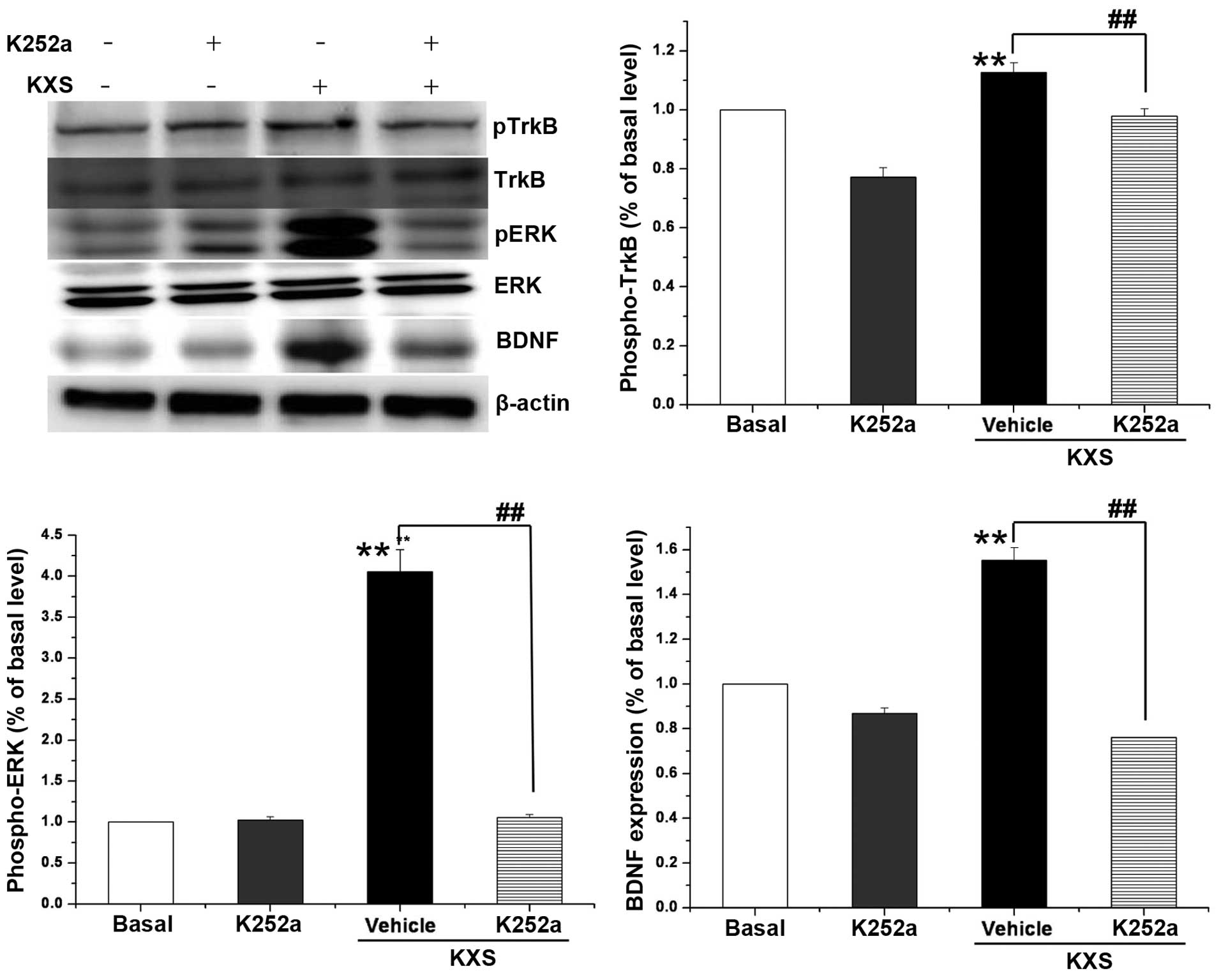
|
1
|
Voleti B and Duman RS: The roles of
neurotrophic factor and Wnt signaling in depression. Clin Pharmacol
Ther. 91:333–338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sen S, Duman R and Sanacora G: Serum
brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression and antidepressant
medications: Meta-analyses and implications. Biol Psychiatry.
64:527–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Karege F, Vaudan G, Schwald M, Perroud N
and La Harpe R: Neurotrophin levels in postmortem brains of suicide
victims and the effects of antemortem diagnosis and psychotropic
drugs. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 136:29–37. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hsiung SC, Adlersberg M, Arango V, Mann
JJ, Tamir H and Liu KP: Attenuated 5-HT1A receptor signaling in
brains of suicide victims: Involvement of adenylyl cyclase,
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt and mitogen-activated protein
kinase. J Neurochem. 87:182–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jernigan CS, Goswami DB, Austin MC, Iyo
AH, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA and Karolewicz B: The mTOR signaling
pathway in the prefrontal cortex is compromised in major depressive
disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 35:1774–1779.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Zhang H, Roberts RC,
Conley RR and Pandey GN: Modulation in activation and expression of
phosphatase and tensin homolog on chromosome ten, Akt1 and
3-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1: Further evidence
demonstrating altered phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in
postmortem brain of suicide subjects. Biol Psychiatry.
67:1017–1025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Molteni R, Calabrese F, Racagni G,
Fumagalli F and Riva MA: Antipsychotic drug actions on gene
modulation and signaling mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. 124:74–85.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fishback JA, Robson MJ, Xu YT and
Matsumoto RR: Sigma receptors: Potential targets for a new class of
antidepressant drug. Pharmacol Ther. 127:271–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Blendy JA: The role of CREB in depression
and antidepressant treatment. Biol Psychiatry. 59:1144–1150. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Milnerwood AJ and Raymond LA: Early
synaptic pathophysiology in neurodegeneration: Insights from
Huntington's disease. Trends Neurosci. 33:513–523. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu Y, Duan X, Huang F, Cheng X, Zhang L,
Liu P, Shulan S, Duan JA, Dong TT and Tsim KW: Kai-Xin-San, a
traditional Chinese medicine formula, induces neuronal
differentiation of cultured PC12 Cells: Modulating neurotransmitter
regulation enzymes and potentiating NGF inducing neurite outgrowth.
J Ethnopharmacol. 193:272–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qiong W, Yong-Liang Z, Ying-Hui L,
Shan-Guang C, Jiang-Hui G, Yi-Xi C, Ning J and Xin-Min L: The
memory enhancement effect of Kai Xin San on cognitive deficit
induced by simulated weightlessness in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
187:9–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu KY, Xu SL, Choi RCY, Yan AL, Dong TTX
and Tsim KWK: Kai-Xin-San, a Chinese Herbal Decoction Containing
Ginseng Radix et Rhizoma, Polygalae Radix, Acori Tatarinowii
Rhizoma, and Poria, Stimulates the Expression and Secretion of
Neurotrophic Factors in Cultured Astrocytes. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 7313852013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dang H, Sun L, Liu X, Peng B, Wang Q, Jia
W, Chen Y, Pan A and Xiao P: Preventive action of Kai Xin San
aqueous extract on depressive-like symptoms and cognition deficit
induced by chronic mild stress. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
234:785–793. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu Y, Liu P, Guo DH, Rahman K, Wang DX,
Chen ML and Xie TT: Behavioral and biochemical effects of
Kaixin-San, a traditional Chinese medicinal empirical formula. Drug
Develop Res. 69:267–271. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou XJ, Liu M, Yan JJ, Cao Y and Liu P:
Antidepressant-like effect of the extracted of Kai Xin San, a
traditional Chinese herbal prescription, is explained by modulation
of the central monoaminergic neurotransmitter system in mouse. J
Ethnopharmacol. 139:422–428. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong XZ, Li ZL, Zheng XL, Mu LH, Zhang G
and Liu P: A representative prescription for emotional disease,
Ding-Zhi-Xiao-Wan restores 5-HT system deficit through interfering
the synthesis and transshipment in chronic mild stress-induced
depressive rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 150:1053–1061. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao Y, Hu Y, Liu P, Zhao HX, Zhou XJ and
Wei YM: Effects of a Chinese traditional formula Kai Xin San (KXS)
on chronic fatigue syndrome mice induced by forced wheel running. J
Ethnopharmacol. 139:19–25. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Pharmacopoeia Committee, .
Pharmacopoeia of People's Republic of China [M]. Part 1. Beijing:
Chemical Industry Press; 2010, pp. 7–437
|
|
20
|
Mu LH, Huang ZX, Liu P, Hu Y and Gao Y:
Acute and subchronic oral toicity assessment of the herbal formula
Kai-Xin-San. J Ethnopharmacol. 138:351–357. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu Y, Cao Y, Liu M, Liu P, Cui H and
Dai-Hong G: Behavioral and biochemical effects of a formulation of
the traditional Chinese medicine, Kai-Xin-San, in fatigued rats.
Exp Ther Med. 6:973–976. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu Y, Liu M, Liu P, Guo DH, Wei RB and
Rahman K: Possible mechanism of the antidepressant effect of
3,6′-disinapoyl sucrose from polygala tenuifolia willd. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 63:869–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu D, Zhang H, Gu W, Liu Y and Zhang M:
Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on high glucose-induced
neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. PLoS
One. 8:e793992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He XL, Zhang P, Dong XZ, Yang MH, Chen SL
and Bi MG: JR6, a new compound isolated from Justicia procumbens,
induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer EJ cells through
caspase-dependent pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 144:284–292. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu Y, Zhou XJ, Liu P, Dong XZ, Mu LH, Chen
YB, Liu MY and Yu BY: Anti-depressant and neuroprotective effect of
the Chinese herb KaiXinSan against lentiviral shRNA Knockdown
brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced injury in vitro and in
vivo. Neuropsychobiology. 69:129–139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu H and Chen ZY: The role of BDNF in
depression on the basis of its location in the neural circuitry.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:3–11. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sen S, Duman R and Sanacora G: Serum
brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression and antidepressant
medications: Meta-analyses and implications. Biol Psychiatry.
64:527–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bernard R, Kerman IA, Thompson RC, Jones
EG, Bunney WE, Barchas JD, Schatzberg AF, Myers RM, Akil H and
Watson SJ: Altered expression of glutamate signaling, growth factor
and glia genes in the locus coeruleus of patients with major
depression. Mol Psychiatry. 16:634–646. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kozicz T, Tilburg-Ouwens D, Faludi G,
Palkovits M and Roubos E: Gender-related urocortin 1 and
brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in the adult human
midbrain of suicide victims with major depression. Neuroscience.
152:1015–1023. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Altar CA, Whitehead RE, Chen R, Wörtwein G
and Madsen TM: Effects of electroconvulsive seizures and
antidepressant drugs on brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein
in rat brain. Biol Psychiatry. 54:703–709. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shirayama Y, Chen AC, Nakagawa S, Russell
DS and Duman RS: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces
antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J
Neurosci. 22:3251–3261. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deltheil T, Tanaka K, Reperant C, Hen R,
David DJ and Gardier AM: Synergistic neurochemical and behavioural
effects of acute intrahippocampal injection of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor and antidepressants in adult mice. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 12:905–915. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jain V, Baitharu I, Prasad D and
Ilavazhagan G: Enriched Environment prevents hypobaric hypoxia
induced memory impairment and neurodegeneration: Role of
BDNF/PI3K/GSK3β pathway coupled with CREB activation. PLoS One.
8:e622352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yan X, Liu J, Ye Z, Huang J, He F, Xiao W,
Hu X and Luo Z: CaMKII-Mediated CREB Phosphorylation Is Involved in
Ca2+-Induced BDNF mRNA Transcription and Neurite
Outgrowth Promoted by Electrical Stimulation. PLoS One.
11:e01627842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fišar Z and Hroudová J: Intracellular
signalling pathways and mood disorders. Folia Biol (Praha).
56:135–148. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong XZ, Huang CL, Yu BY, Hu Y, Mu LH and
Liu P: Effect of Tenuifoliside a isolated from polygala tenuifolia
on the ERK and PI3K pathways in C6 glioma cells. Phytomedicine.
21:1178–1188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang JS, Herreros-Villanueva M, Koenig A,
Deng Z, de Narvajas AA, Gomez TS, Meng X, Bujanda L, Ellenrieder V,
Li XK, Kaufmann SH and Billadeau DD: Differential activity of GSK-3
isoforms regulates NF-κB and TRAIL- or TNFα induced apoptosis in
pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11422004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, Zhao H, Zhang X, Chen L, Zhao X,
Bai X and Zhang J: Nobiletin protects against cerebral ischemia via
activating the p-Akt, p-CREB, BDNF and Bcl-2 pathway and
ameliorating BBB permeability in rat. Brain Res Bull. 96:45–53.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|