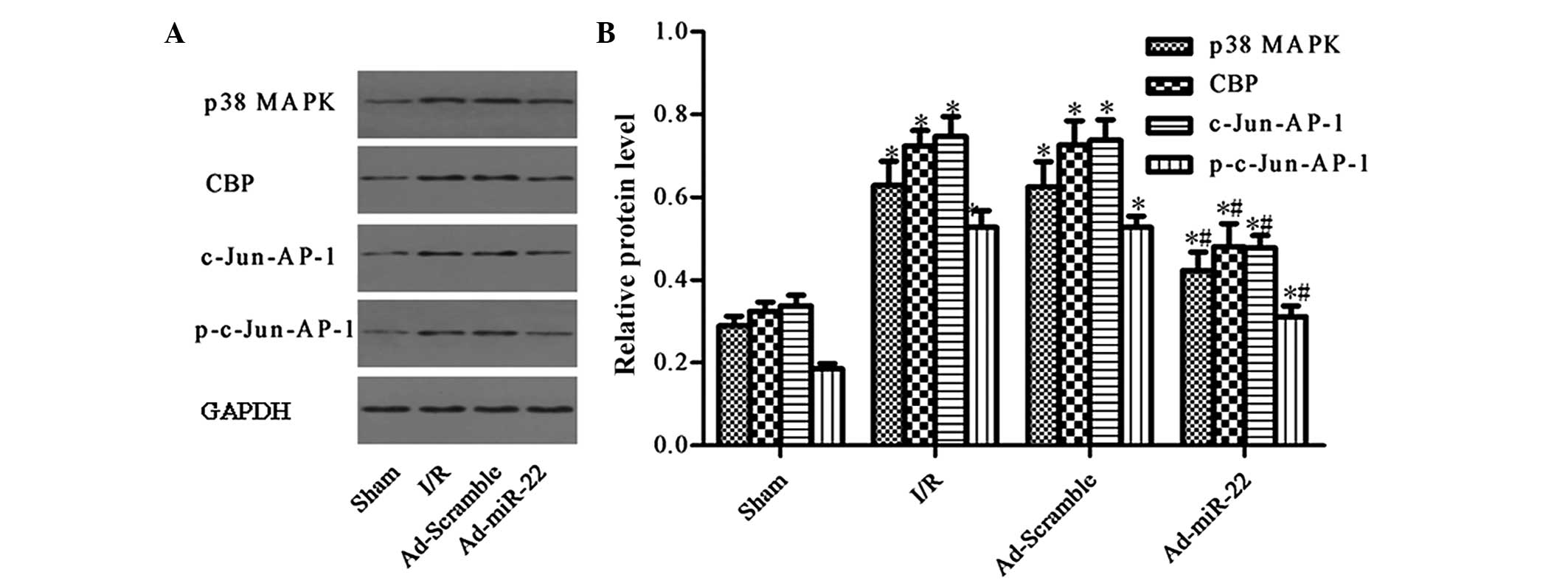
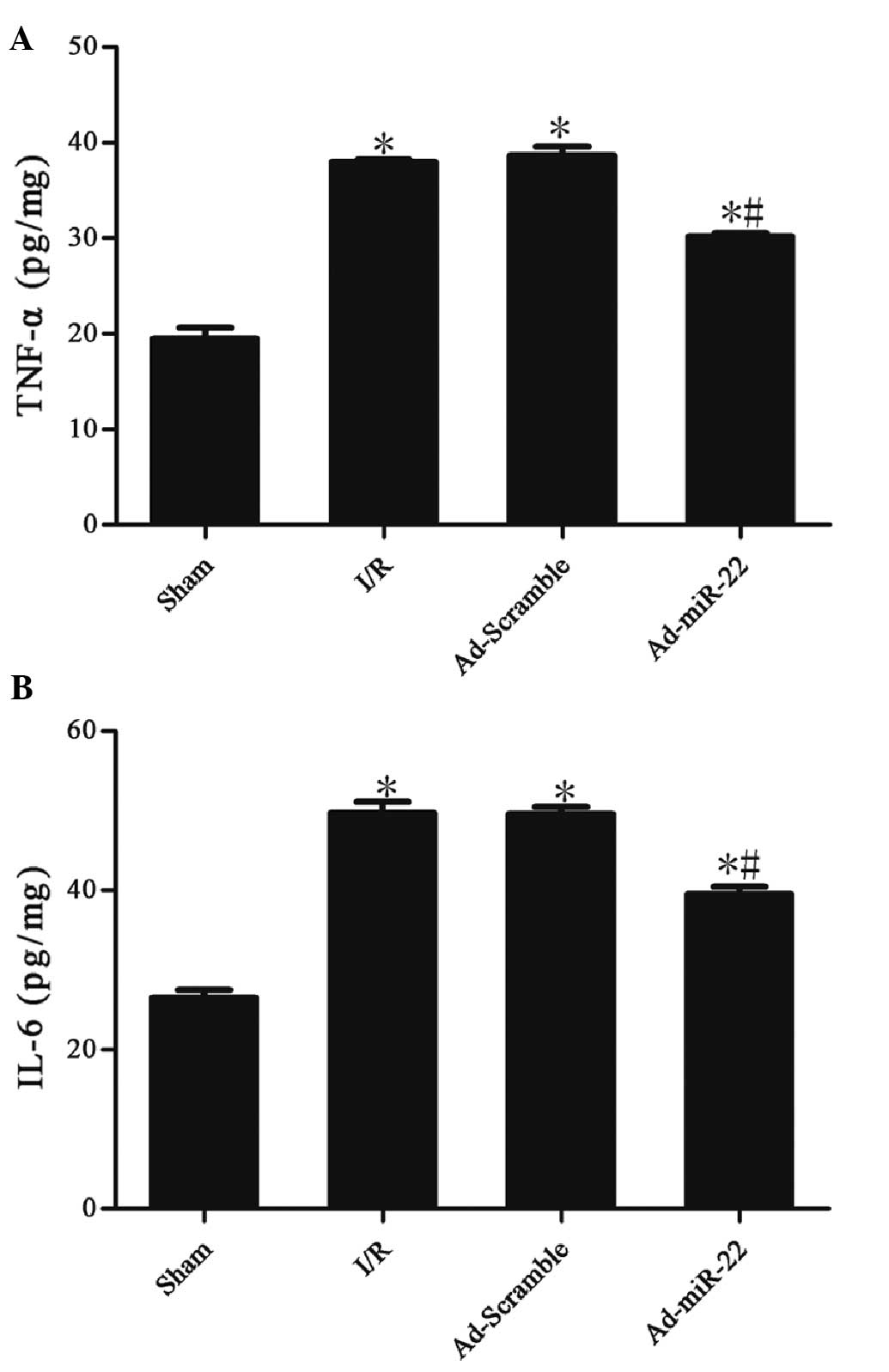
|
1
|
Ndrepepa G: Improving myocardial injury,
infarct size, and myocardial salvage in the era of primary PCI for
STEMI. Coron Artery Dis. 26:341–355. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kloner RA: Does reperfusion injury exist
in humans? J Am Coll Cardiol. 21:537–545. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion - from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu H, Zhai C, Qian G, Gu A, Liu J, Ying F,
Xu W, Jin D, Wang H, Hu H, Zhang Y and Tang G: Protective effects
of tanshinone IIA on myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by
reducing oxidative stress, HMGB1 expression and inflammatory
reaction. Pharm Biol. 53:1752–1758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Du X, Hu X and Wei J: Anti-inflammatory
effect of exendin-4 postconditioning during myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion. Mol Biol Rep. 41:3853–3857. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Doddakula KK, Neary PM, Wang JH, Sookhai
S, O'Donnell A, Aherne T, Bouchier-Hayes DJ and Redmond HP: The
antiendotoxin agent taurolidine potentially reduces
ischemia/reperfusion injury through its metabolite taurine.
Surgery. 148:567–572. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan ZX and Yang J: Microribonucleic acids
and vascular restenosis. Saudi Med J. 35:796–801. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suzuki HI and Miyazono K: Emerging
complexity of microRNA generation cascades. J Biochem. 149:15–25.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peterson SM, Thompson JA, Ufkin ML,
Sathyanarayana P, Liaw L and Congdon CB: Common features of
microRNA target prediction tools. Front Genet. 5:232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thum T and Condorelli G: Long noncoding
RNAs and microRNAs in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Circ Res.
116:751–762. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lorenzen JM, Batkai S and Thum T:
Regulation of cardiac and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by
microRNAs. Free Radic Biol Med. 64:78–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang J, Chen L, Yang J, Ding J, Li S, Wu
H, Zhang J, Fan Z, Dong W and Li X: MicroRNA-22 targeting CBP
protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through
anti-apoptosis in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 41:555–561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Shah A, Gangwani MR, Silverstein
PS, Fu M and Kumar A: HIV-1 Nef induces CCL5 production in
astrocytes through p38-MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathway and utilizes
NF-kB, CEBP and AP-1 transcription factors. Sci Rep.
4:44502014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McManus KJ and Hendzel MJ: CBP, a
transcriptional coactivator and acetyltransferase. Biochem Cell
Biol. 79:253–266. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sugden PH and Clerk A: ‘Stress-responsive’
mitogen-activated protein kinases (c-Jun N-terminal kinases and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinases) in the myocardium. Circ Res.
83:345–352. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zenz R, Eferl R, Scheinecker C, Redlich K,
Smolen J, Schonthaler HB, Kenner L, Tschachler E and Wagner EF:
Activator protein 1 (Fos/Jun) functions in inflammatory bone and
skin disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:2012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karin M: The regulation of AP-1 activity
by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 270:16483–16486.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma L, Liu H, Xie Z, Yang S, Xu W, Hou J
and Yu B: Ginsenoside Rb3 protects cardiomyocytes against
ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of JNK-mediated
NF-κB pathway: A mouse cardiomyocyte model. PLoS One.
9:e1036282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang W, Shao J, Bai X and Zhang G:
Expression of plasma microRNA-1/21/208a/499 in myocardial ischemic
reperfusion injury. Cardiology. 130:237–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumphune S, Surinkaew S, Chattipakorn SC
and Chattipakorn N: Inhibition of p38 MAPK activation protects
cardiac mitochondria from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Pharm Biol.
53:1831–1841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Surinkaew S, Kumphune S, Chattipakorn S
and Chattipakorn N: Inhibition of p38 MAPK during ischemia, but not
reperfusion, effectively attenuates fatal arrhythmia in
ischemia/reperfusion heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 61:133–141.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Jiang H, Chen SS, Chen J, Li WQ,
Xu SK and Wang JC: Lentivirus-mediated RNAi targeting CREB binding
protein attenuates neointimal formation and promotes
re-endothelialization in balloon injured rat carotid artery. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 26:441–448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ait-Si-Ali S, Ramirez S, Barre FX, Dkhissi
F, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Girault JA, Robin P, Knibiehler M, Pritchard
LL, Ducommun B, Trouche D and Harel-Bellan A: Histone
acetyltransferase activity of CBP is controlled by cycle-dependent
kinases and oncoprotein E1A. Nature. 396:184–186. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Avantaggiati ML, Ogryzko V, Gardner K,
Giordano A, Levine AS and Kelly K: Recruitment of p300/CBP in
p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell. 89:1175–1184. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kappelmann M, Bosserhoff A and Kuphal S:
AP-1/c-Jun transcription factors: Regulation and function in
malignant melanoma. Eur J Cell Biol. 93:76–81. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karin M and Gallagher E: From JNK to pay
dirt: Jun kinases, their biochemistry, physiology and clinical
importance. IUBMB Life. 57:283–295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|