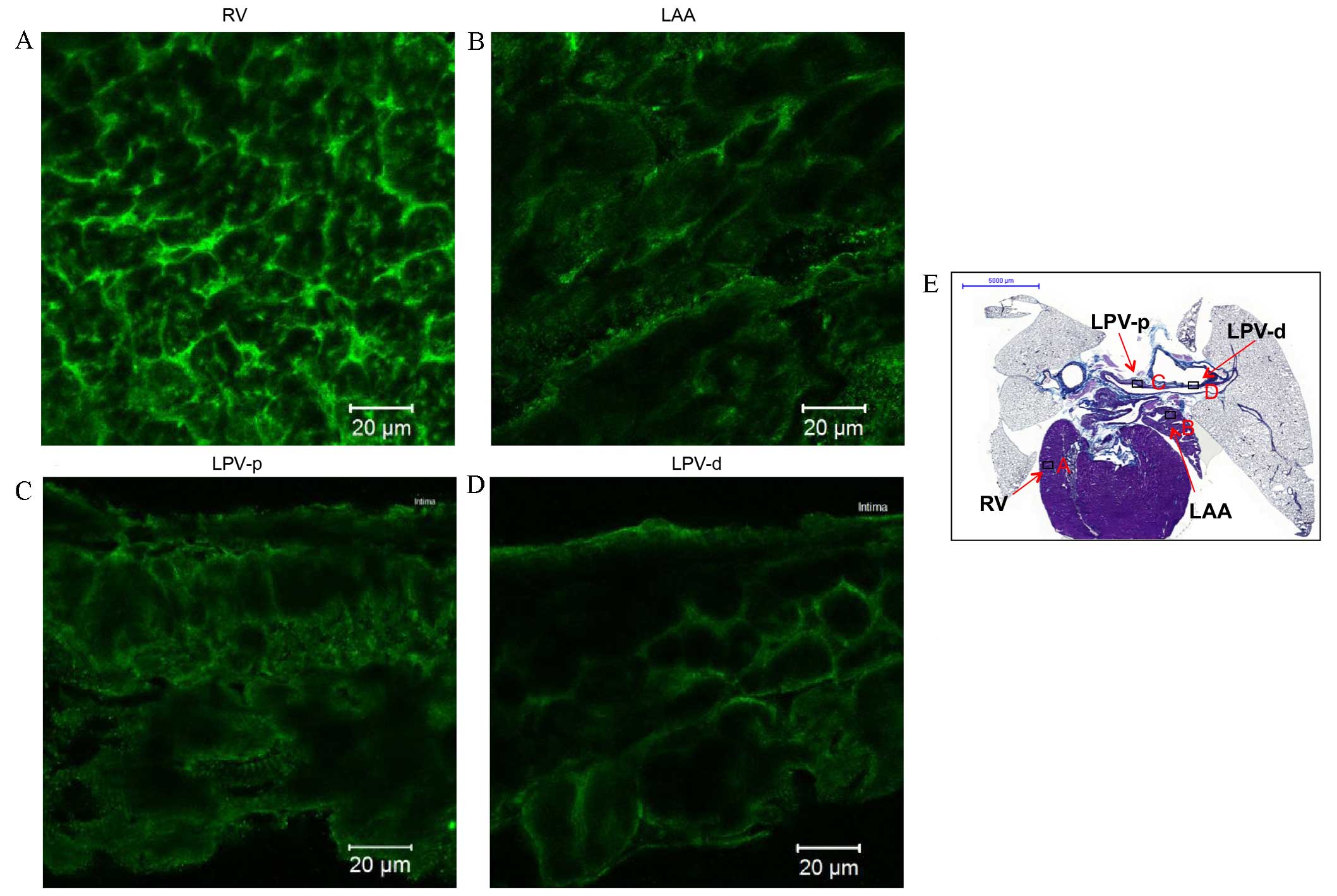
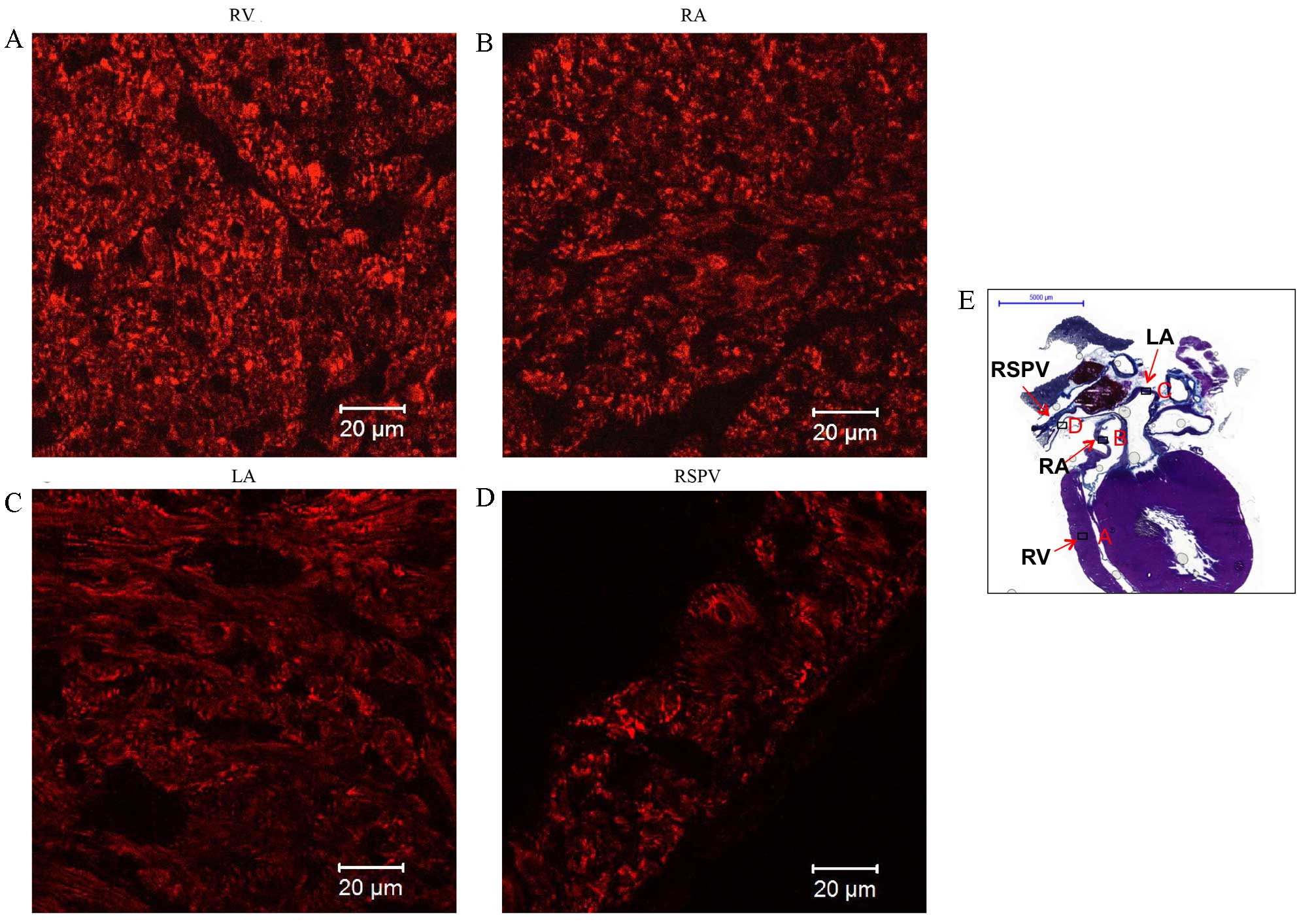
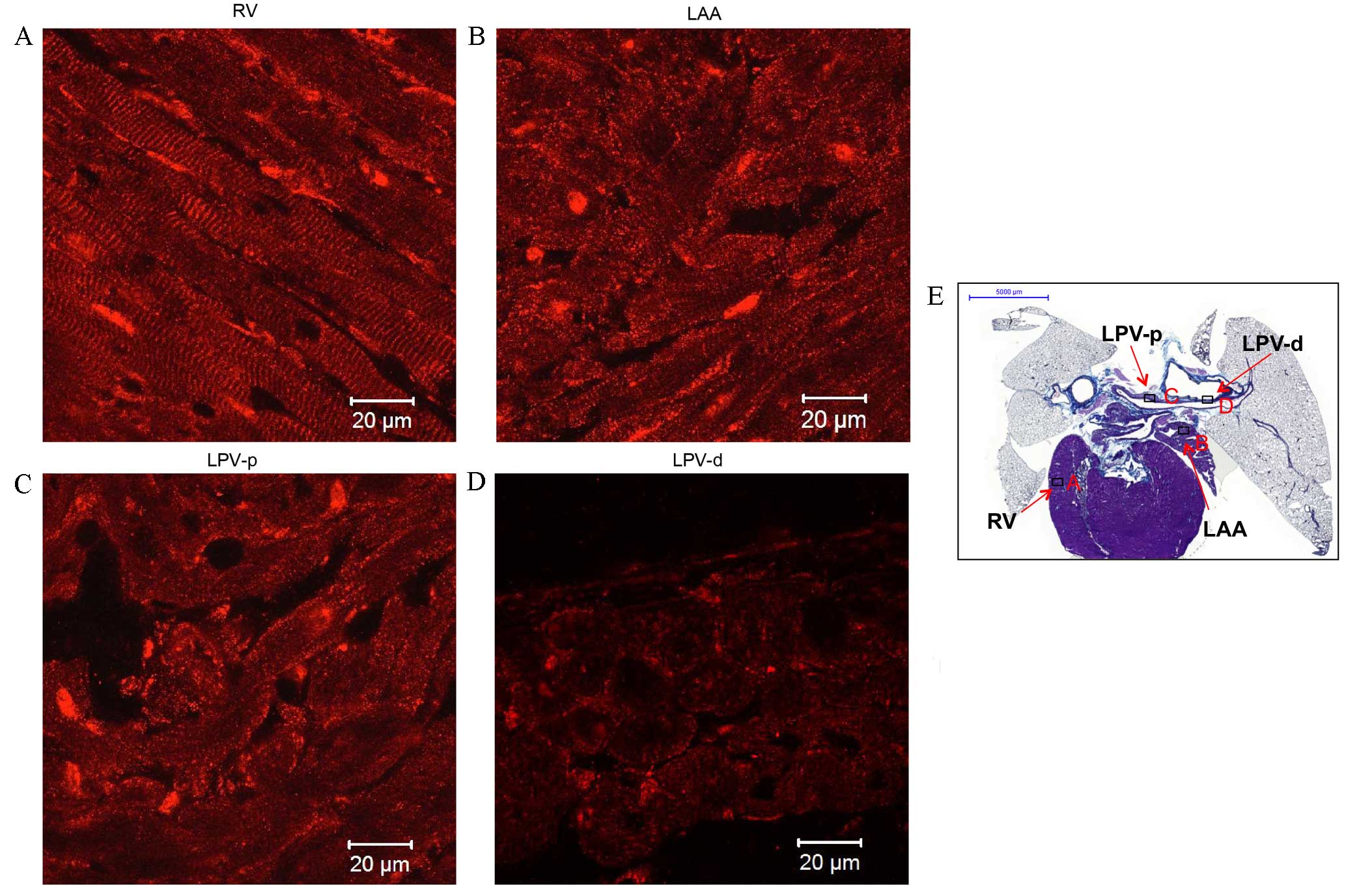
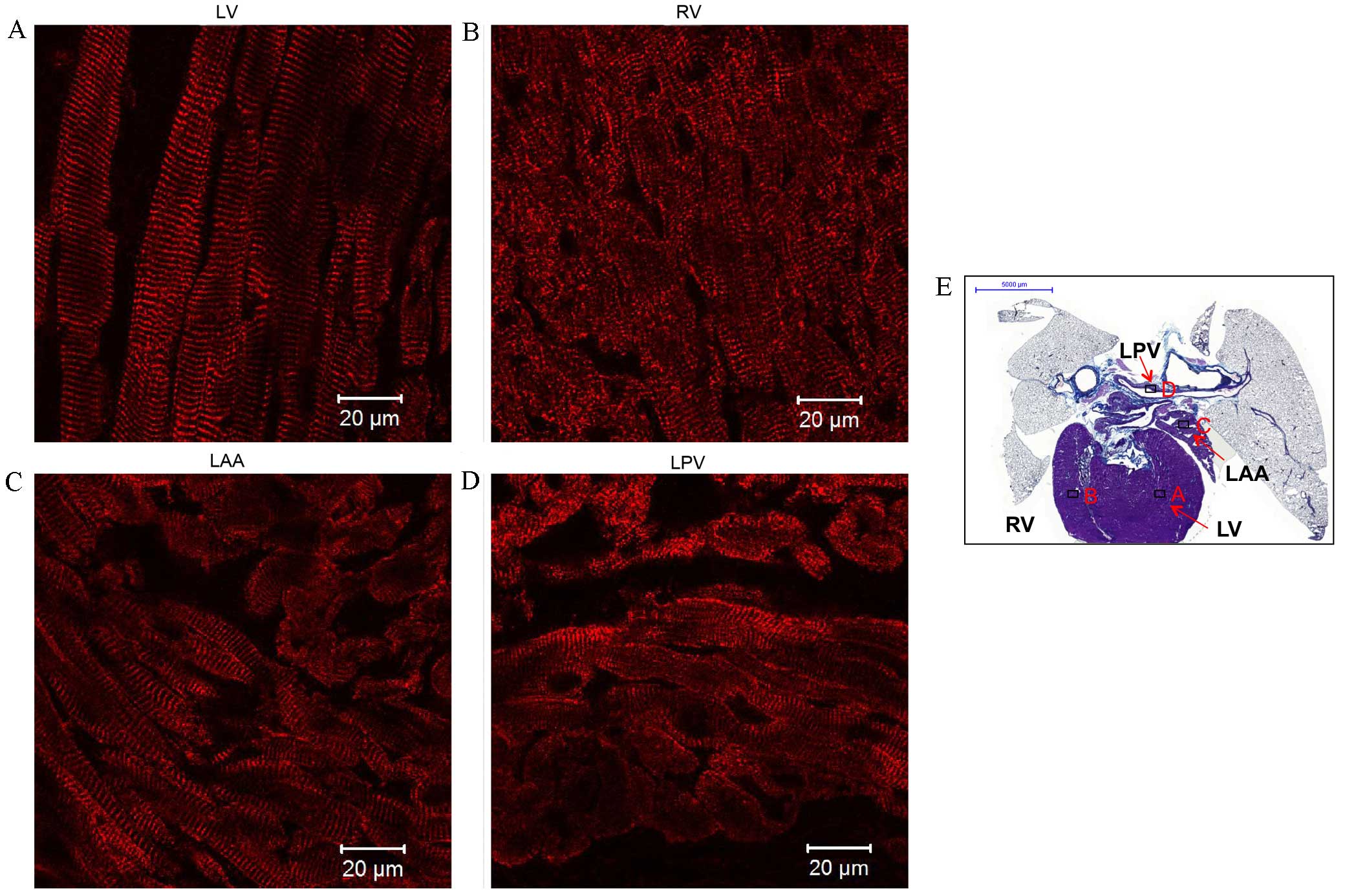
|
1
|
Iwasaki YK, Nishida K, Kato T and Nattel
S: Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: Implications for
management. Circulation. 124:2264–2274. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen LY and Shen WK: Epidemiology of
atrial fibrillation: A current perspective. Heart Rhythm. 4(3
Suppl): S1–S6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ and Levy
D: Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predisposing conditions
for atrial fibrillation: Population-based estimates. Am J Cardiol.
82:2N–9N. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang TJ, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, Leip
EP, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Murabito JM, Kannel WB and Benjamin EJ:
Temporal relations of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart
failure and their joint influence on mortality: The framingham
heart study. Circulation. 107:2920–2925. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stewart S, Hart CL, Hole DJ and McMurray
JJ: A population-based study of the long-term risks associated with
atrial fibrillation: 20-year follow-up of the Renfrew/Paisley
study. Am J Med. 113:359–364. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ott A, Breteler MM, de Bruyne MC, van
Harskamp F, Grobbee DE and Hofman A: Atrial fibrillation and
dementia in a population-based study. The rotterdam study. Stroke.
28:316–321. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, Calkins H,
Cigarroa JE, Cleveland JC Jr, Conti JB, Ellinor PT, Ezekowitz MD,
Field ME, et al: 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of
patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College
of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice
Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol.
64:e1–e76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Haissaguerre M, Jaïs P, Shah DC, Takahashi
A, Hocini M, Quiniou G, Garrigue S, Le Mouroux A, Le Métayer P and
Clémenty J: Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by
ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med.
339:659–666. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cappato R, Calkins H, Chen SA, Davies W,
Iesaka Y, Kalman J, Kim YH, Klein G, Natale A, Packer D, et al:
Updated worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of
catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm
Electrophysiol. 3:32–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Po SS, Li Y, Tang D, Liu H, Geng N,
Jackman WM, Scherlag B, Lazzara R and Patterson E: Rapid and stable
re-entry within the pulmonary vein as a mechanism initiating
paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 45:1871–1877.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Corradi D, Callegari S, Gelsomino S,
Lorusso R and Macchi E: Morphology and pathophysiology of target
anatomical sites for ablation procedures in patients with atrial
fibrillation: Part II: Pulmonary veins, caval veins, ganglionated
plexi, and ligament of Marshall. Int J Cardiol. 168:1769–1778.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan AY, Li H, Wachsmann-Hogiu S, Chen LS,
Chen PS and Fishbein MC: Autonomic innervation and segmental
muscular disconnections at the human pulmonary vein-atrial
junction: Implications for catheter ablation of atrial-pulmonary
vein junction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 48:132–143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nathan H and Gloobe H: Myocardial
atrio-venous junctions and extensions (sleeves) over the pulmonary
and caval veins. Anatomical observations in various mammals.
Thorax. 25:317–324. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stillitano F, Lonardo G, Zicha S, Varro A,
Cerbai E, Mugelli A and Nattel S: Molecular basis of funny current
(If) in normal and failing human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
45:289–299. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yeh YH, Wakili R, Qi XY, Chartier D,
Boknik P, Kääb S, Ravens U, Coutu P, Dobrev D and Nattel S:
Calcium-handling abnormalities underlying atrial arrhythmogenesis
and contractile dysfunction in dogs with congestive heart failure.
Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 1:93–102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hocini M, Ho SY, Kawara T, Linnenbank AC,
Potse M, Shah D, Jaïs P, Janse MJ, Haïssaguerre M and De Bakker JM:
Electrical conduction in canine pulmonary veins:
Electrophysiological and anatomic correlation. Circulation.
105:2442–2448. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Verheule S, Wilson EE, Arora R, Engle SK,
Scott LR and Olgin JE: Tissue structure and connexin expression of
canine pulmonary veins. Cardiovasc Res. 55:727–738. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arora R, Verheule S, Scott L, Navarrete A,
Katari V, Wilson E, Vaz D and Olgin JE: Arrhythmogenic substrate of
the pulmonary veins assessed by high-resolution optical mapping.
Circulation. 107:1816–1821. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hollands C: The Animals (scientific
procedures) Act 1986. Lancet. 2:32–33. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Combes RD and Balls M: The Three
Rs-opportunities for improving animal welfare and the quality of
scientific research. Altern Lab Anim. 42:245–259. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chandler NJ, Greener ID, Tellez JO, Inada
S, Musa H, Molenaar P, Difrancesco D, Baruscotti M, Longhi R,
Anderson RH, et al: Molecular architecture of the human sinus node:
Insights into the function of the cardiac pacemaker. Circulation.
119:1562–1575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mueller-Hoecker J, Beitinger F, Fernandez
B, Bahlmann O, Assmann G, Troidl C, Dimomeletis I, Kääb S and
Deindl E: Of rodents and humans: A light microscopic and
ultrastructural study on cardiomyocytes in pulmonary veins. Int J
Med Sci. 5:152–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Logantha SJ, Cruickshank SF, Rowan EG and
Drummond RM: Spontaneous and electrically evoked Ca2+
transients in cardiomyocytes of the rat pulmonary vein. Cell
Calcium. 48:150–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Spach MS, Barr RC and Jewett PH: Spread of
excitation from the atrium into thoracic veins in human beings and
dogs. Am J Cardiol. 30:844–854. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ehrlich JR, Cha TJ, Zhang L, Chartier D,
Melnyk P, Hohnloser SH and Nattel S: Cellular electrophysiology of
canine pulmonary vein cardiomyocytes: Action potential and ionic
current properties. J Physiol. 551:801–813. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boyett MR, Honjo H and Kodama I: The
sinoatrial node, a heterogeneous pacemaker structure. Cardiovasc
Res. 47:658–687. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boyett MR, Inada S, Yoo S, Li J, Liu J,
Tellez J, Greener ID, Honjo H, Billeter R, Lei M, et al: Connexins
in the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes. Adv Cardiol.
42:175–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dobrzynski H, Boyett MR and Anderson RH:
New insights into pacemaker activity: Promoting understanding of
sick sinus syndrome. Circulation. 115:1921–1932. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Saez JC, Berthoud VM, Branes MC, Martinez
AD and Beyer EC: Plasma membrane channels formed by connexins:
Their regulation and functions. Physiol Rev. 83:1359–1400. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Severs NJ, Bruce AF, Dupont E and Rothery
S: Remodelling of gap junctions and connexin expression in diseased
myocardium. Cardiovasc Res. 80:9–19. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bikou O, Thomas D, Trappe K, Lugenbiel P,
Kelemen K, Koch M, Soucek R, Voss F, Becker R, Katus HA and Bauer
A: Connexin 43 gene therapy prevents persistent atrial fibrillation
in a porcine model. Cardiovasc Res. 92:218–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Igarashi T, Finet JE, Takeuchi A, Fujino
Y, Strom M, Greener ID, Rosenbaum DS and Donahue JK: Connexin gene
transfer preserves conduction velocity and prevents atrial
fibrillation. Circulation. 125:216–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamamoto M, Dobrzynski H, Tellez J, Niwa
R, Billeter R, Honjo H, Kodama I and Boyett MR: Extended atrial
conduction system characterised by the expression of the HCN4
channel and connexin45. Cardiovasc Res. 72:271–281. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Perez-Lugones A, McMahon JT, Ratliff NB,
Saliba WI, Schweikert RA, Marrouche NF, Saad EB, Navia JL, McCarthy
PM, Tchou P, et al: Evidence of specialized conduction cells in
human pulmonary veins of patients with atrial fibrillation. J
Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 14:803–809. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Morel E, Meyronet D, Thivolet-Bejuy F and
Chevalier P: Identification and distribution of interstitial Cajal
cells in human pulmonary veins. Heart Rhythm. 5:1063–1067. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li YD, Hong YF, Zhang Y, Zhou XH, Ji YT,
Li HL, Hu GJ, Li JX, Sun L, Zhang JH, et al: Association between
reversal in the expression of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic
nucleotide-gated (HCN) channel and age-related atrial fibrillation.
Med Sci Monit. 20:2292–2297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Priori SG, Pandit SV, Rivolta I, Berenfeld
O, Ronchetti E, Dhamoon A, Napolitano C, Anumonwo J, di Barletta
MR, Gudapakkam S, et al: A novel form of short QT syndrome (SQT3)
is caused by a mutation in the KCNJ2 gene. Circ Res. 96:800–807.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen YJ, Chen SA, Chen YC, Yeh HI, Chan P,
Chang MS and Lin CI: Effects of rapid atrial pacing on the
arrhythmogenic activity of single cardiomyocytes from pulmonary
veins: Implication in initiation of atrial fibrillation.
Circulation. 104:2849–2854. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Melnyk P, Ehrlich JR, Pourrier M,
Villeneuve L, Cha TJ and Nattel S: Comparison of ion channel
distribution and expression in cardiomyocytes of canine pulmonary
veins versus left atrium. Cardiovasc Res. 65:104–116. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Marks AR: Calcium cycling proteins and
heart failure: Mechanisms and therapeutics. J Clin Invest.
123:46–52. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Frank KF, Bölck B, Erdmann E and Schwinger
RH: Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase modulates cardiac
contraction and relaxation. Cardiovasc Res. 57:20–27. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Musa H, Lei M, Honjo H, Jones SA,
Dobrzynski H, Lancaster MK, Takagishi Y, Henderson Z, Kodama I and
Boyett MR: Heterogeneous expression of Ca(2+) handling proteins in
rabbit sinoatrial node. J Histochem Cytochem. 50:311–324. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lyashkov AE, Juhaszova M, Dobrzynski H,
Vinogradova TM, Maltsev VA, Juhasz O, Spurgeon HA, Sollott SJ and
Lakatta EG: Calcium cycling protein density and functional
importance to automaticity of isolated sinoatrial nodal cells are
independent of cell size. Circ Res. 100:1723–1731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Thiagalingam A, Reddy VY, Cury RC, Abbara
S, Holmvang G, Thangaroopan M, Ruskin JN and d'Avila A: Pulmonary
vein contraction: Characterization of dynamic changes in pulmonary
vein morphology using multiphase multislice computed tomography
scanning. Heart Rhythm. 5:1645–1650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rietdorf K, Masoud S, McDonald F,
Sanderson MJ and Bootman MD: Pulmonary vein sleeve cell
excitation-contraction-coupling becomes dysynchronized by
spontaneous calcium transients. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:410–416.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bogdanov KY, Vinogradova TM and Lakatta
EG: Sinoatrial nodal cell ryanodine receptor and Na(+)-Ca(2+)
exchanger: Molecular partners in pacemaker regulation. Circ Res.
88:1254–1258. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Honjo H, Boyett MR, Niwa R, Inada S,
Yamamoto M, Mitsui K, Horiuchi T, Shibata N, Kamiya K and Kodama I:
Pacing-induced spontaneous activity in myocardial sleeves of
pulmonary veins after treatment with ryanodine. Circulation.
107:1937–1943. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|