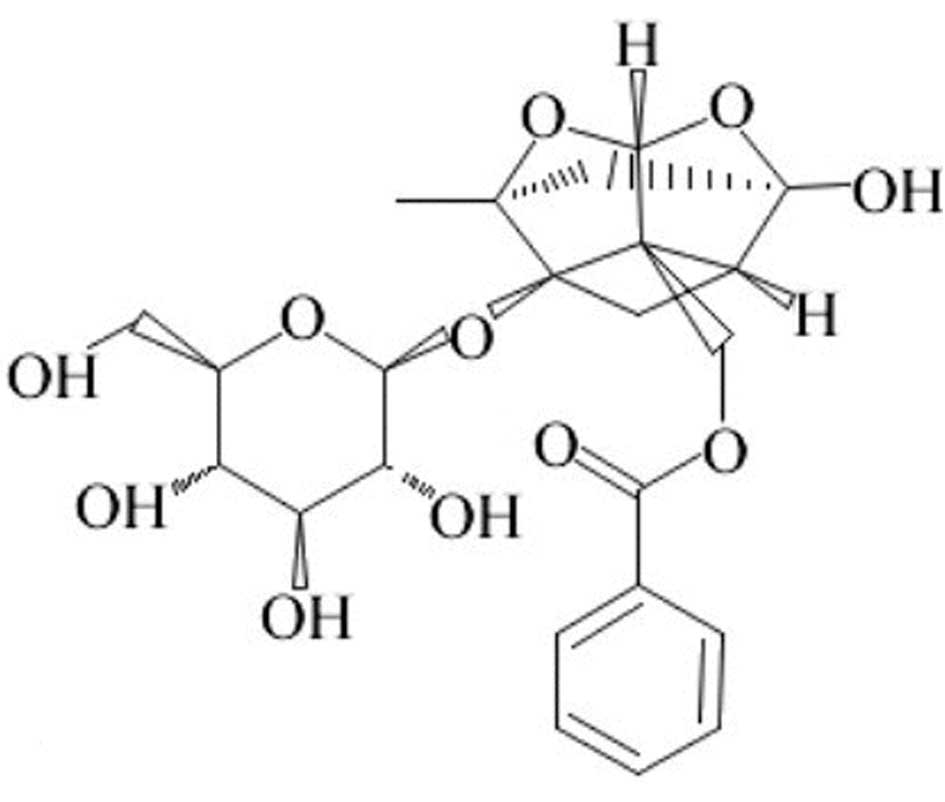
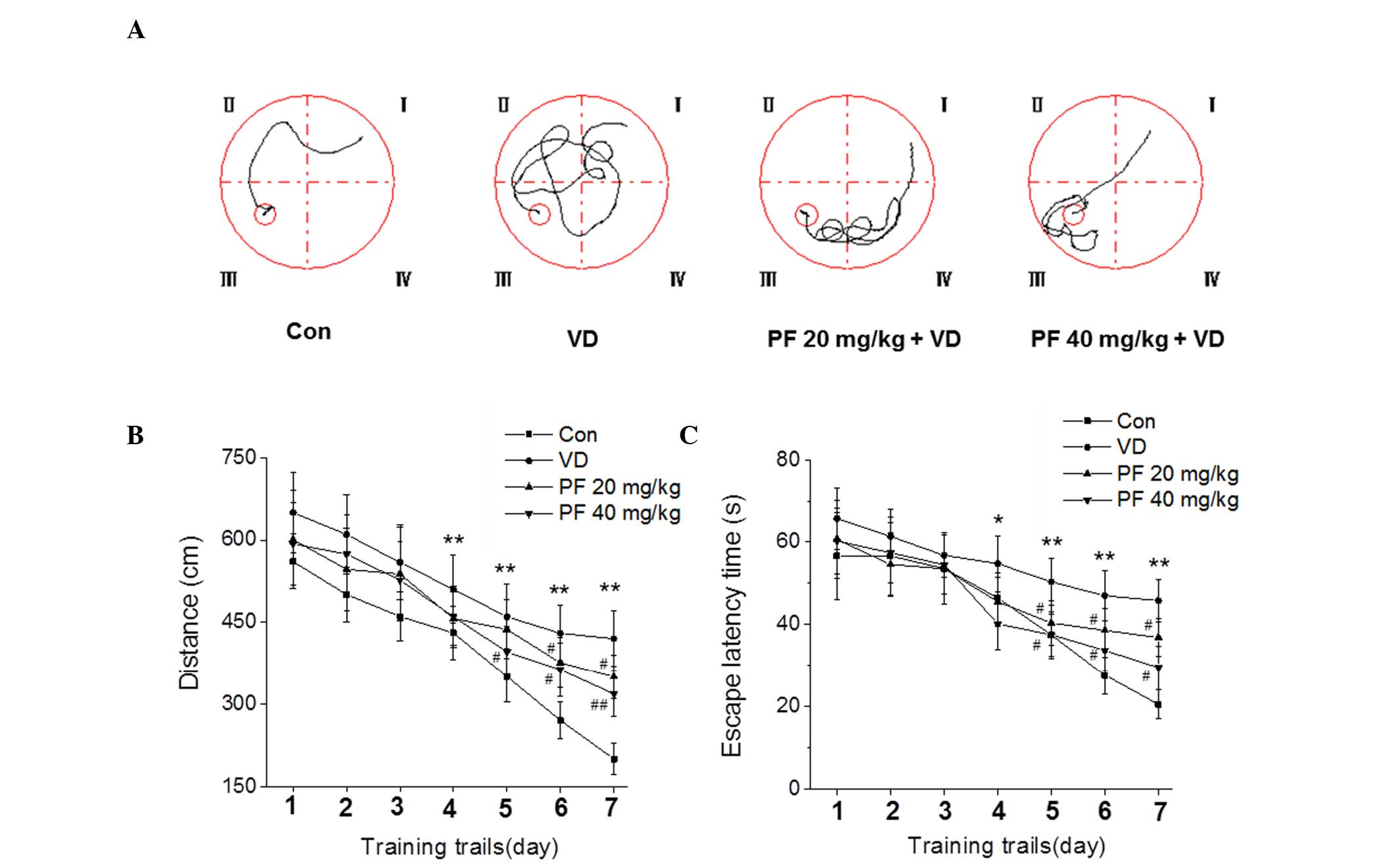
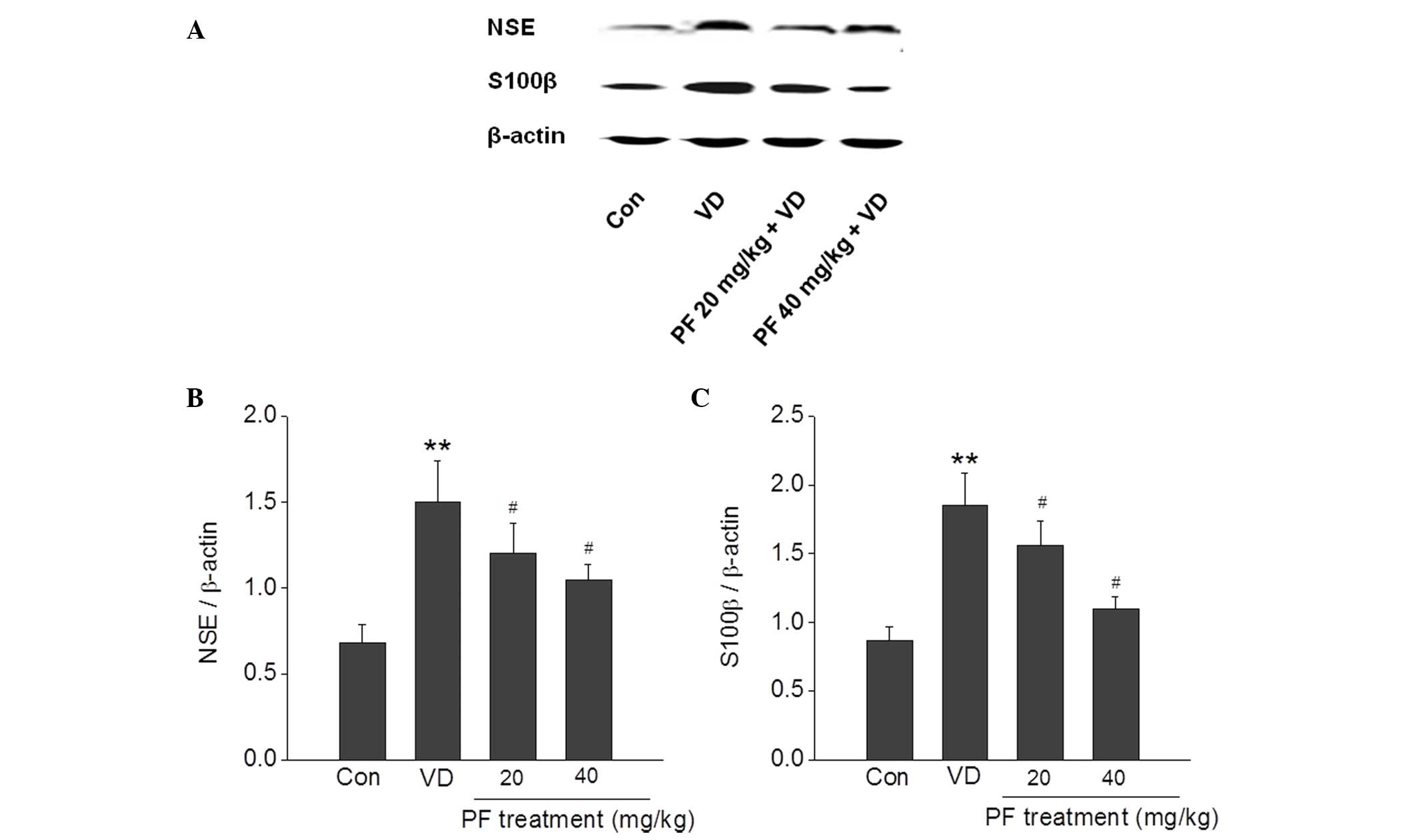
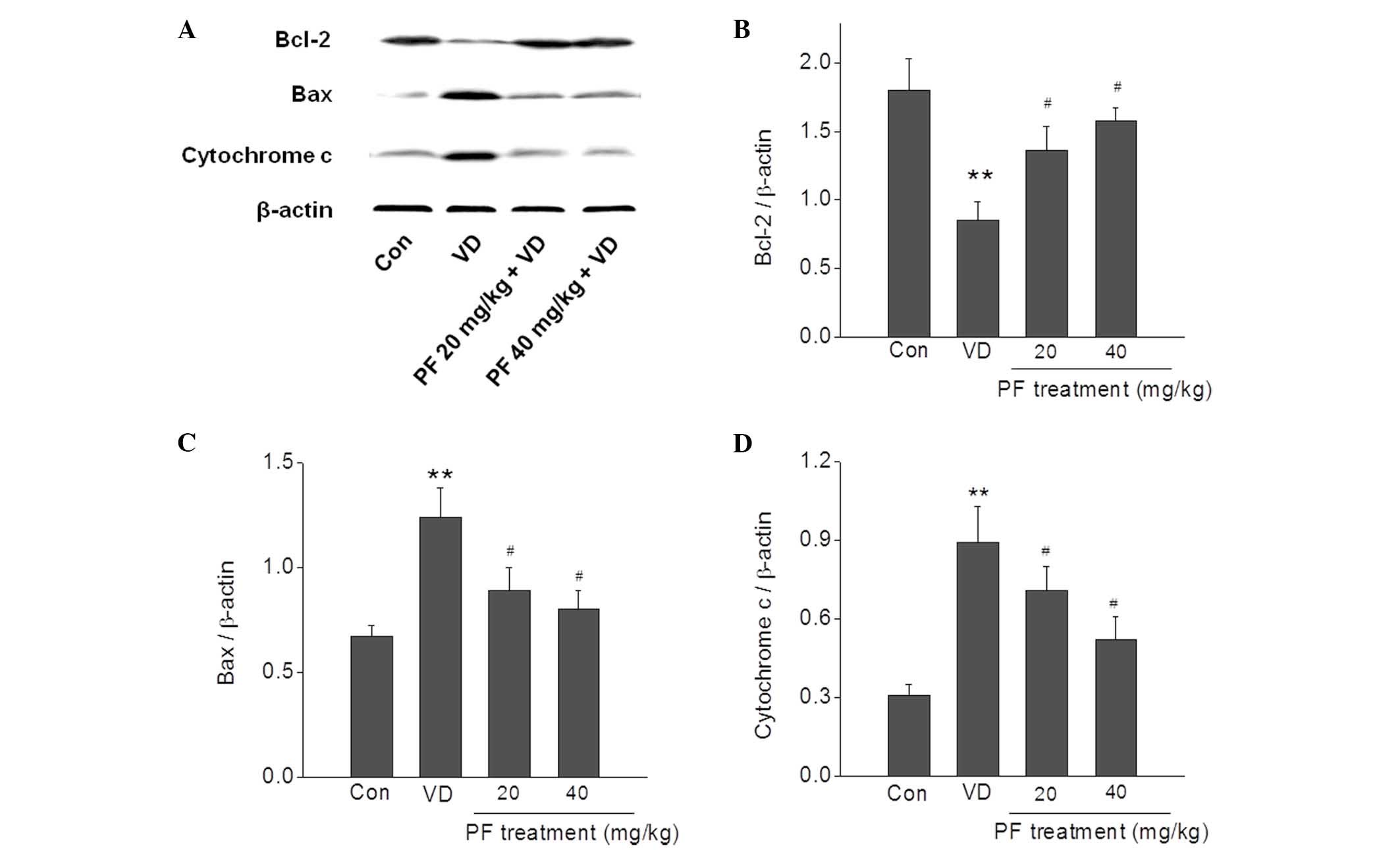
|
1
|
Ronnemaa E, Zethelius B, Lannfelt L and
Kilander L: Vascular risk factors and dementia: 40-Year follow-up
of a population-based cohort. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord.
31:460–466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Malouf R and Birks J: Donepezil for
vascular cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev CD004395.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H,
Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y,
et al: Global prevalence of dementia: A Delphi consensus study.
Lancet. 366:2112–2117. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang S, Zhou GG, Liu H, et al: Portective
effects of p38 MAPK inhibitor SB202190 against hippocampal
apoptosis and spatial learning and memory deficits in a rat model
of vascular dementia. Biomed Res Int,. 2013:2157982013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jellinger KA: The enigma of vascular
cognitive disorder and vascular dementia. Acta Neuropathol.
113:349–388. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Levine DA and Langa KM: Vascular cognitive
impairment: Disease mechanisms and therapeutic implications.
Neurotherapeutics. 8:361–373. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bennett S, Grant MM and Aldred S:
Oxidative stress in vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease: A
common pathology. J Alzheimers Dis. 17:245–257. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Zhang HY and Tang XC: Cholinergic
deficiency involved in vascular dementia: Possible mechanism and
strategy of treatment. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:879–888. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gong X, Ma M, Fan X, Li M, Liu Q, Liu X
and Xu G: Down-regulation of IGF-1/IGF-1R in hippocampus of rats
with vascular dementia. Neurosci Lett. 513:20–24. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kasparova S, Brezova V, Valko M, et al:
Study of the oxidative stress in a rat model of chronic brain
hypoperfusion. Neurochem Int. 46:601–611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nizamutdinoval IT, Jim YC, Kim JS, et al:
Paconol and paconiflorin, the main active principles of
Paconiaalbiflora, protect the heart from myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Planta Med. 74:14–18. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Watanabe H: Candidates for cognitive
enhancer extracted from medicinal plants: Paeoniflorin and
tetramethylpyrazine. Behav Brain Res. 83:135–141. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang NY, Liu CH, Hsieh CT and Hsieh CL:
The anti-inflammatory effect of paeoniflorin on cerebral infarction
induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Am J
Chin Med. 38:51–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao L, Wang YZ, Liu J, Luo XT, Ye Y and
Zhu XZ: Effects of paeoniflorin on the cerebral infarction,
behavioral and cognitive impairments at the chronic stage of
transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Life Sci.
78:413–420. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang LG, Wang LJ, Shen QQ, et al:
Paeoniflorin Improves Regional Cerebral Blood Flow and Suppresses
Inflammatory Factors in the Hippocampus of Rats with Vascular
Dementia. Chin J Integr Med. Epub ahead of print.
|
|
16
|
Institute of Laboratory Animal Research,
Commission on Life Sciences, National Research Council, . Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 7th. National Academy
Press; Washington, D.C.: pp. 56–66. 1996
|
|
17
|
D'Hooge R and De Devn PP: Applications of
the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain
Res Brain Res Rev. 36:60–90. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Farkas E, Luiten PG and Bari F: Permanent,
bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: A model for
chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Brain Res Rev. 54:162–180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berger RP, Dulani T, Adelson PD, Leventhal
JM, Richichi R and Kochanek PM: Identification of inflicted
traumatic brain injury in well-appearing infants using serum and
cerebrospinal markers: A possible screening tool. Pediatrics.
117:325–332. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gonçalves CA, Leite MC and Nardin P:
Biological and methodological features of the measurement of S100B,
a putative marker of brain injury. Clin Biochem. 41:755–763. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mecocci P, Parnetti L, Romano G, Scarelli
A, Chionne F, Cecchetti R, Polidori MC, Palumbo B, Cherubini A and
Senin U: Serum anti-GFAP and anti-S100 autoantibodies in brain
aging, Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. J Neuroimmunol.
57:165–170. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Parnetti L, Palumbo B, Cardinali L, Loreti
F, Chionne F, Cecchetti R and Senin U: Cerebrospinal fluid
neuron-specific enolase in Alzheimer's disease and vascular
dementia. Neurosci Lett. 183:43–45. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun ZK, Ma XR, Jia YJ, et al: Effects of
resveratrol on apoptosis in a rat model of vascular dementia. Exp
Ther Med. 7:843–848. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Min JJ, Huo XL, Xiang LY, et al:
Protective effect of Dl-3n-butylphthalide on learning and memory
impairment induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia-hypercapnia
exposure. Sci Rep. 4:55552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hwang L, Choi IY, Kim SE, Ko IG, Shin MS,
Kim CJ, Kim SH, Jin JJ, Chung JY and Yi JW: Dexmedetomidine
ameliorates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced memory impairment by
inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic
factor expression in the rat hippocampus. Int J Mol Med.
31:1047–1056. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shimizu S, Narita M and Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2
family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by
the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature. 399:483–487. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: A
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chuang DM: The antiapoptotic actions of
mood stabilizers: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potentials.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1053:195–204. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schinder AF and Poo M: The neurotrophin
hypothesis for synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 23:639–645.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizuno M, Yamada K, Olariu A, Nawa H and
Nabeshima T: Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in
spatial memory formation and maintenance in a radial arm maze test
in rats. J Neurosci. 20:7116–7121. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Laske C, Stransky E, Leyhe T, Eschweiler
GW, Maetzler W, Wittorf A, Soekadar S, Richartz E, Koehler N,
Bartels M, et al: BDNF serum and CSF concentrations in Alzheimer's
disease, normal pressure hydrocephalus and healthy controls. J
Psychiatr Res. 41:387–394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Murer MG, Yan Q and Raisman-Vozari R:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the control human brain and in
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol.
63:71–124. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|