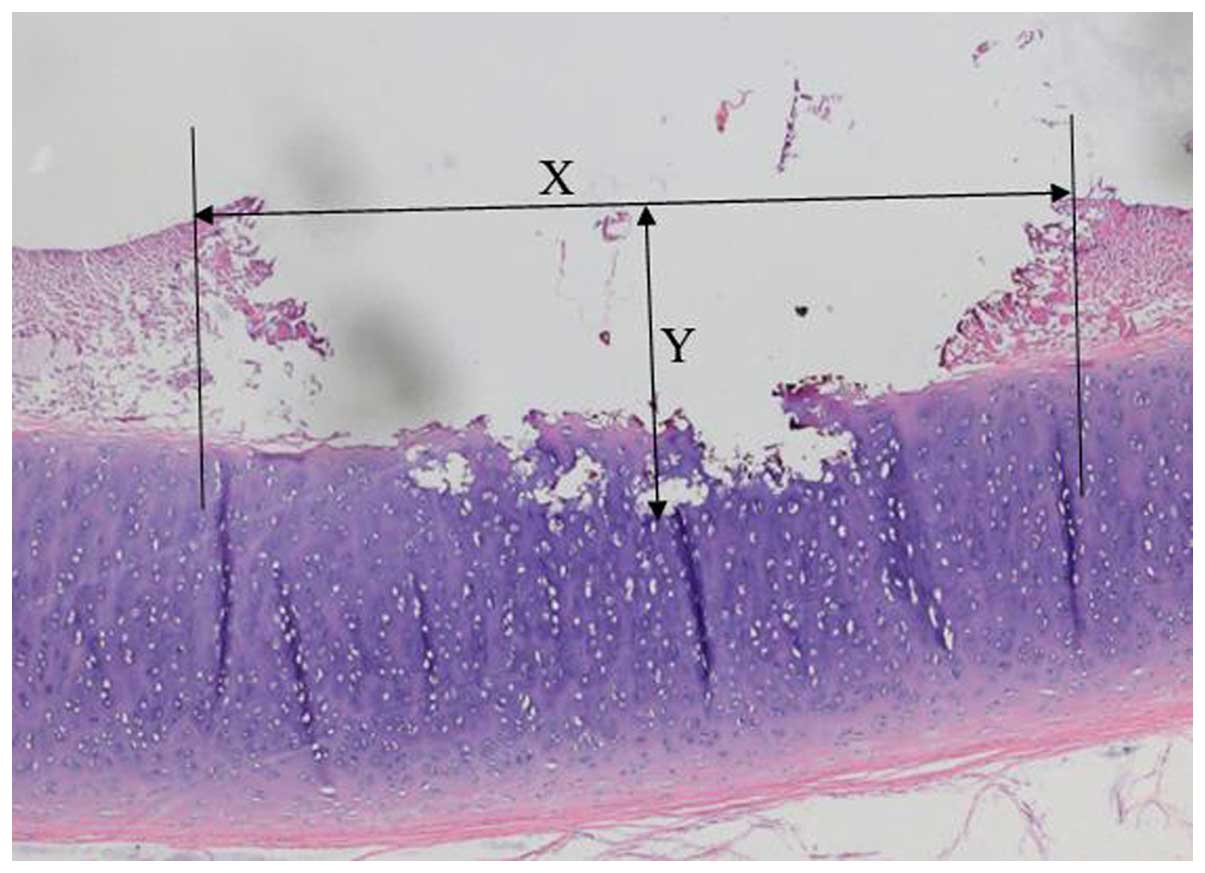
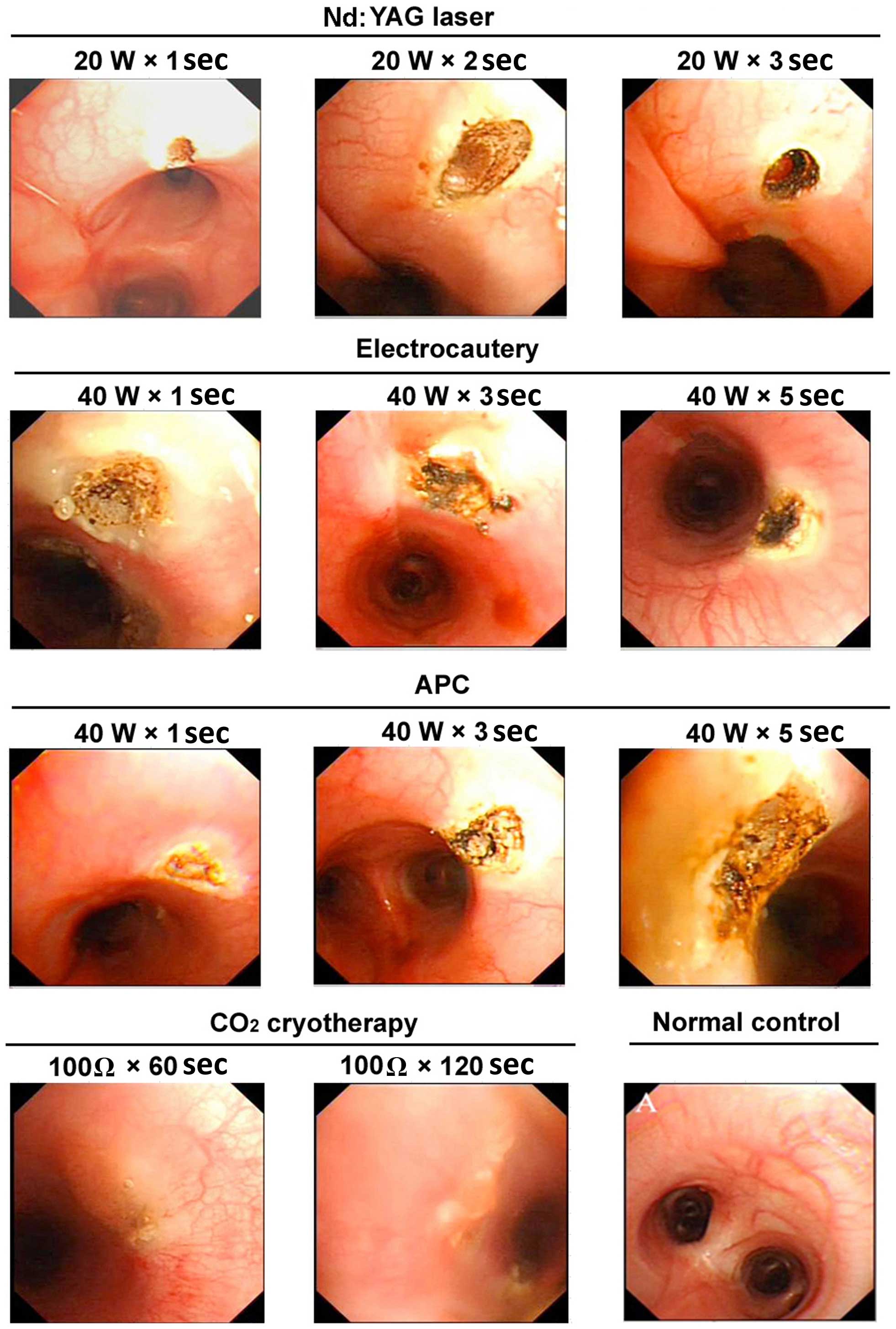
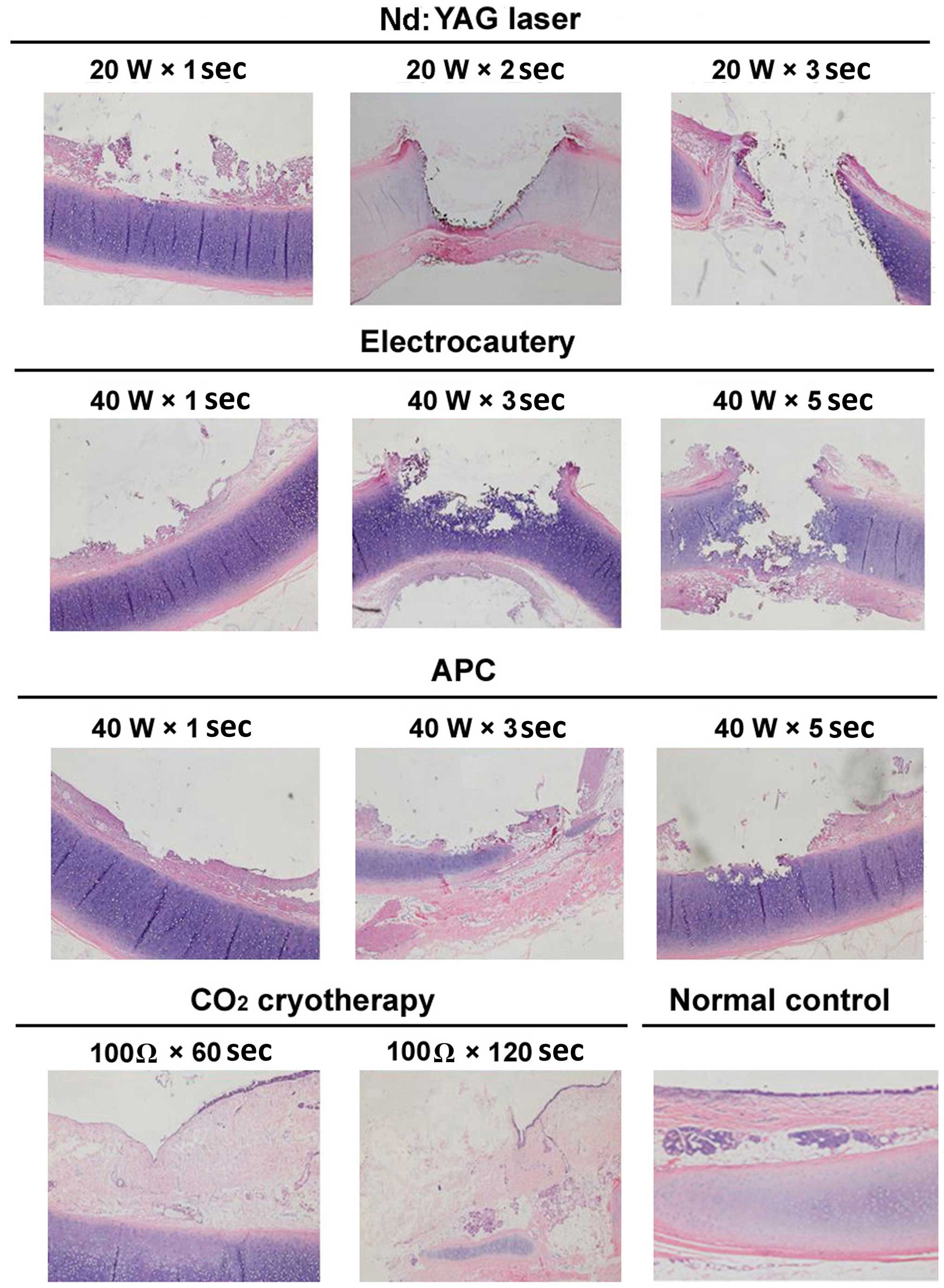
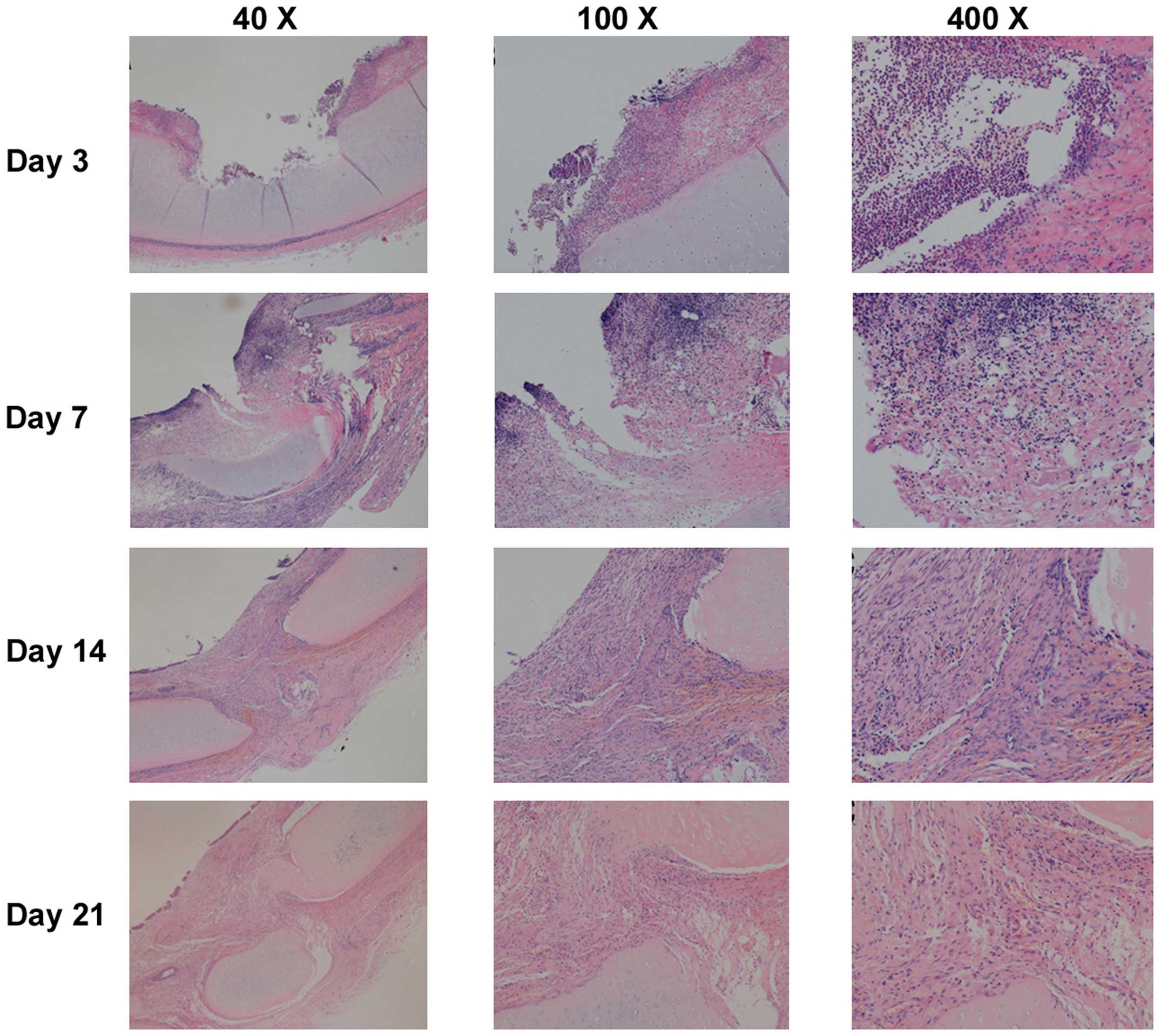
|
1
|
Bhamra-Ariza P, Keogh AM and Muller DW:
Percutaneous interventional therapies for the treatment of patients
with severe pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 63:611–618.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Andersen PE and Kjeldsen AD:
Interventional treatment of pulmonary arteriovenous malformations.
World J Radiol. 2:339–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Keogh AM, Mayer E, Benza RL, Corris P,
Dartevelle PG, Frost AE, Kim NH, Lang IM, Pepke-Zaba J and Sandoval
J: Interventional and surgical modalities of treatment in pulmonary
hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:(Suppl 1). S67–S77. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gudausky TM and Beekman RH III: Current
options and long-term results for interventional treatment of
pulmonary valvar stenosis. Cardiol Young. 16:418–427. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mantovani G, Astara G, Manca G, Versace R,
Contu P and Carai A: Endoscopic laser ablation as palliative
treatment of endobronchial, nonresectable, or recurrent lung
cancer: Assessment of its impact on quality of life. Clin Lung
Cancer. 1:277–285; discussion 286. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taber SW, Buschemeyer WC III, Fingar VH
and Wieman TJ: The treatment of malignant endobronchial obstruction
with laser ablation. Surgery. 126:730–733; discussion 733–735.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chua AP and Mehta AC: Barotrauma from
novel endobronchial ablation techniques. J Bronchology Interv
Pulmonol. 16:75–77. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Manali ED, Stathopoulos GT, Gildea TR,
Fleming P, Thornton J, Xu M, Papiris SA, Mehta AC and Mughal MM:
High dose-rate endobronchial radiotherapy for proximal airway
obstruction due to lung cancer: 8-year experience of a referral
center. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 25:207–213. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Y, Wang WJ and Wang HF: Therapeutic
effect of tracheal anastomosis versus interventional bronchoscopy
in the treatment of airway stenosis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
30:1359–1362. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Yao XP, Bai C, Huang Y, Wang Q, Zhao
LJ, Dong YC, Teng HY and Li Q: Therapeutic efficacy analysis of
bronchoscopic interventional therapy on severe tuberculous main
bronchial stenosis complicated with unilateral atelectasis.
Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 34:454–458. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang J, Wang J, Wang T, Xu M, Dang BW,
Pei YH and Zhang CY: A pilot study on interventional bronchoscopy
in the management of airway stenosis with benign hyperplasia.
Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 34:334–338. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ost DE, Ernst A, Grosu HB, Lei X,
Diaz-Mendoza J, Slade M, Gildea TR, Machuzak M, Jimenez CA, Toth J,
et al: Therapeutic bronchoscopy for malignant central airway
obstruction: success rates and impact on dyspnea and quality of
life. Chest. 147:1282–1298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Saji H, Furukawa K, Tsutsui H, Tsuboi M,
Ichinose S, Usuda J, Ohira T and Ikeda N: Outcomes of airway
stenting for advanced lung cancer with central airway obstruction.
Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 11:425–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Beamis JF Jr: Interventional pulmonology
techniques for treating malignant large airway obstruction: An
update. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 11:292–295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jones GS and Baldwin DR: Lung cancer
screening and management. Minerva Med. 106:339–354. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Colt HG and Murgu SD: Interventional
bronchoscopy from bench to bedside: New techniques for early lung
cancer detection. Clin Chest Med. 31:29–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pasic A, Brokx HAP, Noordegraaf AV, Paul
RMA, Postmus PE and Sutedja TG: Cost-effectiveness of early
intervention: Comparison between intraluminal bronchoscopic
treatment and surgical resection for T1N0 lung cancer patients.
Respiration. 71:391–396. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morrison SA, Hill SL, Rogers GS and Graham
RA: Efficacy and safety of continuous low-irradiance photodynamic
therapy in the treatment of chest wall progression of breast
cancer. J Surg Res. 192:235–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Simone CB II, Friedberg JS, Glatstein E,
Stevenson JP, Sterman DH, Hahn SM and Cengel KA: Photodynamic
therapy for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Dis. 4:63–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bai C, Dong YC, Song XL, Huang Y, Shi H,
Hu ZL and Li Q: In vitro study of safety and co-efficiency of the
transbronchial coagulation techniques. Chin Med J (Engl).
126:124–128. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhikai Z, Lizhi N, Liang Z, Jianying Z,
Fei Y, Jibing C, Jialiang L and Kecheng X: Treatment of central
type lung cancer by combined cryotherapy: Experiences of 47
patients. Cryobiology. 67:225–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schumann C, Hetzel M, Babiak AJ, Hetzel J,
Merk T, Wibmer T, Lepper PM and Krüger S: Endobronchial tumor
debulking with a flexible cryoprobe for immediate treatment of
malignant stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 139:997–1000. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rojas-Tula DG, Gómez-Fernández M,
García-López JJ, Cobos-Ceballos MJ, Gil-Fuentes A, Pérez-Laya JM,
Serrano-Rebollo JC, Ortega-González A, Vargas-Hidalgo T, de
Oña-Lacasta JM Ruíz and Celdrán-Gil J: Endobronchial cryotherapy
for a mycetoma. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 20:330–332. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mu D, Nan D, Li W, Fu E, Xie Y, Liu T and
Jin F: Efficacy and safety of bronchoscopic cryotherapy for
granular endobronchial tuberculosis. Respiration. 82:268–272. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SH, Choi WJ, Sung SW, Kim YK, Kim CH,
Zo JI and Park KJ: Endoscopic cryotherapy of lung and bronchial
tumors: A systematic review. Korean J Intern Med. 26:137–144. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fitzmaurice GJ, Redmond KC, Fitzpatrick DA
and Bartosik W: Endobronchial cryotherapy facilitates end-stage
treatment options in patients with bronchial stenosis: A case
series. Ann Thorac Med. 9:120–123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lai JP, Tao ZD, Xiao JY, Chen XH, Zhao SP,
Tian YQ and Betz CS: Microinvasive Nd:YAG laser therapy of early
glottic carcinoma and its effect on soluble interleukin-2 receptor,
interleukin-2 and natural killer cells. Laryngoscope.
111:1585–1588. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hermes A, Heigener D, Gatzemeier U, Schatz
J and Reck M: Efficacy and safety of bronchoscopic laser therapy in
patients with tracheal and bronchial obstruction: A retrospective
single institution report. Clin Respir J. 6:67–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wahidi MM, Unroe MA, Adlakha N, Beyea M
and Shofer SL: The use of electrocautery as the primary ablation
modality for malignant and benign airway obstruction. J Thorac
Oncol. 6:1516–1520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Verkindre C, Brichet A, Maurage CA, Ramon
P, Homasson JP and Marquette CH: Morphological changes induced by
extensive endobronchial electrocautery. Eur Respir J. 14:796–799.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sindhwani G, Rawat J and Keserwani V: Role
of endobronchial electrocautery in management of neoplastic central
airway obstruction: Initial experience with seven cases. Indian J
Chest Dis Allied Sci. 54:165–168. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rolle A, Pereszlenyi A, Koch R, Richard M
and Baier B: Is surgery for multiple lung metastases reasonable? A
total of 328 consecutive patients with multiple-laser
metastasectomies with a new 1318-nm Nd:YAG laser. J Thoracic
Cardiovasc Surg. 131:1236–1242. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Seaman JC and Musani AI: Endobronchial
ablative therapies. Clin Chest Med. 34:417–425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nikfarjam M, Muralidharan V,
Malcontenti-Wilson C, McLaren W and Christophi C: Impact of blood
flow occlusion on liver necrosis following thermal ablation. ANZ J
Surg. 76:84–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reddy C, Majid A, Michaud G, Feller-Kopman
D, Eberhardt R, Herth F and Ernst A: Gas embolism following
bronchoscopic argon plasma coagulation: A case series. Chest.
134:1066–1069. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin F, Mu D, Xie Y, Fu E and Guo Y:
Application of bronchoscopic argon plasma coagulation in the
treatment of tumorous endobronchial tuberculosis: Historical
controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 145:1650–1653. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bolliger CT, Sutedja TG, Strausz J and
Freitag L: Therapeutic bronchoscopy with immediate effect: Laser,
electrocautery, argon plasma coagulation and stents. Eur Respir J.
27:1258–1271. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boujaoude Z, Young D, Lotano R and
Abouzgheib W: Cryosurgery for the immediate treatment of acute
central airway obstruction. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol.
20:45–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yu CH, Lin HP, Cheng SJ, Sun A and Chen
HM: Cryotherapy for oral precancers and cancers. J Formos Med
Assoc. 113:272–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vergnon JM, Huber RM and Moghissi K: Place
of cryotherapy, brachytherapy and photodynamic therapy in
therapeutic bronchoscopy of lung cancers. Eur Respir J. 28:200–218.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|