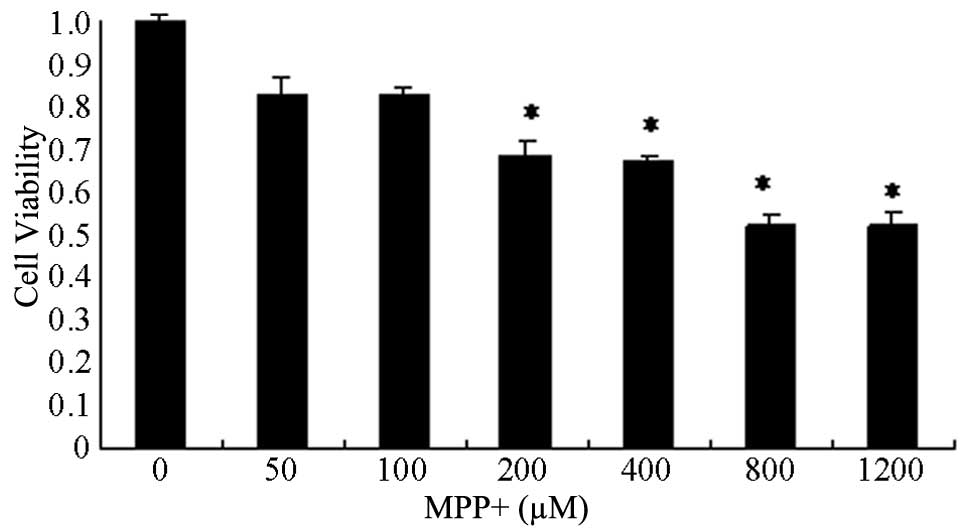
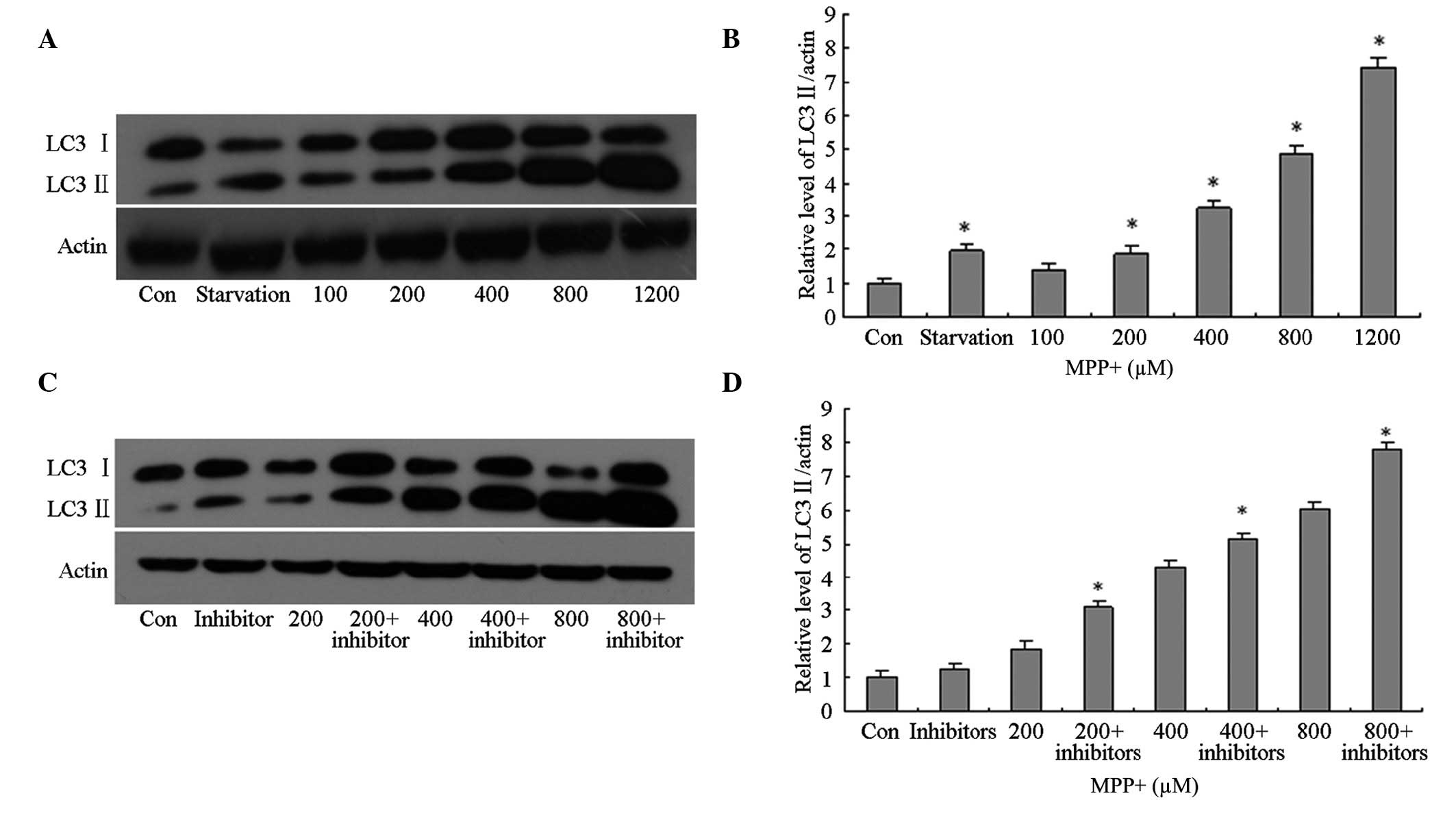
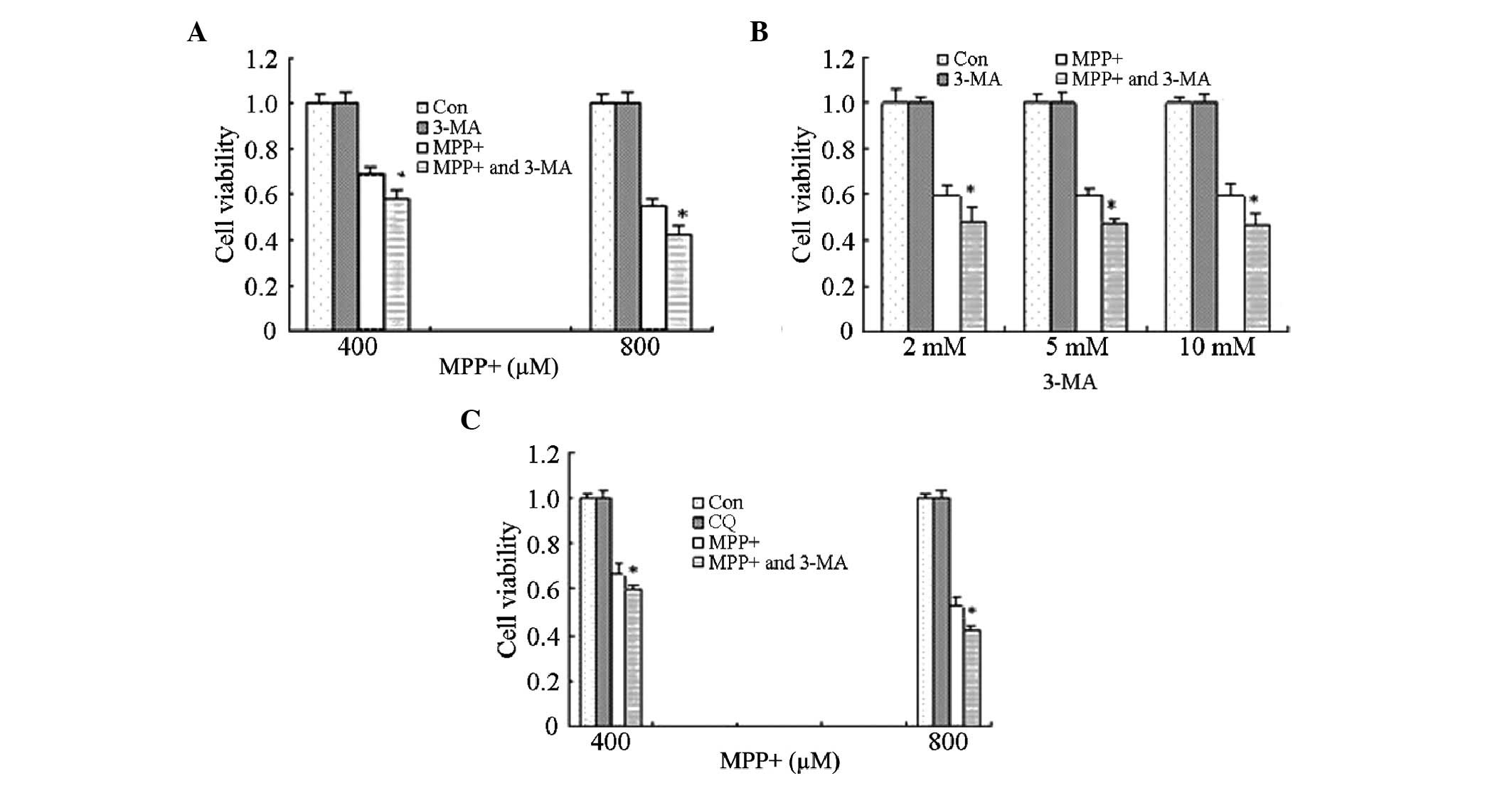
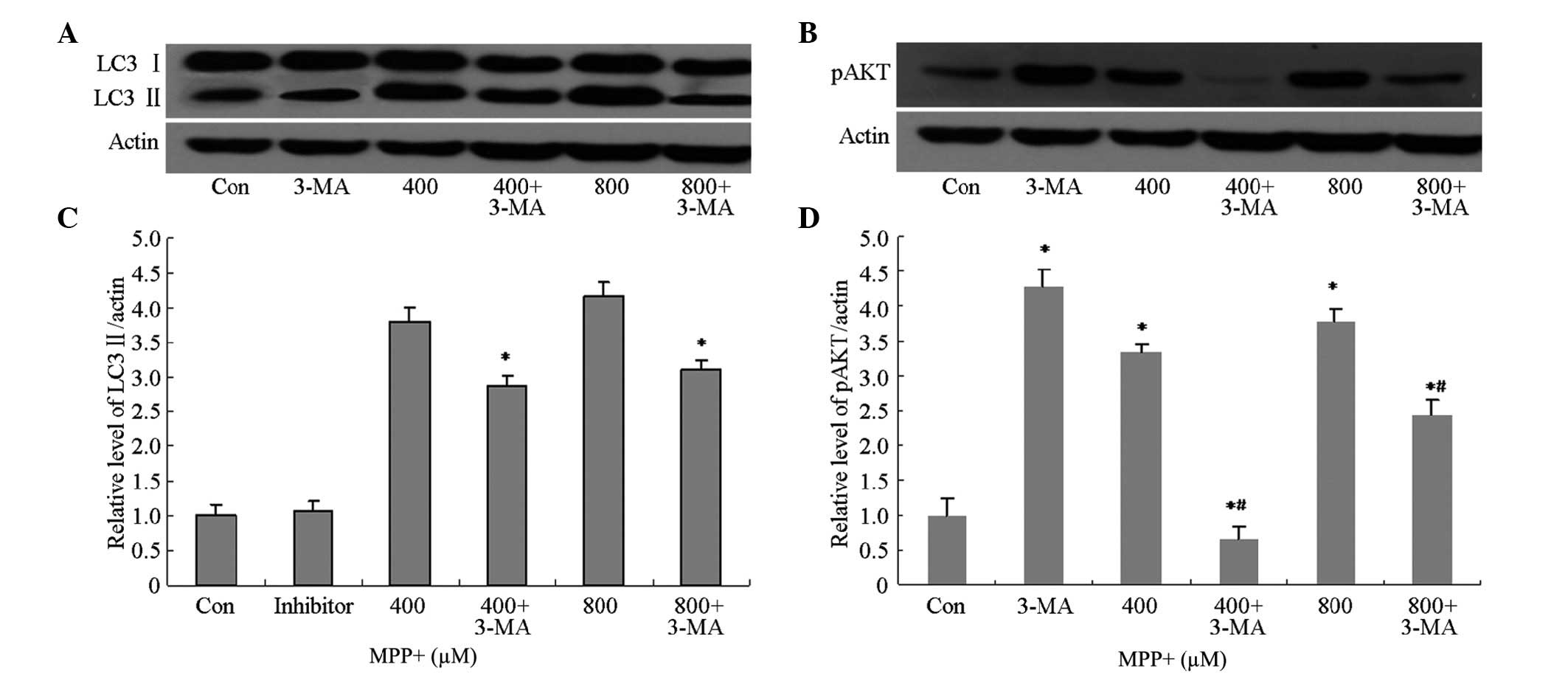
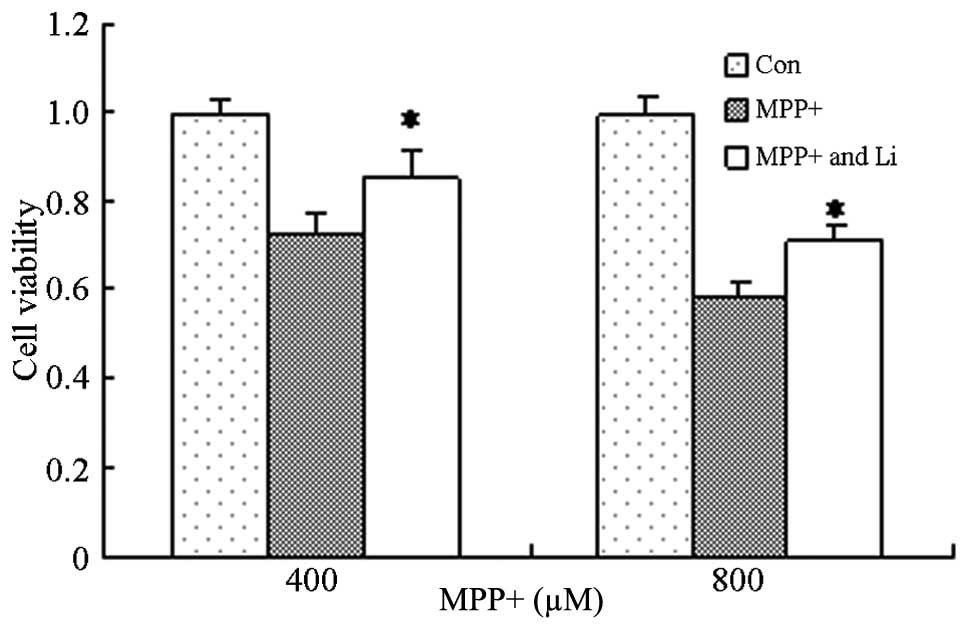
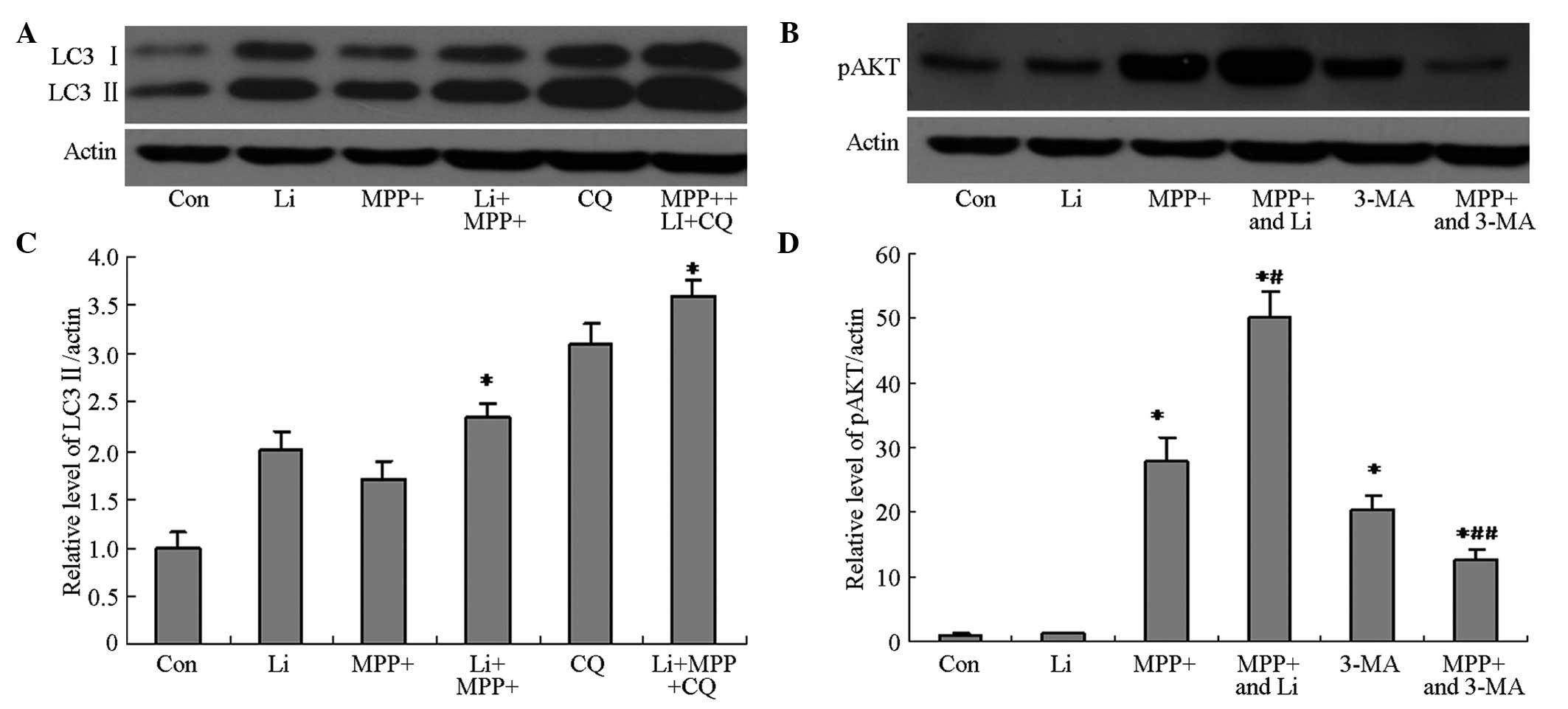
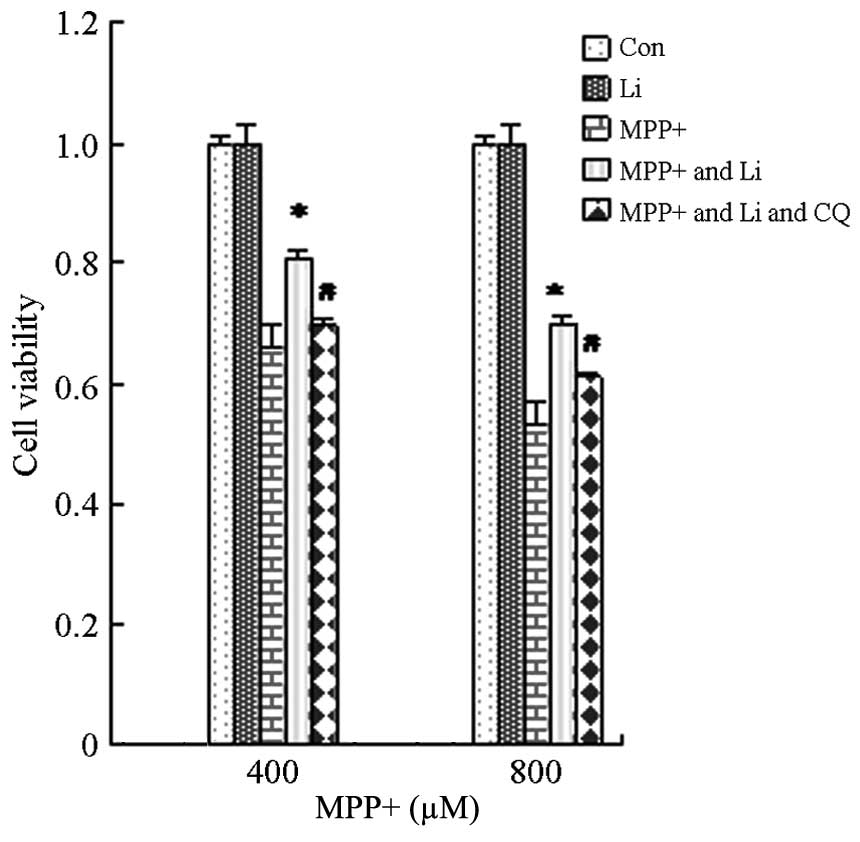
|
1
|
Dauer W and Przedborski S: Parkinson's
disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron. 39:889–909. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW and
Irwin I: Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of
meperidine-analog synthesis. Science. 219:979–980. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vives BC, Zhou C, Huang Y, Cui M, de Vries
RL, Kim J, May J, Tocilescu MA, Liu W, Ko HS, et al:
PINK1-dependent recruitment of Parkin to mitochondria in mitophagy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:378–383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Narendra DP, Jin SM, Tanaka A, Suen DF,
Gautier CA, Shen J, Cookson MR and Youle RJ: PINK1 is selectively
stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol.
8:e10002982010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Geisler S, Holmström KM, Skujat D, Fiesel
FC, Rothfuss OC, Kahle PJ and Springer W: PINK1/Parkin-mediated
mitophagy is dependent on VDAC1 and p62/SQSTM1. Nat Cell Biol.
12:119–131. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawajiri S, Saiki S, Sato S, Sato F,
Hatano T, Eguchi H and Hattori N: PINK1 is recruited to
mitochondria with parkin and associates with LC3 in mitophagy. FEBS
Lett. 584:1073–1079. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levitt P, Pintar JE and Breakefield XO:
Immunocytochemical demonstration of monoamine oxidase B in brain
astrocytes and serotonergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
79:6385–6389. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zigmond MJ and Stricker EM: Animal models
of parkinsonism using selective neurotoxins: Clinical and basic
implications. Int Rev Neurobiol. 31:1–79. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu JH, Horbinski C, Guo F, Watkins S,
Uchiyama Y and Chu CT: Regulation of autophagy by extracellular
signal-regulated protein kinases during
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced cell death. Am J Pathol.
170:75–86. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nopparat C, Porter JE, Ebadi M and
Govitrapong P: 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced cell death via
autophagy through a Bcl-2/Beclin 1 complex-dependent pathway.
Neurochem Res. 39:225–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodríguez-Blanco J, Martín V,
García-Santos G, Herrera F, Casado-Zapico S, Antolín I and
Rodriguez C: Cooperative action of JNK and AKT/mTOR in
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced autophagy of neuronal PC12
cells. J Neurosci Res. 90:1850–1860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hung KC, Huang HJ, Lin MW, Lei YP and Lin
AM: Roles of autophagy in MPP+ -induced neurotoxicity in vivo: The
involvement of mitochondria and α-synuclein aggregation. PLoS One.
9:e910742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pekny M and Nilsson M: Astrocyte
activation and reactive gliosis. Glia. 50:427–434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hirsch EC, Breidert T, Rousselet E, Hunot
S, Hartmann A and Michel PP: The role of glial reaction and
inflammation in Parkinson's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 991:214–228.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Teismann P and Schulz JB: Cellular
pathology of Parkinson's disease: Astrocytes, microglia and
inflammation. Cell Tissue Res. 318:149–161. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qin AP, Liu CF, Qin YY, Hong LZ, Xu M,
Yang L, Liu J, Qin ZH and Zhang HL: Autophagy was activated in
injured astrocytes and mildly decreased cell survival following
glucose and oxygen deprivation and focal cerebral ischemia.
Autophagy. 6:738–753. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jakel RJ, Townsend JA, Kraft AD and
Johnson JA: Nrf2-mediated protection against 6-hydroxy-dopamine.
Brain Res. 1144:197–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen PC, Vargas MR, Pani AK, Smeyne RJ,
Johnson DA, Kan YW and Johnson JA: Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection in
the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson's disease: Critical role for the
astrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:2933–2938. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Plowey ED, Cherra SJ III, Liu YJ and Chu
CT: Role of autophagy in G2019S-LRRK2-associated neurite shortening
in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem. 105:1048–1056. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsuda N, Sato S, Shiba K, Okatsu K,
Saisho K, Gautier CA, Sou YS, Saiki S, Kawajiri S, Sato F, et al:
PINK1 stabilized by mitochondrial depolarization recruits Parkin to
damaged mitochondria and activates latent Parkin for mitophagy. J
Cell Biol. 189:211–221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tong Y, Yamaguchi H, Giaime E, Boyle S,
Kopan R, Kelleher RJ III and Shen J: Loss of leucine-rich repeat
kinase 2 causes impairment of protein degradation pathways,
accumulation of alpha-synuclein and apoptotic cell death in aged
mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:9879–9884. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alegre-Abarrategui J, Christian H, Lufino
MM, Mutihac R, Venda LL, Ansorge O and Wade-Martins R: LRRK2
regulates autophagic activity and localizes to specific membrane
microdomains in a novel human genomic reporter cellular model. Hum
Mol Genet. 18:4022–4034. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pan T, Rawal P, Wu Y, Xie W, Jankovic J
and Le W: Rapamycin protects against rotenone-induced apoptosis
through autophagy induction. Neuroscience. 164:541–551. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sarkar S, Floto RA, Berger Z, Imarisio S,
Cordenier A, Pasco M, Cook LJ and Rubinsztein DC: Lithium induces
autophagy by inhibiting inositol monophosphatase. J Cell Biol.
170:1101–1111. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sarkar S and Rubinsztein DC: Inositol and
IP3 levels regulate autophagy: Biology and therapeutic
speculations. Autophagy. 2:132–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chuang DM: The antiapoptotic actions of
mood stabilizers: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1053:195–204. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cappuccio I, Calderone A, Busceti CL,
Biagioni F, Pontarelli F, Bruno V, Storto M, Terstappen GT,
Gaviraghi G, Fornai F, et al: Induction of Dickkopf-1, a negative
modulator of the Wnt pathway, is required for the development of
ischemic neuronal death. J Neurosci. 25:2647–2657. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Busceti CL, Biagioni F, Aronica E, Riozzi
B, Storto M, Battaglia G, Giorgi FS, Gradini R, Fornai F,
Caricasole A, et al: Induction of the Wnt inhibitor, Dickkopf-1, is
associated with neurodegeneration related to temporal lobe
epilepsy. Epilepsia. 48:694–705. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Loo DT and Rilleman JR: Measurement of
cell death. Methods Cell Biol. 57:251–264. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seglen PO and Gordon PB: 3-Methyladenine:
Specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:1889–1892.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schu PV, Takegawa K, Fry MJ, Stack JH,
Waterfield MD and Emr SD: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by
yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science. 260:88–91.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarkar S, Krishna G, Imarisio SA, Saiki S,
O'Kane CJ and Rubinsztein DC: A rational mechanism for combination
treatment of Huntington's disease using lithium and rapamycin. Hum
Mol Genet. 17:170–178. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Norenberg MD: Astrocyte responses to CNS
injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 53:213–220. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Norenberg MD: Active and passive roles of
astrocytes in neurologic disease: Commentary on forum position
paper. Neurotoxicology. 19:23–26. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ridet JL, Malhotra SK, Privat A and Gage
FH: Reactive astrocytes: Cellular and molecular cues to biological
function. Trends Neurosci. 20:570–577. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Amédée T, Robert A and Coles JA: Potassium
homeostasis and glial energy metabolism. Glia. 21:46–55. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N and Schousboe
A: Glutamate transport and metabolism in astrocytes. Glia.
21:56–63. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tansey FA, Farooq M and Cammer W:
Glutamine synthetase in oligodendrocytes and astrocytes: New
biochemical and immunocytochemical evidence. J Neurochem.
56:266–272. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schurr A, Payne RS, Miller JJ and Rigor
BM: Brain lactate is an obligatory aerobic energy substrate for
functional recovery after hypoxia: Further in vitro validation. J
Neurochem. 69:423–426. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gerhart DZ, Enerson BE, Zhdankina OY,
Leino RL and Drewes LR: Expression of monocarboxylate transporter
MCT1 by brain endothelium and glia in adult and suckling rats. Am J
Physiol. 273(1)1E207–E213. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koehler-Stec EM, Simpson IA, Vannucci SJ,
Landschulz KT and Landschulz WH: Monocarboxylate transporter
expression in mouse brain. Am J Physiol. 275(3)1E516–E524.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aschner M: Astrocytic functions and
physiological reactions to injury: The potential to induce and/or
exacerbate neuronal dysfunction-a forum position paper.
Neurotoxicology. 19:7–17. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Raps SP, Lai JC, Hertz L and Cooper AJ:
Glutathione is present in high concentrations in cultured
astrocytes but not in cultured neurons. Brain Res. 493:398–401.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Youdim MB and Arraf Z: Prevention of MPTP
(N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) dopaminergic
neurotoxicity in mice by chronic lithium: Involvements of Bcl-2 and
Bax. Neuropharmacology. 46:1130–1140. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lai JS, Zhao C, Warsh JJ and Li PP:
Cytoprotection by lithium and valproate varies between cell types
and cellular stresses. Eur J Pharmacol. 539:18–26. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yeste M, Alvira1 D, Verdaguer E, Tajes M,
Folch J, Rimbau V, Pallàs M and Camins A: Evaluation of acute
antiapoptotic effects of Li+ in neuronal cell cultures. J Neural
Transm. 114:405–416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
King TD, Bijur GN and Jope RS: Caspase-3
activation induced by inhibition of mitochondrial complex I is
facilitated by glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and attenuated by
lithium. Brain Res. 919:106–114. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|