|
1
|
Stein B and Smith BD: Treatment options
for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who are resistant to or
unable to tolerate imatinib. Clinical Therapeutics. 32:804–820.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chaudhary V, Sachdeva P, Karanth P and
Arora R: Spontaneous hemoperitoneum in chronic myeloid leukemia: An
unusual etiology. J Hematol (Brossard). 2:40–41. 2013.
|
|
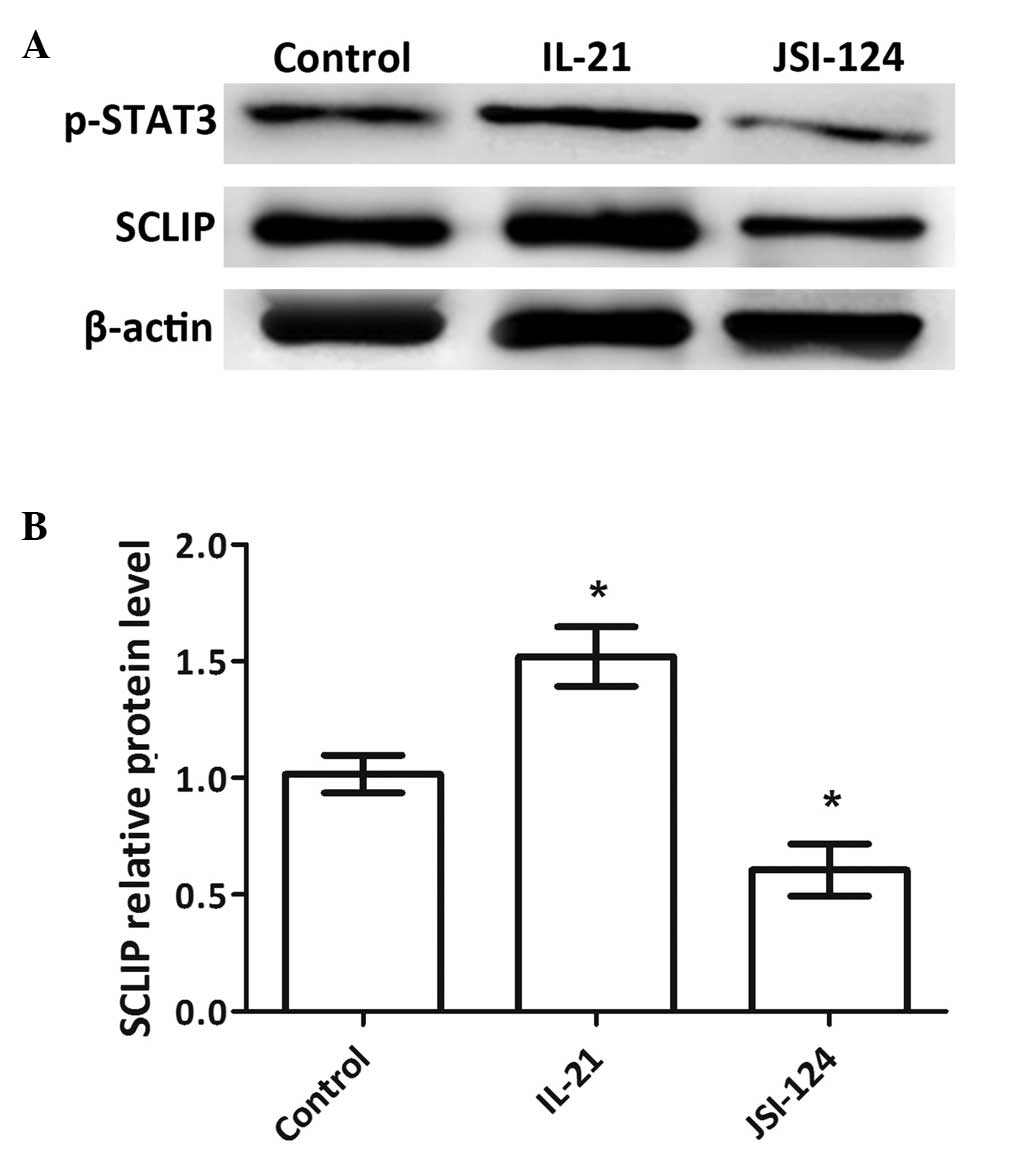
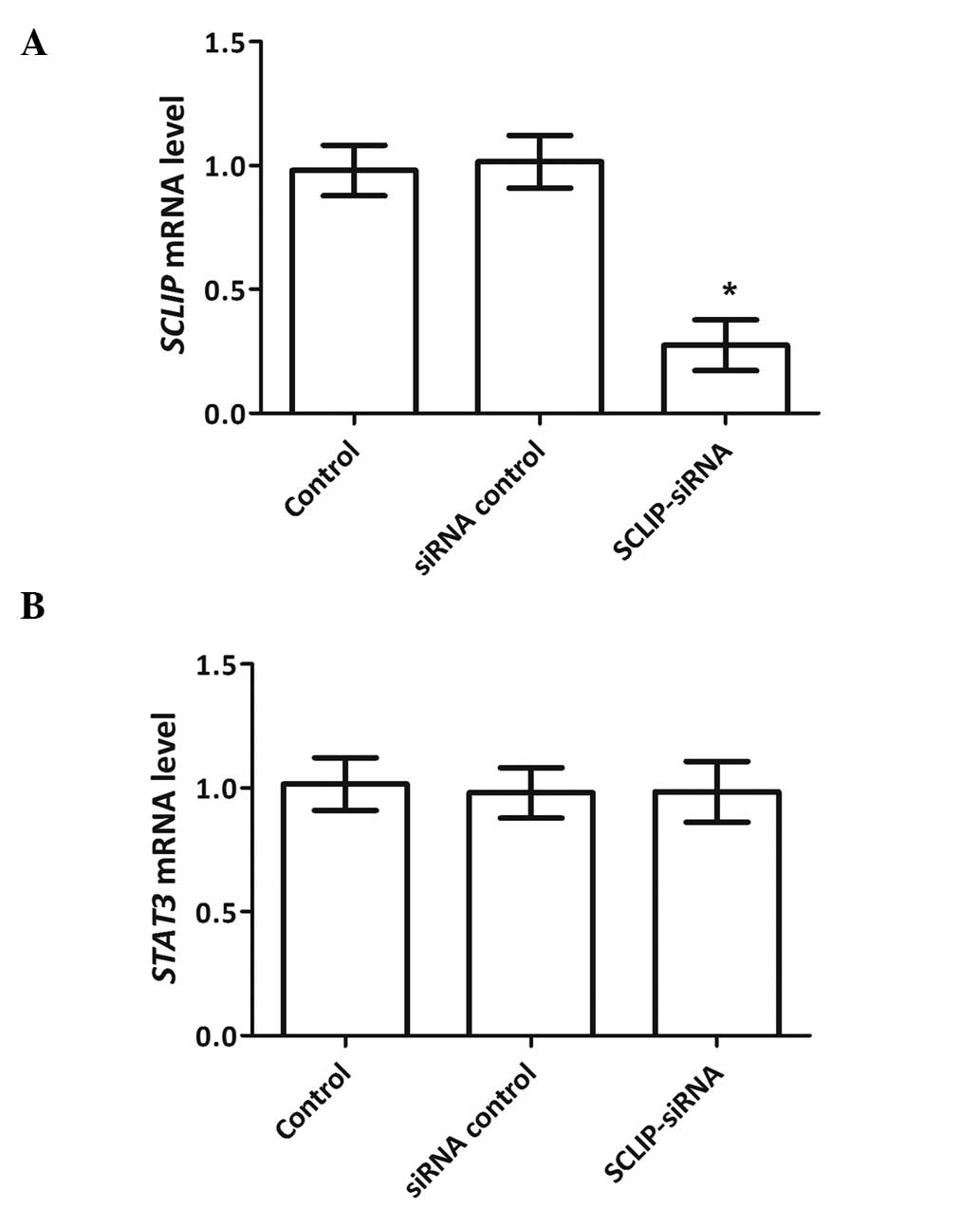
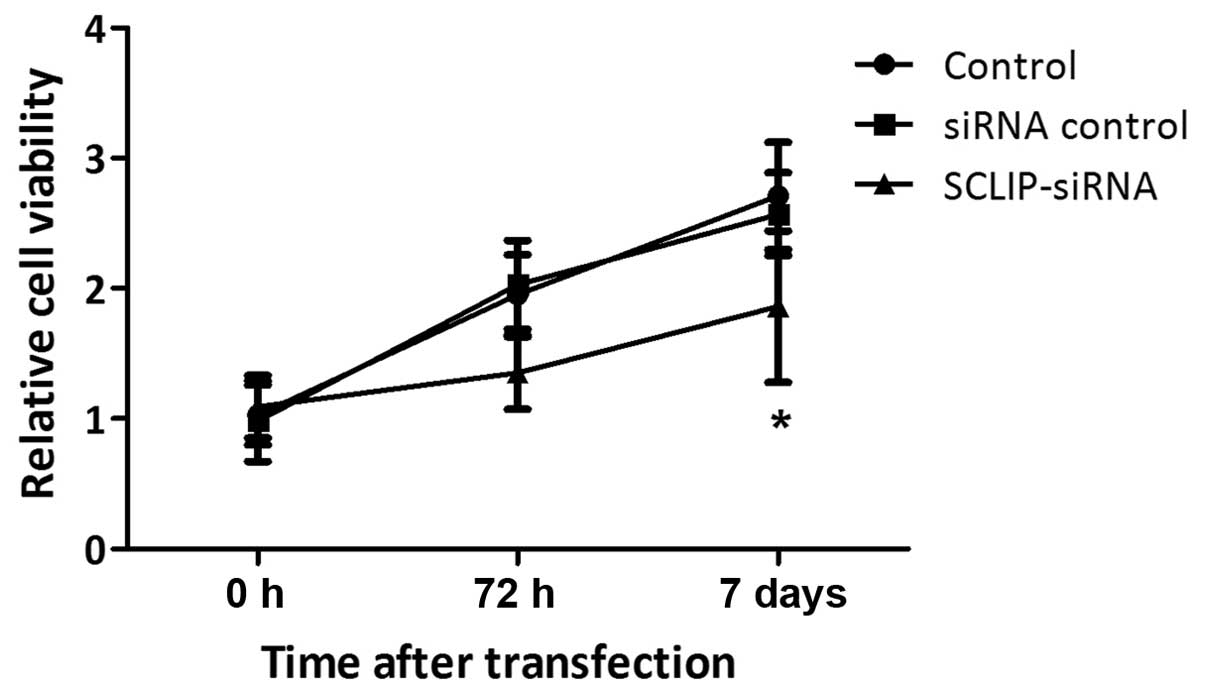
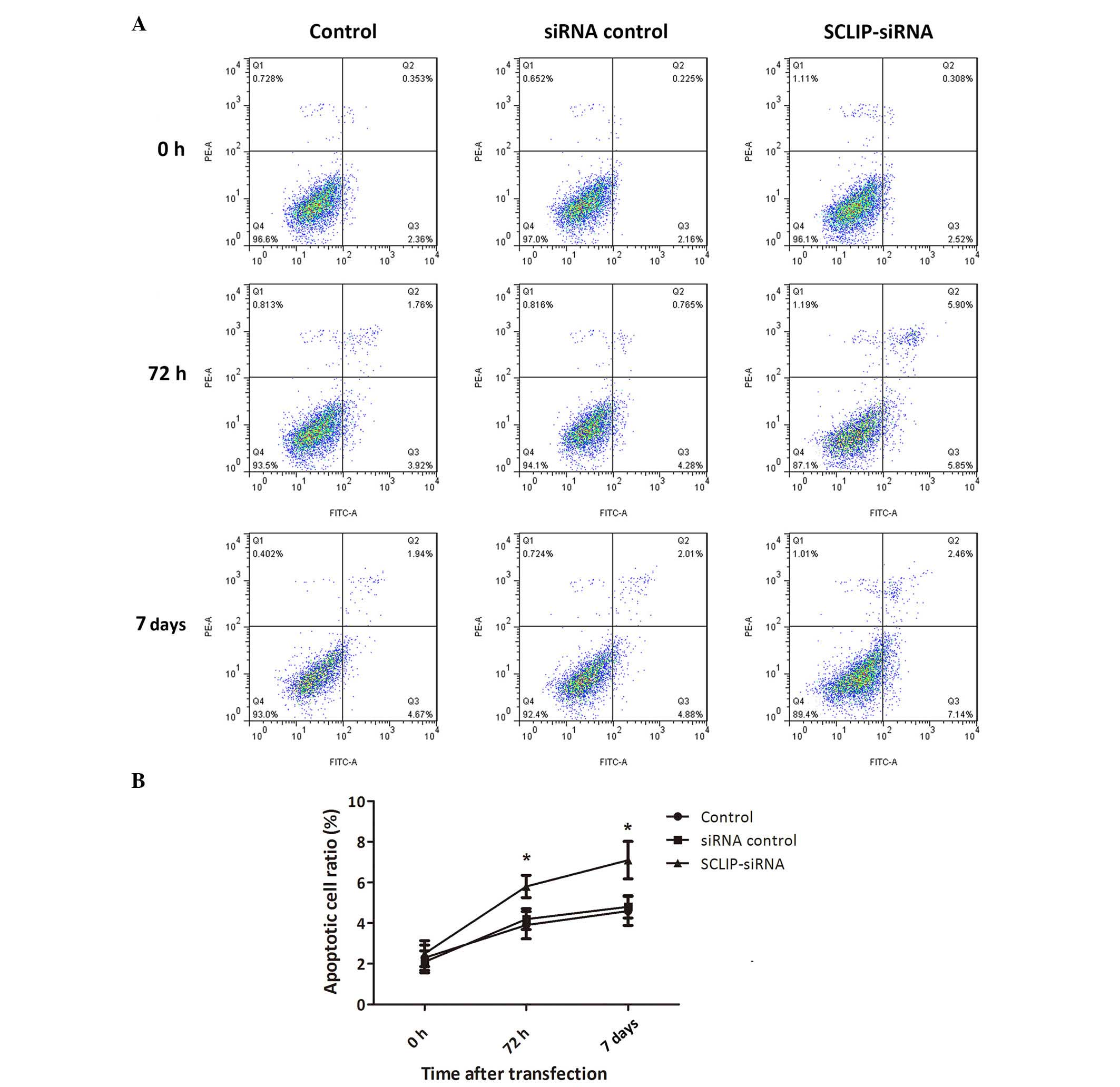
3
|
Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z and
Kantarjian HM: Chronic myelogenous leukemia: Biology and therapy.
Ann Intern Med. 131:207–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A and Baccarani M:
European LeukemiaNet: Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet.
370:342–350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kabel AM and Elmaaboud MAA: Cancer: Role
of nutrition, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. World Journal
of Nutrition and Health. 2:48–51. 2014.
|
|
6
|
Shah NP, Guilhot F, Cortes JE, Schiffer
CA, le Coutre P, Brümmendorf TH, Kantarjian HM, Hochhaus A,
Rousselot P, Mohamed H, et al: Long-term outcome with dasatinib
after imatinib failure in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia:
Follow-up of a phase 3 study. Blood. 123:2317–2324. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bixby D and Talpaz M: Seeking the causes
and solutions to imatinib-resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 25:7–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Cowan-Jacob SW,
Hochhaus A and Griffin JD: Second generation inhibitors of BCR-ABL
for the treatment of imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia.
Nat Rev Cancer. 7:345–356. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pavlů J and Apperley JF: Allogeneic stem
cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr Hematol
Malig Rep. 8:43–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deininger MW, Goldman JM and Melo JV: The
molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 96:3343–3356.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chai SK, Nichols GL and Rothman P:
Constitutive activation of JAKs and STATs in BCR-Abl-expressing
cell lines and peripheral blood cells derived from leukemic
patients. J Immunol. 159:4720–4728. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu JF, Ll ZI, Zhang GS, Meng K, Kuang WY,
Li J, Zhou XF, Ll RJ, Peng HI, Dai CW, et al: Icaritin shows potent
anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in
vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3/AKT signalings. PLoS
One. 6:e237202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jung JH, Kwon TR, Jeong SJ, Kim EO, Sohn
EJ, Yun M and Kim SH: Apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA and
cryptotanshinone is mediated by distinct JAK/STAT3/5 and SHP1/2
signaling in chronic myeloid leukemia K562 cells. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:8056392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kiper HD, Kaymaz B Tezcanli, Gokbulut AA,
Selvi N, Avci CB, Kosova B, Iskender G, Yandim MK, Gunduz C, Sahin
F, et al: STAT pathway in the regulation of zoledronic acid-induced
apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
67:527–532. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaymaz BT, Cetintaş VB, Aktan C and Kosova
B: MicroRNA-520a-5p displays a therapeutic effect upon chronic
myelogenous leukemia cells by targeting STAT3 and enhances the
anticarcinogenic role of capsaicin. Tumour Biol. 35:8733–8742.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ng DC, Lim CP, Lin BH, Zhang T and Cao X:
SCG10-like protein (SCLIP) is a STAT3-interacting protein involved
in maintaining epithelial morphology in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Biochem J. 425:95–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu M, Pleasic-Williams S, Lin TH,
Wunderlich DA, Cheng JB and Masferrer JL: pSTAT3: A target
biomarker to study the pharmacology of the anti-IL-21R antibody
ATR-107 in human whole blood. J Transl Med. 11:652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qi J, Xia G, Huang CR, Wang JX and Zhang
J: JSI-124 (Cucurbitacin I) inhibits tumor angiogenesis of human
breast cancer through reduction of STAT3 phosphorylation. Am J Chin
Med. 43:337–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Ni S, Huang B, Wang L, Zhang X
and Li X, Wang H, Liu S, Hao A and Li X: Overexpression of SCLIP
promotes growth and motility in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Biol
Ther. 16:97–105. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gritsko T, Williams A, Turkson J, Kaneko
S, Bowman T, Huang M, Nam S, Eweis I, Diaz N, Sullivan D, et al:
Persistent activation of stat3 signaling induces survivin gene
expression and confers resistance to apoptosis in human breast
cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:11–19. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang D, He D, Xue Y, Wang R, Wu K, Xie H,
Zeng J, Wang X, Zhau HE, Chung LW, et al: PrLZ protects prostate
cancer cells from apoptosis induced by androgen deprivation via the
activation of Stat3/Bcl-2 pathway. Cancer Res. 71:2193–2202. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nair S, Bora-Singhal N, Perumal D and
Chellappan S: Nicotine-mediated invasion and migration of non-small
cell lung carcinoma cells by modulating STMN3 and GSPT1 genes in an
ID1-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 13:1732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang SW, Shin YJ, Shim YJ, Jeong SY, Park
IS and Min BH: Clusterin interacts with SCLIP (SCG10-like protein)
and promotes neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells. Exp Cell Res.
309:305–315. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD, Vandenberg
CJ, Chen L, Czabotar PE, Willis SN, Scott CL, Day CL, Cory S, et
al: The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and
efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized.
Cancer Cell. 10:389–399. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang Y, Li M, Zang W, Ma Y, Wang N, Li P,
Wang T and Zhao G: MiR-429 up-regulation induces apoptosis and
suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal
carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 36:385–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spruck CH, Won KA and Reed SI: Deregulated
cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature. 401:297–300. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gurzov EN and Izquierdo M: Cyclin E1
knockdown induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Neurol Res.
28:493–499. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou J, Wulfkuhle J, Zhang H, Gu P, Yang
Y, Deng J, Margolick JB, Liotta LA, Petricoin E III and Zhang Y:
Activation of the PTEN/mTOR/STAT3 pathway in breast cancer
stem-like cells is required for viability and maintenance. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:16158–16163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Galante JM, Mortenson MM, Bowles TL,
Virudachalam S and Bold RJ: ERK/BCL-2 pathway in the resistance of
pancreatic cancer to anoikis. J Surg Res. 152:18–25. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Buchholz TA, Garg AK, Chakravarti N,
Aggarwal BB, Esteva FJ, Kuerer HM, Singletary SE, Hortobagyi GN,
Pusztai L, Cristofanilli M and Sahin AA: The nuclear transcription
factor kappaB/bcl-2 pathway correlates with pathologic complete
response to doxorubicin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in human
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8398–8402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Möröy T and Geisen C: Cyclin E. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 36:1424–1439. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|