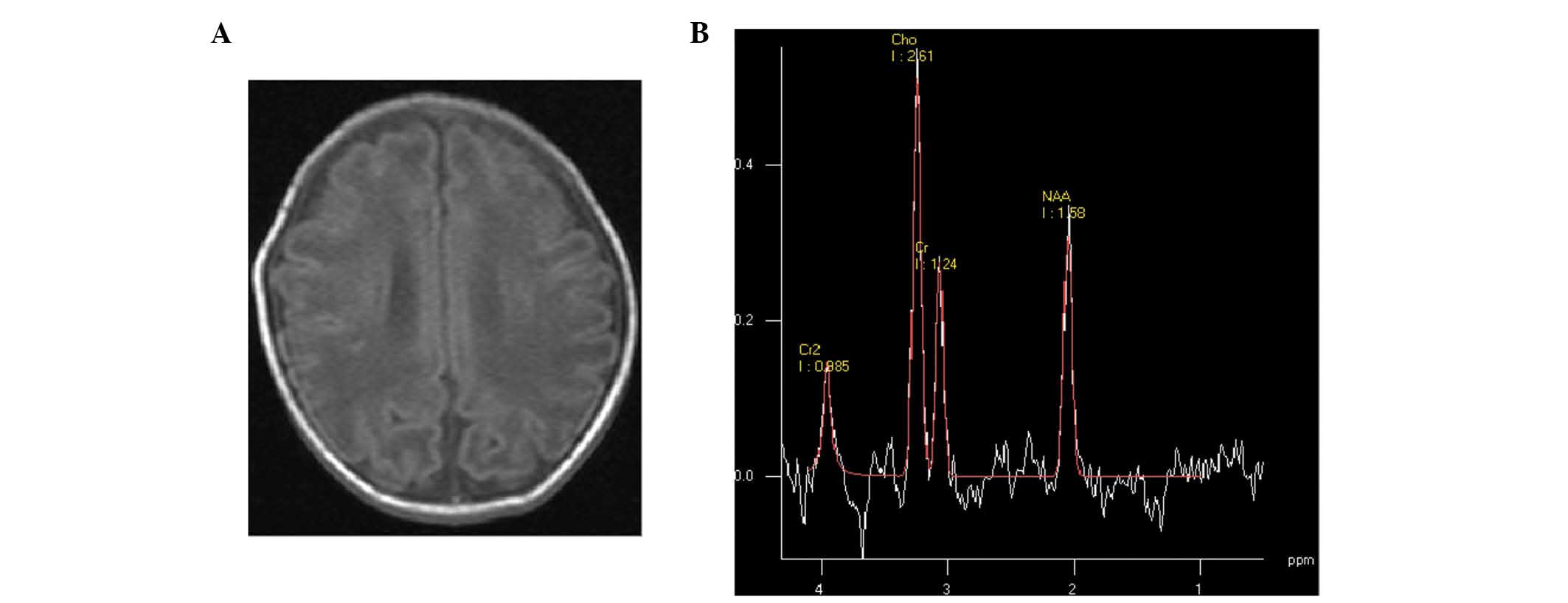
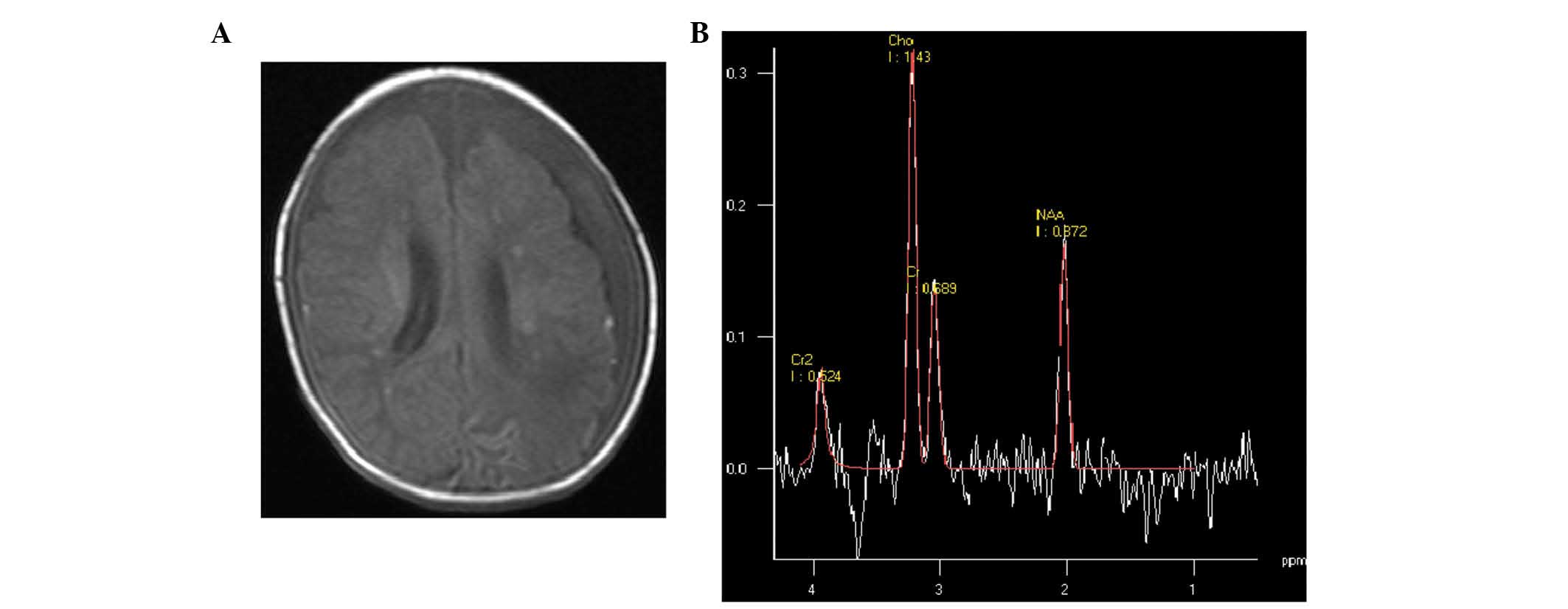
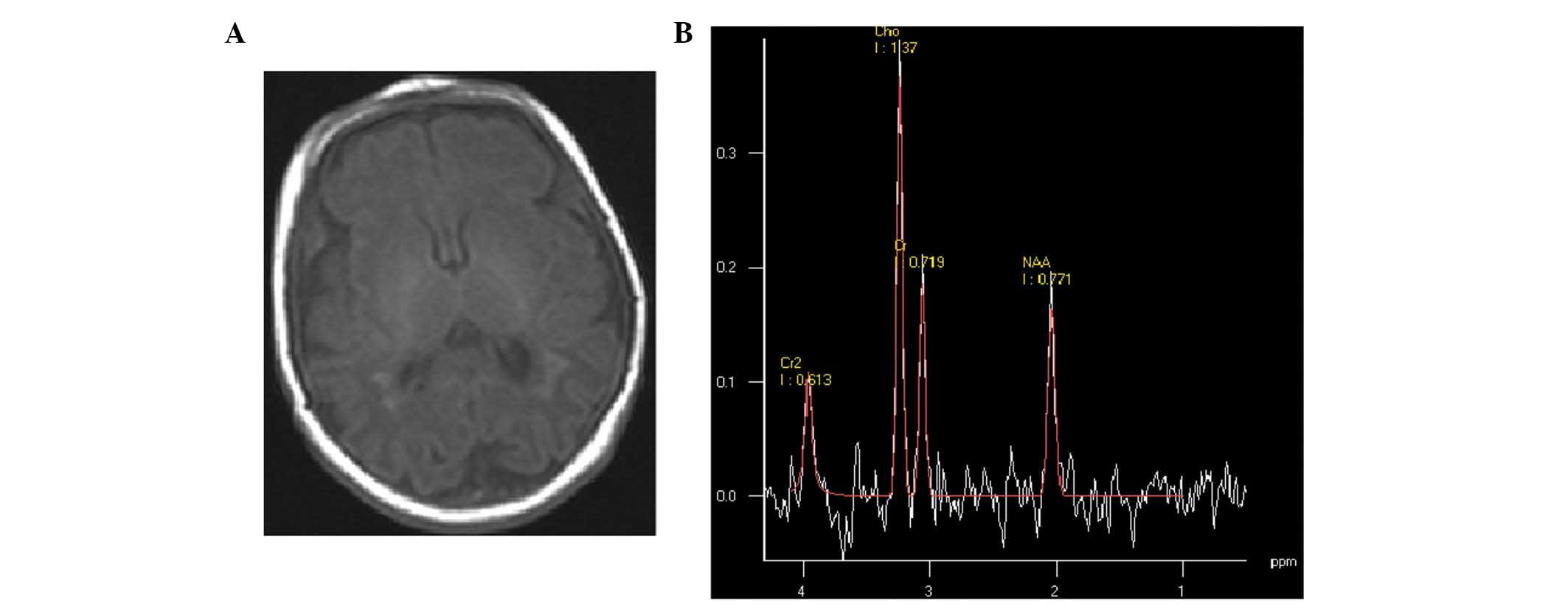
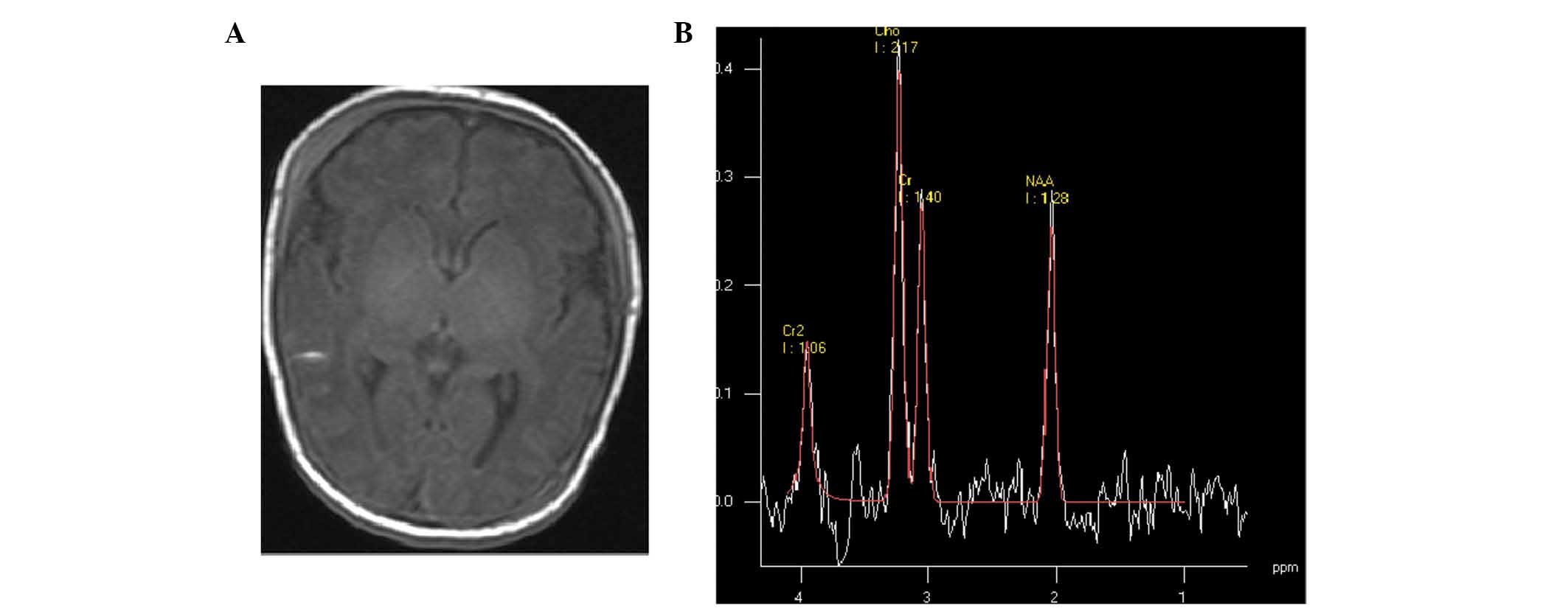
|
1
|
Dilenge ME, Majnemer A and Shevell MI:
Long-term developmental outcome of asphyxiated term neonates. J
Child Neurol. 16:781–792. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yin XJ, Wei W, Han T, Shang MX, Han X,
Chai YN and Feng ZC: Value of amplitude-integrated
electroencephalograph in early diagnosis and prognosis prediction
of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Int J Clin Exp Med.
7:1099–1104. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jadas V, Brasseur-Daudruy M, Chollat C,
Pellerin L, Devaux AM and Marret S: et le réseau de périnatalité de
Haute-Normandie: The contribution of the clinical examination,
electroencephalogram and brain MRI in assessing the prognosis in
term newborns with neonatal encephalopathy. A cohort of 30 newborns
before the introduction of treatment with hypothermia. Arch
Pediatr. 21:125–133. 2014.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sie LT, van der Knaap MS, Oosting J, de
Vries LS, Lafeber HN and Valk J: MR patterns of hypoxic-ischemic
brain damage after prenatal, perinatal or postnatal asphyxia.
Neuropediatrics. 31:128–136. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liauw L, Palm-Meinders IH, van der Grond
J, Leijser LM, le Cessie S, Laan LA, Heeres BC, van Buchem MA and
van Wezel-Meijler G: Differentiating normal myelination from
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy on T1-weighted MR Images: A new
approach. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28:660–665. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liauw L, van der Grond J, van den
Berg-Huysmans AA, Laan LA, van Buchem MA and van Wezel-Meijler G:
Is there a way to predict outcome in (near) term neonates with
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy based on MR imaging? AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 29:1789–1794. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ancora G, Testa C, Grandi S, Tonon C,
Sbravati F, Savini S, Manners DN, Gramegna LL, Tani G, Malucelli E,
et al: Prognostic value of brain proton mr spectroscopy and
diffusion tensor imaging in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy treated by brain cooling. Neuroradiology.
55:1017–1025. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barkovich AJ, Baranski K, Vigneron D,
Partridge JC, Hallam DK, Hajnal BL and Ferriero DM: Proton MR
spectroscopy for the evaluation of brain injury in asphyxiated,
term neonates. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 20:1399–1405. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barkovich AJ, Westmark KD, Bedi HS,
Partridge JC, Ferriero DM and Vigneron DB: Proton spectroscopy and
diffusion imaging on the first day of life after perinatal
asphyxia: Preliminary report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 22:1786–1794.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheong JL, Cady EB, Penrice J, Wyatt JS,
Cox IJ and Robertson NJ: Proton MR spectroscopy in neonates with
perinatal cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury: Metabolite peak-area
ratios, relaxation times and absolute concentrations. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 27:1546–1554. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu W, Zhong W, Qi J, Yin P, Wang C and
Chang L: Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in neonates with
hypoxic ischemic injury and its prognostic value. Transl Res.
152:225–232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hanrahan JD, Sargentoni J, Azzopardi D,
Manji K, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Cox IJ, Bell JD, Bryant DJ and
Edwards AD: Cerebral metabolism within 18 hours of birth asphyxia:
A proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Pediatr Res.
39:584–590. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
de Vries LS and Cowan FM: Evolving
understanding of Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy in the term
infants. Semin Pediatr Neurol. 16:216–225. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thayyil S, Chandrasekaran M, Taylor A,
Bainbridge A, Cady EB, Chong WK, Murad S, Omar RZ and Robertson NJ:
Cerebral magnetic resonance biomarkers in neonatal encephalopathy:
A meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 125:e382–e395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Meyer-Witte S, Brissaud O, Brun M,
Lamireau D, Bordessoules M and Chateil JF: Prognostic value of MR
in term neonates with neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: MRI
score and spectroscopy. About 26 cases. Arch Pediatr. 15:9–23.
2008.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brissaud O, Amirault M, Villega F, Periot
O, Chateil JF and Allard M: Efficiency of fractional anisotropy and
apparent diffusion coefficient on diffusion tensor imaging in
prognosis of neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A
methodologic prospective pilot study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
31:282–287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
de Vries LS and Toet MC: Amplitude
integrated electroencephalography in the full-term newborn. Clin
Perinatol. 33:619–632. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mia AH, Akter KR, Rouf MA, Islam MN, Hoque
MM, Hossain MA and Chowdhury AK: Grading of perinatal asphyxia by
clinical parameters and agreement between this grading and Sarnat
& Sarnat stages without measures. Mymensingh Med J. 22:807–813.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dyet LE, Kennea N, Counsell SJ, Maalouf
EF, Ajayi-Obe M, Duggan PJ, Harrison M, Allsop JM, Hajnal J,
Herlihy AH, et al: Natural history of brain lesions in extremely
preterm infants studied with serial magnetic resonance imaging from
birth and neurodevelopmental assessment. Pediatrics. 118:536–548.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramenghi LA, Fumagalli M, Righini A, Bassi
L, Groppo M, Parazzini C, Bianchini E, Triulzi F and Mosca F:
Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of brain maturation in
preterm neonates with punctate white matter lesions.
Neuroradiology. 49:161–167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Niwa T, de Vries LS, Benders MJ, Takahara
T, Nikkels PG and Groenendaal F: Punctate white matter lesions in
infants: New insights using susceptibility-weighted imaging.
Neuroradiology. 53:669–679. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Laerhoven H, de Haan TR, Offringa M,
Post B and van der Lee JH: Prognostic tests in term neonates with
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A systematic review. Pediatrics.
131:88–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gano D, Chau V, Poskitt KJ, Hill A, Roland
E, Brant R, Chalmers M and Miller SP: Evolution of pattern of
injury and quantitative MRI on days 1 and 3 in term newborns with
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Res. 74:82–87. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nikas I, Dermentzoglou V, Theofanopoulou M
and Theodoropoulos V: Parasagittal lesions and ulegyria in
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: Neuroimaging findings and review
of the pathogenesis. J Child Neurol. 23:51–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wagner F, Haenggi MM, Wagner B, Weck A,
Weisstanner C, Grunt S, Z'Graggen WJ, Gralla J, Wiest R and Verma
RK: The value of susceptibility-weighted imaging (swi) in patients
with non-neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Resuscitation.
88:75–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ment LR, Bada HS, Barnes P, Grant PE,
Hirtz D, Papile LA, Pinto-Martin J, Rivkin M and Slovis TL:
Practice parameter: Neuroimaging of the neonate: Report of the
quality standards subcommittee of the American academy of neurology
and the practice committee of the child neurology society.
Neurology. 58:1726–1738. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martinez-Biarge M, Diez-Sebastian J,
Wusthoff CJ, Lawrence S, Aloysius A, Rutherford MA and Cowan FM:
Feeding and communication impairments in infants with central grey
matter lesions following perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic injury. Eur J
Paediatr Neurol. 16:688–696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rutherford MA, Ward P and Malamatentiou C:
Advanced MR techniques in the term-born neonate with perinatal
brain injury. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 10:445–460. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu D and Vigneron D: Magnetic resonance
spectroscopy imaging of the newborn brain-a technical review. Semin
Perinatol. 34:20–27. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Barkovich AJ, Miller SP, Bartha A, Newton
N, Hamrick SE, Mukherjee P, Glenn OA, Xu D, Partridge JC, Ferriero
DM and Vigneron DB: MR imaging, MR spectroscopy and diffusion
tensor imaging of sequential studies in neonates with
encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 27:533–547. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Alderliesten T, de Vries LS, Benders MJ,
Koopman C and Groenendaal F: MR imaging and outcome of term
neonates with perinatal asphyxia: Value of diffusion-weighted MR
imaging and 1H MR spectroscopy. Radiology. 261:235–242.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|