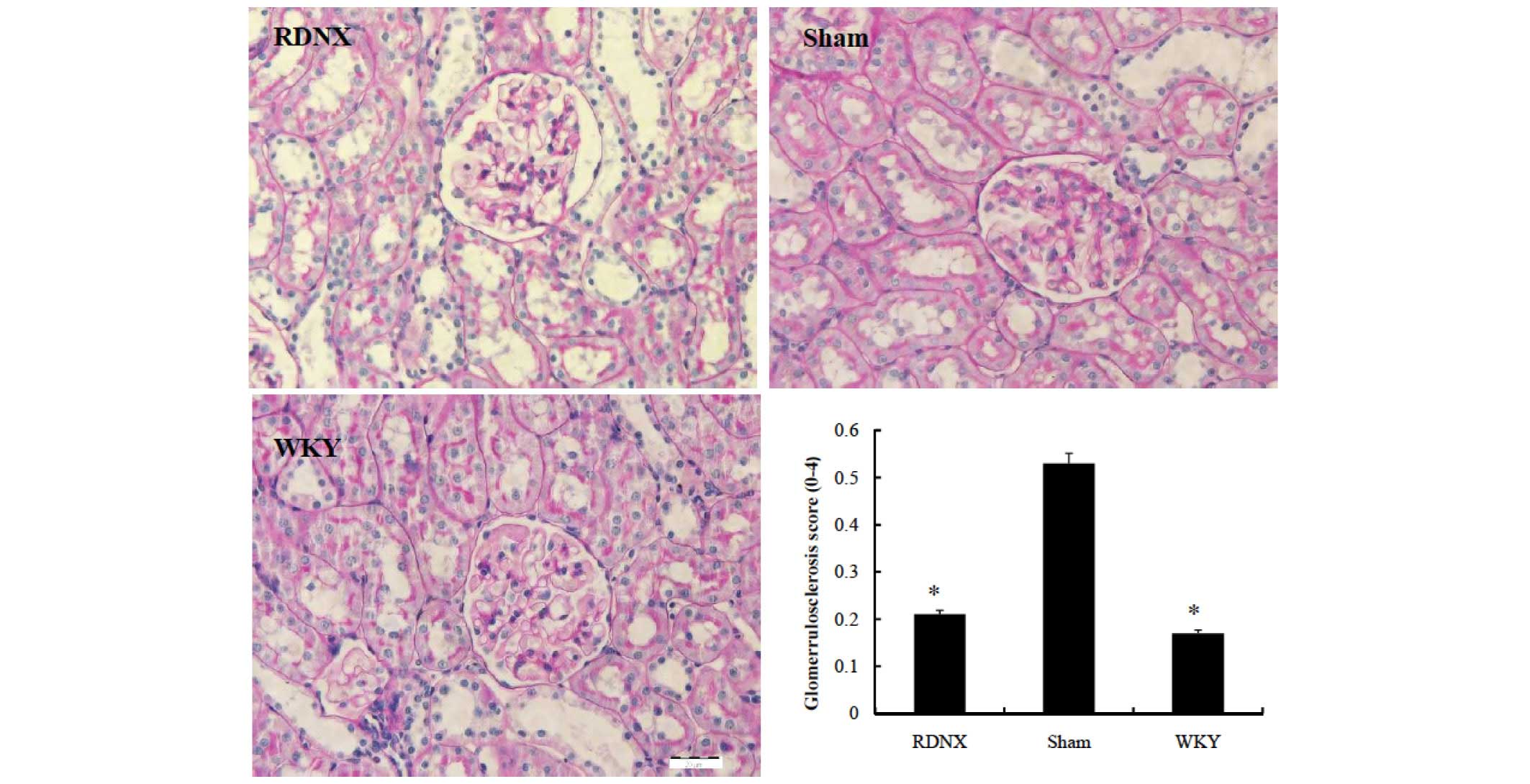
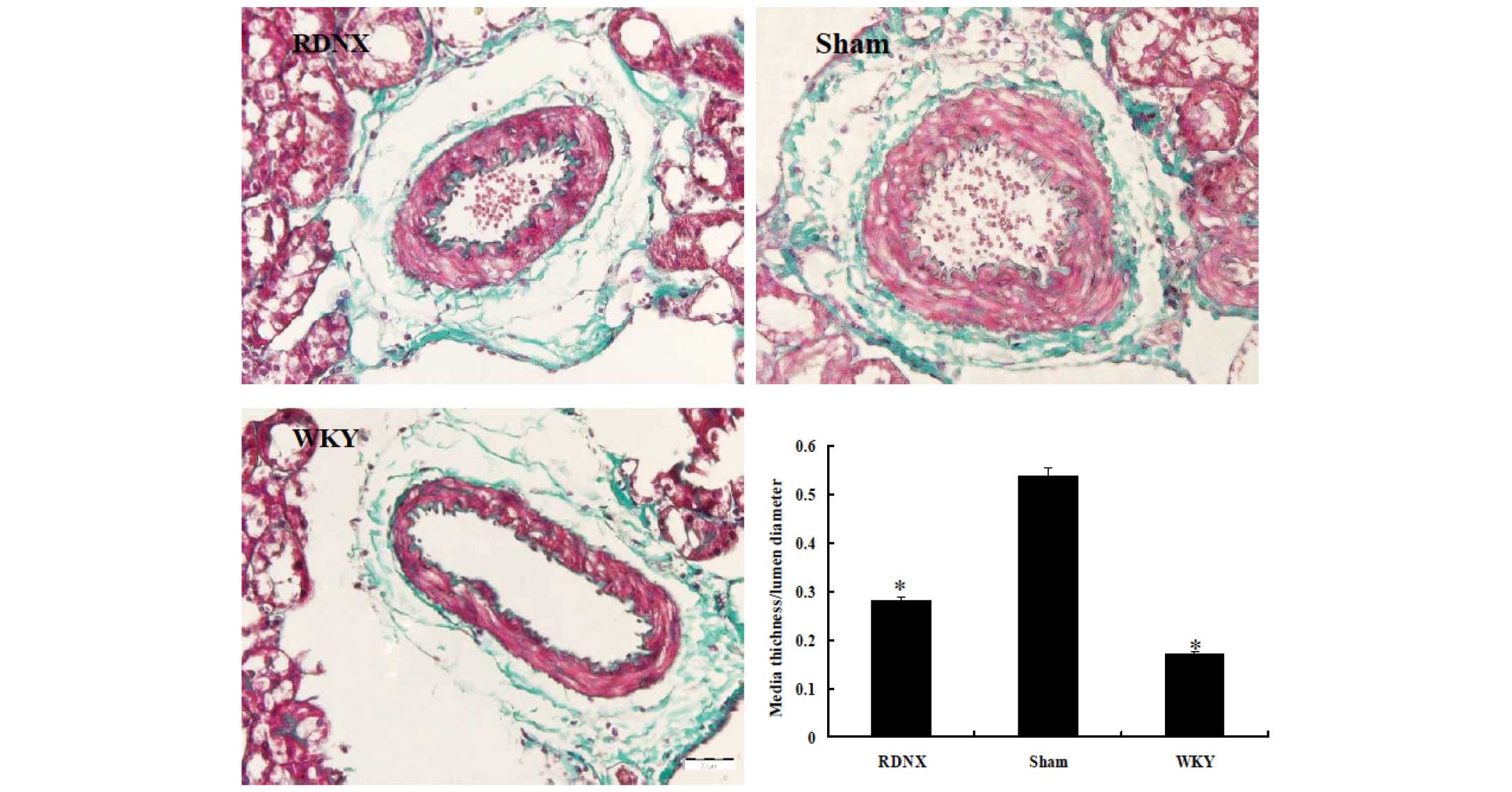
|
1
|
Bakris GL, Williams M, Dworkin L, Elliott
WJ, Epstein M, Toto R, Tuttle K, Douglas J, Hsueh W and Sowers J:
Preserving renal function in adults with hypertension and diabetes:
A consensus approach. National kidney foundation hypertension and
diabetes executive committees working group. Am J Kidney Dis.
36:646–661. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Neumann J, Ligtenberg G, Klein II, Koomans
HA and Blankestijn PJ: Sympathetic hyperactivity in chronic kidney
disease: Pathogenesis, clinical relevance and treatment. Kidney
Int. 65:1568–1576. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nagasu H, Satoh M, Kuwabara A, Yorimitsu
D, Sakuta T, Tomita N and Kashihara N: Renal denervation reduces
glomerular injury by suppressing NAD(P)H oxidase activity in dahl
salt-sensitive rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:2889–2898. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
DiBona GF and Kopp UC: Neural control of
renal function. Physiol Rev. 77:77–197. 1997.
|
|
5
|
Guyton AC, Coleman TG, Cowley AW, Scheel
KW, Manning RD and Norman RA: Arterial pressure regulation:
Overriding dominance of the kidneys in long-term control and in
hypertension. Am J Med. 52:584–594. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Krum H, Schlaich M, Whitbourn R, Sobotka
PA, Sadowski J, Bartus K, Kapelak B, Walton A, Sievert H, Thambar
S, et al: Catheter-based renal sympathetic denervation for
resistant hypertension: A multicentre safety and proof-of-principle
cohort study. Lancet. 373:1275–1281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, Schlaich MP,
Schmieder RE and Böhm M: Renal sympathetic denervation in patients
with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial):
A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:1903–1909.
2010.Symplicity HTN-2 Investigators. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krum H, Sobotka P, Mahfoud F, Böhm M,
Esler M and Schlaich M: Device-based antihypertensive therapy:
Therapeutic modulation of the autonomic nervous system.
Circulation. 123:209–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mahfoud F, Cremers B, Janker J, Link B,
Vonend O, Ukena C, Linz D, Schmieder R, Rump LC, Kindermann I, et
al: Renal hemodynamics and renal function after catheter-based
renal sympathetic denervation in patients with resistant
hypertension. Hypertension. 60:419–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guyton AC: Blood pressure control-special
role of the kidneys and body fluids. Science. 252:1813–1816. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jacob F, Ariza P and Osborn JW: Renal
denervation chronically lowers arterial pressure independent of
dietary sodium intake in normal rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 284:H2302–H2310. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bonjour JP, Churchill PC and Malvin RL:
Change of tubular reabsorption of sodium and water after renal
denervation in the dog. J Physiol. 204:571–582. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blake WD and Jurf AN: Renal sodium
reabsorption after acute renal denervation in the rabbit. J
Physiol. 196:65–73. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boer PA, Morelli JM, Figueiredo JF and
Gontijo JA: Early altered renal sodium handling determined by
lithium clearance in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR): Role of
renal nerves. Life Sci. 76:1805–1815. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salman IM, Sattar MA, Abdullah NA, Ameer
OZ, Basri F, Hussain NM, Yam MF, Swarup KR, Rathore HA, Kazi RN, et
al: Role of renal sympathetic nervous system in the control of
renal potassium handling. J Nephrol. 23:291–296. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salman IM, Sattar MA, Abdullah NA, Ameer
OZ, Hussain FB, Hye Khan MA, Yam MF, Rathore KR, Kazi RN, Salman HM
and Johns EJ: Renal functional & haemodynamic changes following
acute unilateral renal denervation in sprague dawley rats. Indian J
Med Res. 131:76–82. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kubota Y, Umegaki K, Kagota S, Tanaka N,
Nakamura K, Kunitomo M and Shinozuka K: Evaluation of blood
pressure measured by tail-cuff methods (without heating) in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1756–17581.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zou J, Li Y, Yan CH, Wei FF, Zhang L and
Wang JG: Blood pressure in relation to interactions between sodium
dietary intake and renal handling. Hypertension. 62:719–725. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Namikoshi T, Tomita N, Fujimoto S, Haruna
Y, Ohzeki M, Komai N, Sasaki T, Yoshida A and Kashihara N:
Isohumulones derived from hops ameliorate renal injury via an
anti-oxidative effect in dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertens Res.
30:175–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Namikoshi T, Tomita N, Satoh M, Haruna Y,
Kobayashi S, Komai N, Sasaki T and Kashihara N: Pioglitazone
enhances the antihypertensive and renoprotective effects of
candesartan in zucker obese rats fed a high-protein diet. Hypertens
Res. 31:745–755. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reddi AS and Bollineni JS:
Selenium-deficient diet induces renal oxidative stress and injury
via TGF-beta1 in normal and diabetic rats. Kidney Int.
59:1342–1353. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kowalski R, Kreft E, Kasztan M, Jankowski
M and Szczepanska-Konkel M: Chronic renal denervation increases
renal tubular response to P2X receptor agonists in rats:
Implication for renal sympathetic nerve ablation. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 27:3443–3448. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beevers G, Lip GY and O'Brien E: ABC of
hypertension: The pathophysiology of hypertension. BMJ.
322:912–916. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roman RJ and Cowley AW Jr: Abnormal
pressure-diuresis-natriuresis response in spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol. 248:F199–F205. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Heckmann U, Zidek W and Schurek HJ: Sodium
reabsorption in the isolated perfused kidney of normotensive and
spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens Suppl. 7:S172–S173.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vieira-Coelho MA and Moura E: Effect of
clonidine on renal sodium handling in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 119:122–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Katholi RE, Naftilan AJ, Bishop SP and
Oparil S: Role of the renal nerves in the maintenance of DOCA-salt
hypertension in the rat. Influence on the renal vasculature and
sodium excretion. Hypertension. 5:427–435. 1983.
|
|
28
|
Katayama T, Sueta D, Kataoka K, Hasegawa
Y, Koibuchi N, Toyama K, Uekawa K, Mingjie M, Nakagawa T, Maeda M,
et al: Long-term renal denervation normalizes disrupted blood
pressure circadian rhythm and ameliorates cardiovascular injury in
a rat model of metabolic syndrome. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0001972013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Healy V, Thompson C and Johns EJ: The
adrenergic regulation of proximal tubular Na +/H+ exchanger 3 in
the rat. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 210:678–689. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
DiBona GF: Neural control of the kidney:
Functionally specific renal sympathetic nerve fibers. Am J Physiol
Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 279:R1517–R1524. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Greenberg SG, Enders C and Osborn JL:
Renal nerves affect rate of achieving sodium balance in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 22:1–8. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rogenes PR and Gottschalk CW: Renal
function in conscious rats with chronic unilateral renal
denervation. Am J Physiol. 242:F140–F148. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rudd MA, Grippo RS and Arendshorst WJ:
Acute renal denervation produces a diuresis and natriuresis in
young SHR but not WKY rats. Am J Physiol. 251:F655–F661.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oparil S, Sripairojthikoon W and Wyss JM:
The renal afferent nerves in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Can
J Physiol Pharmacol. 65:1548–1558. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kline RL: Renal nerves and experimental
hypertension: Evidence and controversy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
65:1540–1547. 1987. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Giebisch G: Renal potassium transport:
Mechanisms and regulation. Am J Physiol. 274:F817–F833.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ljutić D and Kes P: The role of arterial
hypertension in the progression of non-diabetic glomerular
diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 18 Suppl 5:v28–v30. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Petras D, Koutroutsos K, Kordalis A,
Tsioufis C and Stefanadis C: The role of sympathetic nervous system
in the progression of chronic kidney disease in the era of catheter
based sympathetic renal denervation. Curr Clin Pharmacol.
8:197–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Amann K, Nichols C, Tornig J, Schwarz U,
Zeier M, Mall G and Ritz E: Effect of ramipril, nifedipine and
moxonidine on glomerular morphology and podocyte structure in
experimental renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 11:1003–1011.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fenton C, Keating GM and Lyseng-Williamson
KA: Moxonidine: A review of its use in essential hypertension.
Drugs. 66:477–496. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Krespi PG, Makris TK, Hatzizacharias AN,
Triposkiadis P, Tsoukala C, Kyriaki D, Votteas V and Kyriakidis M:
Moxonidine effect on microalbuminuria, thrombomodulin and
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels in patients with essential
hypertension. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 12:463–467. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Luippold G, Beilharz M and Mühlbauer B:
Chronic renal denervation prevents glomerular hyperfiltration in
diabetic rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 19:342–347. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|