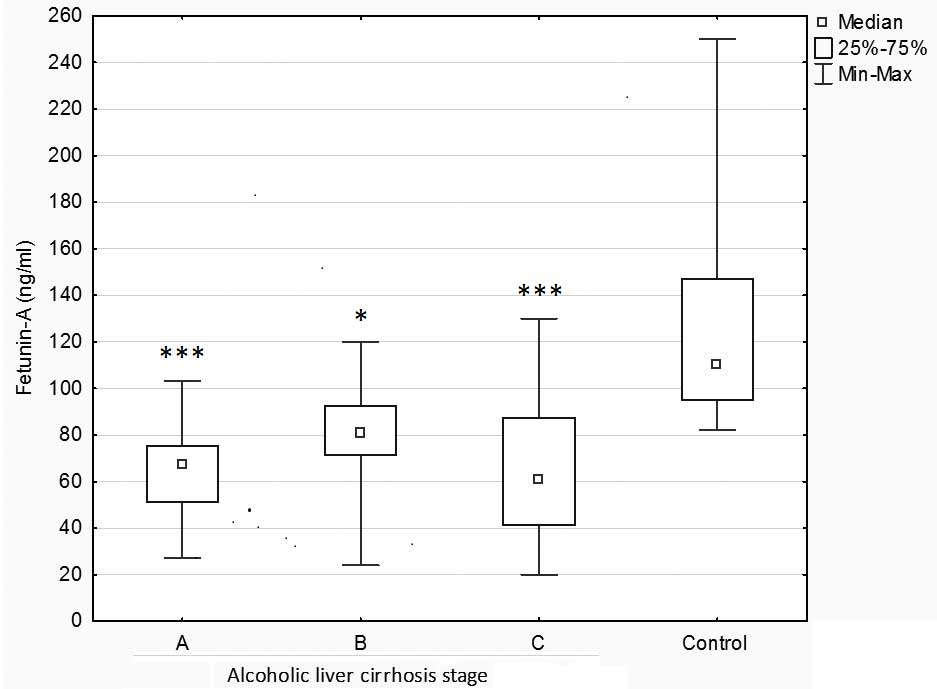
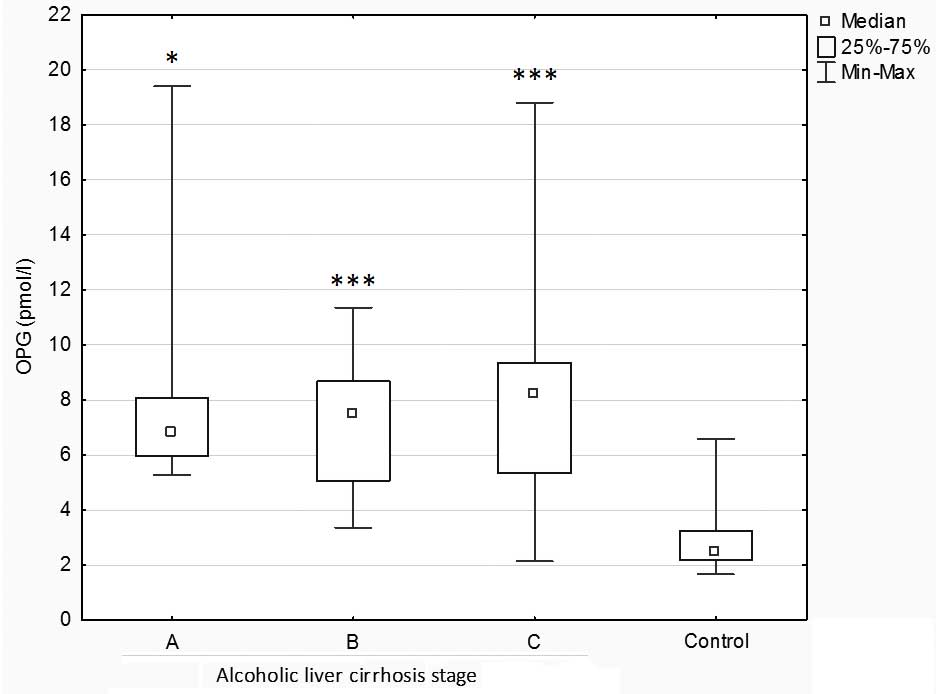
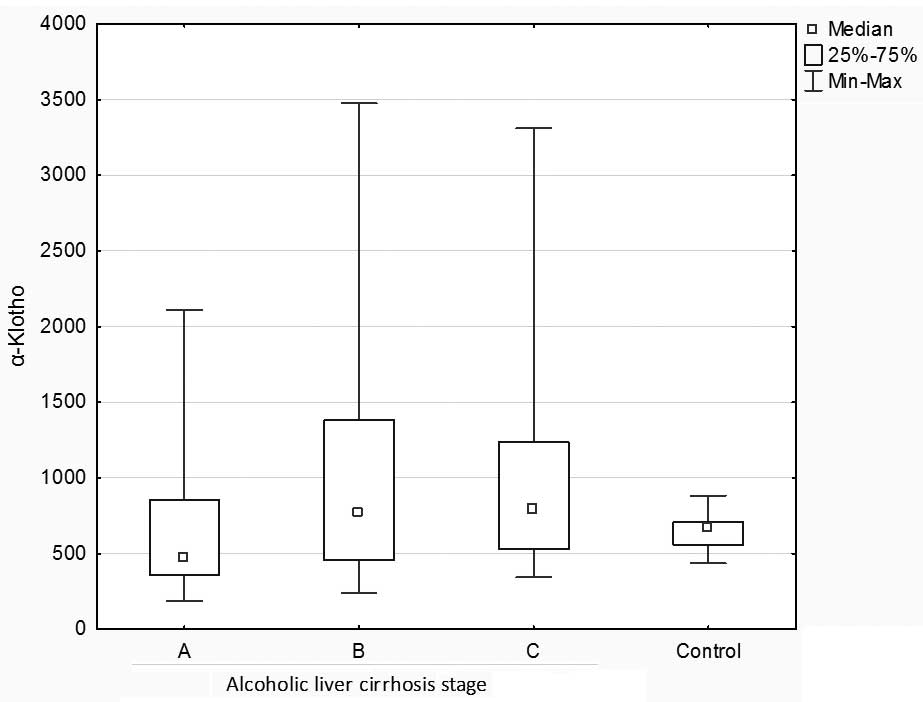
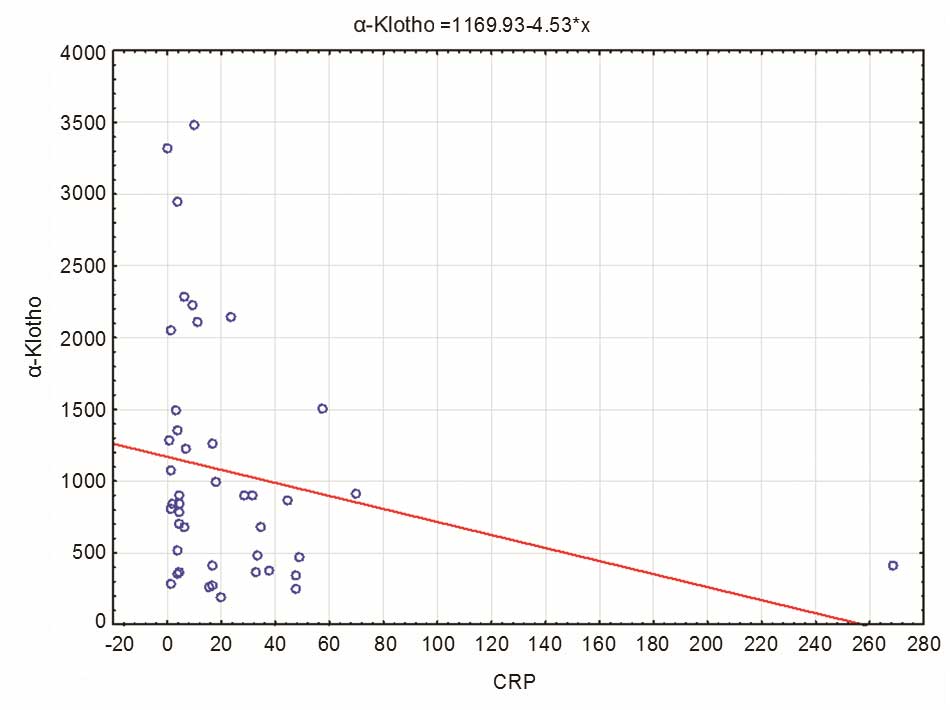
|
1
|
Prystupa A, Szpetnar M,
Boguszewska-Czubara A, Grzybowski A, Sak J and Załuska W: Activity
of MMP1 and MMP13 and amino acid metabolism in patients with
alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Med Sci Monit. 21:1008–1014. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schinke T, Amendt C, Trindl A, Pöschke O,
Müller-Esterl W and Jahnen-Dechent W: The serum protein alpha2-HS
glycoprotein/fetuin inhibits apatite formation in vitro and in
mineralizing calvaria cells. A possible role in mineralization and
calcium homeostasis. J Biol Chem. 271:20789–20796. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Karabakan M, Bozkurt A, Gunay M, Aktas BK,
Hirik E, Aydın M and Nuhoglu B: Association between serum fetuin-A
level and erectile function. Andrologia. 48:787–792. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swallow CJ, Partridge EA, Macmillan JC,
Tajirian T, DiGuglielmo GM, Hay K, Szweras M, Jahnen-Dechent W,
Wrana JL, Redston M, et al: Alpha2HS-glycoprotein, an antagonist of
transforming growth factor beta in vivo, inhibits intestinal tumor
progression. Cancer Res. 64:6402–6409. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sato M, Kamada Y, Takeda Y, Kida S, Ohara
Y, Fujii H, Akita M, Mizutani K, Yoshida Y, Yamada M, et al:
Fetuin-A negatively correlates with liver and vascular fibrosis in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease subjects. Liver Int. 35:925–935.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yilmaz Y, Yonal O, Kurt R, Oral AY, Eren
F, Ozdogan O, Ari F, Celikel CA, Korkmaz S, Ulukaya E, et al: Serum
levels of osteoprotegerin in the spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 70:541–546. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lipton A, Ali SM, Leitzel K, Chinchilli V,
Witters L, Engle L, Holloway D, Bekker P and Dunstan CR: Serum
osteoprotegerin levels in healthy controls and cancer patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 8:2306–2310. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kainuma S, Otsuka T, Kuroyanagi G,
Yamamoto N, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Kozawa O and Tokuda H: Possible
involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase in PGE1-induced
synthesis of osteoprotegerin in osteoblasts. Exp Ther Med.
11:2042–2048. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tomiyama K, Maeda R, Urakawa I, Yamazaki
Y, Tanaka T, Ito S, Nabeshima Y, Tomita T, Odori S, Hosoda K, et
al: Relevant use of Klotho in FGF19 subfamily signaling system in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:1666–1671. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamazaki Y, Imura A, Urakawa I, Shimada T,
Murakami J, Aono Y, Hasegawa H, Yamashita T, Nakatani K, Saito Y,
et al: Establishment of sandwich ELISA for soluble alpha-Klotho
measurement: Age-dependent change of souble alpha-Klotho levels in
healthy subjects. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:513–518. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
García-Valdecasas-Campelo E,
González-Reimers E, Santolaria-Fernández F, De la Vega-Prieto MJ,
Milena-Abril A, Sánchez-Pérez MJ, Martínez-Riera A and
Gómez-Rodríguez Mde L: Serum osteoprotegerin and RANKL levels in
chronic alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Alcohol. 41:261–266. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kalabay L, Gráf L, Vörös K, Jakab L, Benko
Z, Telegdy L, Fekete B, Prohászka Z and Füst G: Human serum fetuin
A/alpha2HS-glycoprotein level is associated with long-term survival
in patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis, comparison with the
Child-Pugh and MELD scores. BMC Gastroenterol. 7:152007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dabrowska AM, Tarach JS, Wojtysiak-Duma B
and Duma D: Fetuin-A (AHSG) and its usefulness in clinical
practice. Review of the literature. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky
Olomouc Czech Repub. 159:352–359. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Denecke B, Gräber S, Schäfer C, Heiss A,
Wöltje M and Jahnen-Dechent W: Tissue distribution and activity
testing suggest a similar but not identical function of fetuin-B
and fetuin-A. Biochem J. 376:135–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ix JH, Shlipak MG, Brandenburg VM, Ali S,
Ketteler M and Whooley MA: Association between human fetuin-A and
the metabolic syndrome: Data from the heart and soul study.
Circulation. 113:1760–1767. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeng YI, Sun R, Li X, Liu M, Chen S and
Zhang P: Pathophysiology of valvular heart disease. Exp Ther Med.
11:1184–1188. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohnishi T, Nakamura O, Arakaki N and
Daikuhara Y: Effect of phosphorylated rat fetuin on the growth of
hepatocytes in primary cultures in the presence of human
hepatocyte-growth factor. Evidence that phosphorylated fetuin is a
natural modulator of hepatocyte-growth factor. Eur J Biochem.
243:753–761. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kalabay L, Jakab L, Prohászka Z, Füst G,
Benkö Z, Telegdy L, Lörincz Z, Závodszky P, Arnaud P and Fekete B:
Human fetuin/alpha2HS-glycoprotein level as a novel indicator of
liver cell function and short-term mortality in patients with liver
cirrhosis and liver cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:389–394. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jezequel M, Seta NS, Corbic MM, Feger JM
and Durand GM: Modifications of concanavalin A patterns of alpha
1-acid glycoprotein and alpha 2-HS glycoprotein in alcoholic liver
disease. Clin Chim Acta. 176:49–57. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hofbauer LC, Khosla S, Dunstan CR, Lacey
DL, Boyle WJ and Riggs BL: The roles of osteoprotegerin and
osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone
resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 15:2–12. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szalay F, Hegedus D, Lakatos PL, Tornai I,
Bajnok E, Dunkel K and Lakatos P: High serum osteoprotegerin and
low RANKL in primary biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 38:395–400.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fábrega E, Orive A, García-Suarez C,
García-Unzueta M, Amado J Antonio and Pons-Romero F:
Osteoprotegerin and RANKL in alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Liver Int.
25:305–310. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moschen AR, Kaser A, Stadlmann S, Millonig
G, Kaser S, Mühllechner P, Habior A, Graziadei I, Vogel W and Tilg
H: The RANKL/OPG system and bone mineral density in patients with
chronic liver disease. J Hepatol. 43:973–983. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kwon BS, Wang S, Udagawa N, Haridas V, Lee
ZH, Kim KK, Oh KO, Greene J, Li Y, Su J, et al: TR1, a new member
of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, induces
fibroblast proliferation and inhibits osteoclastogenesis and bone
resorption. FASEB J. 12:845–854. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Daniluk J, Szuster-Ciesielska A, Drabko J
and Kandefer-Szerszeń M: Serum cytokine levels in alcohol-related
liver cirrhosis. Alcohol. 23:29–34. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sasso GR, Florencio-Silva R, Simões RS,
Baracat MC, Júnior JM Soares and Baracat EC: Elevated serum
osteoprotegerin levels in women: Friend or foe? Rev Assoc Med Bras
(1992). 61:524–529. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gaudio A, Lasco A, Morabito N, Atteritano
M, Vergara C, Catalano A, Fries W, Trifiletti A and Frisina N:
Hepatic osteodystrophy: Does the osteoprotegerin/receptor activator
of nuclear factor-kB ligand system play a role? J Endocrinol
Invest. 28:677–682. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsujikawa H, Kurotaki Y, Fujimori T,
Fukuda K and Nabeshima Y: Klotho, a gene related to a syndrome
resembling human premature aging, functions in a negative
regulatory circuit of vitamin D endocrine system. Mol Endocrinol.
17:2393–2403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kuro-o M: Klotho as a regulator of
oxidative stress and senescence. Biol Chem. 389:233–241. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao Y, Banerjee S, Dey N, LeJeune WS,
Sarkar PS, Brobey R, Rosenblatt KP, Tilton RG and Choudhary S:
Klotho depletion contributes to increased inflammation in kidney of
the db/db mouse model of diabetes via RelA (serine)536
phosphorylation. Diabetes. 60:1907–1916. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Martín-Núñez E, Donate-Correa J,
Muros-de-Fuentes M, Mora-Fernández C and Navarro-González JF:
Implications of Klotho in vascular health and disease. World J
Cardiol. 6:1262–1269. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Moreno JA, Izquierdo MC, Sanchez-Niño MD,
Suárez-Alvarez B, Lopez-Larrea C, Jakubowski A, Blanco J, Ramirez
R, Selgas R, Ruiz-Ortega M, et al: The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK
and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 22:1315–1325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Navarro-González JF, Donate-Correa J, de
Fuentes M Muros, Pérez-Hernández H, Martínez-Sanz R and
Mora-Fernández C: Reduced Klotho is associated with the presence
and severity of coronary artery disease. Heart. 100:34–40. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie B, Zhou J, Shu G, Liu DC, Zhou J, Chen
J and Yuan L: Restoration of klotho gene expression induces
apoptosis and autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Tumor suppressive
role of klotho in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 13:182013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xie B, Zhou J, Yuan L, Ren F, Liu DC, Li Q
and Shu G: Epigenetic silencing of Klotho expression correlates
with poor prognosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Pathol.
44:795–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shu G, Xie B, Ren F, Liu DC and Zhou J, Li
Q, Chen J, Yuan L and Zhou J: Restoration of klotho expression
induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Cell Onco (Dordr). 36:121–129. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen L, Liu H, Liu J, Zhu Y, Xu L, He H,
Zhang H, Wang S, Wu Q, Liu W, et al: Klotho endows hepatoma cells
with resistance to anoikis via VEGFR2/PAK1 activation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e584132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|