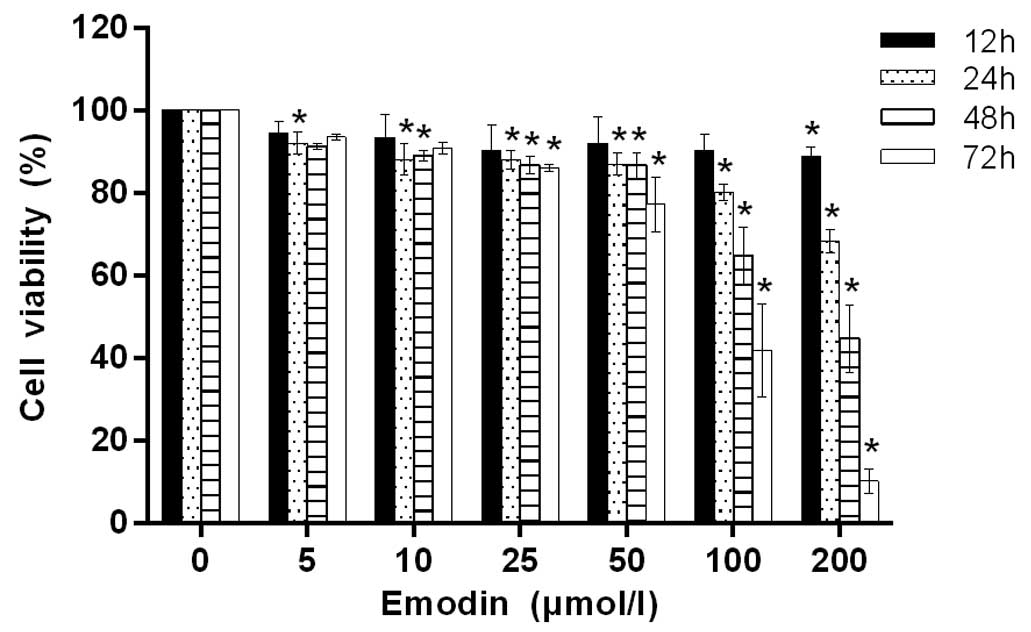
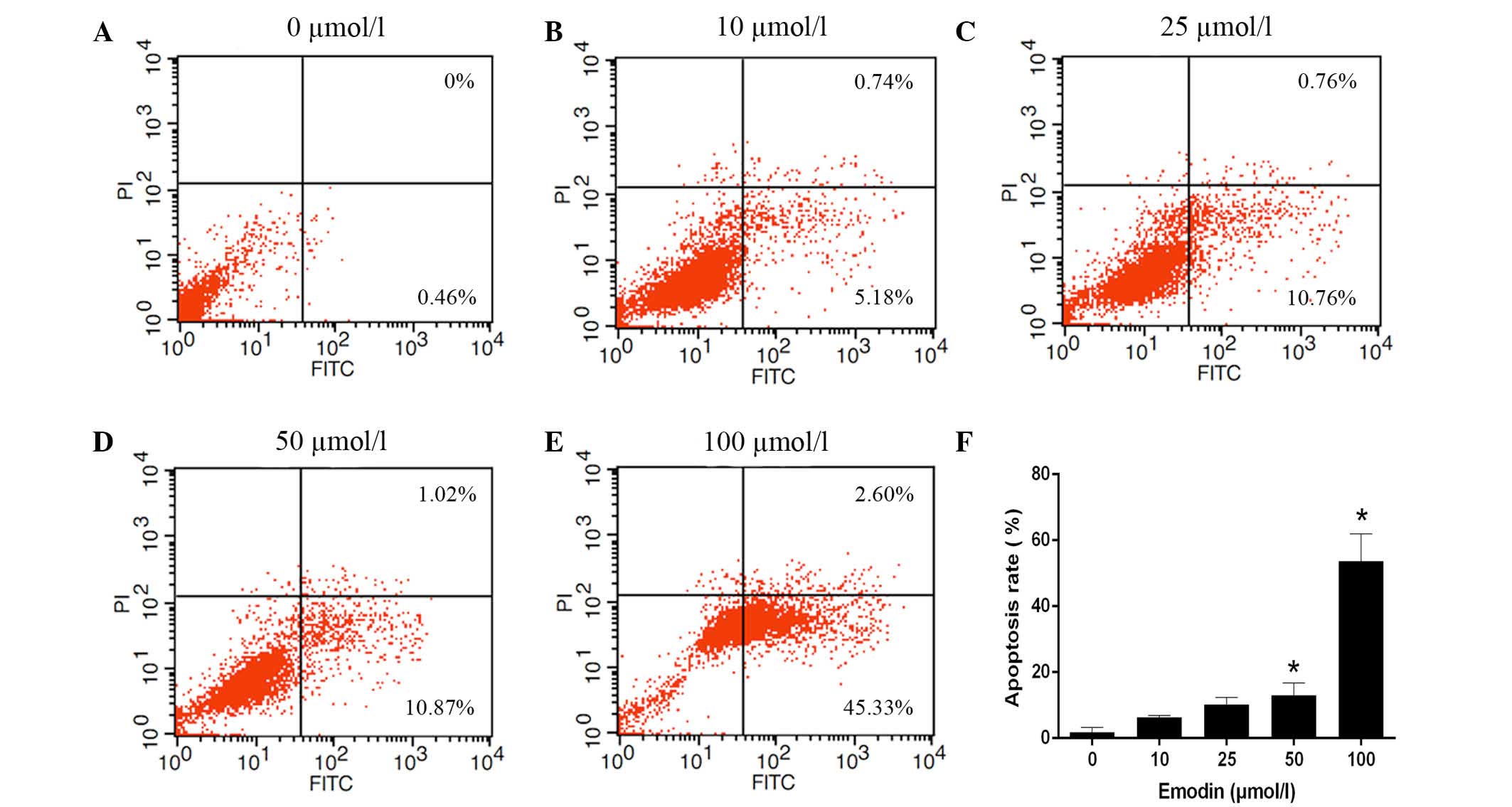
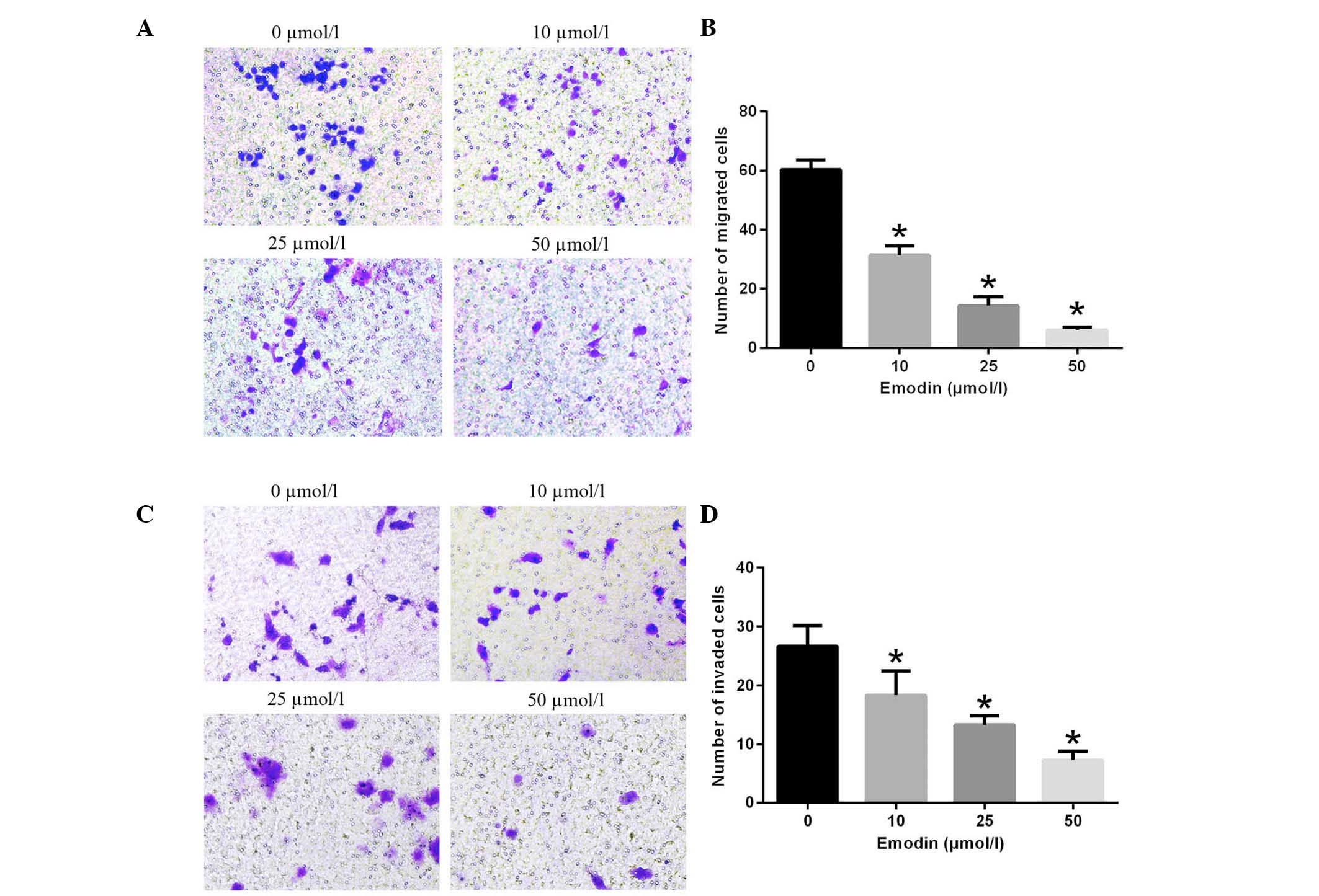
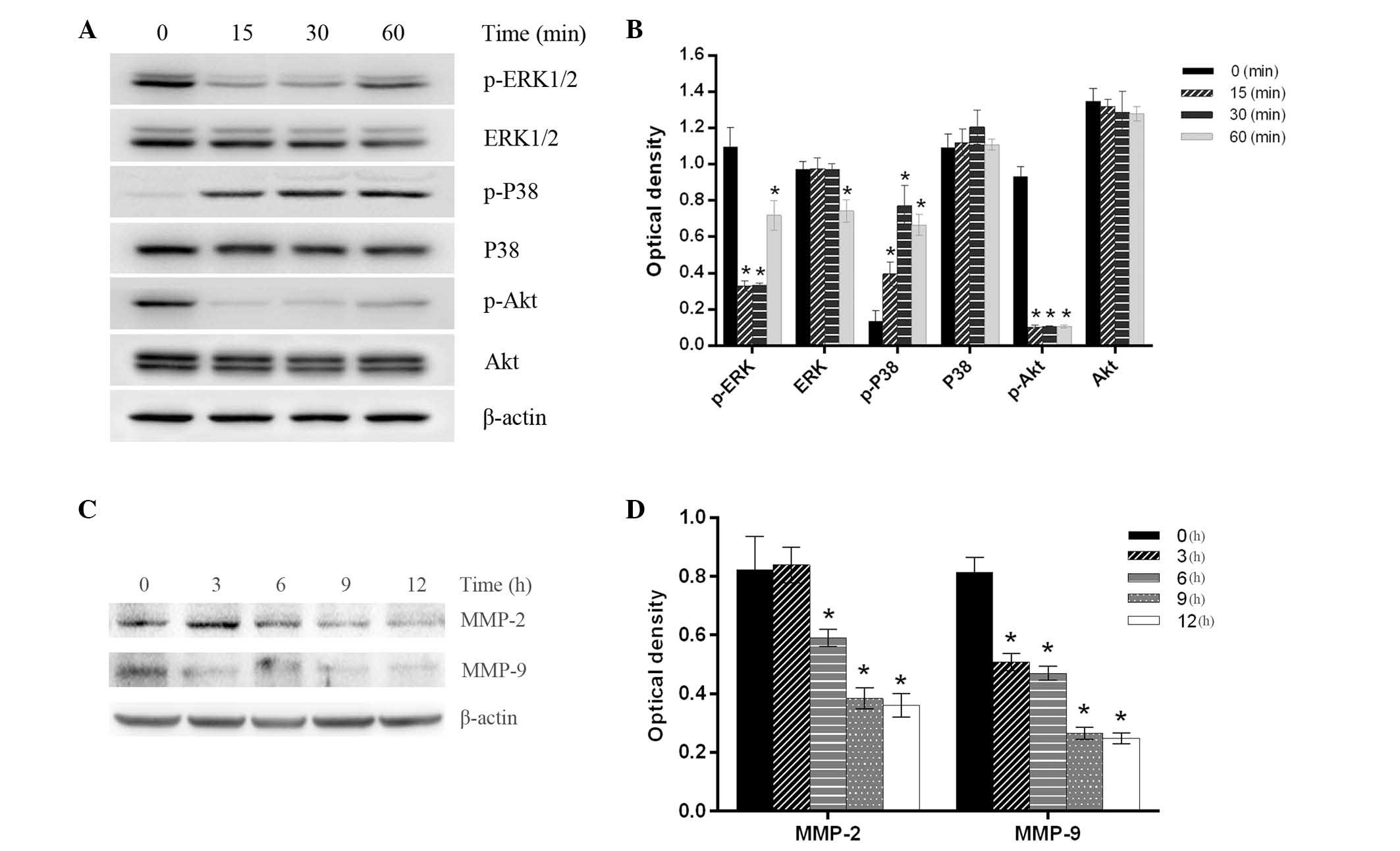
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bosetti C, Turati F and La Vecchia C:
Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 28:753–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maluccio M and Covey A: Recent progress in
understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma.
CA Cancer J Clin. 62:394–399. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Forner A, Reig ME, de Lope CR and Bruix J:
Current strategy for staging and treatment: The BCLC update and
future prospects. Semin Liver Dis. 30:61–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baffy G: Decoding multifocal
hepatocellular carcinoma: An opportune pursuit. Hepatobiliary Surg
Nutr. 4:206–210. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lui GY, Kovacevic Z, Richardson V, Merlot
AM, Kalinowski DS and Richardson DR: Targeting cancer by binding
iron: Dissecting cellular signaling pathways. Oncotarget.
6:18748–18779. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ling CQ, Yue XQ and Ling C: Three
advantages of using traditional Chinese medicine to prevent and
treat tumor. J Integr Med. 12:331–335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li F and Zhang W: Role of traditional
Chinese medicine and its chemical components in anti-tumor
metastasis. J Cancer Res Ther. 10(Suppl 1): S20–S26. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Wang N, Cheung F, Lao L, Li C and
Feng Y: Chinese medicines for prevention and treatment of human
hepatocellular carcinoma: Current progress on pharmacological
actions and mechanisms. J Integr Med. 13:142–164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun ZH and Bu P: Downregulation of
phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 is involved in the inhibition
of proliferation and apoptosis induced by emodin in the SGC-7901
human gastric carcinoma cell line. Exp Ther Med. 3:1077–1081.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shrimali D, Shanmugam MK, Kumar AP, Zhang
J, Tan BK, Ahn KS and Sethi G: Targeted abrogation of diverse
signal transduction cascades by emodin for the treatment of
inflammatory disorders and cancer. Cancer Lett. 341:139–149. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang H, Chen L, Bu HQ, Yu QJ, Jiang DD,
Pan FP, Wang Y, Liu DL and Lin SZ: Effects of emodinon the
demethylation of tumor-suppressor genes in pancreatic cancer PANC-1
cells. Oncol Rep. 33:3015–3023. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pooja T and Karunagaran D: Emodin
suppresses Wnt signaling in human colorectal cancer cells SW480 and
SW620. Eur J Pharmacol. 742:55–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma J, Lu H, Wang S, Chen B, Liu Z, Ke X,
Liu T and Fu J: The anthraquinone derivative Emodin inhibits
angiogenesis and metastasis through downregulating Runx2 activity
in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 46:1619–1628. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei WT, Lin SZ, Liu DL and Wang ZH: The
distinct mechanisms of the antitumor activity of emodin in
different types of cancer (Review). Oncol Rep. 30:2555–2562.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Ong TH, Li F,
Perumal E, Chen L, Vali S, Abbasi T, Kapoor S, Ahn KS, et al:
Emodin inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in an orthotopic
hepatocellular carcinoma model by blocking activation of STAT3. Br
J Pharmacol. 170:807–821. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Manu KA, Shanmugam MK, Ong TH, Subramaniam
A, Siveen KS, Perumal E, Samy RP, Bist P, Lim LH, Kumar AP, et al:
Emodin suppresses migration and invasion through the modulation of
CXCR4 expression in an orthotopic model of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. PloS One. 8:e570152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Polacheck WJ, Zervantonakis IK and Kamm
RD: Tumor cell migration in complex microenvironments. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 70:1335–1356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Tumor
angiogenesis: MMP-mediated induction of intravasation-and
metastasis-sustaining neovasculature. Matrix Biol 44–46. 94–112.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kessenbrock K, Wang CY and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases in stem cell regulation and cancer. Matrix Biol
44–46. 184–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Daniele A, Divella R, Quaranta M, Mattioli
V, Casamassima P, Paradiso A, Garrisi VM, Gadaleta CD,
Gadaleta-Caldarola G, Savino E, et al: Clinical and prognostic role
of circulating MMP-2 and its inhibitor TIMP-2 in HCC patients prior
to and after trans-hepatic arterial chemo-embolization. Clin
Biochem. 47:184–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen R, Cui J, Xu C, Xue T, Guo K, Gao D,
Liu Y, Ye S and Ren Z: The significance of MMP-9 over MMP-2 in HCC
invasiveness and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after
curative resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 19(Suppl 3): S375–S384. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peti W and Page R: Molecular basis of MAP
kinase regulation. Protein Sci. 22:1698–1710. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin ZH, Wang L, Zhang JB, Liu Y, Li XQ,
Guo L, Zhang B, Zhu WW and Ye QH: MST4 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via
activation of the p-ERK pathway. Int J Oncol. 45:629–640.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Grossi V, Peserico A, Tezil T and Simone
C: p38α MAPK pathway: A key factor in colorectal cancer therapy and
chemoresistance. World J Gastroenterol. 20:9744–9758. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Compromised MAPK
signaling in human diseases: An update. Arch Toxicol. 89:867–882.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Olson JM and Hallahan AR: p38 MAP kinase:
A convergence point in cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med. 10:125–129.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koul HK, Pal M and Koul S: Role of p38 MAP
kinase signal transduction in solid tumors. Genes Cancer.
4:342–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin JJ, Su JH, Tsai CC, Chen YJ, Liao MH
and Wu YJ: 11-epi-Sinulariolide acetate reduces cell migration and
invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma by reducing the
activation of ERK1/2, p38MAPK and FAK/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling
pathways. Mar Drug. 12:4783–4798. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Schmitz KJ, Wohlschlaeger J, Lang H,
Sotiropoulos GC, Malago M, Steveling K, Reis H, Cicinnati VR,
Schmid KW and Baba HA: Activation of the ERK and AKT signalling
pathway predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and ERK
activation in cancer tissue is associated with hepatitis C virus
infection. J Hepatol. 48:83–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu YJ, Neoh CA, Tsao CY, Su JH and Li HH:
Sinulariolide suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell
migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
16:16469–16482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|