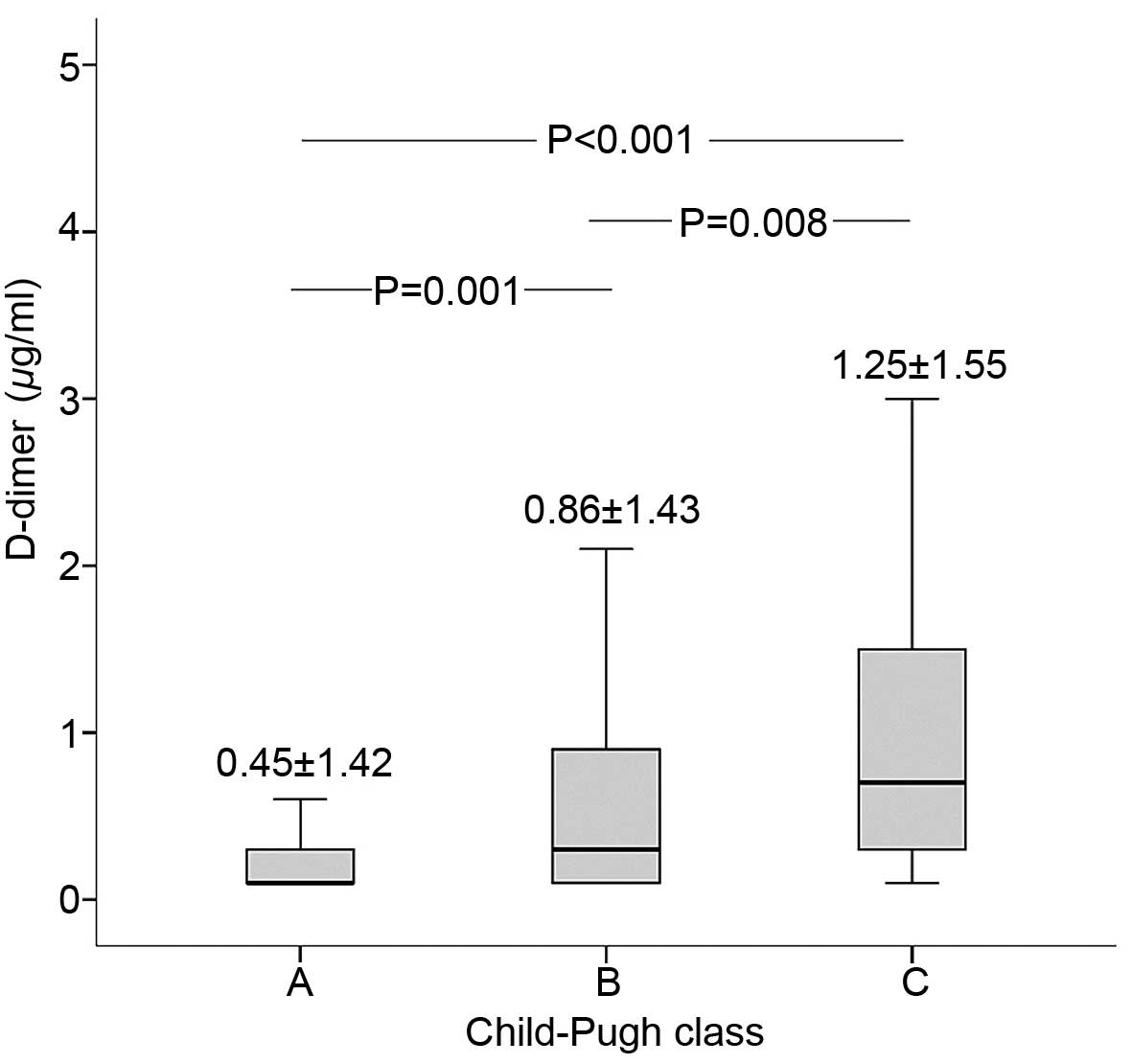
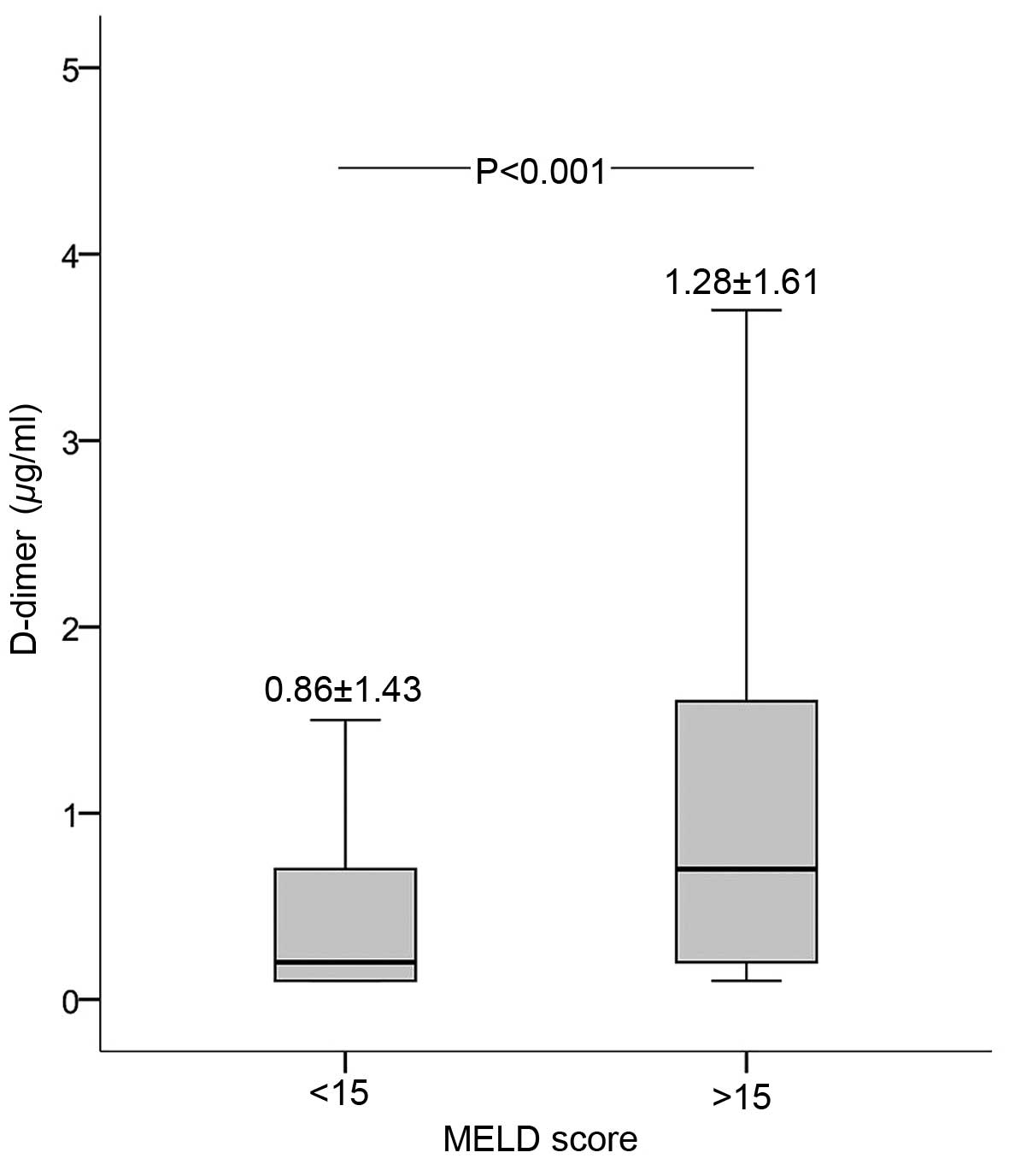
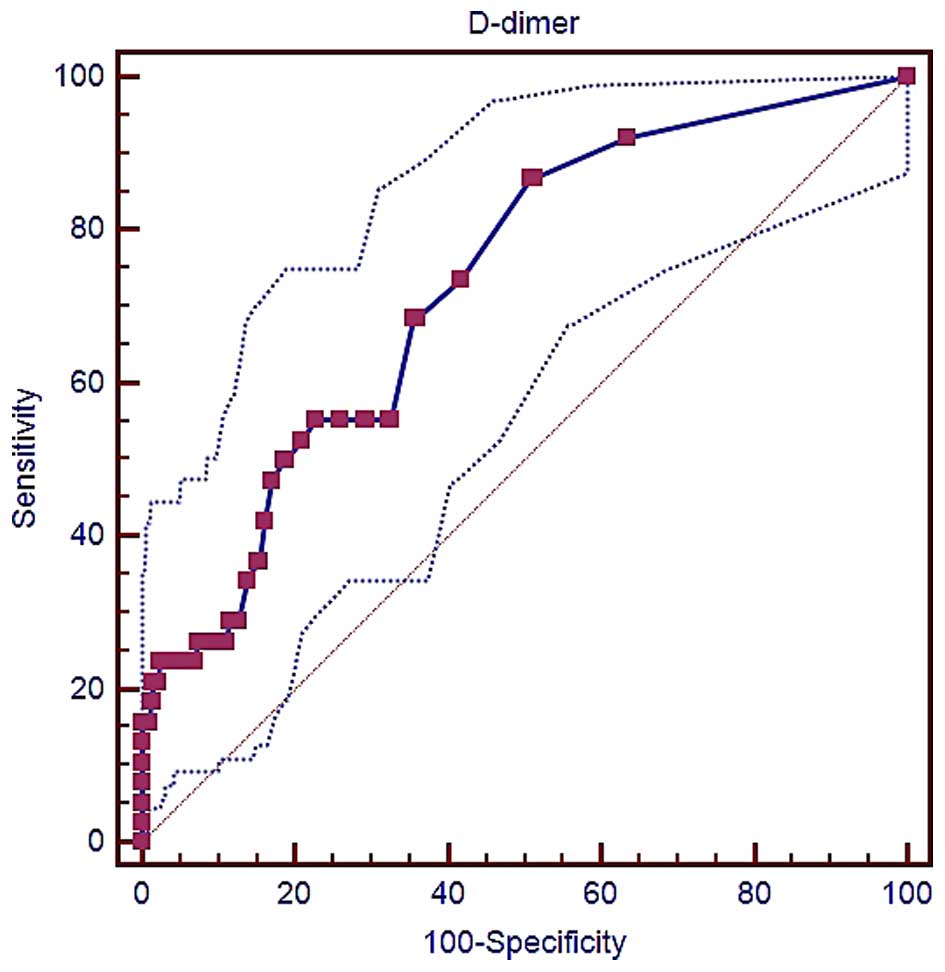
|
1
|
Le Gal G, Righini M and Wells PS: D-dimer
for pulmonary embolism. JAMA. 313:1668–1669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodger MA, Le Gal G, Wells P, Baglin T,
Aujesky D, Righini M, Palareti G, Huisman M and Meyer G: Clinical
decision rules and D-Dimer in venous thromboembolism: Current
controversies and future research priorities. Thromb Res.
134:763–768. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geersing GJ, Janssen KJ, Oudega R, Bax L,
Hoes AW, Reitsma JB and Moons KG: Excluding venous thromboembolism
using point of care D-dimer tests in outpatients: A diagnostic
meta-analysis. BMJ. 339:b29902009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Palareti G, Legnani C, Cosmi B, Guazzaloca
G, Pancani C and Coccheri S: Risk of venous thromboembolism
recurrence: High negative predictive value of D-dimer performed
after oral anticoagulation is stopped. Thromb Haemost. 87:7–12.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palareti G, Cosmi B, Legnani C, Antonucci
E, De Micheli V, Ghirarduzzi A, Poli D, Testa S, Tosetto A, Pengo
V, et al: D-dimer to guide the duration of anticoagulation in
patients with venous thromboembolism: A management study. Blood.
124:196–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Palareti G, Cosmi B, Legnani C, Tosetto A,
Brusi C, Iorio A, Pengo V, Ghirarduzzi A, Pattacini C, Testa S, et
al: D-dimer testing to determine the duration of anticoagulation
therapy. N Engl J Med. 355:1780–1789. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gram J, Duscha H, Zurborn KH and Bruhn HD:
Increased levels of fibrinolysis reaction products (D-dimer) in
patients with decompensated alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 26:1173–1178. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cioni G, Cristani A, Mussini C, Grandi S,
Pentore R, Zeneroli ML, Tizzanini W, Zagni G and Ventura E:
Incidence and clinical significance of elevated fibrin(ogen)
degradation product and/or D-dimer levels in liver cirrhosis
patients. Ital J Gastroenterol. 22:70–74. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saray A, Mesihovic R, Gornjakovic S, Vanis
N, Mehmedovic A, Nahodovic K, Glavas S and Papovic V: Association
between high D-dimer plasma levels and ascites in patients with
liver cirrhosis. Med Arch. 66:372–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai J, Qi X, Li H and Guo X: Role of
D-dimer in the development of portal vein thrombosis in liver
cirrhosis: A meta-analysis. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 21:165–174.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qi X, Li H, Chen J, Xia C, Peng Y, Dai J,
Hou Y, Deng H, Li J and Guo X: Serum liver fibrosis markers for
predicting the presence of gastroesophageal varices in liver
cirrhosis: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Gastroenterol Res
Pract. 2015:2745342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng Y, Qi X, Dai J, Li H and Guo X:
Child-Pugh versus MELD score for predicting the in-hospital
mortality of acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding in liver
cirrhosis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:751–757. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qi X, Peng Y, Li H, Li H and Guo X:
Diabetes is associated with an increased risk of in-hospital
mortality in liver cirrhosis with acute upper gastrointestinal
bleeding. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:476–477. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu C, Qi X, Li H, Peng Y, Dai J, Chen J,
Xia C, Hou Y, Zhang W and Guo X: Correlation of serum liver
fibrosis markers with severity of liver dysfunction in liver
cirrhosis: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:5989–5998. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL,
Pietroni MC and Williams R: Transection of the oesophagus for
bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 60:646–649. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kamath PS and Kim WR: The model for
end-stage liver disease (MELD). Hepatology. 45:797–805. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
El-Sayed R, El-Karaksy H, El-Raziky M,
El-Hawary M, El Koofy N, Helmy H and Fahmy M: Assessment of
coagulation and fibrinolysis in children with chronic liver
disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 24:113–117. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cong YL, Wei YX, Zhang LW, Yin ZJ and Bai
J: The relationship between hemostatic changes in liver cirrhosis
patients with different degrees of liver lesions in reference to
Child-Pugh scores. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 13:31–34.
2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Violi F, Ferro D, Basili S, Saliola M,
Quintarelli C, Alessandri C and Cordova C: Association between
low-grade disseminated intravascular coagulation and endotoxemia in
patients with liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 109:531–539. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Primignani M, Dell'Era A, Bucciarelli P,
Bottasso B, Bajetta MT, de Franchis R and Cattaneo M: High-D-dimer
plasma levels predict poor outcome in esophageal variceal bleeding.
Dig Liver Dis. 40:874–881. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|