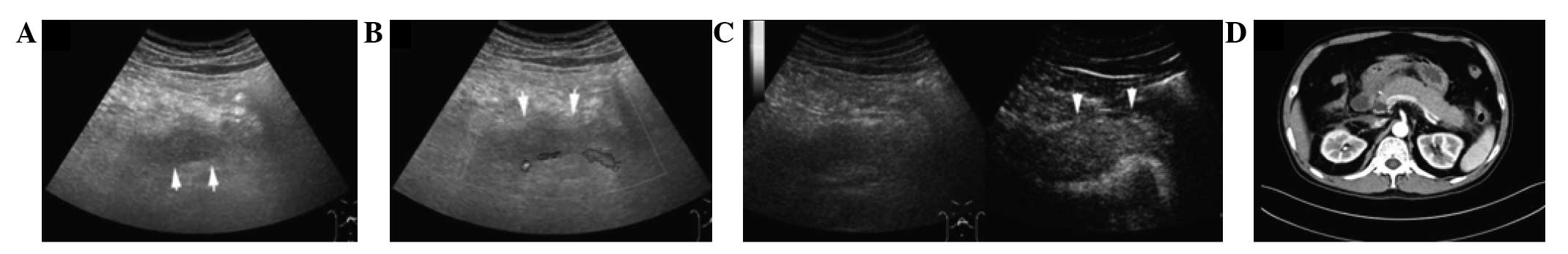
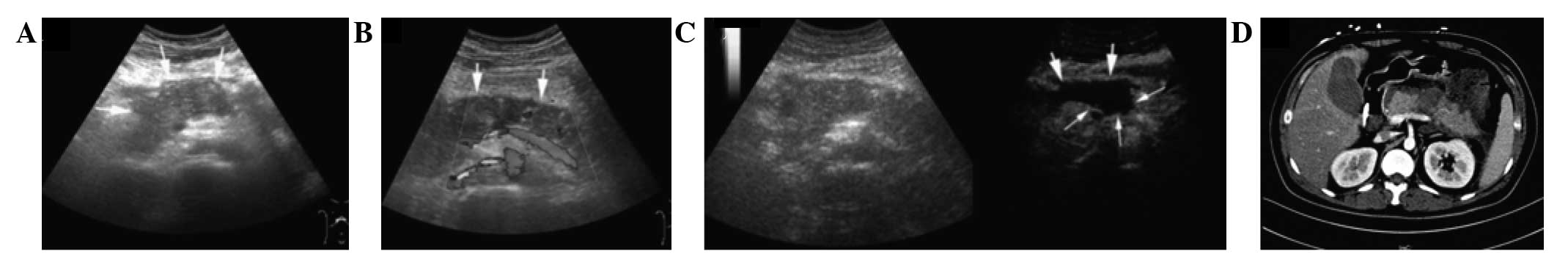
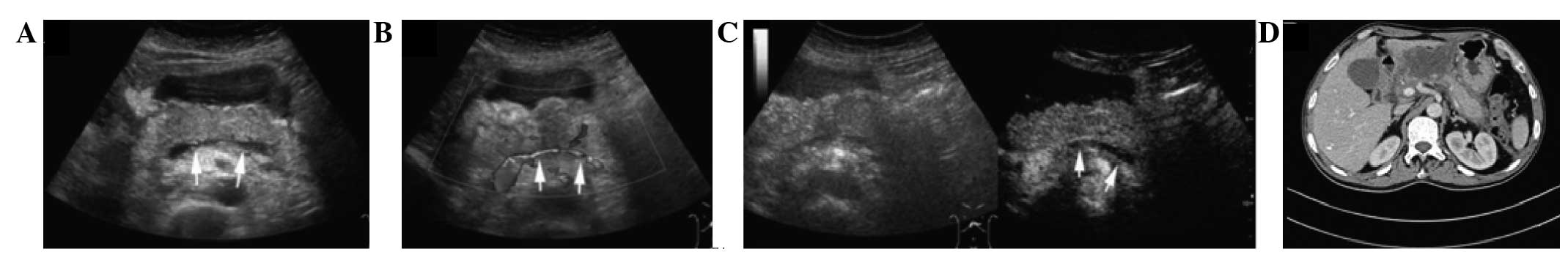
|
1
|
Harvey C, Hart JL and Lloyd CR: Ultrasound
in the acute abdomen. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 69:M116–M119. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pach R, Kulig P, Kołodziejczyk P,
Szczepanik A and Sierżęga M: Ultrasonography in the diagnosis of
acute abdominal disorders. Pol Przegl Chir. 84:590–600.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ćwik G: Standards of the Polish Ultrasound
Society - update. Pancreas examination. J Ultrason. 13:167–177.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frossard JL, Steer ML and Pastor CM: Acute
pancreatitis. Lancet. 371:143–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dellinger EP, Forsmark CE, Layer P, Lévy
P, Maraví-Poma E, Petrov MS, Shimosegawa T, Siriwardena AK, Uomo G,
Whitcomb DC, et al: Determinant-based classification of acute
pancreatitis severity: An international multidisciplinary
consultation. Ann Surg. 256:875–880. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Triester SL and Kowdley KV: Prognostic
factors in acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 34:167–176.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bollen TL, Singh VK, Maurer R, Repas K,
van Es HW, Banks PA and Mortele KJ: A comparative evaluation of
radiologic and clinical scoring systems in the early prediction of
severity in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 107:612–619.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bai Y, Liu Y, Jia L, Jiang H, Ji M, Lv N,
Huang K, Zou X, Li Y, Tang C, et al: Severe acute pancreatitis in
China: Etiology and mortality in 1976 patients. Pancreas.
35:232–237. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gandolfi L, Torresan F, Solmi L and
Puccetti A: The role of ultrasound in biliary and pancreatic
diseases. Eur J Ultrasound. 16:141–159. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rickes S, Uhle C, Kahl S, Kolfenbach S,
Monkemuller K, Effenberger O and Malfertheiner P: Echo enhanced
ultrasound: A new valid initial imaging approach for severe acute
pancreatitis. Gut. 55:74–78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ardelean M, Şirli R, Sporea I, Bota S,
Martie A, Popescu A, Dănila M, Timar B, Buzas R and Lighezan D:
Contrast enhanced ultrasound in the pathology of the pancreas - a
monocentric experience. Med Ultrason. 16:325–331. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balthazar EJ: Acute pancreatitis:
Assessment of severity with clinical and CT evaluation. Radiology.
223:603–613. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Faccioli N, Crippa S, Bassi C and
D'Onofrio M: Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography of the pancreas.
Pancreatology. 9:560–566. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu Q, Zhong Y, Wen XR, Huang ZW, Fan YT,
Xia Q and Luo Y: Can contrast-enhanced ultrasound evaluate the
severity of acute pancreatitis? Dig Dis Sci. 56:1578–1584. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rickes S, Rauh P, Uhle C, Ensberg D,
Mönkemüller K and Malfertheiner P: Contrast-enhanced sonography in
pancreatic diseases. Eur J Radiol. 64:183–188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rickes S, Mönkemüller K and Malfertheiner
P: Acute severe pancreatitis: Contrast-enhanced sonography. Abdom
Imaging. 32:362–364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murphy KP, O'Connor OJ and Maher MM:
Updated imaging nomenclature for acute pancreatitis. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 203:W464–W469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Windsor JA and Petrov MS: Acute
pancreatitis reclassified. Gut. 62:4–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shanaman MM, Schwarz T, Gal A and O'Brien
RT: Comparison between survey radiography, B-mode ultrasonography,
contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and contrast-enhanced
multi-detector computed tomography findings in dogs with acute
abdominal signs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 54:591–604. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dhaka N, Samanta J, Kochhar S, Kalra N,
Appasani S, Manrai M and Kochhar R: Pancreatic fluid collections:
What is the ideal imaging technique? World J Gastroenterol.
21:13403–13410. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bollen TL, van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG,
van Es WH, Gooszen HG and van Leeuwen MS: Update on acute
pancreatitis: Ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic
resonance imaging features. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 28:371–383.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Golea A, Badea R, Socaciu M, Diaconu B and
Iacob D: Quantitative analysis of tissue perfusion using
contrast-enhanced transabdominal ultrasound (CEUS) in the
evaluation of the severity of acute pancreatitis. Med Ultrason.
12:198–204. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Patil PV, Khalil A and Thaha MA: Splenic
parenchymal complications in pancreatitis. JOP. 12:287–291.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hayashi H, Beppu T, Okabe K, Masuda T,
Okabe H and Baba H: Risk factors for complications after partial
splenic embolization for liver cirrhosis. Br J Surg. 95:744–750.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang L, Liu GJ, Chen YX, Dong HP and Wang
LX: Sinistral portal hypertension: Clinical features and surgical
treatment of chronic splenic vein occlusion. Med Princ Pract.
21:20–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heider R and Behrns KE: Pancreatic
pseudocysts complicated by splenic parenchymal involvement: Results
of operative and percutaneous management. Pancreas. 23:20–25. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carr SC, Mahvi DM, Hoch JR, Archer CW and
Turnipseed WD: Visceral artery aneurysm rupture. J Vasc Surg.
33:806–811. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Malka D, Hammel P, Lévy P, Sauvanet A,
Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J and Bernades P: Splenic complications in
chronic pancreatitis: Prevalence and risk factors in a
medical-surgical series of 500 patients. Br J Surg. 85:1645–1649.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mortelé KJ, Mergo PJ, Taylor HM, Ernst MD
and Ros PR: Splenic and perisplenic involvement in acute
pancreatitis: Determination of prevalence and morphologic helical
CT features. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 25:50–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Madoff DC, Denys A, Wallace MJ, Murthy R,
Gupta S, Pillsbury EP, Ahrar K, Bessoud B and Hicks ME: Splenic
arterial interventions: Anatomy, indications, technical
considerations, and potential complications. Radiographics.
25(Suppl 1): S191–S211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Koito K, Namieno T, Nagakawa T and Morita
K: Splenic artery prior to rupture in the pancreatic pseudocyst:
Detection by endoscopic color Doppler ultrasonography. J Ultrasound
Med. 15:721–724. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dietrich CF: Comments and illustrations
regarding the guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations
for contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS)-update 2008. Ultraschall
Med. 29(Suppl 4): S188–S202. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cai DM, Parajuly SS, Ling WW, Li YZ and
Luo Y: Diagnostic value of contrast enhanced ultrasound for splenic
artery complications following acute pancreatitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:1088–1094. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai DM, Luo Y, Li YZ, Tang WF, Huang ZW
and Song B: Assessing splenic vein complications in patients with
acute pancreatitis using color Doppler ultrasound and contrast
enhanced ultrasound. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 45:850–853.
2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Garcea G, Jackson B, Pattenden CJ, Sutton
CD, Neal CP, Dennison AR and Berry DP: Early warning scores predict
outcome in acute pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 10:1008–1015.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ruiz R, Pozo E and Gonzáles M: Early
prognostic risk factors in acute pancreatitis: Study of a
representative population from Peru. Rev Gastroenterol Peru.
12:5–11. 1992.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Horzić M, Bunoza D and Marić K: Meaning of
prognostic factors in patients with acute pancreatitis. Acta Med
Croatica. 51:49–52. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Topal NB, Kaya E, Ercan I, Pourbagher MA
and Topal U: The role of Doppler sonography in predicting severity
of acute pancreatitis. J Clin Ultrasound. 36:141–147. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Luo Y, Yuan CX, Peng YL, Wei PL, Zhang ZD,
Jiang JM, Dai L and Hu YK: Can ultrasound predict the severity of
acute pancreatitis early by observing acute fluid collection? World
J Gastroenterol. 7:293–295. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ripollés T, Martínez MJ, López E, Castelló
I and Delgado F: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the staging of
acute pancreatitis. Eur Radiol. 20:2518–2523. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|