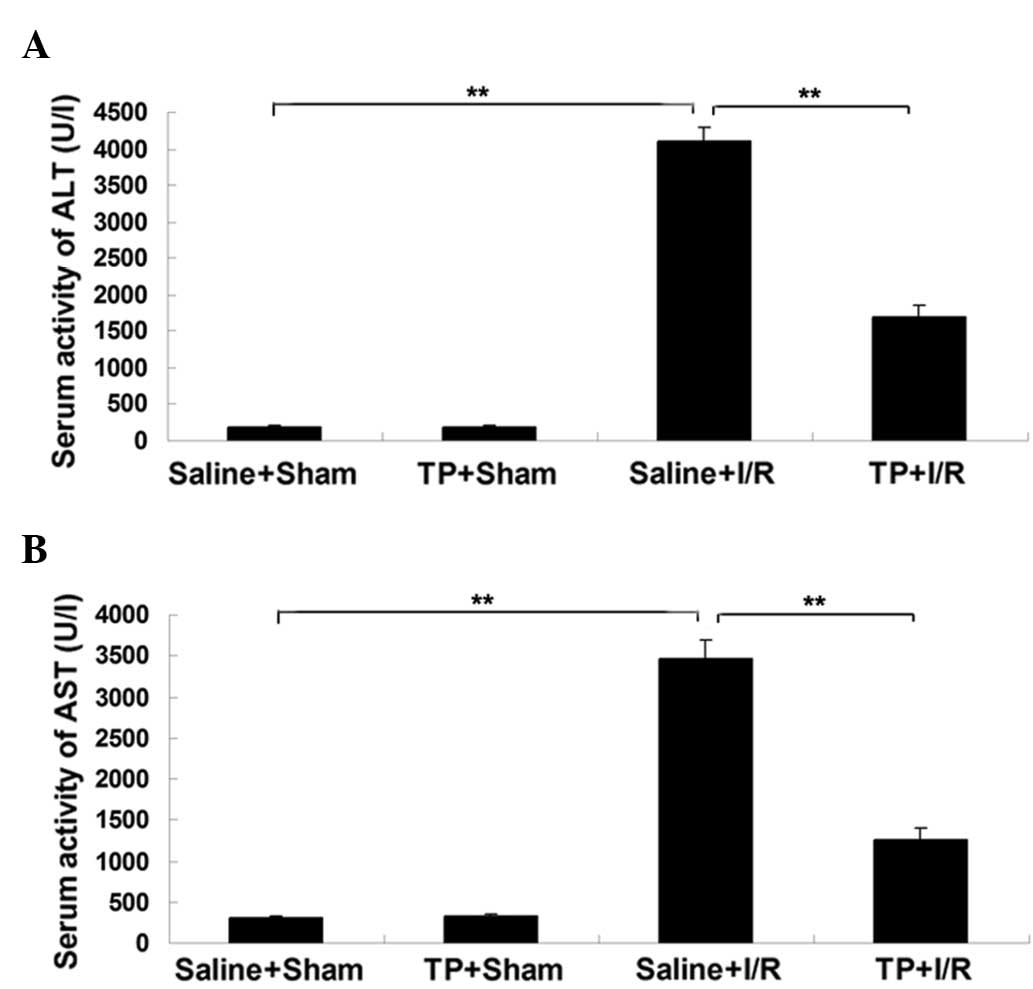
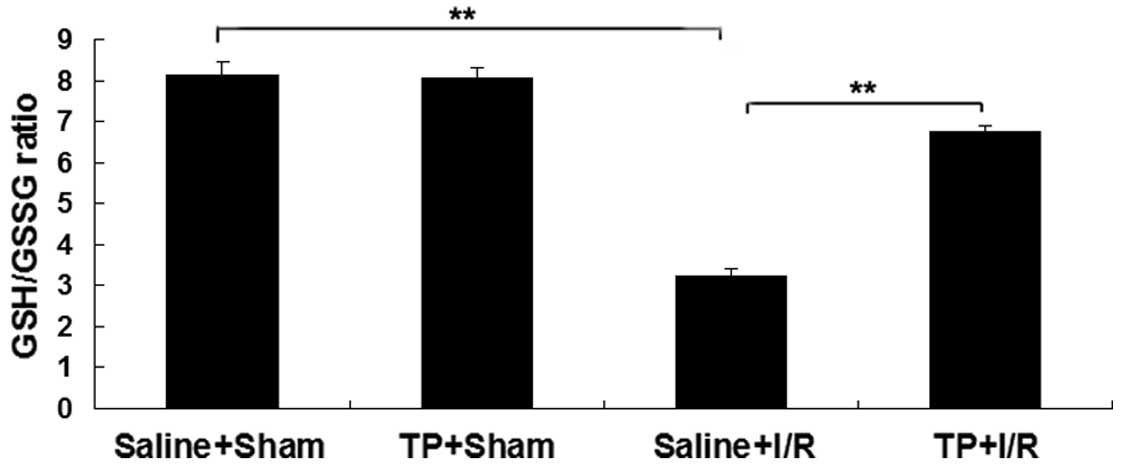
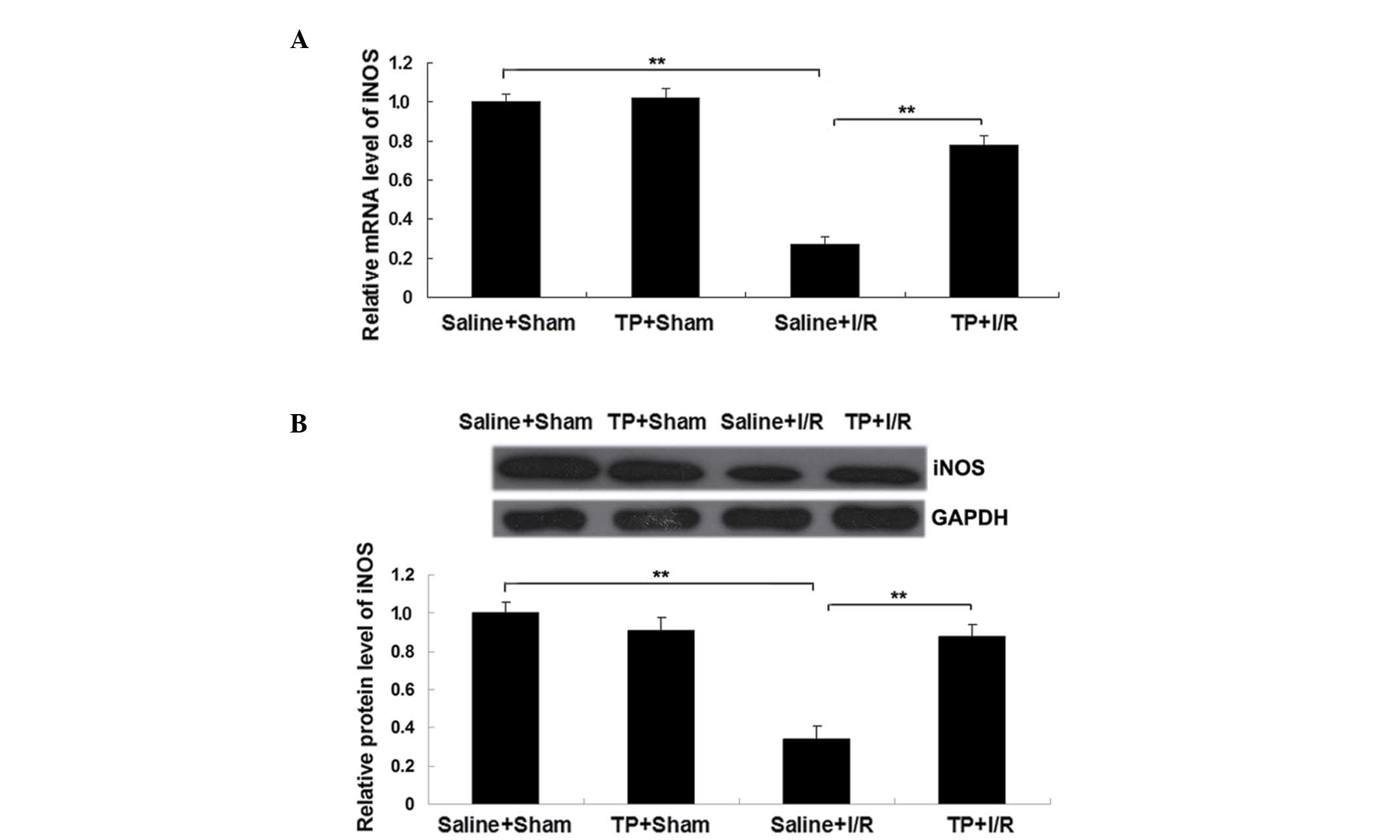
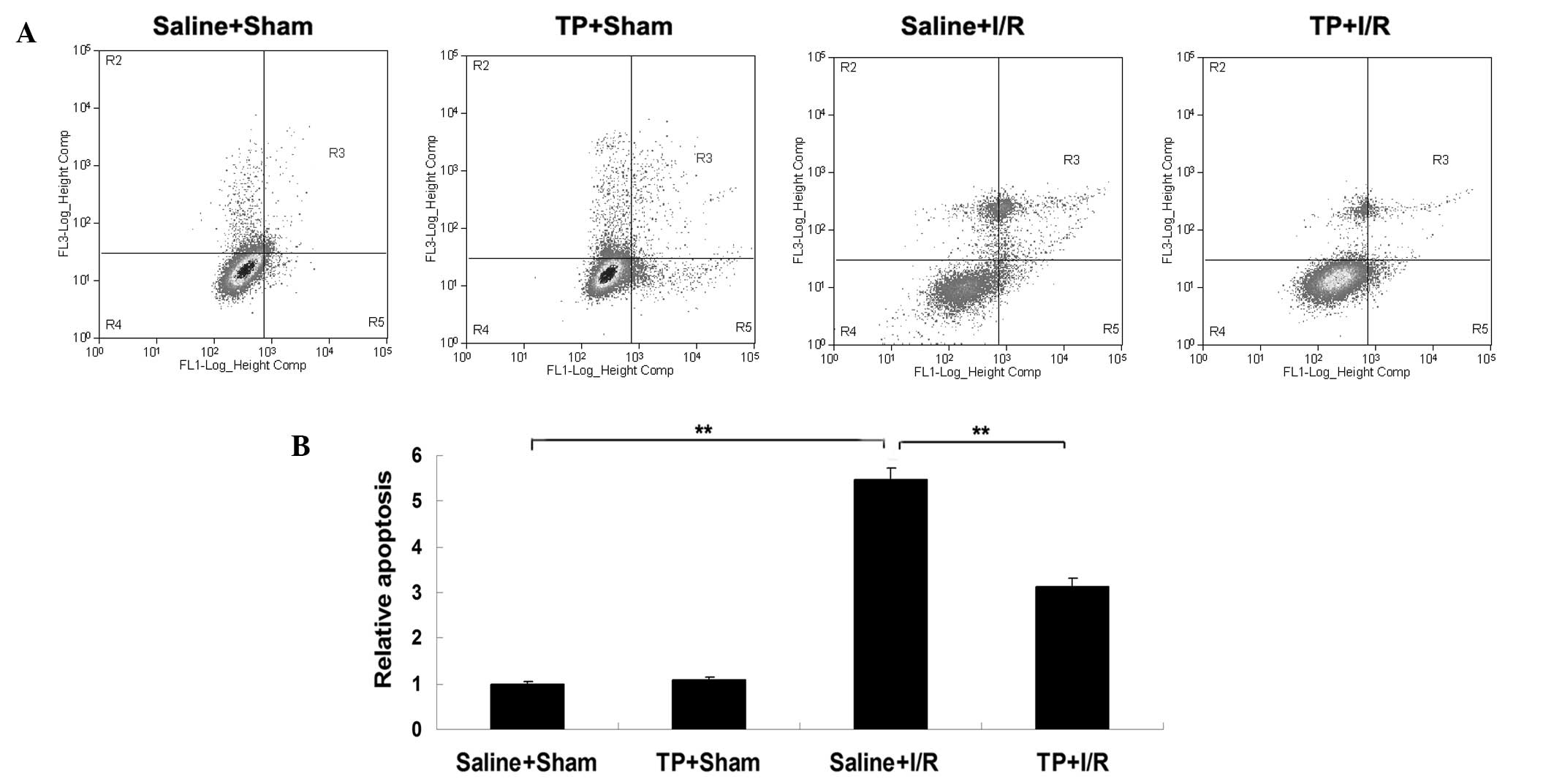
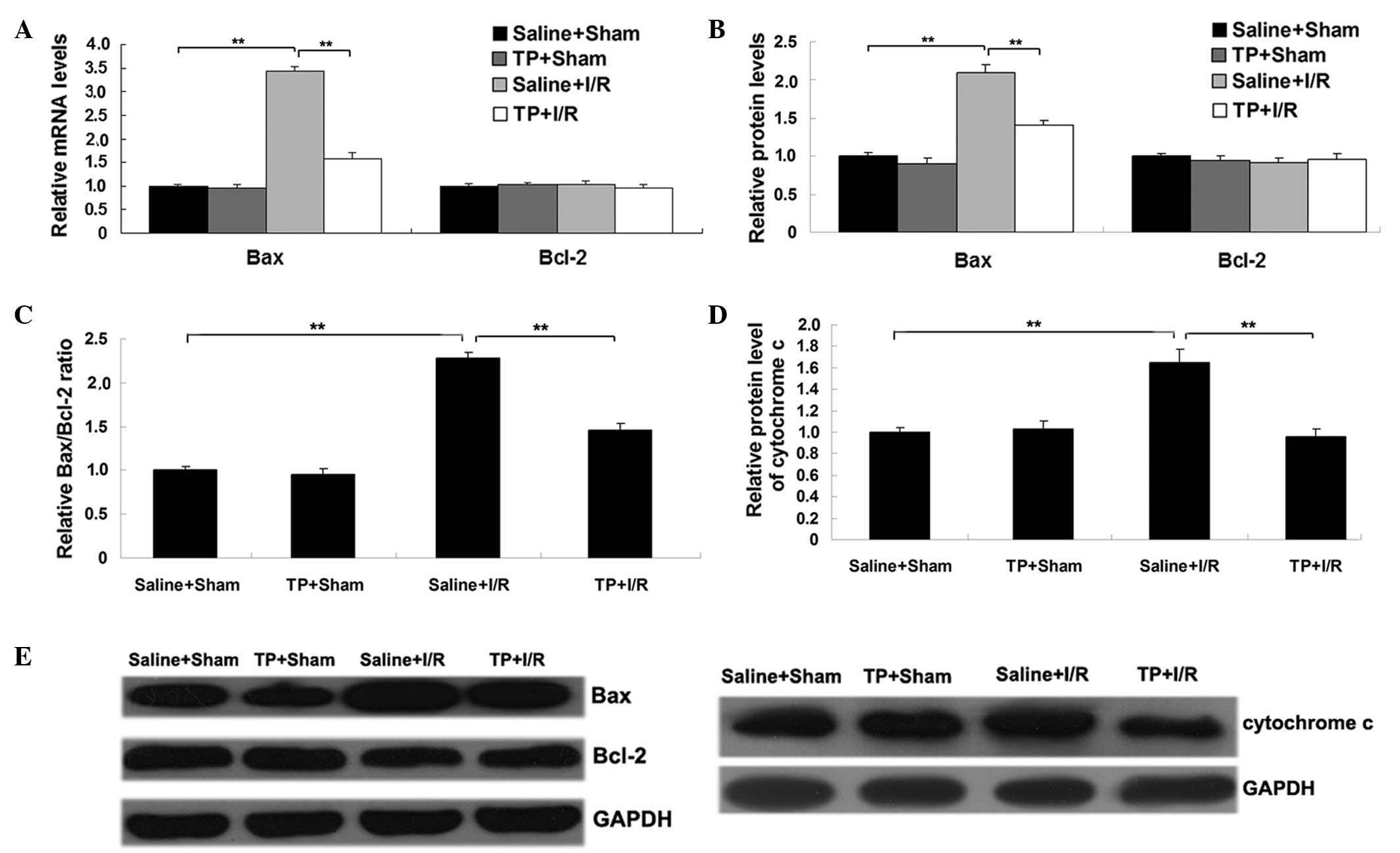
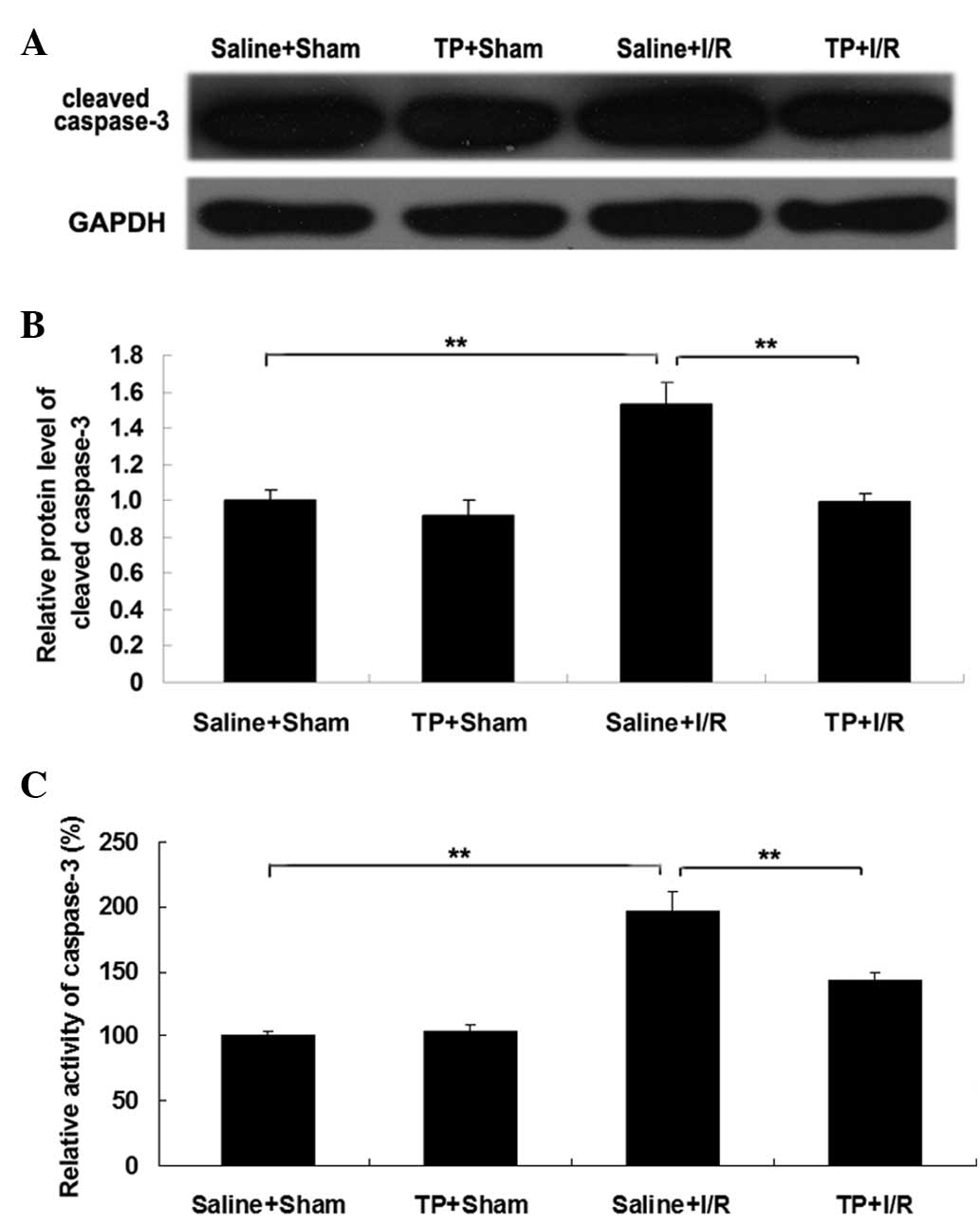
|
1
|
Mendes-Braz M, Elias-Miró M,
Jiménez-Castro MB, Casillas-Ramírez A, Ramalho FS and Peralta C:
The current state of knowledge of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
injury based on its study in experimental models. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2012:2986572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhuonan Z, Sen G, Zhipeng J, Maoyou Z,
Linglan Y, Gangping W, Cheng J, Zhongliang M, Tian J, Peijian Z and
Kesen X: Hypoxia preconditioning induced HIF-1α promotes glucose
metabolism and protects mitochondria in liver I/R injury. Clin Res
Hepatol Gastroenterol. 39:610–619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Trocha M, Merwid-Ląd A, Chlebda E,
Sozański T, Pieśniewska M, Gliniak H and Szeląg A: Influence of
ezetimibe on selected parameters of oxidative stress in rat liver
subjected to ischemia/reperfusion. Arch Med Sci. 10:817–824. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bae UJ, Yang JD, Ka SO, Koo JH, Woo SJ,
Lee YR, Yu HC, Cho BH, Zhao HY, Ryu JH, et al: SPA0355 attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury in mice. Exp Mol Med.
46:e1092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sheng M, Zhou Y, Yu W, Weng Y, Xu R and Du
H: Protective effect of Berberine pretreatment in hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury of rat. Transplant Proc. 47:275–282.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rehman H, Krishnasamy Y, Haque K, Thurman
RG, Lemasters JJ, Schnellmann RG and Zhong Z: Green tea polyphenols
stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and improve renal function after
chronic cyclosporin a treatment in rats. PLoS One. 8:e650292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen CL, Chyu MC and Wang JS: Tea and bone
health: Steps forward in translational nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr.
98(Suppl 6): 1694S–1699S. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Clifford MN, van der Hooft JJ and Crozier
A: Human studies on the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and
excretion of tea polyphenols. Am J Clin Nutr. 98(Suppl 6):
1619S–1630S. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yokozawa T, Noh JS and Park CH: Green tea
polyphenols for the protection against renal damage caused by
oxidative stress. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:8459172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu Y, Zhang JJ, Xiong L, Zhang L, Sun D
and Liu H: Green tea polyphenols inhibit cognitive impairment
induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via modulating oxidative
stress. J Nutr Biochem. 21:741–748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang M and Lei YX: Effects of tea
polyphenols on proliferation and apoptosis of cadmium-transformed
cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:3054–3062. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xue R, Wu G, Wei X, Lv J, Fu R, Lei X,
Zhang Z, Li W, He J, et al: Tea polyphenols may attenuate the
neurocognitive impairment caused by global cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis. Nutr Neurosci. Nov
20–2014.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhong Z, Froh M, Connor HD, Li X,
Conzelmann LO, Mason RP, Lemasters JJ and Thurman RG: Prevention of
hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by green tea extract. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 283:G957–G964. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources
(US). Committee on Care, Use of Laboratory Animals, and National
Institutes of Health (US). Division of Research Resources, . Guide
for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th. National Academies
Press; Washington, DC: 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mahale A, Othman MW, Al Shahwan S, Al
Jadaan I, Owaydha O, Khan Z and Edward DP: Altered expression of
fibrosis genes in capsules of failed Ahmed glaucoma valve implants.
PLoS One. 10:e01224092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li YN, Wang XJ, Li B, Liu K, Qi JS, Liu BH
and Tian Y: Tongxinluo inhibits cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric
oxide synthase, hypoxia-inducible factor-2α/vascular endothelial
growth factor to antagonize injury in hypoxia-stimulated cardiac
microvascular endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 128:1114–1120.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cui Y, Yang X, Lu X, Chen J and Zhao Y:
Protective effects of polyphenols-enriched extract from Huangshan
Maofeng green tea against CCl4-induced liver injury in
mice. Chem Biol Interact. 220:75–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yuan GJ, Gong ZJ, Sun XM, Zheng SH and Li
X: Tea polyphenols inhibit expressions of iNOS and TNF-alpha and
prevent lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in rats.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 5:262–267. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li YM, Zhang XG, Zhou HL, Chen SH, Zhang Y
and Yu CH: Effects of tea polyphenols on hepatic fibrosis in rats
with alcoholic liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
3:577–579. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhong Z and Lemasters JJ: Role of free
radicals in failure of fatty liver grafts caused by ethanol.
Alcohol. 34:49–58. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cetinkunar S, Tokgoz S, Bilgin BC, Erdem
H, Aktimur R, Can S, Erol HS, Isgoren A, Sozen S and Polat Y: The
effect of silymarin on hepatic regeneration after partial
hepatectomy: Is silymarin effective in hepatic regeneration? Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:2578–2585. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Korge P, Calmettes G and Weiss JN:
Increased reactive oxygen species production during reductive
stress: The roles of mitochondrial glutathione and thioredoxin
reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1847:514–525. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tao X, Wan X, Xu Y, Xu L, Qi Y, Yin L, Han
X, Lin Y and Peng J: Dioscin attenuates hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats through inhibition of
oxidative-nitrative stress, inflammation and apoptosis.
Transplantation. 98:604–611. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo Y, Hu B, Huang H, Tsung A, Gaikwad NW,
Xu M, Jiang M, Ren S, Fan J, Billiar TR, et al: Estrogen
sulfotransferase is an oxidative stress responsive gene that
gender-specifically affects liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. J
Biol Chem. 290:14754–14764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan Y, Li G, Tian X, Ye Y, Gao Z, Yao J,
Zhang F and Wang S: Ischemic preconditioning increases
GSK-3β/β-catenin levels and ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion
injury in rats. Int J Mol Med. 35:1625–1632. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Renault TT, Teijido O, Antonsson B, Dejean
LM and Manon S: Regulation of Bax mitochondrial localization by
Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L): Keep your friends close but your enemies
closer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:64–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shamas-Din A, Kale J, Leber B and Andrews
DW: Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0087142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Renault TT and Manon S: Bax: Addressed to
kill. Biochimie. 93:1379–1391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bernardi P and Rasola A: Calcium and cell
death: The mitochondrial connection. Subcell Biochem. 45:481–506.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McIlwain DR, Berger T and Mak TW: Caspase
functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 5:a0086562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hua P, Liu J, Tao J, Liu J and Yang S:
Influence of caspase-3 silencing on the proliferation and apoptosis
of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:1624–1633. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qin Y, Hoek TL Vanden, Wojcik K, Anderson
T, Li CQ, Shao ZH, Becker LB and Hamann KJ: Caspase-dependent
cytochrome c release and cell death in chick cardiomyocytes after
simulated ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
286:H2280–H2286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|