Article
Retrospective analysis of seven breast tuberculosis cases
- Authors:
- Beyhan Çakar
- Aydin Çiledağ
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Department of Chest Diseases, Ankara Tuberculosis Control Dispensary No. 7, 06100 Ankara, Turkey, Department of Chest Diseases, Ankara University School of Medicine, 01710 Ankara, Turkey
-
Pages:
3053-3057
|
Published online on:
September 15, 2016
https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3705
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
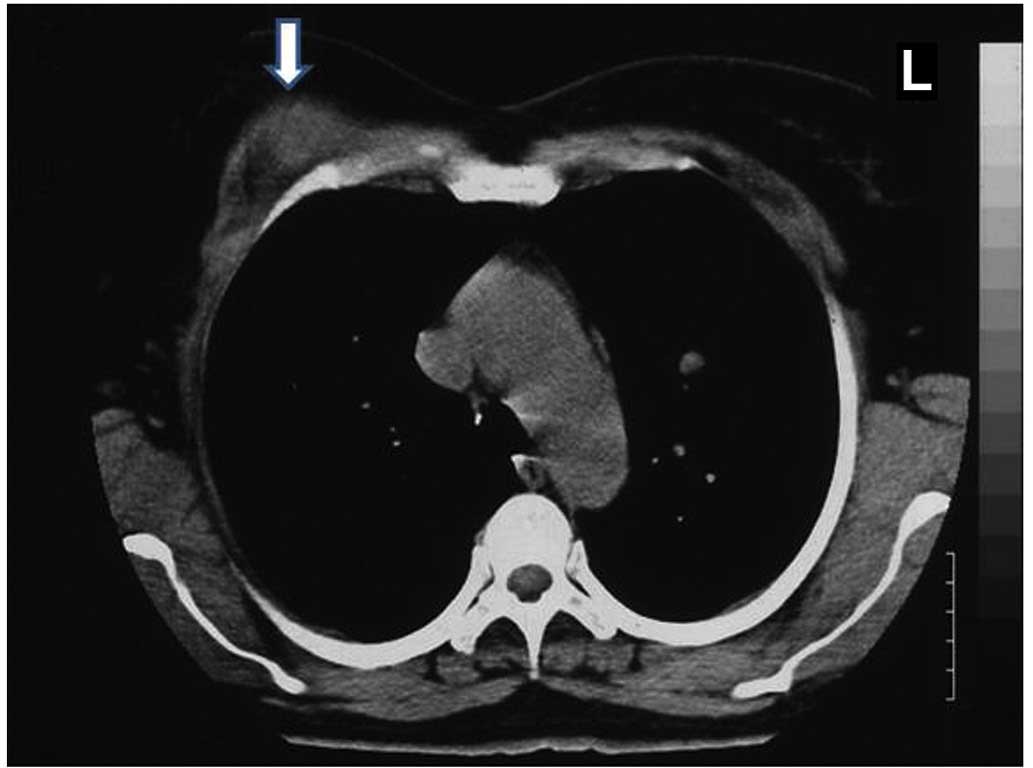
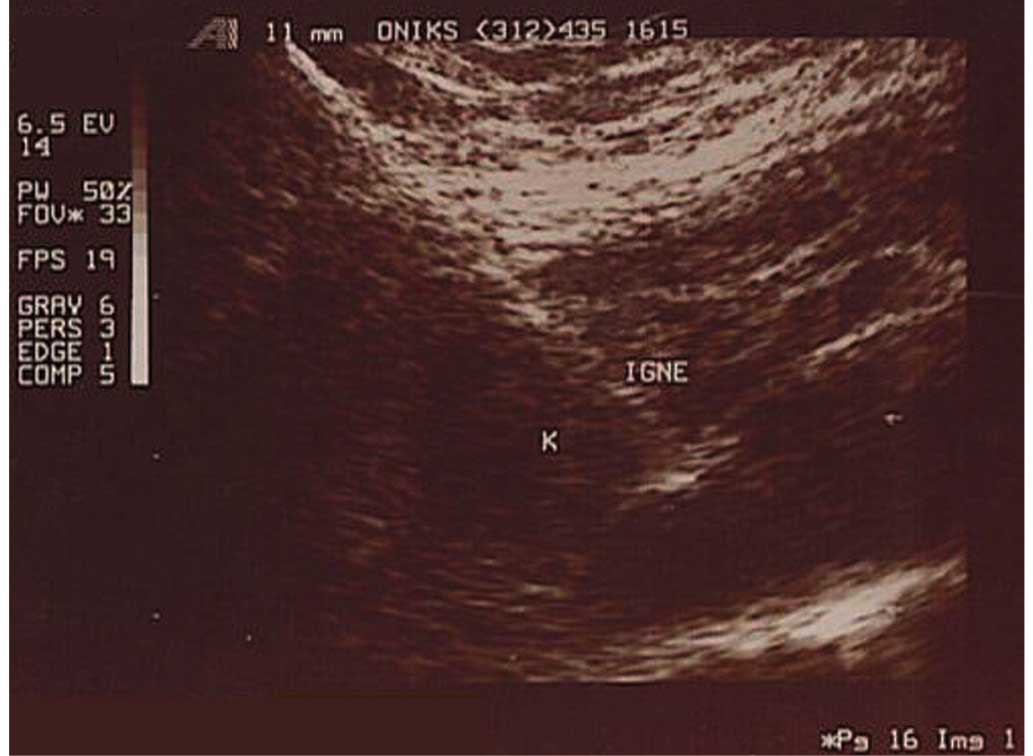
The present study aimed to evaluate the demographic data, diagnostic methods, therapeutic regimens and duration of therapy in 7 breast tuberculosis (BTB) cases. The data of BTB cases treated between January 2006 and December 2013 were retrospectively evaluated, with a total of 648 tuberculosis (TB) cases recorded during the 8‑year period. Among these cases, 296 patients (50%) suffered from pulmonary TB, 278 (43%) from non‑pulmonary TB and 45 (7%) from PTB plus NPTB. In total, 7 BTB were diagnosed, which constituted 1.08% (7/648) of all TB cases and 2.51% (7/278) of all NPTB cases. The mean age of patients was 34±9.46 years, with no pregnant or lactating women. Bilateral breast involvement was detected in only 1 case, while all cases had a BCG scar, and obtained a mean tuberculin skin test (TST) result of 14.28±6.79 mm (range, 7‑26 mm). The symptoms included presence of a mass, tenderness, pain, swelling and fluctuation in the breast, with or without discharging sinuses. In 1 case, history of contact with TB was found. All patients were newly‑diagnosed BTB cases, with no other organ involvement. Upon histopathological examination of breast tissue, granulomatous inflammation with typical caseous necrosis was observed in 1 case, non‑caseous necrosis inflammation was detected in 2 cases, granulomatous inflammation was observed in 3 cases, and mastitis and fat necrosis inflammation was observed in 1 case. Acid‑fast bacilli (AFB) staining was positive in only 2 cases, and all patient were treated with anti‑TB drugs with a successful outcome and no recurrence. In conclusion, BTB is a rare form of TB and the present retrospective study reported 7 cases of BTB along with the results of histopathological examination, microbiological examination and treatment. TB must be considered when there is presence of breast masses presenting with tenderness, pain, swelling and fluctuation, with or without discharging sinuses.
View References
|
1
|
Banerjee SN, Ananthakrishnan N, Mehta RB
and Parkash S: Tuberculous mastitis: A continuing problem. World J
Surg. 11:105–109. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tewari M and Shukla HS: Breast
tuberculosis: Diagnosis, clinical features & management. Indian
J Med Res. 122:103–110. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baharoon S: Tuberculosis of breast. Ann
Thorac Med. 3:110–114. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
da Silva BB, Dos Santos LG, Costa PV,
Pires CG and Borges AS: Primary tuberculosis of the breast
mimicking carcinoma. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 73:975–976. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kakkar S, Kapila K, Singh MK and Verma K:
Tuberculosis of the breast: A cytomorphologic study. Acta Cytol.
44:292–296. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Al-Marri MR, Almosleh A and Almoslmani Y:
Primary tuberculosis of the breast in Qatar: Ten year experience
and review of the literature. Eur J Surg. 166:687–690. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gon S, Bhattacharyya A, Majumdar B and
Kundu S: Tubercular mastitis-a great masquerader. Turk Patoloji
Derg. 29:61–63. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kalaç N, Ozkan B, Bayiz H, Dursun AB and
Demirağ F: Breast tuberculosis. Breast. 11:346–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kervancıoğlu S, Kervancıoğlu R, Özkur A
and Sirikçi A: Primary tuberculosis of the breast. Diagn Interv
Radiol. 11:210–212. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marinopoulos S, Lourantou D, Gatzionis T,
Dimitrakakis C, Papaspyrou I and Antsaklis A: Breast tuberculosis.
Diagnosis, management and treatment. Int J Surg Case Rep.
3:548–550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Afridi SP, Memon A, Rehman SU, Memon A and
Baig N: Spectrum of breast tuberculosis. J Coll Physicians Surg
Pak. 19:158–161. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sen M, Gorpelioglu C and Bozer M: Isolated
primary breast tuberculosis: Report of three cases and review of
the literature. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 64:607–610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tanrikulu AC, Abakay A, Abakay O and Kapan
M: Breast tuberculosis in southeast turkey: Report of 27 cases.
Breast Care (Basel). 5:154–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khanna R, Prasanna GV, Gupta P, Kumar M,
Khanna S and Khanna AK: Mammary tuberculosis: Report on 52 cases.
Postgrad Med J. 78:422–424. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ben Hassouna J, Gamoudi A, Bouzaiene H,
Dhiab T, Khomsi F, Chargui R, Sifi H, Mtaallah M, Makhlouf R,
Chebbi A, et al: Mammary tuberculosis: A retrospective study of 65
cases. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 33:870–876. 2005.(In French).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harris SH, Khan MA, Khan R, Haque F, Syed
A and Ansari MM: Mammary tuberculosıs: Analysis of thirty-eight
patients. ANZ J Surg. 76:234–237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sharma PK, Babel AL and Yadav SS:
Tuberculosis of breast (study of 7 cases). J Postgrad Med. 3724–26.
(26A)1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fukuoka K, Choh S, Hamada K, Yoneda T and
Narita N: A case of tuberculosis of the breast-review of the
literature published during the last 10 years in Japan. Kekkaku.
70:111–115. 1995.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morsad F, Ghazli M, Boumzgou K, Abbassi H,
El Kerroumi M, Matar N, Belabidia B, Aderdour M and El Mansouri A:
Mammary tuberculosis: A series of 14 cases. J Gynecol Obstet Biol
Reprod (Paris). 30:331–337. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|