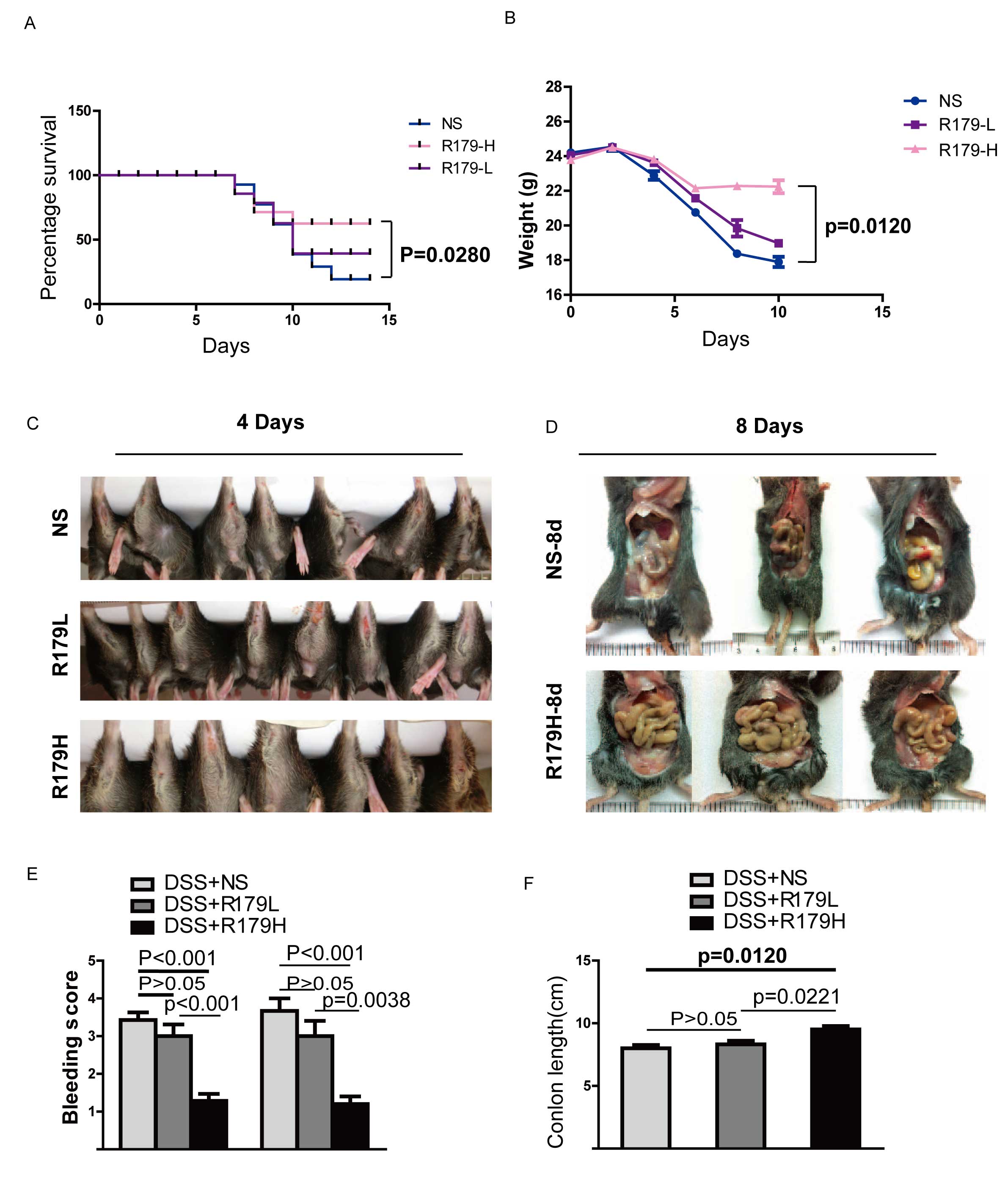
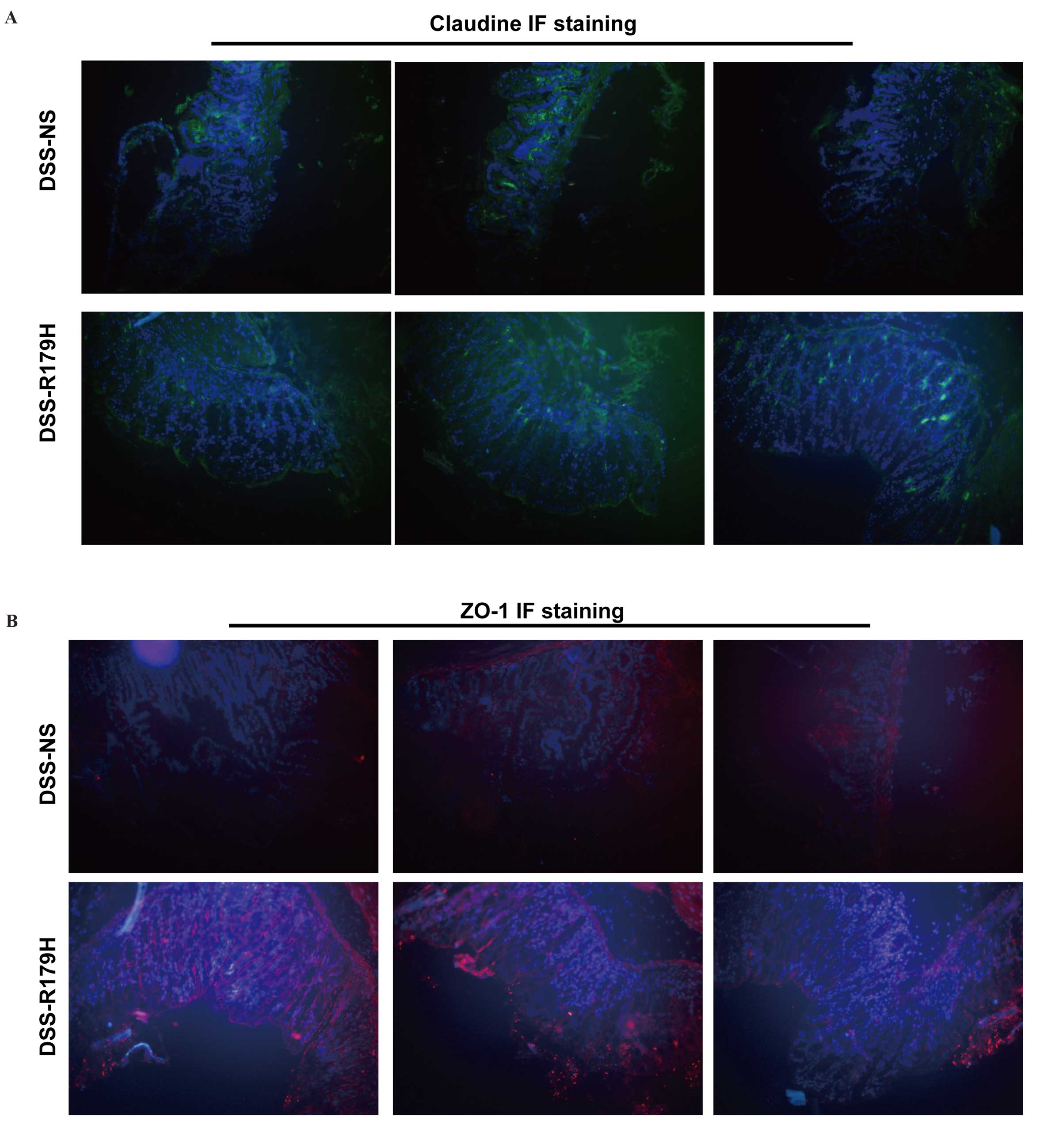
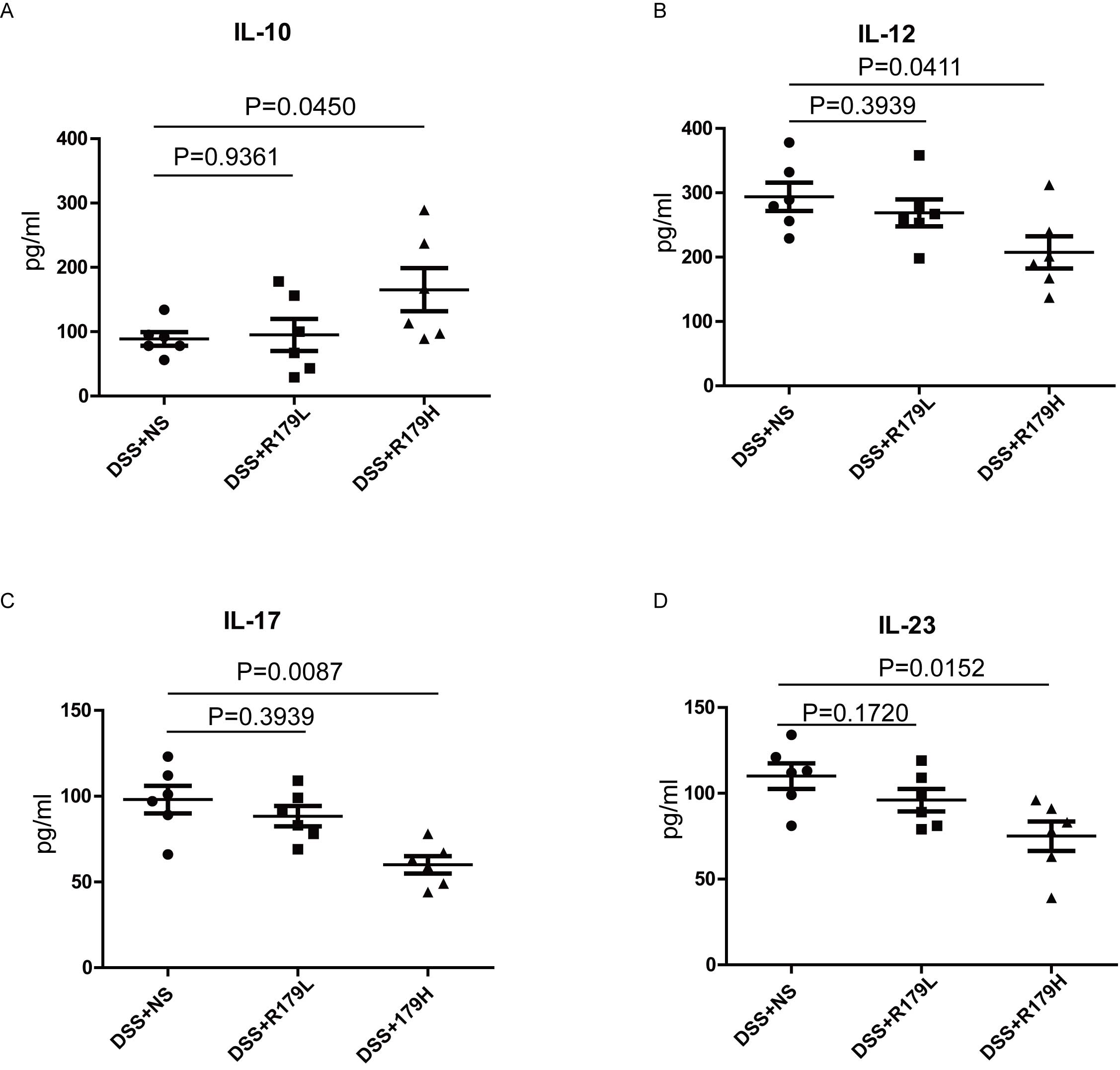
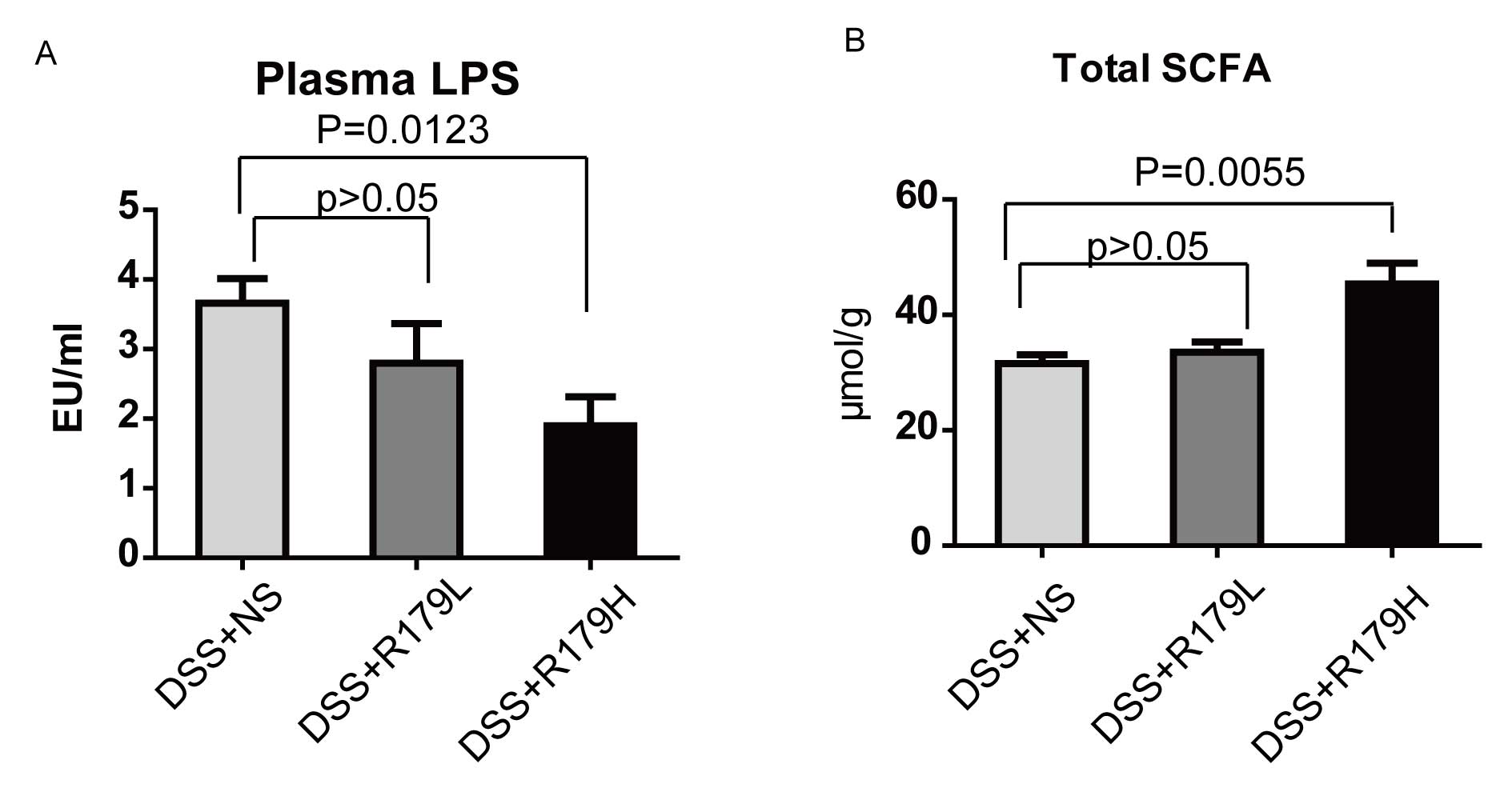
|
1
|
Mosli MH, Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, D'Haens
G, Behling C, Kaplan K, Driman DK, Shackelton LM, Baker KA,
Macdonald JK, et al: Histologic evaluation of ulcerative colitis: A
systematic review of disease activity indices. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
20:564–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rosenberg L, Nanda KS, Zenlea T, Gifford
A, Lawlor GO, Falchuk KR, Wolf JL, Cheifetz AS, Goldsmith JD and
Moss AC: Histologic markers of inflammation in patients with
ulcerative colitis in clinical remission. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 11:991–996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Manichanh C, Borruel N, Casellas F and
Guarner F: The gut microbiota in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 9:599–608. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Conrad K, Roggenbuck D and Laass MW:
Diagnosis and classification of ulcerative colitis. Autoimmun Rev.
13:463–466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suzuki T: Regulation of intestinal
epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:631–659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buning C, Geissler N, Prager M, Sturm A,
Baumgart DC, Büttner J, Bühner S, Haas V and Lochs H: Increased
small intestinal permeability in ulcerative colitis: Rather genetic
than environmental and a risk factor for extensive disease? Inflamm
Bowel Dis. 18:1932–1939. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen J, Zuo ZX and Mao AP: Effect of
probiotics on inducing remission and maintaining therapy in
ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and pouchitis: Meta-analysis
of randomized controlled trials. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:21–35. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aly SM, Ahmed Y Abdel-Galil, Abdel-Aziz
Ghareeb A and Mohamed MF: Studies on Bacillus subtilis and
Lactobacillus acidophilus, as potential probiotics, on the immune
response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus)
to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 25:128–136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sarra M, Pallone F, Macdonald TT and
Monteleone G: IL-23/IL-17 axis in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
16:1808–1813. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nell S, Suerbaum S and Josenhans C: The
impact of the microbiota on the pathogenesis of IBD: Lessons from
mouse infection models. Nat Rev Microbiol. 8:564–577. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okamoto K, Fujiya M, Nata T, Ueno N, Inaba
Y, Ishikawa C, Ito T, Moriichi K, Tanabe H, Mizukami Y, et al:
Competence and sporulation factor derived from Bacillus subtilis
improves epithelial cell injury in intestinal inflammation via
immunomodulation and cytoprotection. Int J Colorectal Dis.
27:1039–1046. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Selvam R, Maheswari P, Kavitha P,
Ravichandran M, Sas B and Ramchand CN: Effect of Bacillus subtilis
PB6, a natural probiotic on colon mucosal inflammation and plasma
cytokines levels in inflammatory bowel disease. Indian J Biochem
Biophys. 46:79–85. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Axelsson LG, Landström E, Goldschmidt TJ,
Grönberg A and Bylund-Fellenius AC: Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)
induced experimental colitis in immunodeficient mice: Effects in
CD4(+)-cell depleted, athymic and NK-cell depleted SCID mice.
Inflamm Res. 45:181–191. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lindén SK, Florin TH and McGuckin MA:
Mucin dynamics in intestinal bacterial infection. PLoS One.
3:e39522008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Olson TS, Reuter BK, Scott KG, Morris MA,
Wang XM, Hancock LN, Burcin TL, Cohn SM, Ernst PB, Cominelli F, et
al: The primary defect in experimental ileitis originates from a
nonhematopoietic source. J Exp Med. 203:541–552. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai
B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T,
Garrity GM and Tiedje JM: The ribosomal database project: Improved
alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:(Database Issue). D141–D145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li W and Godzik A: Cd-hit: A fast program
for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide
sequences. Bioinformatics. 22:1658–1659. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peñna AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chassaing B, Aitken JD, Malleshappa M and
Vijay-Kumar M: Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in
mice. Curr Protoc Immunol. 104:Unit 15-25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goto Y, Kurashima Y and Kiyono H: Roles of
the gut mucosal immune system in symbiosis and immunity. Rinsho
Ketsueki. 56:2205–2212. 2015.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Genser L, Poitou C, Brot-Laroche É,
Rousset M, Vaillant JC, Clément K, Thenet S and Leturque A:
Alteration of intestinal permeability: The missing link between gut
microbiota modifications and inflammation in obesity? Med Sci
(Paris). 32:461–469. 2016.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fujino S, Andoh A, Bamba S, Ogawa A, Hata
K, Araki Y, Bamba T and Fujiyama Y: Increased expression of
interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 52:65–70. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Calvano SE, Xiao W, Richards DR, Felciano
RM, Baker HV, Cho RJ, Chen RO, Brownstein BH, Cobb JP, Tschoeke SK,
et al: A network-based analysis of systemic inflammation in humans.
Nature. 437:1032–1037. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cetin S, Ford HR, Sysko LR, Agarwal C,
Wang J, Neal MD, Baty C, Apodaca G and Hackam DJ: Endotoxin
inhibits intestinal epithelial restitution through activation of
Rho-GTPase and increased focal adhesions. J Biol Chem.
279:24592–24600. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maslowski KM, Vieira AT, Ng A, Kranich J,
Sierro F, Yu D, Schilter HC, Rolph MS, Mackay F, Artis D, et al:
Regulation of inflammatory responses by gut microbiota and
chemoattractant receptor GPR43. Nature. 461:1282–1286. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mirmonsef P, Zariffard MR, Gilbert D,
Makinde H, Landay AL and Spear GT: Short-chain fatty acids induce
pro-inflammatory cytokine production alone and in combination with
toll-like receptor ligands. Am J Reprod Immunol. 67:391–400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Magri G and Cerutti A: A touch of youth in
gut microbiota development. Immunity. 45:12–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergogne-Bérézin E and Towner KJ:
Acinetobacter spp. as nosocomial pathogens: Microbiological,
clinical, and epidemiological features. Clin Microbiol Rev.
9:148–165. 1996.
|
|
29
|
Sokol H, Leducq V, Aschard H, Pham HP,
Jegou S, Landman C, Cohen D, Liguori G, Bourrier A, Nion-Larmurier
I, et al: Fungal microbiota dysbiosis in IBD. Gut.
pii:gutjnl-2015-310746. 2016.
|
|
30
|
Nones K, Knoch B, Dommels YE, Paturi G,
Butts C, McNabb WC and Roy NC: Multidrug resistance gene deficient
(mdr1a-/-) mice have an altered caecal microbiota that precedes the
onset of intestinal inflammation. J Appl Microbiol. 107:557–566.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kummen M, Holm K, Anmarkrud JA, Nygård S,
Vesterhus M, Høivik ML, Trøseid M, Marschall HU, Schrumpf E, Moum
B, et al: The gut microbial profile in patients with primary
sclerosing cholangitis is distinct from patients with ulcerative
colitis without biliary disease and healthy controls. Gut.
pii:gutjnl-2015-310500. 2016.
|
|
32
|
Gevers D, Kugathasan S, Denson LA,
Vázquez-Baeza Y, van Treuren W, Ren B, Schwager E, Knights D, Song
SJ, Yassour M, et al: The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset
Crohn's disease. Cell Host Microbe. 15:382–392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schreiber S, Heinig T, Thiele HG and
Raedler A: Immunoregulatory role of interleukin 10 in patients with
inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 108:1434–1444. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Steinbach EC and Plevy SE: The role of
macrophages and dendritic cells in the initiation of inflammation
in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 20:166–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schoultz I, Söderholm JD and McKay DM: Is
metabolic stress a common denominator in inflammatory bowel
disease? Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:2008–2018. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eeckhaut V, Machiels K, Perrier C, Romero
C, Maes S, Flahou B, Steppe M, Haesebrouck F, Sas B, Ducatelle R,
et al: Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum in inflammatory bowel disease.
Gut. 62:1745–1752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Frank DN, Robertson CE, Hamm CM, Kpadeh Z,
Zhang T, Chen H, Zhu W, Sartor RB, Boedeker EC, Harpaz N, et al:
Disease phenotype and genotype are associated with shifts in
intestinal-associated microbiota in inflammatory bowel diseases.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:179–184. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kamada N, Kim YG, Sham HP, Vallance BA,
Puente JL, Martens EC and Núñez G: Regulated virulence controls the
ability of a pathogen to compete with the gut microbiota. Science.
336:1325–1329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
van Nood E, Vrieze A, Nieuwdorp M, Fuentes
S, Zoetendal EG, de Vos WM, Visser CE, Kuijper EJ, Bartelsman JF,
Tijssen JG, et al: Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent
Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med. 368:407–415. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meijer BJ and Dieleman LA: Probiotics in
the treatment of human inflammatory bowel diseases: Update 2011. J
Clin Gastroenterol. 45(Suppl): S139–S144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|