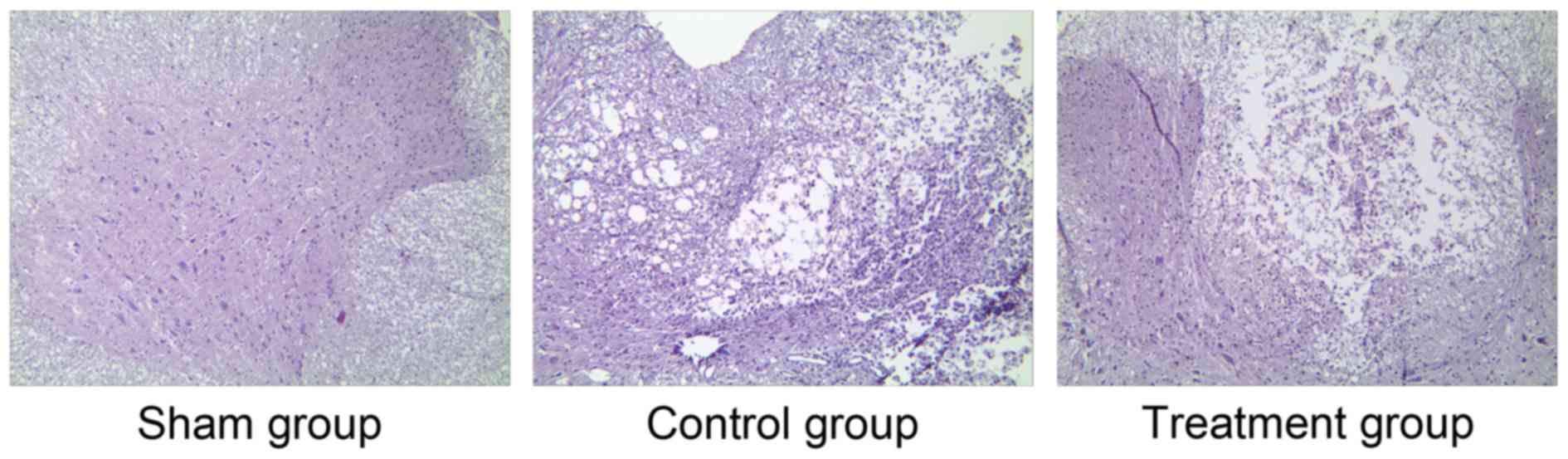
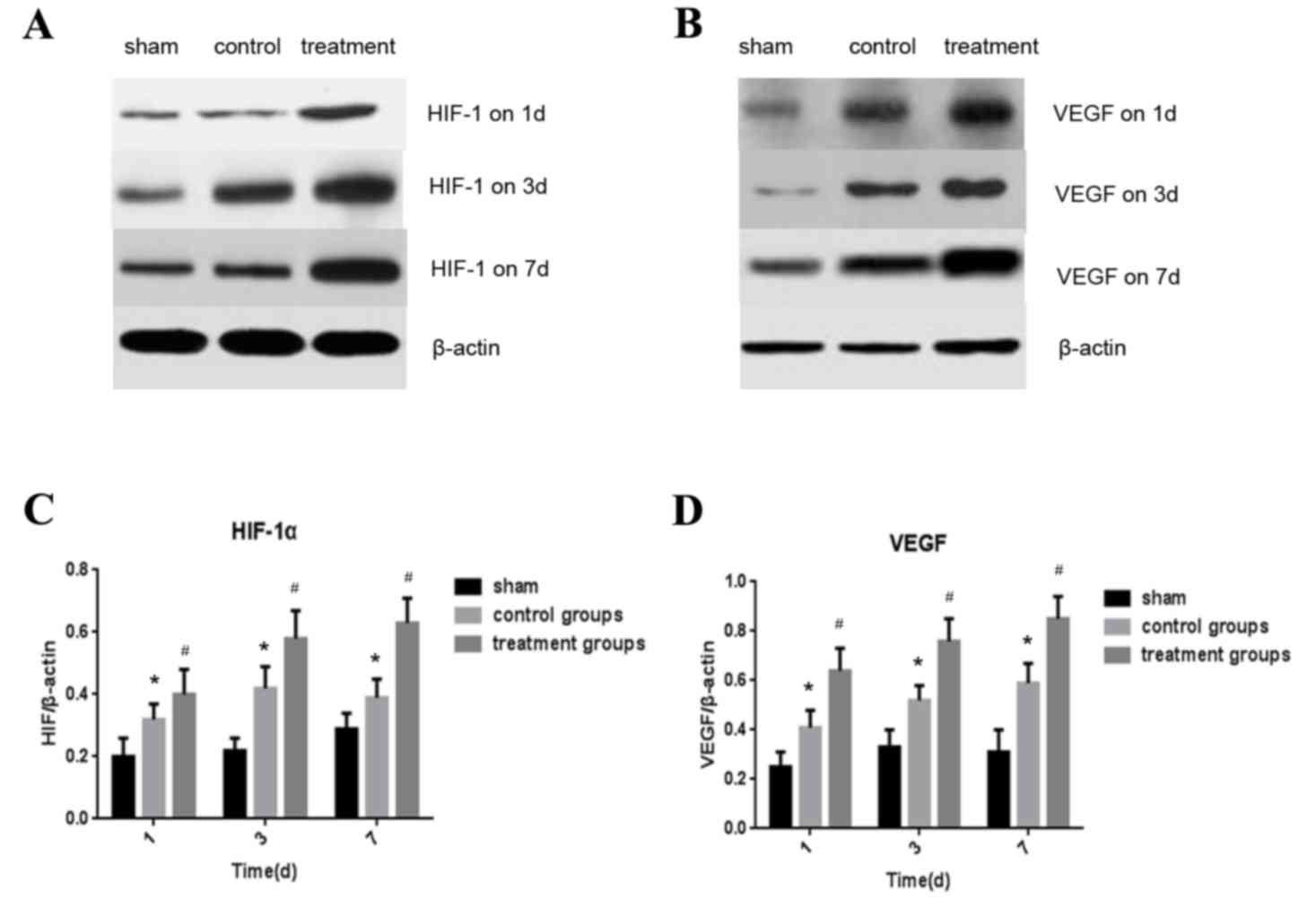
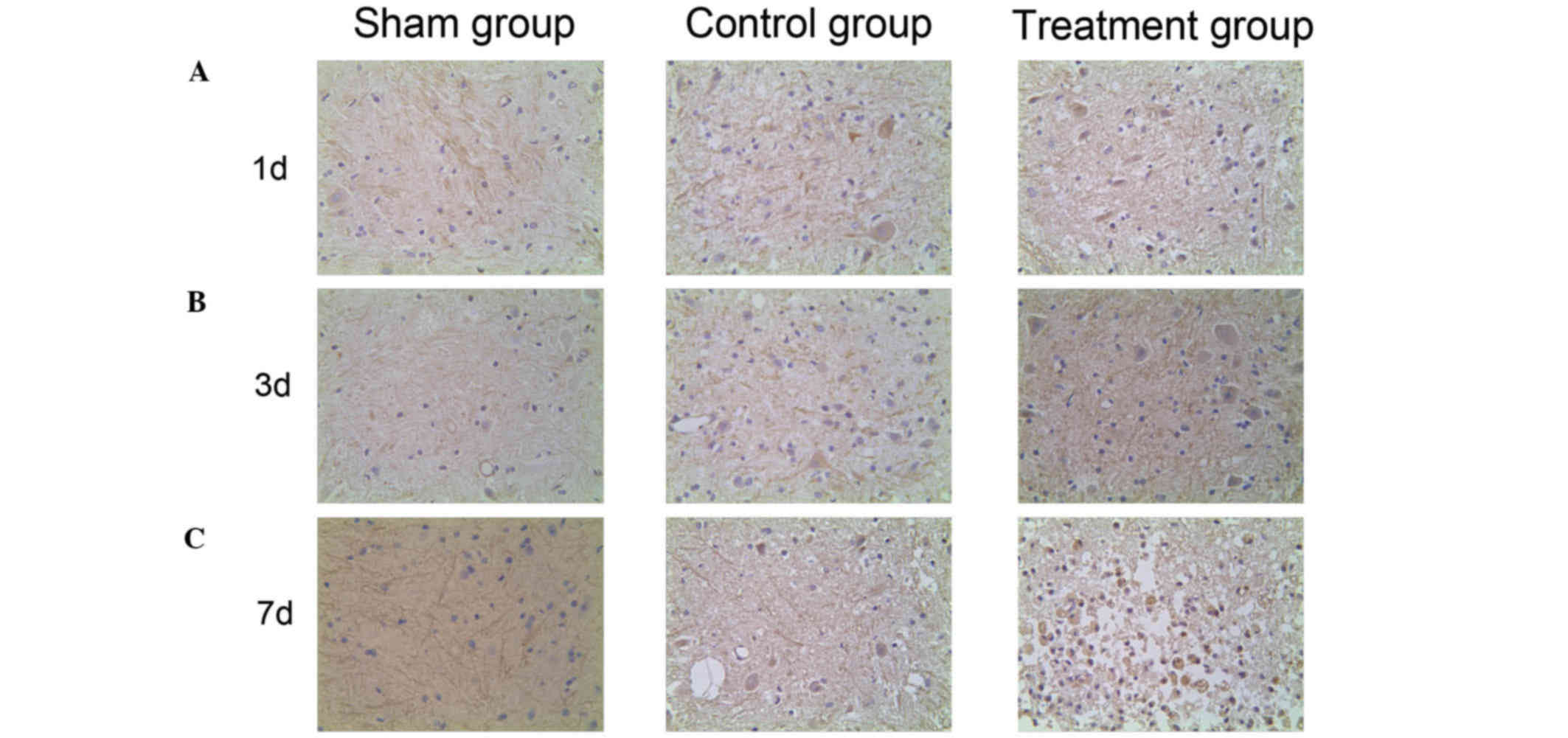
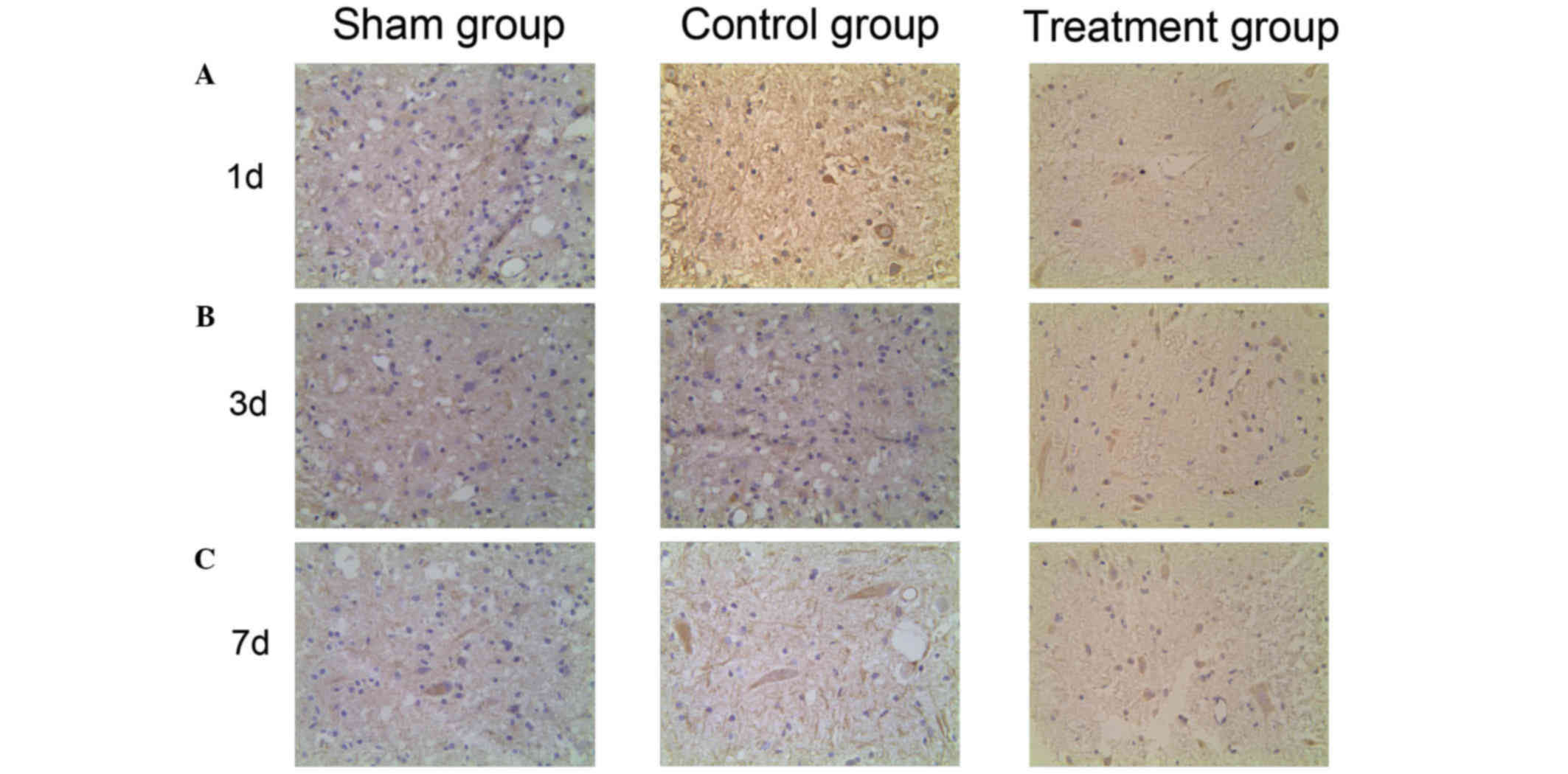
|
1
|
Anwar MA, Al Shehabi TS and Eid AH:
Inflammogenesis of secondary spinal cord Injury. Front Cell
Neurosci. 10:982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schwab JM, Zhang Y, Kopp MA, Brommer B and
Popovich PG: The paradox of chronic neuroinflammation, systemic
immune suppression, autoimmunity after traumatic chronicspinal cord
injury. Exp Neurol. 258:121–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jeong W, Bazer FW, Song G and Kim J:
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by trophectoderm cells in
response to hypoxia and epidermal growth factor. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 469:176–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stampas A and Tansey KE: Spinal cord
injury medicine and rehabilitation. Semin Neurol. 34:524–533. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gui L, Liu B and Lv G: Hypoxia induces
autophagy in cardiomyocytes via a hypoxia-inducible factor
1-dependent mechanism. Exp Ther Med. 11:2233–2239. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kimura H, Weisz A, Ogura T, Hitomi Y,
Kurashima Y, Hashimoto K, D'Acquisto F, Makuuchi M and Esumi H:
Identification of hypoxia-inducible factor1 ancillary sequence and
its function in vascular endothelial growth factor gene induction
by hypoxia and nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 276:2292–2298. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Savas S, Savas C, Altuntas I and Adiloglu
A: The correlation between nitric oxide and vascular endothelial
growth factor in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 46:113–117. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xing J and Lu J: HIF-1α activation
attenuates IL-6 and TNF-α pathways in hippocampus of rats following
transient global ischemia. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:511–520. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Theriault JR, Felts AS, Bates BS, Perez
JR, Palmer M, Gilbert SR, Dawson ES, Engers JL, Lindsley CW and
Emmitte KA: Discovery of a new molecular probe ML228: An activator
of the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) pathway. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 22:76–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open filed
testing in rats. Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Scheff SW, Saucier DA and Cain ME: A
statistical method for analyzing rating scale data: The BBB
locomotor score. J Neurotrauma. 19:1251–1260. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu P, Graham L, Wang Y, Wu D and Tuszynski
M: Promotion of survival and differentiation of neural stem cells
with fibrin and growth factor cocktails after severe spinal cord
injury. J Vis Exp. e506412014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chavez JC and LaManna JC: Activation of
hypoxia-inducibled factor-1 in the rat cerebral cortex after
transient global ischemia: Potential role of insulin-like growth
faetor-l. J Neurosci. 22:8922–8931. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Linke S, Stojkoski C, Kewley RJ, Booker
GW, Whitelaw ML and Peet DJ: Substrate reqnirements of the
oxygen-sensing asparaginyl hydroxylase factor inhibiting
hypoxia-inducible factor. J Bid Chem. 279:14391–14397. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jantsch J and Schödel J: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors in myeloid cell-driven host defense and
tissue homeostasis. Immunobiology. 220:305–314. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Manalo DJ, Rowan A, Lavoie T, Natarajan L,
Kelly BD, Ye SQ, Garcia JG and Semenza GL: Transcriptional
regulation of vascular endothelial cell responses to hypoxia by
HIF-1. Blood. 105:659–669. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zimna A and Kurpisz M: Hypoxia-Inducible
Factor-1 in physiological and pathophysiological Angiogenesis:
Applications and therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2015:5494122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Basagiannis D, Zografou S, Murphy C,
Fotsis T, Morbidelli L, Ziche M, Bleck C, Mercer J and
Christoforidis S: VEGF induces signalling and angiogenesis by
directing VEGFR2 internalisation via macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci.
pii(jcs): 1882192016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vasta S, Di Martino A, Zampogna B, Torre
G, Papalia R and Denaro V: Role of VEGF, nitric oxide, and
sympathetic neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of tendinopathy:
A review of the current evidences. Front Aging Neurosci. 8:1862016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
D'Alessio A, Proietti G, Lama G, Biamonte
F, Lauriola L, Moscato U, Vescovi A, Mangiola A, Angelucci C and
Sica G: Analysis of angiogenesis related factors in glioblastoma,
peritumoral tissue and their derived cancer stem cells. Oncotarget.
2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ortuzar N, Argandoña EG, Bengoetxea H and
Lafuente JV: Combination of intracortically administered VEGF and
environmental enrichment enhances brain protection in developing
rats. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 118:135–144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tovar-Y-Romo LB and Tapia R: VEGF protects
spinal motor neurons against chronic excitotoxic degeneration in
vivo by activation of PI3-K pathway and inhibition of p38MAPK. J
Neurochem. 115:1090–1101. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song S, Park JT, Na JY, Park MS, Lee JK,
Lee MC and Kim HS: Early expressions of hypoxia-inducible factor
1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor increase the neuronal
plasticity of activated endogenous neural stem cells after focal
cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 9:912–918. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ding XM, Mao BY, Jiang S, Li SF and Deng
YL: Neuroprotective effect of exogenous vascular endothelial growth
factor on rat spinal cord neurons on vitro hypoxia. Chin Med
J(Engl). 118:1644–1650. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jin K, Mao XO and Greenberg DA: Vascular
endothelial growth factor stimulates neurite outgrowth from
cerebral cortical neurons via Rho kinase signaling. J Neurobiol.
66:236–242. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu K, Liang CL, Chen HJ, Chen SD, Hsu HC,
Liliang PC, Lin TK and Cho CL: Injury severity and cell death
mechanisms: Effects of concomitant hypovolemic hypotension on
spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Exp Neurol. 185:120–132.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Natarajan R, Salloum FN, Fisher BJ,
Kukreja RC and Fowler AA III: Hypoxia inducible factor-1
upregulates adiponectin in diabetic mouse hearts and attenuates
post-ischemic injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 51:178–187. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tamosaityte S, Galli R, Uckermann O,
Sitoci-Ficici KH, Later R, Beiermeister R, Doberenz F, Gelinsky M,
Leipnitz E, Schackert G, et al: Biochemical monitoring of spinal
cord injury by FT-IR spectroscopy-effects of therapeutic alginate
implant in rat models. PLoS One. 10:e01426602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mahon PC, Hirota K and Semenza GL: FIH·1:
A novel protein that interacts with HIF-lalpha transcriptional
activivity. Genes Dev. 15:2675–2686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rhim T, Lee DY and Lee M: Hypoxia as a
target for tissue specific gene therapy. J Control Release.
172:484–494. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Long HQ, Li GS, Hu Y, Wen CY and Xie WH:
HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway may play a dual role in secondary
pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy. Med Hypotheses. 79:82–84.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Herrera JJ, Nesic O and Narayana PA:
Reduced vascular endothelial growth factor expression in contusive
spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 26:995–1003. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Figley S, Spratt SK, Lee G, Ando D,
Surosky R and Fehlings MG: An engineered transcription factor which
activates VEGF-A enhances recovery after spinal cord injury.
Neurobiol Dis. 37:384–393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|