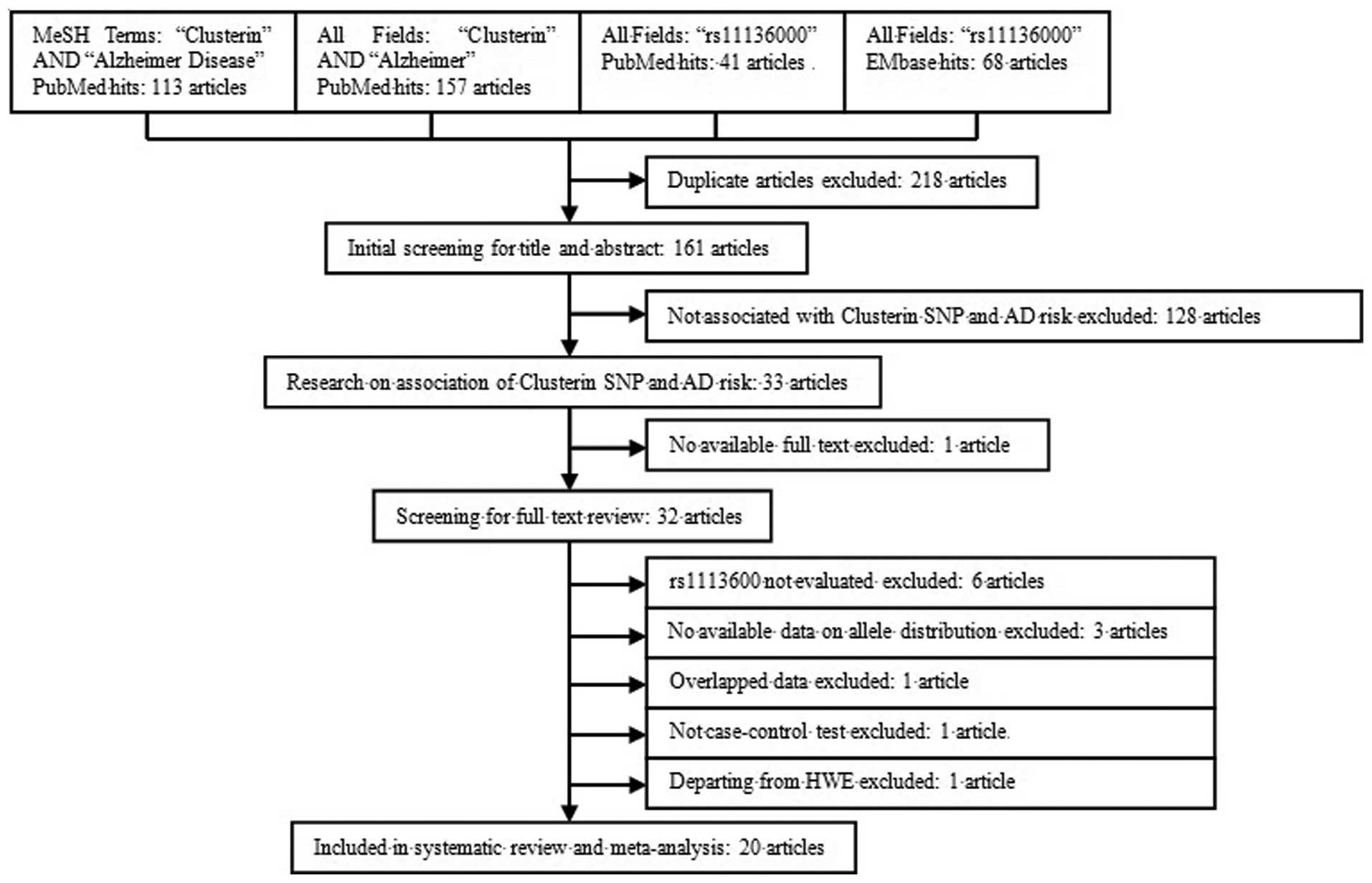
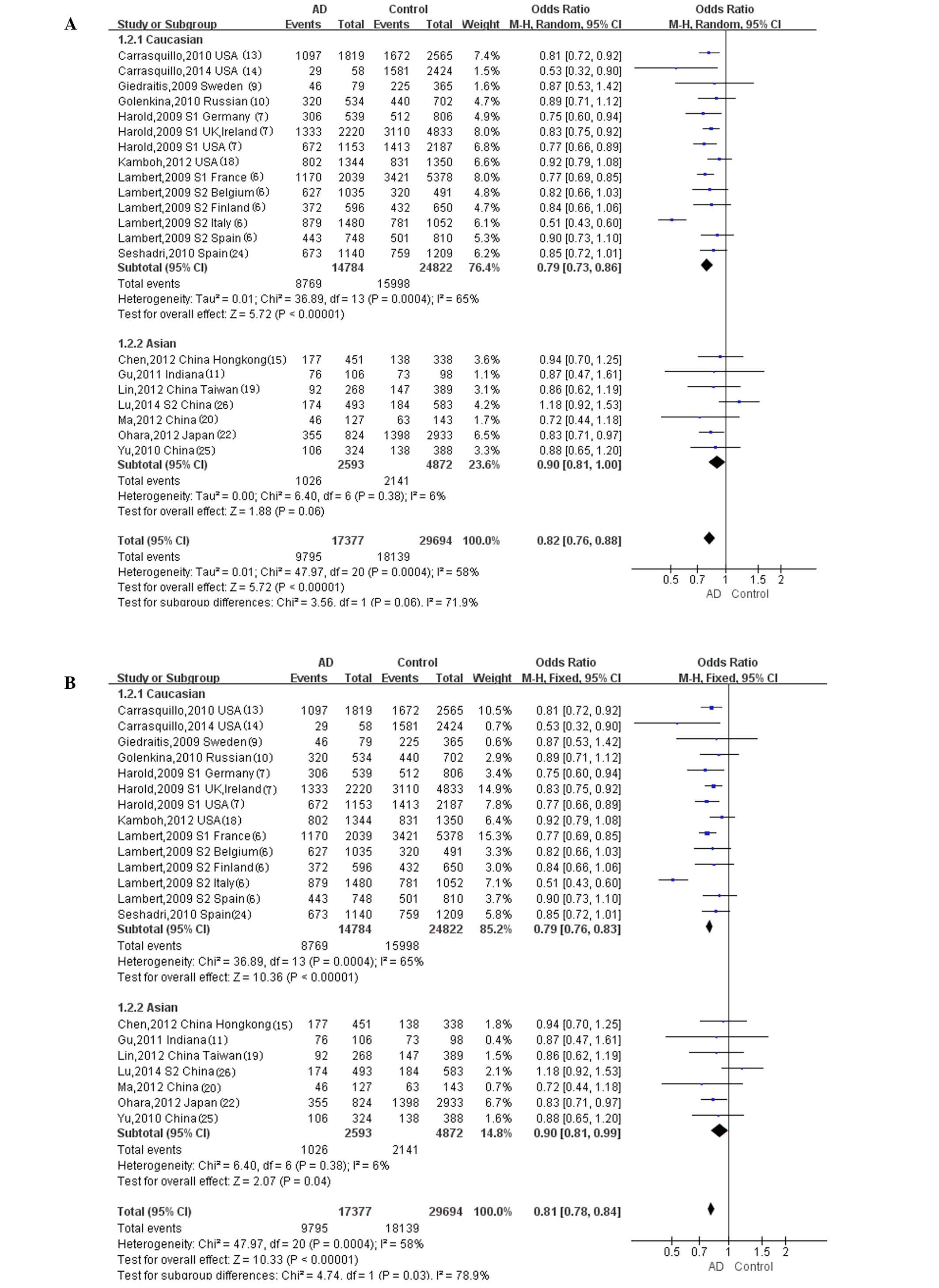
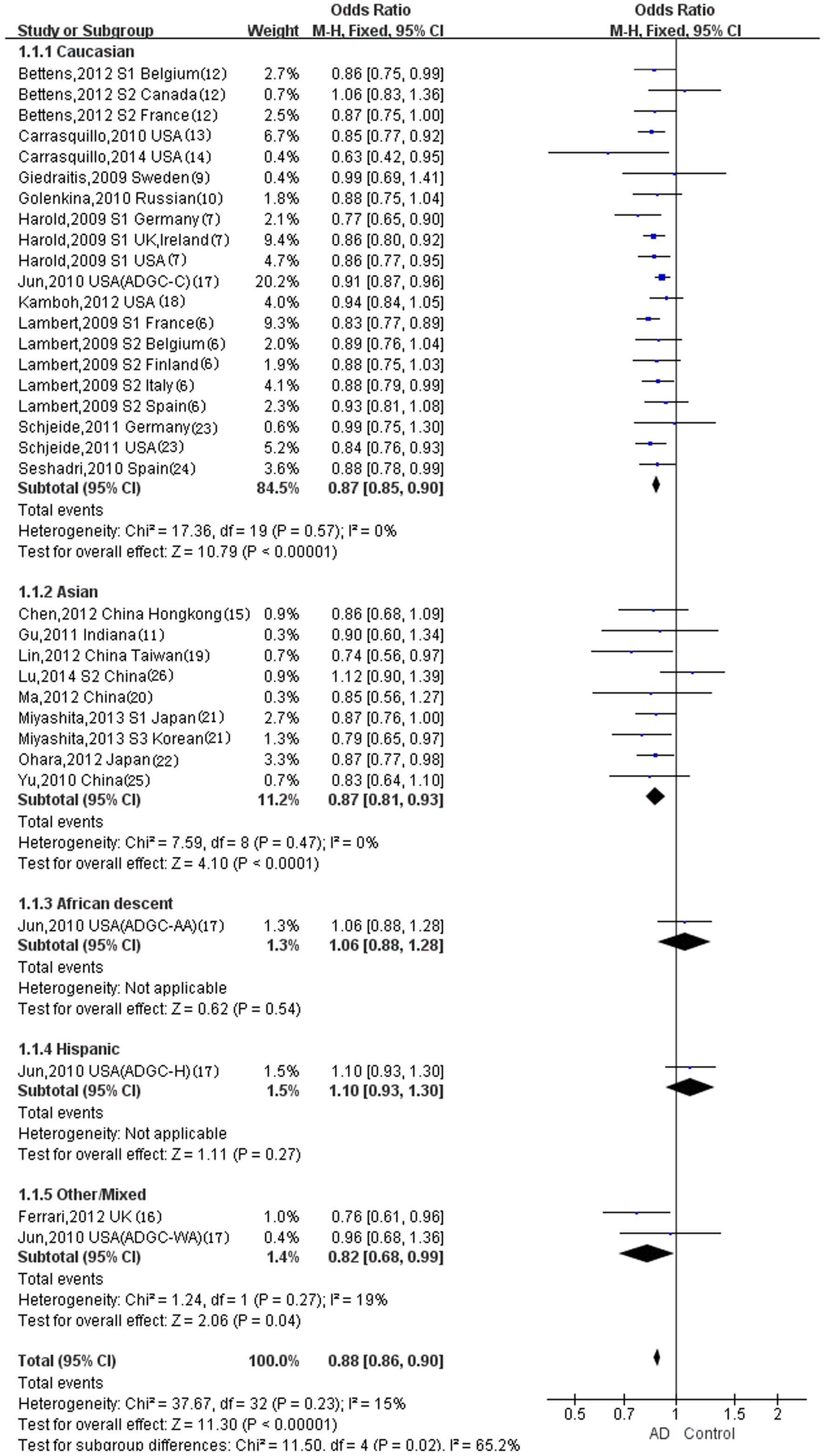
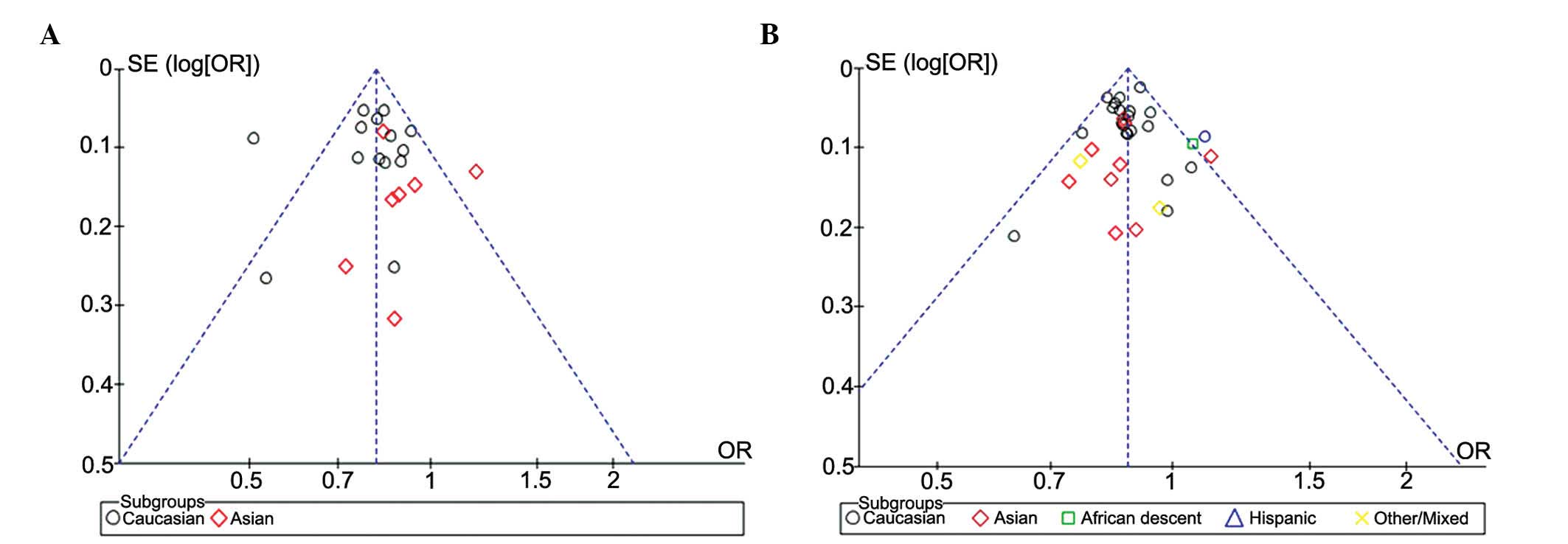
|
1
|
Ossenkoppele R, van der Flier WM, Zwan MD,
Adriaanse SF, Boellaard R, Windhorst AD, Barkhof F, Lammertsma AA,
Scheltens P and van Berckel BN: Differential effect of APOE
genotype on amyloid load and glucose metabolism in AD dementia.
Neurology. 80:359–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tycko B, Feng L, Nguyen L, Francis A, Hays
A, Chung WY, Tang MX, Stern Y, Sahota A, Hendrie H and Mayeux R:
Polymorphisms in the human apolipoprotein-J/clusterin gene: Ethnic
variation and distribution in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Genet.
98:430–436. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bertram L and Tanzi RE: Alzheimer's
disease: New light on an old CLU. Nat Rev Neurol. 6:11–13. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Malkki H: Alzheimer disease: Chaperone
protein clusterin is involved in amyloid-β-associated entorhinal
atrophy in early AD. Nat Rev Neurol. 10:602014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nuutinen T, Suuronen T, Kauppinen A and
Salminen A: Clusterin: A forgotten player in Alzheimer's disease.
Brain Res Rev. 61:89–104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D,
Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, Combarros O, Zelenika D, Bullido MJ,
Tavernier B, et al: Genome-wide association study identifies
variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat
Genet. 41:1094–1099. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims
R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V, Dowzell K,
Williams A, et al: Genome-wide association study identifies
variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat
Genet. 41:1088–1093. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Butler AW, Ng MY, Hamshere ML, Forabosco
P, Wroe R, Al-Chalabi A, Lewis CM and Powell JF: Meta-analysis of
linkage studies for Alzheimer's disease-a web resource. Neurobiol
Aging. 30:1037–1047. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Giedraitis V, Kilander L,
Degerman-Gunnarsson M, Sundelöf J, Axelsson T, Syvänen AC, Lannfelt
L and Glaser A: Genetic analysis of Alzheimer's disease in the
Uppsala Longitudinal Study of Adult Men. Dement Geriatr Cogn
Disord. 27:59–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Golenkina SA, Gol'tsov AIu, Kuznetsova IL,
Grigorenko AP, Andreeva TV, Reshetov DA, Kunizheva SS, Shagam LI,
Morozova IIu, Goldenkova-Pavlova IV, et al: Analysis of clustering
gene (CLU/APOJ) polymorphism in Alzheimer's disease patients and in
normal cohorts from Russian populations. Mol Biol (Mosk).
44:620–626. 2010.(In Russian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu H, Wei X, Chen S, Kurz A, Müller U,
Gasser T, Dodel RC, Farlow MR and Du Y: Association of clusterin
gene polymorphisms with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Dement
Geriatr Cogn Disord. 32:198–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bettens K, Brouwers N, Engelborghs S,
Lambert JC, Rogaeva E, Vandenberghe R, Le Bastard N, Pasquier F,
Vermeulen S, Van Dongen J, et al: Both common variations and rare
non-synonymous substitutions and small insertion/deletions in CLU
are associated with increased AD risk. Mol Neurodegener. 7:32012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carrasquillo MM, Belbin O, Hunter TA, Ma
L, Bisceglio GD, Zou F, Crook JE, Pankratz VS, Dickson DW,
Graff-Radford NR, et al: Replication of CLU, CR1 and PICALM
associations with alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 67:961–964.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carrasquillo MM, Khan Qu, Murray ME,
Krishnan S, Aakre J, Pankratz VS, Nguyen T, Ma L, Bisceglio G,
Petersen RC, et al: Late-onset Alzheimer disease genetic variants
in posterior cortical atrophy and posterior AD. Neurology.
82:1455–1462. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen LH, Kao PY, Fan YH, Ho DT, Chan CS,
Yik PY, Ha JC, Chu LW and Song YQ: Polymorphisms of CR1, CLU and
PICALM confer susceptibility of Alzheimer's disease in a southern
Chinese population. Neurobiol Aging. 33:210.e1–210.e7. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ferrari R, Moreno JH, Minhajuddin AT,
O'Bryant SE, Reisch JS, Barber RC and Momeni P: Implication of
common and disease specific variants in CLU, CR1 and PICALM.
Neurobiol Aging. 33:1846.e7–1846.e18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jun G, Naj AC, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Buros
J, Gallins PJ, Buxbaum JD, Ertekin-Taner N, Fallin MD, Friedland R,
et al: Meta-analysis confirms CR1, CLU and PICALM as alzheimer
disease risk loci and reveals interactions with APOE genotypes.
Arch Neurol. 67:1473–1484. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kamboh MI, Minster RL, Demirci FY, Ganguli
M, Dekosky ST, Lopez OL and Barmada MM: Association of CLU and
PICALM variants with Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging.
33:518–521. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin YL, Chen SY, Lai LC, Chen JH, Yang SY,
Huang YL, Chen TF, Sun Y, Wen LL, Yip PK, et al: Genetic
polymorphisms of clusterin gene are associated with a decreased
risk of Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Epidemiol. 27:73–75. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ma JF, Liu LH, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Deng YL,
Huang Y, Wang G, Xu W, Cui PJ, Fei QZ, et al: Association study of
clusterin polymorphism rs11136000 with late onset Alzheimer's
disease in Chinese Han population. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen.
26:627–630. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Miyashita A, Koike A, Jun G, Wang LS,
Takahashi S, Matsubara E, Kawarabayashi T, Shoji M, Tomita N, Arai
H, et al: SORL1 is genetically associated with late-onset
Alzheimer's disease in Japanese, Koreans and Caucasians. PLoS One.
8:e586182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohara T, Ninomiya T, Hirakawa Y, Ashikawa
K, Monji A, Kiyohara Y, Kanba S and Kubo M: Association study of
susceptibility genes for late-onset Alzheimer's disease in the
Japanese population. Psychiatr Genet. 22:290–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schjeide BM, Schnack C, Lambert JC, Lill
CM, Kirchheiner J, Tumani H, Otto M, Tanzi RE, Lehrach H, Amouyel
P, et al: The role of clusterin, complement receptor 1 and
phosphatidylinositol binding clathrin assembly protein in Alzheimer
disease risk and cerebrospinal fluid biomarker levels. Arch Gen
Psychiatry. 68:207–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seshadri S, Fitzpatrick AL, Ikram MA,
DeStefano AL, Gudnason V, Boada M, Bis JC, Smith AV, Carassquillo
MM, Lambert JC, et al: Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci
associated with Alzheimer disease. JAMA. 303:1832–1840. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu JT, Li L, Zhu QX, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Wu
ZC, Guan J and Tan L: Implication of CLU gene polymorphisms in
Chinese patients with Alzheimer's disease. Clin Chim Acta.
411:1516–1519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu SJ, Li HL, Sun YM, Liu ZJ, Yang P and
Wu ZY: Clusterin variants are not associated with southern Chinese
patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging.
35:2656.e9–2656.e11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman
R, Price D and Stadlan EM: Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's
disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices
of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on
Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984.34:939–944. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leeb C, Eresheim C and Nimpf J: Clusterin
is a ligand for apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (ApoER2) and very low
density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and signals via the
Reelin-signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 289:4161–4172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Trougakos IP: The molecular chaperone
apolipoprotein J/clusterin as a sensor of oxidative stress:
Implications in therapeutic approaches-a mini-review. Gerontology.
59:514–523. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Song HB, Jun HO and Kim JH, Yu YS, Kim KW,
Min BH and Kim JH: Anti-apoptotic effect of clusterin on
cisplatin-induced cell death of retinoblastoma cells. Oncol Rep.
30:2713–2718. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Ma Y, Wei X, Li Y, Wu H, Zhuang J
and Zhao Z: Clusterin in Alzheimer's disease: A player in the
biological behavior of amyloid-beta. Neurosci Bull. 30:162–168.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yerbury JJ, Poon S, Meehan S, Thompson B,
Kumita JR, Dobson CM and Wilson MR: The extracellular chaperone
clusterin influences amyloid formation and toxicity by interacting
with prefibrillar structures. FASEB J. 21:2312–2322. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Howlett DR, Hortobágyi T and Francis PT:
Clusterin associates specifically with Aβ40 in Alzheimer's disease
brain tissue. Brain Pathol. 23:623–632. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Martin-Rehrmann MD, Hoe HS, Capuani EM and
Rebeck GW: Association of apolipoprotein J-positive beta-amyloid
plaques with dystrophic neurites in Alzheimer's disease brain.
Neurotox Res. 7:231–242. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wahrle SE, Jiang H, Parsadanian M,
Legleiter J, Han X, Fryer JD, Kowalewski T and Holtzman DM: ABCA1
is required for normal central nervous system ApoE levels and for
lipidation of astrocyte-secreted ApoE. J Biol Chem.
279:40987–40993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bell RD, Sagare AP, Friedman AE, Bedi GS,
Holtzman DM, Deane R and Zlokovic BV: Transport pathways for
clearance of human Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide and
apolipoproteins E and J in the mouse central nervous system. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:909–918. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thambisetty M, Simmons A, Velayudhan L,
Hye A, Campbell J, Zhang Y, Wahlund LO, Westman E, Kinsey A,
Güntert A, et al: Association of plasma clusterin concentration
with severity, pathology and progression in Alzheimer disease. Arch
Gen Psychiatry. 67:739–748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jones L, Harold D and Williams J: Genetic
evidence for the involvement of lipid metabolism in Alzheimer's
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1801:754–761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS,
Vardarajan BN, Buros J, Gallins PJ, Buxbaum JD, Jarvik GP, Crane
PK, et al: Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1
are associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet.
43:436–441. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu JT, Ma XY, Wang YL, Sun L and Tan L, Hu
N and Tan L: Genetic variation in Clusterin gene and Alzheimer's
disease risk in Han Chinese. Neurobiol Aging. 34:1921.e17–1921.e23.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|