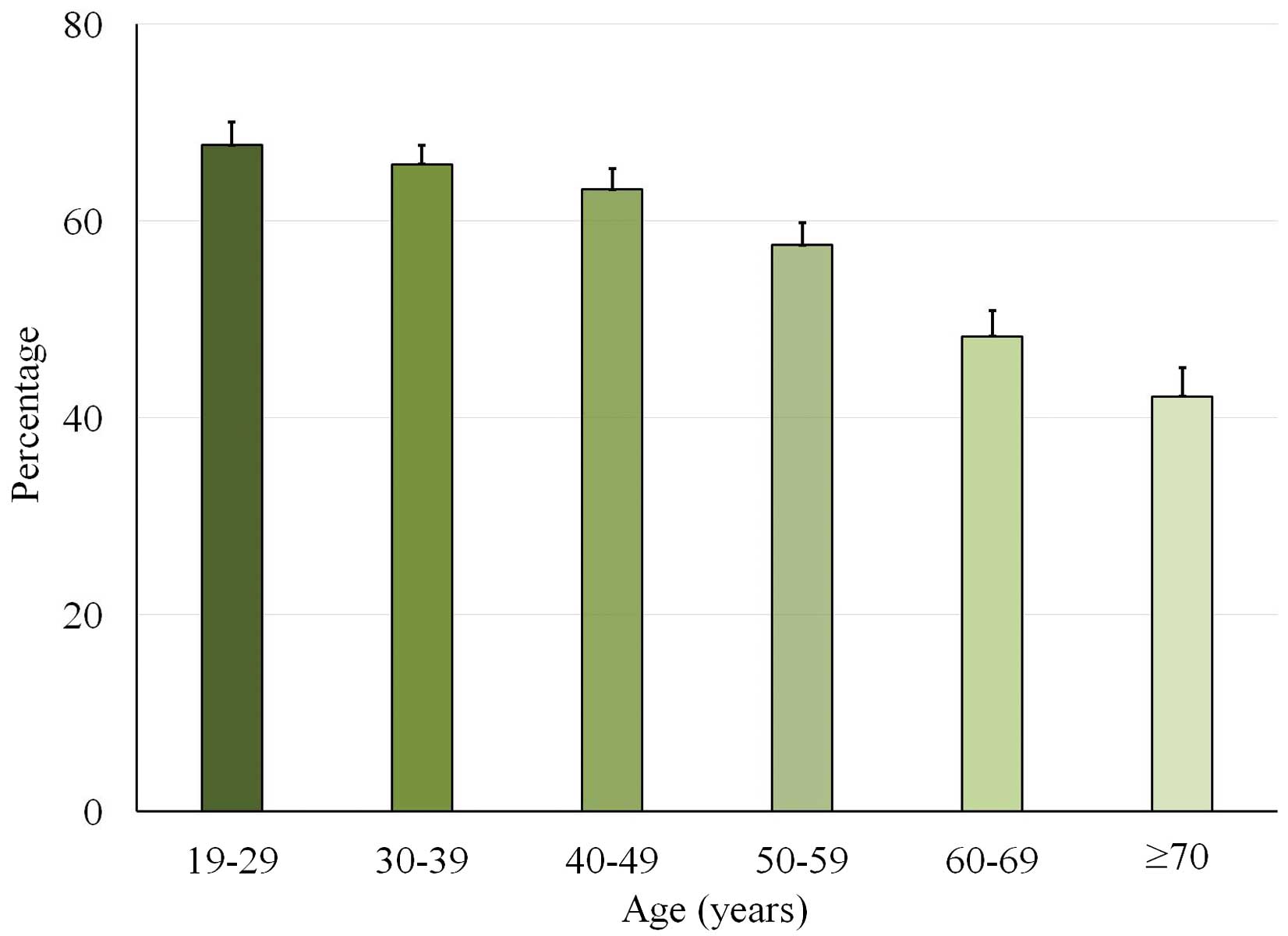
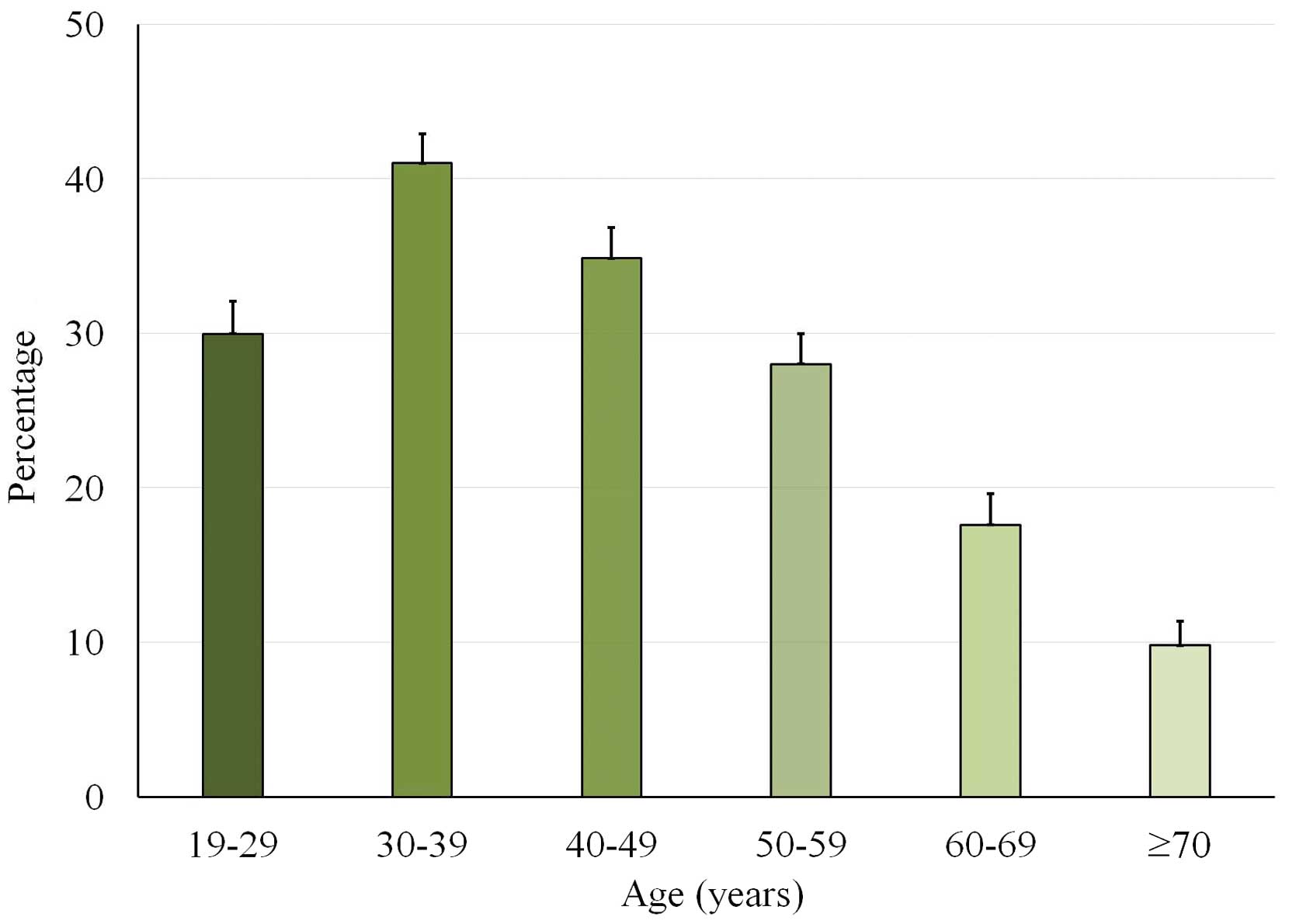
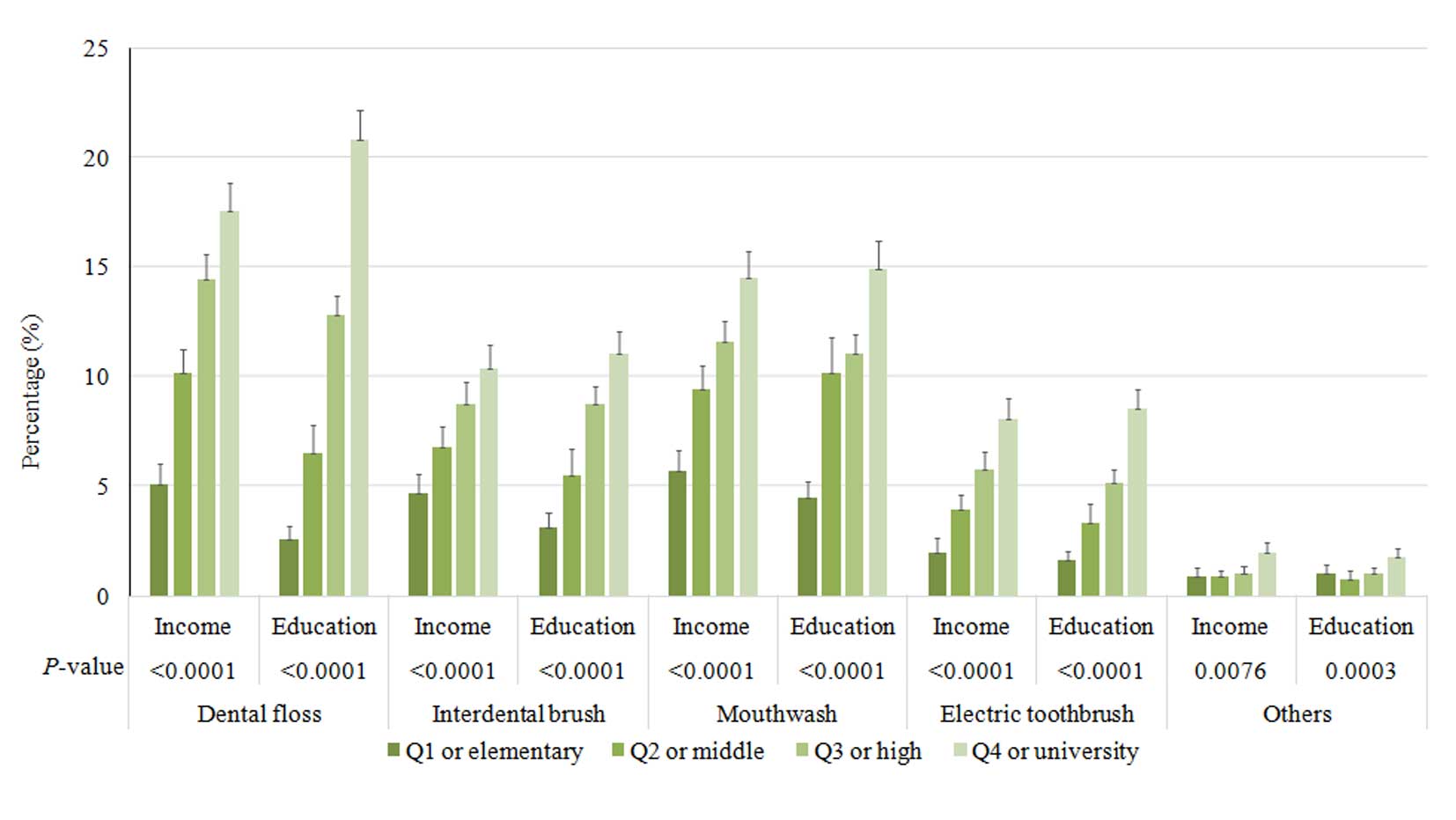
|
1
|
Jin LJ, Lamster IB, Greenspan JS, Pitts
NB, Scully C and Warnakulasuriya S: Global burden of oral diseases:
Emerging concepts, management and interplay with systemic health.
Oral Dis. 2015.
|
|
2
|
Linden GJ, Lyons A and Scannapieco FA:
Periodontal systemic associations: Review of the evidence. J Clin
Periodontol. 40(Suppl)14:S8–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Singh A, Rouxel P, Watt RG and Tsakos G:
Social inequalities in clustering of oral health related behaviors
in a national sample of British adults. Prev Med. 57:102–106. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Espinoza I, Thomson WM, Gamonal J and
Arteaga O: Disparities in aspects of oral-health-related quality of
life among Chilean adults. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol.
41:242–250. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Astrom AN, Haugejorden O, Skaret E, Trovik
TA and Klock KS: Oral Impacts on daily performance in norwegian
adults: The influence of age, number of missing teeth, and
socio-demographic factors. Eur J Oral Sci. 114:115–121. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thomson WM: Social inequality in oral
health. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 40 Suppl 2:S28–S32. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Paula JS, Ambrosano GM and Mialhe FL: The
impact of social determinants on schoolchildren';s oral health in
Brazil. Braz Oral Res. 29:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wennstrom A, Ahlqwist M, Stenman U,
Bjorkelund C and Hakeberg M: Trends in tooth loss in relation to
socio-economic status among Swedish women, aged 38 and 50 years:
Repeated cross-sectional surveys 1968-2004. BMC Oral Health.
13:632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paganini-Hill A, White SC and Atchison KA:
Dental health behaviors, dentition, and mortality in the elderly:
the leisure world cohort study. J Aging Res. 2011:1560612011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hayasaka K, Tomata Y, Aida J, Watanabe T,
Kakizaki M and Tsuji I: Tooth loss and mortality in elderly
Japanese adults: Effect of oral care. J Am Geriatr Soc. 61:815–820.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim DW, Park JC, Rim TT, Jung UW, Kim CS,
Donos N, Cha IH and Choi SH: Socioeconomic disparities of
periodontitis in Koreans based on the KNHANES IV. Oral Dis.
20:551–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim YH, Cho KH, Choi YS, Kim SM, Nam GE,
Lee SH, Ko BJ, Park YG, Han KD, Lee KS and Kim DH: Low bone mineral
density is associated with metabolic syndrome in South Korean men
but not in women: The 2008-2010 Korean national health and
nutrition examination survey. Arch Osteoporos. 8:1422013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Korea Center for Disease Control and
Prevention, . Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination
Survey. 2008, http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr
|
|
14
|
Nam GE, Cho KH, Park YG, Han KD, Choi YS,
Kim SM, Lee KS, Ko BJ, Kim YH, Han BD and Kim do H: Socioeconomic
status and dyslipidemia in Korean adults: The 2008-2010 Korea
national health and nutrition examination survey. Prev Med.
57:304–309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim YH, Kim DH, Lim KS, Ko BJ, Han BD, Nam
GE, Park YG, Han KD, Kim JH and Cho KH: Oral health behaviors and
metabolic syndrome: The 2008-2010 Korean national health and
nutrition examination survey. Clin Oral Investig. 18:1517–1524.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oh JY, Yang YJ, Kim BS and Kang JH:
Validity and reliability of Korean version of International
Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) short form. Journal of the
Korean Academy of Family Medicine. 28:532–541. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Lee K: Body composition and vitamin D
status: The Korea national health and nutrition examination survey
IV (KNHANES IV). J Hum Nutr Diet. 26 Suppl 1:S105–S113. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim DW, Song S, Lee JE, Oh K, Shim J,
Kweon S, Paik HY and Joung H: Reproducibility and validity of an
FFQ developed for the Korea National Health and Nutrition
Examination Survey (KNHANES). Public Health Nutr. 18:1369–1377.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nam GE, Kim do H, Cho KH, Park YG, Han KD,
Choi YS, Kim SM, Ko BJ, Kim YH and Lee KS: Estimate of a predictive
cut-off value for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D reflecting abdominal
obesity in Korean adolescents. Nutr Res. 32:395–402. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Susin C, Kingman A and Albandar JM: Effect
of partial recording protocols on estimates of prevalence of
periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 76:262–267. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kingman A, Susin C and Albandar JM: Effect
of partial recording protocols on severity estimates of periodontal
disease. J Clin Periodontol. 35:659–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim EJ, Jin BH and Bae KH: Periodontitis
and obesity: A study of the fourth Korean national health and
nutrition examination survey. J Periodontol. 82:533–542. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JB, Yi HY and Bae KH: The association
between periodontitis and dyslipidemia based on the fourth Korea
national health and nutrition examination survey. J Clin
Periodontol. 40:437–442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HY, Kim Y, Hwang JM and Park YD: Oral
health behaviours according to demographic characteristics in
Korean adolescents: A national representative sample. Int Dent J.
61:168–173. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hill KB, Chadwick B, Freeman R, O'Sullivan
I and Murray JJ: Adult dental health survey 2009: Relationships
between dental attendance patterns, oral health behaviour and the
current barriers to dental care. Br Dent J. 214:25–32. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gibson S and Williams S: Dental caries in
pre-school children: Associations with social class, toothbrushing
habit and consumption of sugars and sugar-containing foods. Further
analysis of data from the national diet and nutrition survey of
children aged 1.5-4.5 years. Caries Res. 33:101–113. 1999.
|
|
27
|
Freire MC, Sheiham A and Hardy R:
Adolescents' sense of coherence, oral health status, and oral
health-related behaviours. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol.
29:204–212. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Armfield JM, Mejia GC and Jamieson LM:
Socioeconomic and psychosocial correlates of oral health. Int Dent
J. 63:202–209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang Y, Okoro CA, Oh J and Fuller DL:
Sociodemographic and health-related risk factors associated with
tooth loss among adults in Rhode Island. Prev Chronic Dis.
10:E452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bayat F, Vehkalahti MM, Zafarmand AH and
Tala H: Impact of insurance scheme on adults' dental check-ups in a
developing oral health care system. Eur J Dent. 2:3–10.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kiyak HA and Reichmuth M: Barriers to and
enablers of older adults' use of dental services. J Dent Educ.
69:975–986. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Casanova-Rosado AJ, Medina-Solis CE,
Casanova-Rosado JF, Vallejos-Sánchez AA, Maupomé G and Avila-Burgos
L: Dental caries and associated factors in Mexican schoolchildren
aged 6-13 years. Acta Odontol Scand. 63:245–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Geyer S, Schneller T and Micheelis W:
Social gradients and cumulative effects of income and education on
dental health in the fourth german oral health study. Community
Dent Oral Epidemiol. 38:120–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|