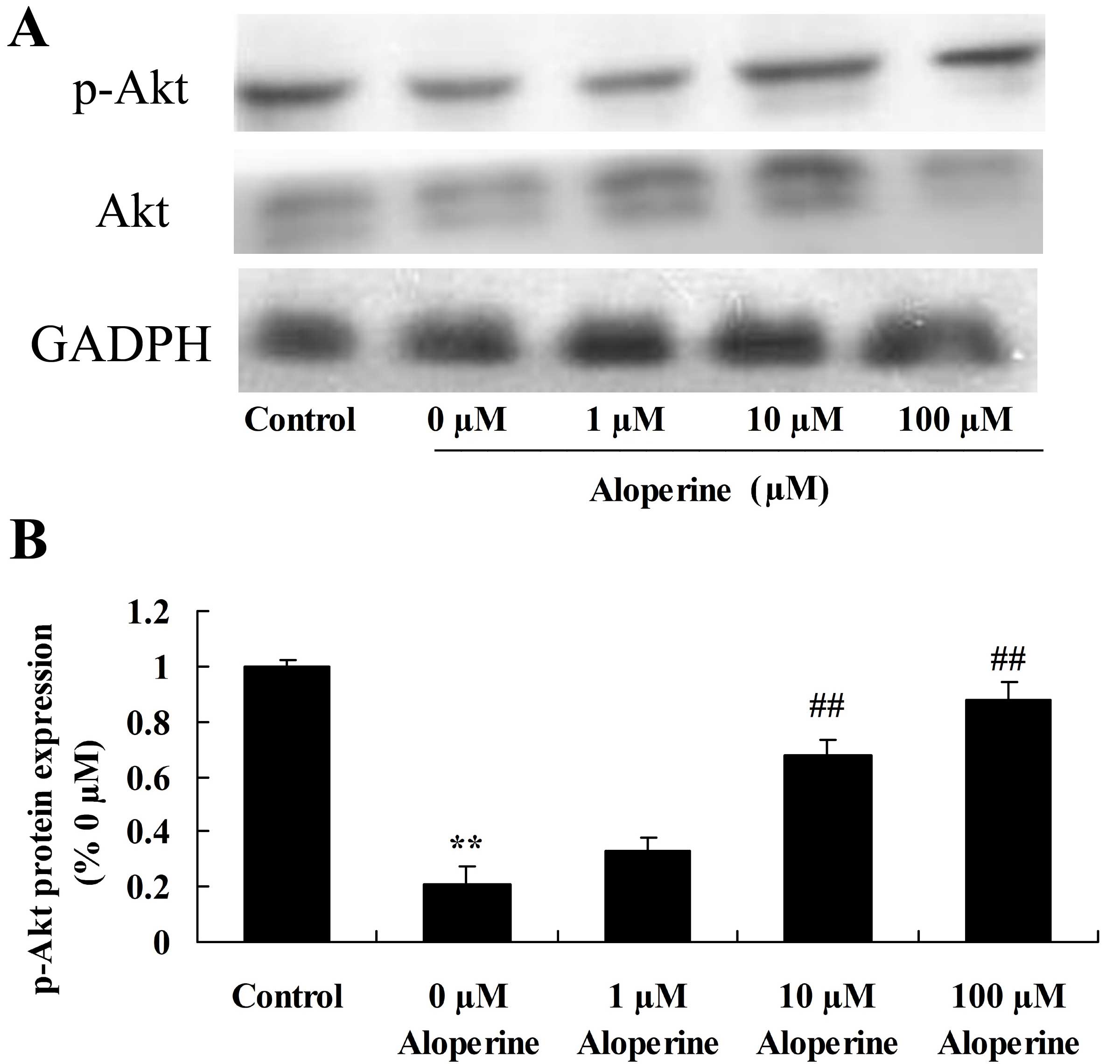
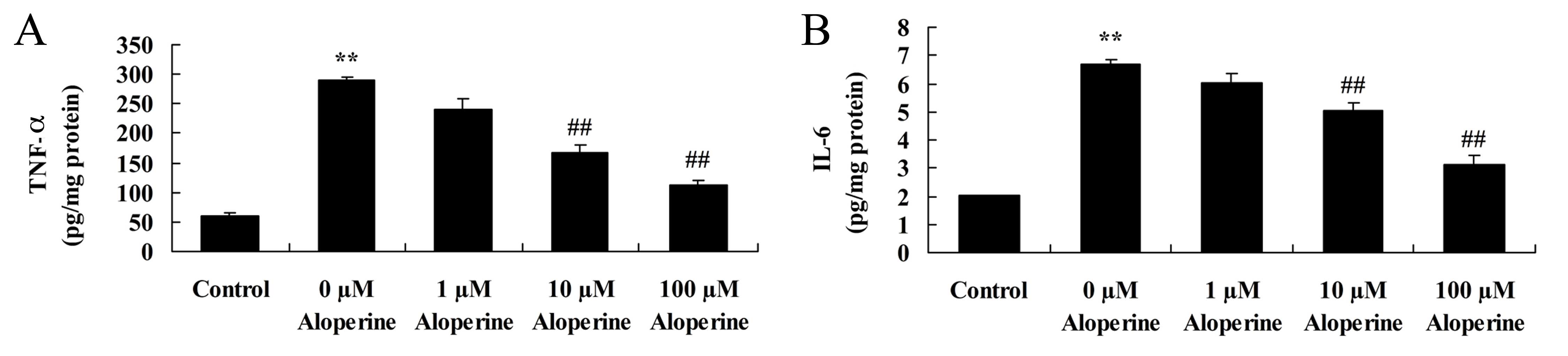
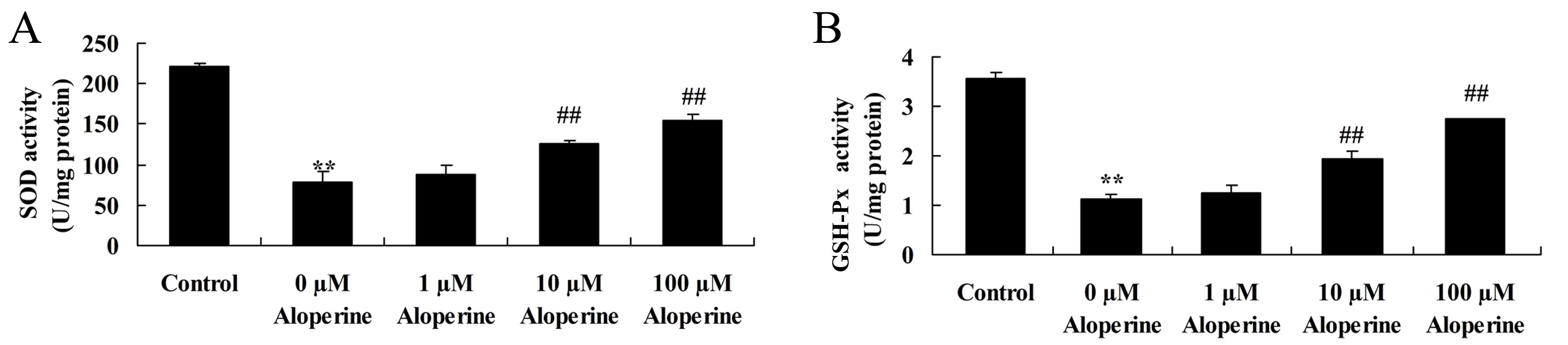
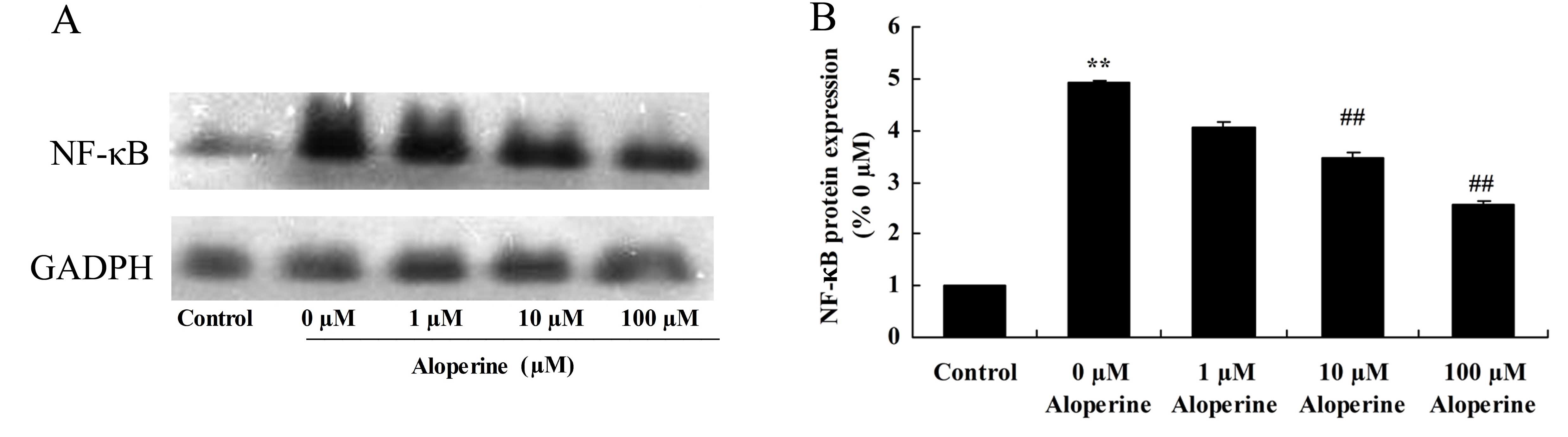
|
1
|
Wang HQ and Samartzis D: Clarifying the
nomenclature of intervertebral disc degeneration and displacement:
From bench to bedside. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:1293–1298.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang QQ, Ding DF, Xi ZJ, Chen Y, Li CG,
Liu SF, Lu S, Zhao YJ, Shi Q and Wang YJ: Protective effect of
ligustrazine on lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration of rats
induced by prolonged upright posture. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2014:5084612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Presciutti SM, Paglia DN, Karukonda T,
Soung do Y, Guzzo R, Drissi H and Moss IL: PDGF-BB inhibits
intervertebral disc cell apoptosis in vitro. J Orthop Res.
32:1181–1188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kermani H Reihani, Pourghazi M and Mahani
SE: Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field on intervertebral disc
cell apoptosis in rats. Electromagn Biol Med. 33:246–249. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ariga K, Yonenobu K, Nakase T, Hosono N,
Okuda S, Meng W, Tamura Y and Yoshikawa H: Mechanical
stress-induced apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes in organ-cultured
mouse intervertebral discs: An ex vivo study. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 28:1528–1533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heyde CE, Tschoeke SK, Hellmuth M,
Hostmann A, Ertel W and Oberholzer A: Trauma induces apoptosis in
human thoracolumbar intervertebral discs. BMC Clin Pathol. 6:52006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gruber HE, Watts JA, Hoelscher GL, Bethea
SF, Ingram JA, Zinchenko NS and Hanley EN Jr: Mitochondrial gene
expression in the human annulus: In vivo data from annulus cells
and selectively harvested senescent annulus cells. Spine J.
11:782–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang L, Rong Z, Zeng M, Cao Y, Gong X, Lin
L, Chen Y, Cao W, Zhu L and Dong W: Pyrroloquinoline quinone
protects nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced
apoptosis by inhibiting the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Eur
Spine J. 24:1702–1710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chu H, Yu H, Ren D, Zhu K and Huang H:
Plumbagin exerts protective effects in nucleus pulposus cells by
attenuating hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress,
inflammation and apoptosis through NF-κB and Nrf-2. Int J Mol Med.
37:1669–1676. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen J, Hou C, Chen X, Wang D, Yang P, He
X, Zhou J and Li H: Protective effect of cannabidiol on hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in
nucleus pulposus cells. Mol Med Rep. 14:2321–2327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuan XY, Ma HM, Li RZ, Wang RY, Liu W and
Guo JY: Topical application of aloperine improves
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin
lesions in NC/Nga mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:263–269. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan XY, Ma HM, Li RZ, Wang RY, Liu W and
Guo JY: Topical application of aloperine improves
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin
lesions in NC/Nga mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:263–269. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miao D and Zhang L: Leptin modulates the
expression of catabolic genes in rat nucleus pulposus cells through
the mitogen-activated protein kinase and Janus kinase 2/signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathways. Mol Med Rep.
12:1761–1768. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen JW, Ni BB, Li B, Yang YH, Jiang SD
and Jiang LS: The responses of autophagy and apoptosis to oxidative
stress in nucleus pulposus cells: implications for disc
degeneration. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1175–1189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nerlich AG, Schleicher ED and Boos N: 1997
Volvo Award winner in basic science studies. Immunohistologic
markers for age-related changes of human lumbar intervertebral
discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:2781–2795. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou X, Zhang HL, Gu GF, Ding Y, Jia JB,
Fu QS and He SS: significant In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol Anim.
49:279–286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Park C, Jin CY, Kim GY, Jeong YK, Kim WJ
and Choi YH: Induction of apoptosis by ethanol extract of Prunus
mume in U937 human leukemia cells through activation of caspases.
Oncol Rep. 26:987–993. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He Q, Bao L, Zimering J, Zan K, Zhang Z,
Shi H, Zu J, Yang X, Hua F, Ye X and Cui G: The protective role of
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in thrombin-induced neuronal cell
apoptosis and JNK-MAPK activation. Neuroreport. 26:416–423. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu TT, Li LF, Du R, Jiang L and Zhu YQ:
Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis in human dental pulp cells via
caspase-9 dependent pathway. J Endod. 39:1151–1155. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park WH: Anti-apoptotic effect of caspase
inhibitors on H2O2-treated HeLa cells through
early suppression of its oxidative stress. Oncol Rep. 31:2413–2421.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Yang S, Zhou H, Sun M, Du L, Wei
M, Luo M, Huang J, Deng H, Feng Y, et al: Aloperine executes
antitumor effects against multiple myeloma through dual apoptotic
mechanisms. J Hematol Oncol. 8:262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun BZ, Chen L, Wu Q, Wang HL, Wei XB,
Xiang YX and Zhang XM: Suppression of inflammatory response by
flurbiprofen following focal cerebral ischemia involves the NF-κB
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:3087–3095. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jia WC, Liu G, Zhang CD and Zhang SP:
Formononetin attenuates hydrogen peroxide
(H2O2)-induced apoptosis and NF-κB activation
in RGC-5 cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:2191–2197.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou CC, Gao HB, Sun XB, Shi HB, Liu W,
Yuan HN and Wang ZX: Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic action of
aloperine. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 10:360–365. 1989.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu YQ, Jin SJ, Liu N, Li YX, Zheng J, Ma
L, Du J, Zhou R, Zhao CJ, Niu Y, et al: Aloperine attenuated
neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury via
anti-oxidation activity and suppression of the nuclear factor kappa
B pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 451:568–573. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|