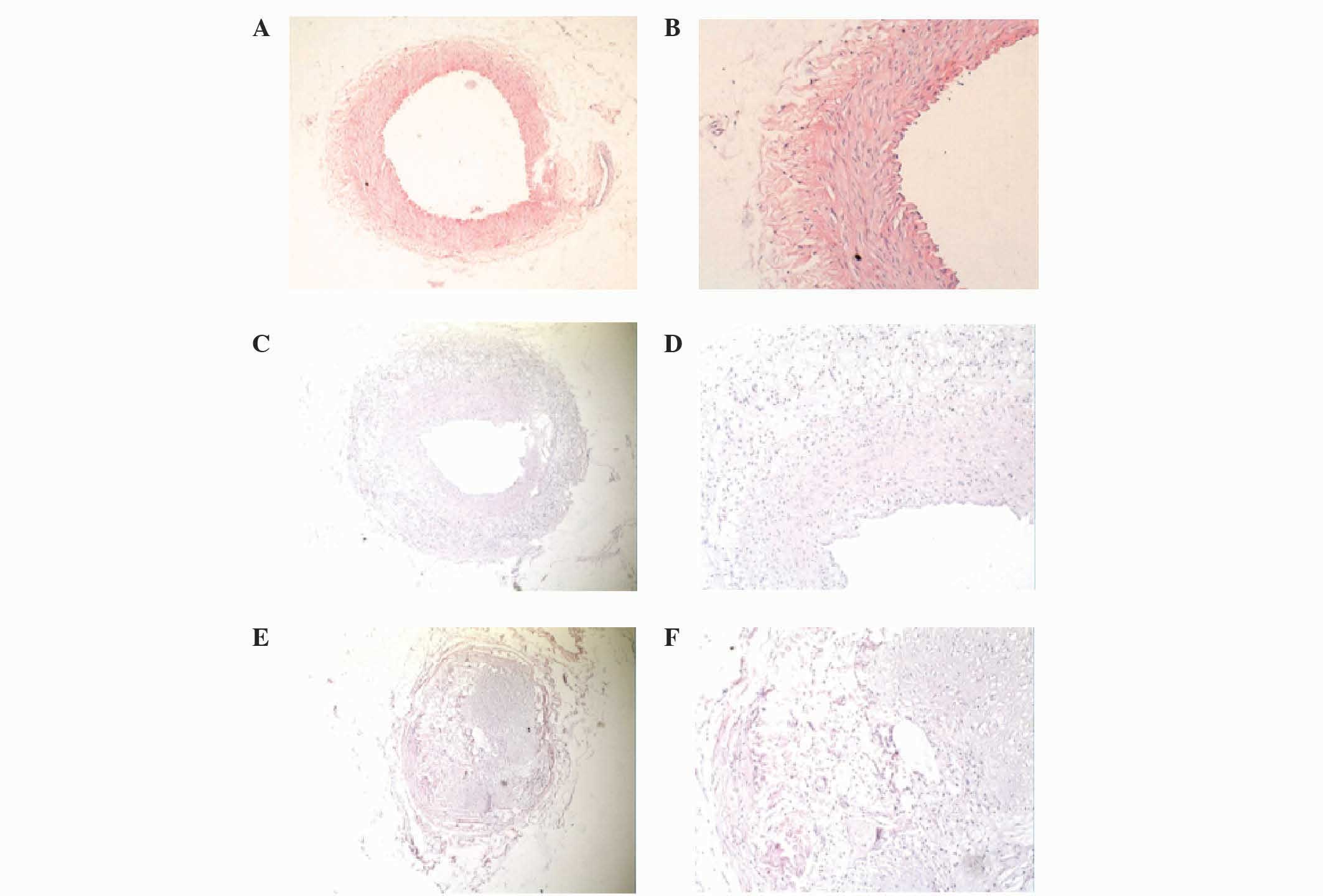
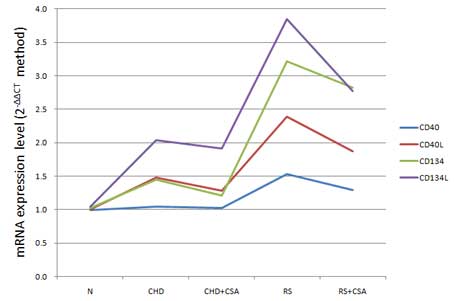
|
1
|
Grundy SM, Benjamin IJ, Burke GL, Chait A,
Eckel RH, Howard BV, Mitch W, Smith SC Jr and Sowers JR: Diabetes
and cardiovascular disease: A statement for healthcare
professionals from the American heart association. Circulation.
100:1134–1146. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeFeudis FV: Coronary atherosclerosis:
Current therapeutic approaches and future trends. Life Sci.
49:689–705. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hansson GK and Libby P: The immune
response in atherosclerosis: A double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol.
6:508–519. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lamb DJ, Eales LJ and Ferns GA:
Immunization with bacillus Calmette-Guerin vaccine increases aortic
atherosclerosis in the cholesterol-fed rabbit. Atherosclerosis.
143:105–113. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Salonen JT, Ylä-Herttuala S, Yamamoto R,
Butler S, Korpela H, Salonen R, Nyyssönen K, Palinski W and Witztum
JL: Autoantibody against oxidised LDL and progression of carotid
atherosclerosis. Lancet. 339:883–887. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hansson GK: Immune mechanisms in
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 21:1876–1890. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lievens D, Zernecke A, Seijkens T,
Soehnlein O, Beckers L, Munnix IC, Wijnands E, Goossens P, van
Kruchten R, Thevissen L, Boon L, et al: Platelet CD40L mediates
thrombotic and inflammatory processes in atherosclerosis. Blood.
116:4317–4327. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schönbeck U, Mach F, Sukhova GK, Atkinson
E, Levesque E, Herman M, Graber P, Basset P and Libby P: Expression
of stromelysin-3 in atheorsclerotic lesions: Regulation via
CD40-CD40Ligand signaling in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med.
189:843–853. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schönbeck U, Mach F, Sukhova GK, Herman M,
Graber P, Kehry MR and Libby P: CD40Ligation induces tissue factor
expression in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Pathol.
156:7–14. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lallemand F, Felt-Baeyens O, Besseghir K,
Behar-Cohen F and Gurny R: Cyclosporine A delivery to the eye: A
pharmaceutical challenge. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 56:307–318. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Noble S and Markham A: Cyclosporin: A
review of the pharmacokinetic properties, clinical efficacy and
tolerability of a microemulsion-based formulation. Drugs.
50:924–941. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Muehlschlegel JD: Closing the pore on
reperfusion injury: Myocardial protection with cyclosporine.
Anesthesiology. 121:212–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sazliyana S, Shahrir MS Mohd, Kong CT, Tan
HJ, Hamidon BB and Azmi MT: Implications of immunosuppressive
agents in cardiovascular risks and carotid intima media thickness
among lupus nephritis patients. Lupus. 20:1260–1266. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nigro P, Satoh K, O'Dell MR, Soe NN, Cui
Z, Mohan A, Abe J, Alexis JD, Sparks JD and Berk BC: Cyclophilin A
is an inflammatory mediator that promotes atherosclerosis in
apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 208:53–66. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Poston RN, Haskard DO, Coucher JR, Gall NP
and Johnson-Tidey RR: Expression of intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 in atherosclerotic Plaques. Am J Pathol. 140:665–673.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zeitler H, Ko Y, Zimmermann C, Nickenig G,
Glänzer K, Walger P, Sachinidis A and Vetter H: Elevated serum
concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules in coronary artery
disease and acute myocardial infarction. Eur J Med Res. 2:389–394.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bou Khzam L, Boulahya R, Abou-Saleh H,
Hachem A, Zaid Y and Merhi Y: Soluble CD40 ligand stimulates the
pro-angiogenic function of peripheral blood angiogenic outgrowth
cells via increased release of matrix metalloproteinase-9. PLoS
One. 8:e842892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ll H, Cybulsdy MI, Gimbrone MA Jr and
Libby P: Inducible expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
by vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and within rabbit
atheroma. Am J Pathol. 143:1551–1559. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smart EJ, Ying Y, Donzell WC and Anderson
RG: A role for caveolin in transport of cholesterol from
endoplasmic reticulum to plasma membrane. J Biol Chem.
271:29427–29435. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu J, Zhang Z, Shen WJ and Azhar S:
Cellular cholesterol delivery, intracellular processing and
utilization for biosynthesis of steroid hormones. Nutr Metab
(Lond). 7:472010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamada H, Suzuki H, Abe J, Suzuki Y,
Suenaga T, Takeuchi T, Yoshikawa N, Shibuta S, Miyawaki M, Oishi K,
Yamaga H, et al: Inflammatory profiles during Cyclosporin treatment
for immunoglobulin-resistant Kawasaki disease. Cytokine.
60:681–685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joo YH, Chang DY, Kim JH, Jung MH, Lee J,
Cho HJ, Jeon SY, Kim SJ and Kim SW: Anti-inflammatory effects of
intranasal cyclosporine for allergic rhinitis in a mouse model. Int
Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Massuda TY, Nagashima LA, Leonello PC,
Kaminami MS, Mantovani MS, Sano A, Uno J, Venancio EJ, Camargo ZP
and Itano EN: Cyclosporin A treatment and decreased fungal
load/antigenemia in experimental murine paracoccidioidomycosis.
Mycopathologia. 171:161–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Houssen ME, Haron MM, Metwally SS and
Ibrahim TM: Effects of immunomodulatory drugs on plasma
inflammatory markers in a rabbit model of atherosclerosis. J
Physiol Biochem. 67:115–120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Watts TH: TNF/TNFR family members in
costimulation of T cell responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 23:23–68.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Antoniades C, Bakogiannis C, Tousoulis D,
Antonopoulos AS and Stefanadis C: The CD40/CD40 ligand system:
Linking inflammation with atherothrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol.
54:669–677. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zirlik A, Maier C, Gerdes N, MacFarlane L,
Soosairajah J, Bavendiek U, Ahrens I, Ernst S, Bassler N, Missiou
A, et al: CD40Ligand mediates inflammation independently of CD40 by
interaction with Mac-1. Circulation. 115:1571–1580. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hauer AD, Uyttenhove C, de Vos P,
Stroobant V, Renauld JC, van Berkel TJ, van Snick J and Kuiper J:
Blockade of interleukin-12 function by protein vaccination
attenuates atherosclerosis. Circulation. 112:1054–1062. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee TS, Yen HC, Pan CC and Chau LY: The
role of interleukin 12 in the development of atherosclerosis in
ApoE-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 19:734–742.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang X, Ria M, Kelmenson PM, Eriksson P,
Higgins DC, Samnegård A, Petros C, Rollins J, Bennet AM, Wiman B,
et al: Positional identification of TNFSF4, encoding OX40 ligand,
as a gene that influences atherosclerosis susceptibility. Nat
Genet. 37:365–372. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gupta AK, Giaglis S, Hasler P and Hahn S:
Efficient neutrophil extracellular trap induction requires
mobilization of both intracellular and extracellular calcium pools
and is modulated by cyclosporine A. PLoS One. 9:e970882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mewton N, Croisille P, Gahide G, Rioufol
G, Bonnefoy E, Sanchez I, Cung TT, Sportouch C, Angoulvant D, Finet
G, et al: Effect of cyclosporine on left ventricular remodeling
after reperfused myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol.
55:1200–1205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dąbrowski MJ: Is further improvement of
the treatment of acute coronary syndromes still possible. Postepy
Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 9:41–44. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|