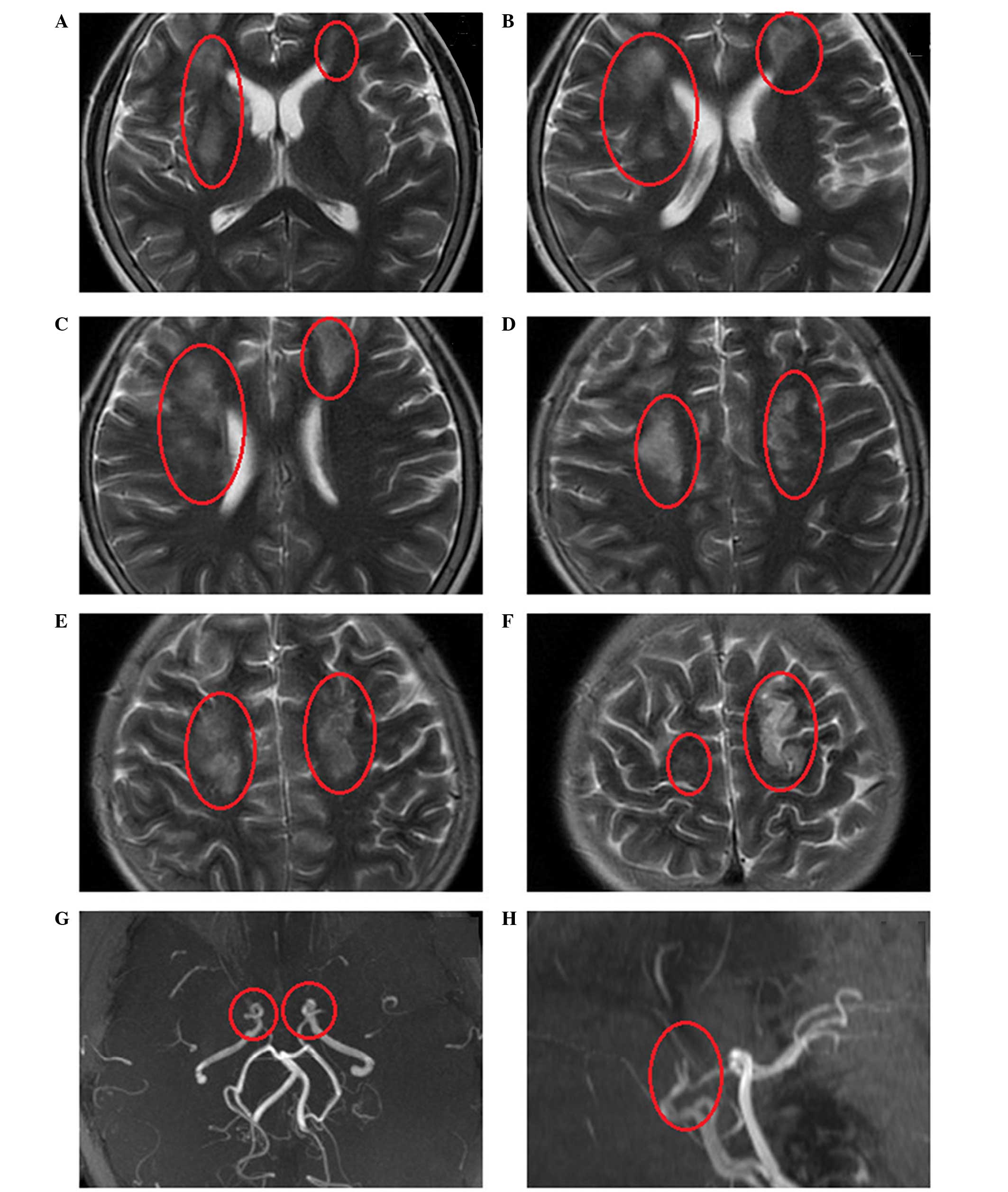
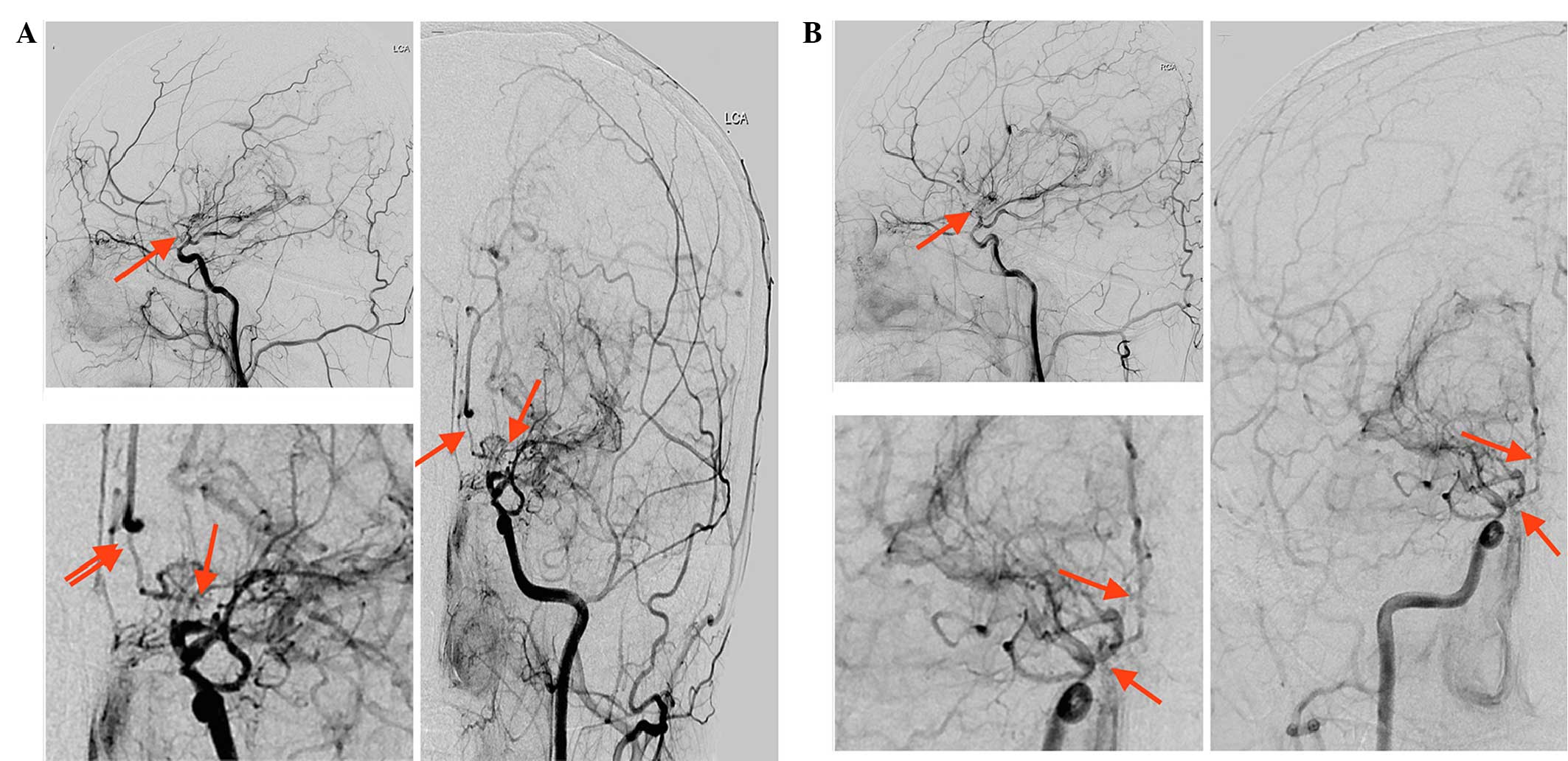
|
1
|
Houkin K, Ito M, Sugiyama T, Shichonohe H,
Nakayama N, Kazumata K and Kuroda S: Review of past research and
current concepts on the etiology of moyamoya disease. Neurol Med
Chir (Tokyo). 52:267–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kudo T: Spontaneous occlusion of the
circle of Willis. A disease apparently confined to Japanese.
Neurology. 18:485–496. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suzuki J and Kodama N: Cerebrovascular
“Moyamoya” disease. 2. Collateral routes to forebrain via ethmoid
sinus and superior nasal meatus. Angiology. 22:223–236. 1971.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen PC, Yang SH, Chien KL, Tsai IJ and
Kuo MF: Epidemiology of moyamoya disease in Taiwan: A nationwide
population-based study. Stroke. 45:1258–1263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kushima K, Satoh Y, Ban Y, Taniyama M, Ito
K and Sugita K: Graves' thyrotoxicosis and Moyamoya disease. Can J
Neurol Sci. 18:140–142. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ohba S, Nakagawa T and Murakami H:
Concurrent Graves' disease and intracranial arterial
stenosis/occlusion: special considerations regarding the state of
thyroid function, etiology, and treatment. Neurosurg Rev.
34:297–304. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hsu SW, Chaloupka JC and Fattal D: Rapidly
progressive fatal bihemispheric infarction secondary to Moyamoya
syndrome in association with Graves thyrotoxicosis. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 27:643–647. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Inaba M, Henmi Y, Kumeda Y, Ueda M, Nagata
M, Emoto M, Ishikawa T, Ishimura E and Nishizawa Y: Increased
stiffness in common carotid artery in hyperthyroid Graves' disease
patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 56:241–246. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ni J, Zhou LX, Wei YP, Li ML, Xu WH, Gao S
and Cui LY: Moyamoya syndrome associated with Graves' disease: A
case series study. Ann Transl Med. 2:772014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li H, Zhang ZS, Dong ZN, Ma MJ, Yang WZ,
Han C, Du MM, Liu YX, Yang H, Liu W, et al: Increased thyroid
function and elevated thyroid autoantibodies in pediatric patients
with moyamoya disease: A case-control study. Stroke. 42:1138–1139.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim SJ, Heo KG, Shin HY, Bang OY, Kim GM,
Chung CS, Kim KH, Jeon P, Kim JS, Hong SC and Lee KH: Association
of thyroid autoantibodies with moyamoya-type cerebrovascular
disease: A prospective study. Stroke. 41:173–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Panegyres PK, Morris JG, O'Neill PJ and
Balleine R: Moyamoya-like disease with inflammation. Eur Neurol.
33:260–263. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tendler BE, Shoukri K, Malchoff C,
MacGillivray D, Duckrow R, Talmadge T and Ramsby GR: Concurrence of
Graves' disease and dysplastic cerebral blood vessels of the
moyamoya variety. Thyroid. 7:625–629. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lip GY and Blann A: von Willebrand factor:
A marker of endothelial dysfunction in vascular disorders?
Cardiovasc Res. 34:255–265. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vischer UM: von Willebrand factor,
endothelial dysfunction, and cardiovascular disease. J Thromb
Haemost. 4:1186–1193. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Samai A, Monlezun D, Shaban A, George A,
Dowell L, Kruse-Jarres R, Schluter L, El Khoury R and Martin-Schild
S: Von Willebrand factor drives the association between elevated
factor VIII and poor outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke.
Stroke. 45:2789–2791. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wieberdink RG, van Schie MC, Koudstaal PJ,
Hofman A, Witteman JC, de Maat MP, Leebeek FW and Breteler MM: High
von Willebrand factor levels increase the risk of stroke: The
Rotterdam study. Stroke. 41:2151–2156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koster T, Blann AD, Briët E, Vandenbroucke
JP and Rosendaal FR: Role of clotting factor VIII in effect of von
Willebrand factor on occurrence of deep-vein thrombosis. Lancet.
345:152–155. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Popławska-Kita A, Szelachowska M,
Modzelewska A, Siewko K, Dzięcioł J, Klimiuk PA and Górska M:
Endothelial dysfunction in Graves' disease. Adv Med Sci. 58:31–37.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Research Committee on the Pathology and
Treatment of Spontaneous Occlusion of the Circle of Willis; Health
Labour Sciences Research Grant for Research on Measures for
Infractable Diseases, . Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of
moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis).
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 52:245–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamasaki H, Takeuchi T, Mikami T, Komeichi
K and Tsutsumi H: A case of graves' disease diagnosed in the course
of bilateral carotid artery stenoses (moyamoya disease); a case
report and review of the literature. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol.
22:39–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Conway DS, Pearce LA, Chin BS, Hart RG and
Lip GY: Prognostic value of plasma von Willebrand factor and
soluble P-selectin as indices of endothelial damage and platelet
activation in 994 patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.
Circulation. 107:3141–3145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Carter AM, Catto AJ, Mansfield MW, Bamford
JM and Grant PJ: Predictive variables for mortality after acute
ischemic stroke. Stroke. 38:1873–1880. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sadler JE: Biochemistry and genetics of
von Willebrand factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 67:395–424. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lenting PJ, Casari C, Christophe OD and
Denis CV: von Willebrand factor: The old, the new and the unknown.
J ThrombHaemost. 10:2428–2437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Müller G: [Structure and function of the
factor VIII/von Willebrand factor complex]. Z Gesamte Inn Med.
45:65–68. 1990.(In German). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hoyer LW: The factor VIII complex:
Structure and function. Blood. 58:1–13. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rao M, Zhang H, Liu Q, Zhang S, Hu L and
Deng F: Clinical and experimental pathology of Moyamoya disease.
Chin Med J (Engl). 116:1845–1849. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ikeda E and Hosoda Y: Distribution of
thrombotic lesions in the cerebral arteries in spontaneous
occlusion of the circle of Willis: Cerebrovascular moyamoya
disease. Clin Neuropathol. 12:44–48. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim YJ, Lee DH, Kwon JY, Kang DW, Suh DC,
Kim JS and Kwon SU: High resolution MRI difference between moyamoya
disease and intracranial atherosclerosis. Eur J Neurol.
20:1311–1318. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hosoda Y, Ikeda E and Hirose S:
Histopathological studies on spontaneous occlusion of the circle of
Willis (cerebrovascular moyamoya disease). Clin Neurol Neurosurg.
99(Suppl 2): S203–S208. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Napoli R, Biondi B, Guardasole V,
Matarazzo M, Pardo F, Angelini V, Fazio S and Saccà L: Impact of
hyperthyroidism and its correction on vascular reactivity in
humans. Circulation. 104:3076–3080. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vischer UM, Lang U and Wollheim CB:
Autocrine regulation of endothelial exocytosis: Von Willebrand
factor release is induced by prostacyclin in cultured endothelial
cells. FEBS Lett. 424:211–215. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu L, Wang X, Lin Z and Wu H: Elevated
plasma levels of VWF: Ag in hyperthyroidism are mediated through
beta-adrenergic receptors. Endocr Res. 19:123–133. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Burggraaf J, Lalezari S, Emeis JJ, Vischer
UM, de Meyer PH, Pijl H and Cohen AF: Endothelial function in
patients with hyperthyroidism before and after treatment with
propranolol and thiamazol. Thyroid. 11:153–160. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|