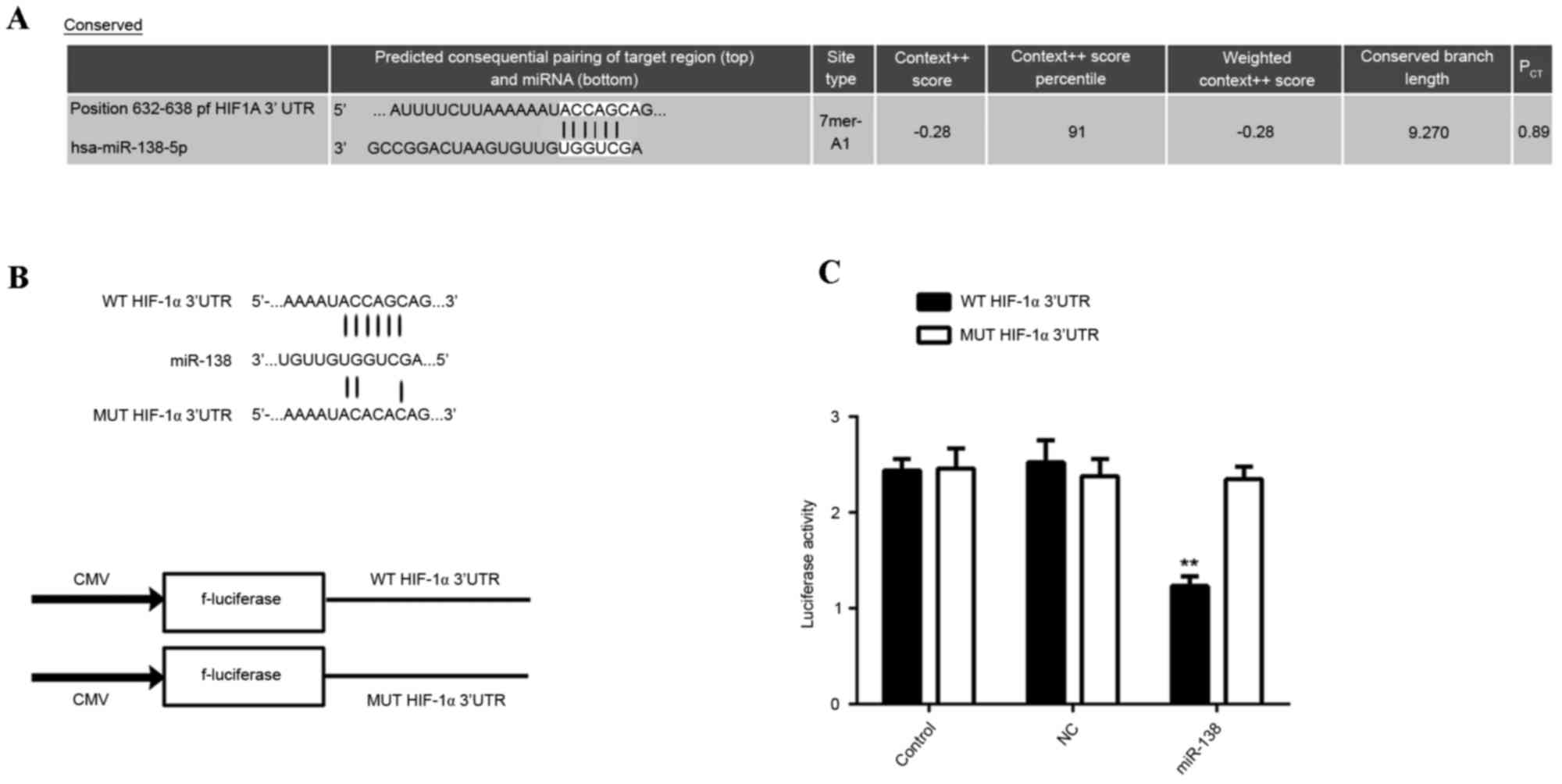
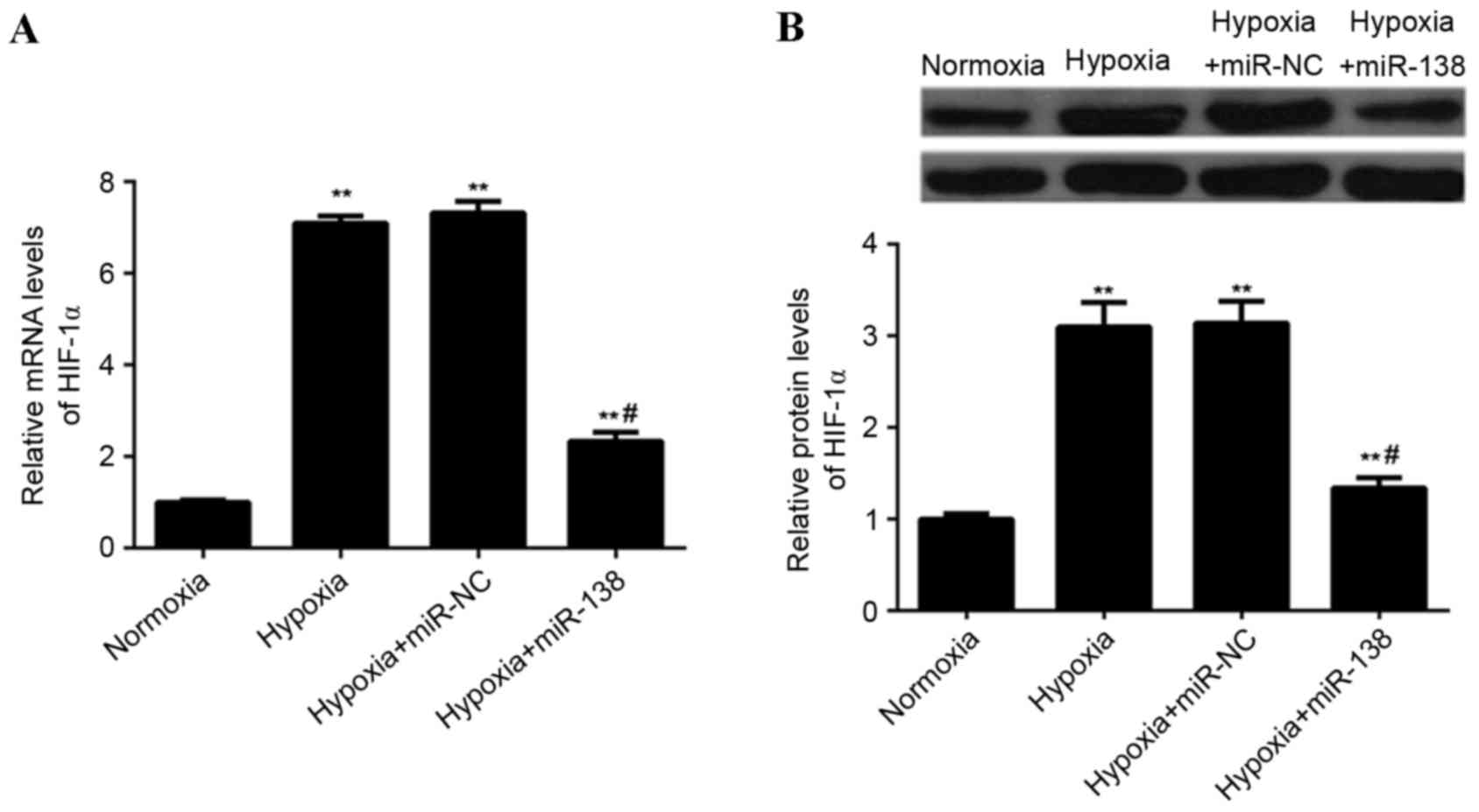
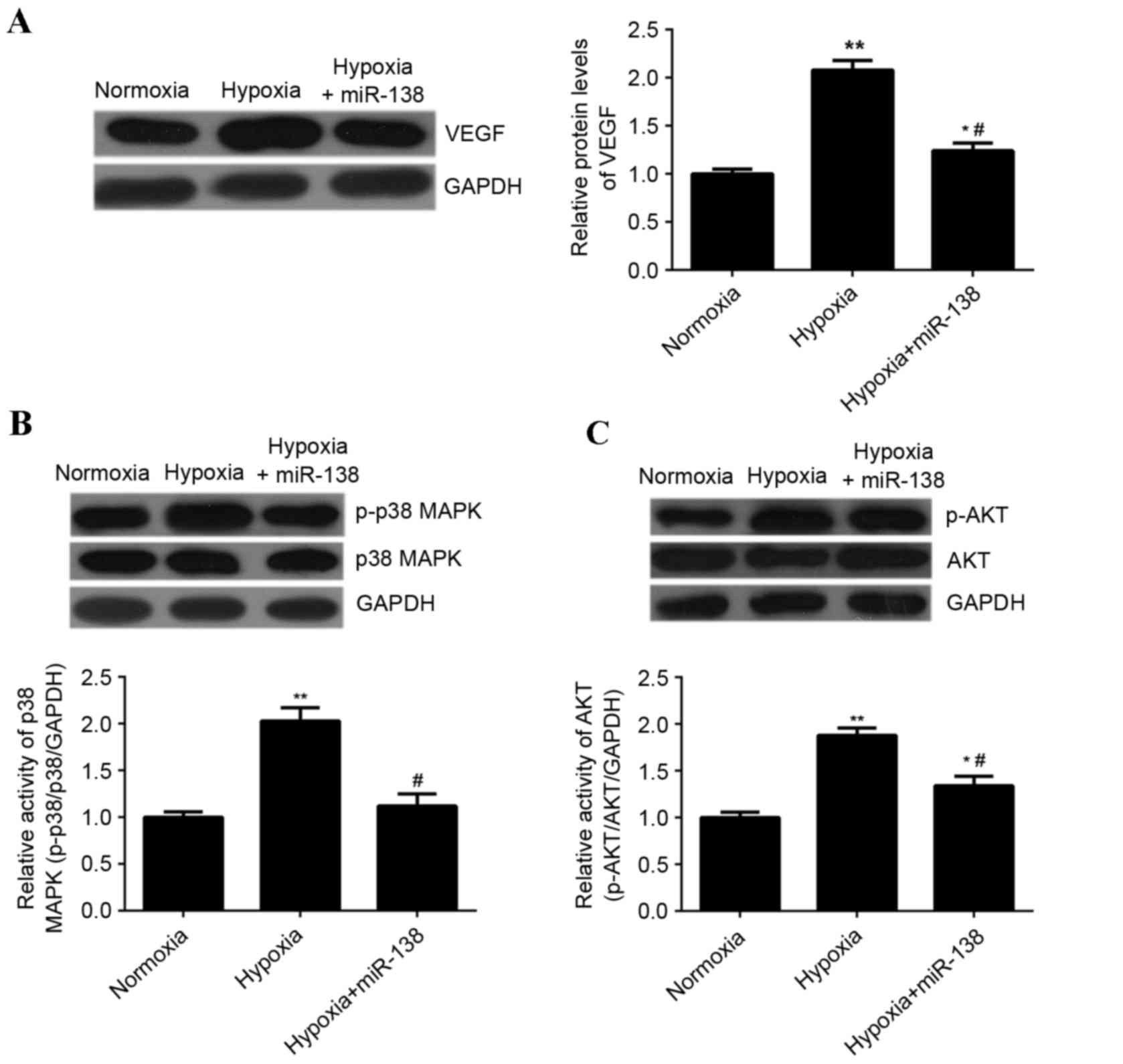
|
1
|
Endemann DH and Schiffrin EL: Endothelial
dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:1983–1992. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Simons D, Grieb G, Hristov M, Pallua N,
Weber C, Bernhagen J and Steffens G: Hypoxia-induced endothelial
secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and role in
endothelial progenitor cell recruitment. J Cell Mol Med.
15:668–678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee SH, Lee JH, Yoo SY, Hur J, Kim HS and
Kwon SM: Hypoxia inhibits cellular senescence to restore the
therapeutic potential of old human endothelial progenitor cells via
the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-TWIST-p21 axis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 33:2407–2414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartoszewska S, Kochan K, Piotrowski A,
Kamysz W, Ochocka RJ, Collawn JF and Bartoszewski R: The
hypoxia-inducible miR-429 regulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
expression in human endothelial cells through a negative feedback
loop. FASEB J. 29:1467–1479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou S, Zhang P, Liang P and Huang X: The
expression of miR-125b regulates angiogenesis during the recovery
of heat-denatured HUVECs. Burns. 41:803–811. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feng N, Wang Z, Zhang Z, He X, Wang C and
Zhang L: miR-487b promotes human umbilical vein endothelial cell
proliferation, migration, invasion and tube formation through
regulating THBS1. Neurosci Lett. 591:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Duan Q, Yang L, Gong W, Chaugai S, Wang F,
Chen C, Wang P, Zou MH and Wang DW: MicroRNA-214 is up-regulated in
heart failure patients and suppresses XBP1-mediated endothelial
cells angiogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 230:1964–1973. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sen A, Ren S, Lerchenmüller C, Sun J,
Weiss N, Most P and Peppel K: MicroRNA-138 regulates
hypoxia-induced endothelial cell dysfunction by targeting S100A1.
PLoS One. 8:e786842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li S, Ran Y, Zhang D, Chen J, Li S and Zhu
D: MicroRNA-138 plays a role in hypoxic pulmonary vascular
remodelling by targeting Mst1. Biochem J. 452:281–291. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang M, Wang CQ, Wang BY and Huang DJ:
Inhibitory effect of siRNA targeting HIF-1alpha on differentiation
of peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells. Ai Zheng.
24:1293–1300. 2005.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yeh YM, Chuang CM, Chao KC and Wang LH:
MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis
by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α. Int J Cancer. 133:867–878. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song T, Zhang X, Wang C, Wu Y, Cai W, Gao
J and Hong B: MiR-138 suppresses expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1α (HIF-1α) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma 786-O cells.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:1307–1311. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang Y, Huang B, Sun L, Peng X, Chen X and
Zou X: Ginkgolide B promotes proliferation and functional
activities of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells:
Involvement of Akt/eNOS and MAPK/p38 signaling pathways. Eur Cell
Mater. 21:459–469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ganguly R, Lytwyn MS and Pierce GN:
Differential effects of trans and polyunsaturated fatty acids on
ischemia/reperfusion injury and its associated cardiovascular
disease states. Curr Pharm Des. 19:6858–6863. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang D, Zhang P, Wang T, Gao L, Qiao Z,
Liang Y and Yu B: SalA attenuates ischemia/reperfusion-induced
endothelial barrier dysfunction via down-regulation of VLDL
receptor expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:747–757. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu BY, Xiang MX and Wang JA: Endothelial
progenitor cells and in-stent restenosis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.
10:364–371. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoder MC: Human endothelial progenitor
cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0066922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Machalinska A: The role of circulating
endothelial progenitor cells in the development of vascular retinal
diseases. Klin Oczna. 115:158–162. 2013.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sen A, Most P and Peppel K: Induction of
microRNA-138 by pro-inflammatory cytokines causes endothelial cell
dysfunction. FEBS Lett. 588:906–914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nishimura R, Nishiwaki T, Kawasaki T,
Sekine A, Suda R, Urushibara T, Suzuki T, Takayanagi S, Terada J,
Sakao S and Tatsumi K: Hypoxia-induced proliferation of
tissue-resident endothelial progenitor cells in the lung. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 308:L746–L758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang M, Wang B, Wang C, He B, Fan H, Guo
TB, Shao Q, Gao L and Liu Y: Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha and endothelial progenitor cell differentiation by
adenoviral transfer of small interfering RNA in vitro. J Vasc Res.
43:511–521. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang M, Wang CQ, Wang BY, He B, Shao Q
and Huang DJ: Overexpression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha
(HIF-1alpha) promotes the differentiation of endothelial progenitor
cell ex vivo. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 14:565–570.
2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang M, Wang B, Wang C, He B, Fan H, Guo
TB, Shao Q, Gao L and Liu Y: Angiogenesis by transplantation of
HIF-1 alpha modified EPCs into ischemic limbs. J Cell Biochem.
103:321–334. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian MAPK
signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation:
A 10-year update. Physiol Rev. 92:689–737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiu C, Xie Q, Zhang D, Chen Q, Hu J and Xu
L: GM-CSF induces cyclin D1 expression and proliferation of
endothelial progenitor cells via PI3K and MAPK signaling. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 33:784–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu J, Wang Q, Wang H, Lu W, Li W, Qin Z
and Huang L: Activation of liver X receptor enhances the
proliferation and migration of endothelial progenitor cells and
promotes vascular repair through PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling pathway
activation. Vascul Pharmacol. 62:150–161. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dai T, Zheng H and Fu GS: Hypoxia confers
protection against apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in
endothelial progenitor cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:1425–1431.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|