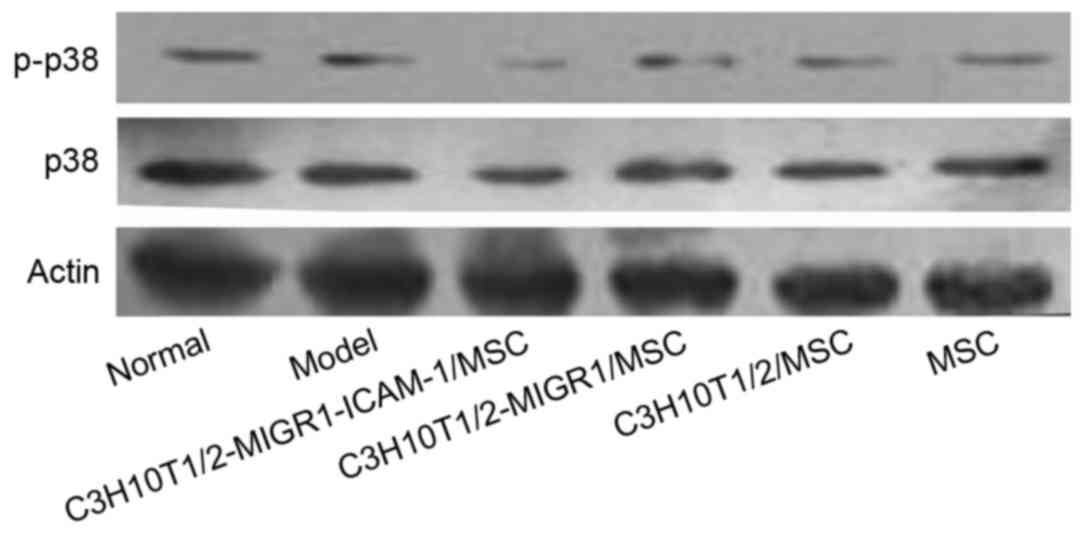
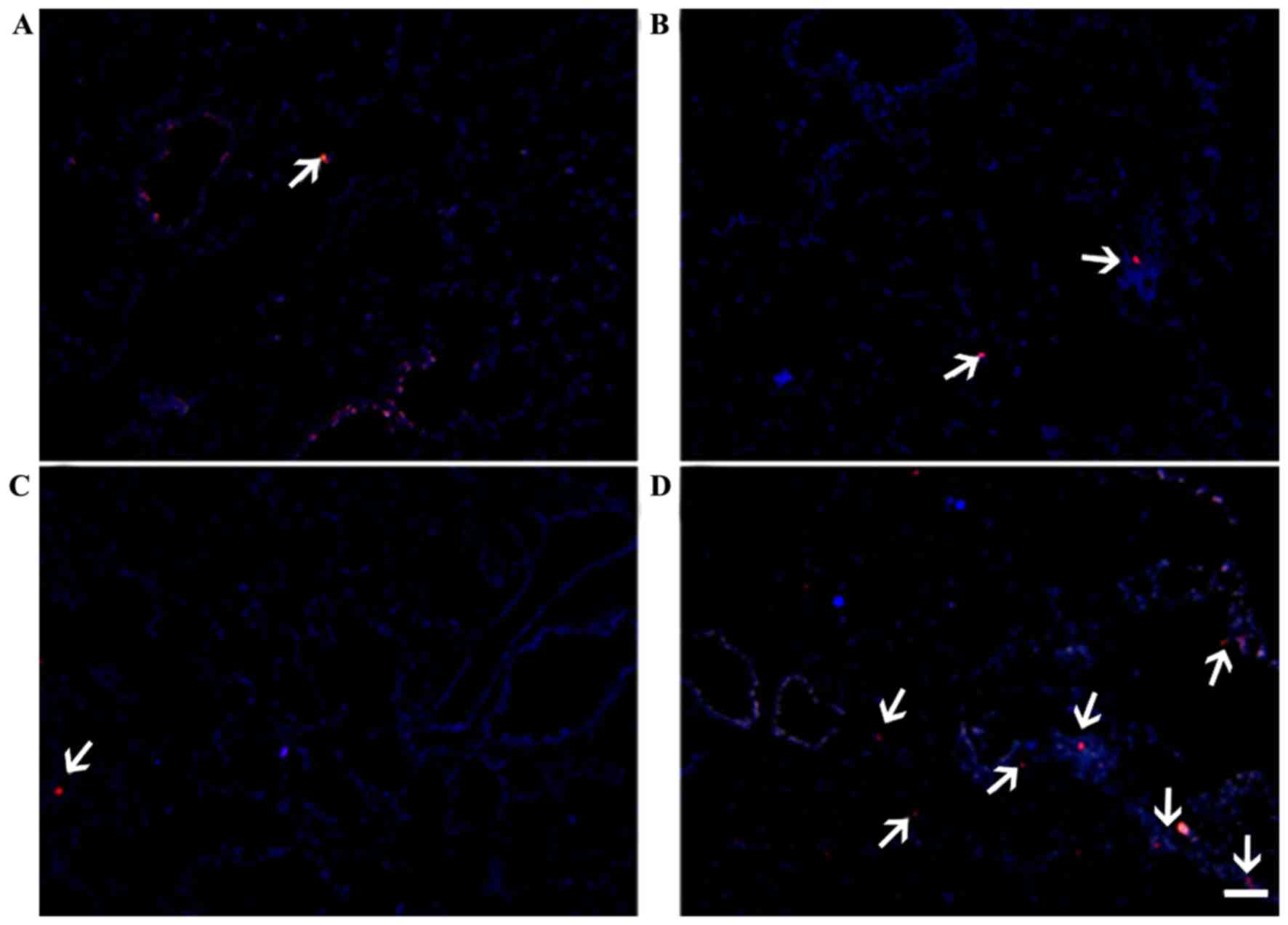
|
1
|
Chistiakov DA: Immunogenetics of
Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J Autoimmune Dis. 2:12005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Vries L, Bulvik S and Phillip M:
Chronic autoimmune thyroiditis in children and adolescents: At
presentation and during long-term follow-up. Arch Dis Child.
94:33–37. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeBoer MD and LaFranchi S: Differential
presentation for children with autoimmune thyroiditis discovered
because of symptomdevelopment or screening. J Pediatr Endocrinol
Metab. 21:753–761. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lichiardopol C and Mota M: The thyroid and
autoimmunity. Rom J Intern Med. 47:207–215. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Heymann WR: Chronic urticaria and
angioedema associated with thyroid autoimmunity: Review and
therapeutic implications. J Am Acad Dermatol. 40:229–232. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cipriani P, Carubbi F, Liakouli V,
Marrelli A, Perricone C, Perricone R, Alesse E and Giacomelli R:
Stem cells in autoimmune diseases: Implications for pathogenesis
and future trends in therapy. Autoimmun Rev. 12:709–716. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oreffo RO, Cooper C, Mason C and Clements
M: Mesenchymal stem cells: Lineage, plasticity, and skeletal
therapeutic potential. Stem Cell Rev. 1:169–178. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding DC, Shyu WC and Lin SZ: Mesenchymal
stem cells. Cell Transplant. 20:5–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu S, Yuan M, Hou K, Zhang L, Zheng X,
Zhao B, Sui X, Xu W, Lu S and Guo Q: Immune characterization of
mesenchymal stem cells in human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and
derived cartilage cells. Cell Immunol. 278:35–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wada N, Gronthos S and Bartold PM:
Immunomodulatory effects of stem cells. Periodontol 2000.
63:198–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Buschmann K, Koch L, Braach N, Mueller H,
Frommhold D, Poeschl J and Ruef P: CXCL1-triggered interaction of
LFA1 and ICAM1 control glucose-induced leukocyte recruitment during
inflammation in vivo. Mediators inflamm. 2012:7391762012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen JD, Xu FF, Zhu H, Li XM, Tang B, Liu
YL and Zhang Y: ICAM-1 regulates differentiation of MSC to
adipocytes via activating MAPK pathway. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue
Za Zhi. 22:160–165. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kong YC: Experimental autoimmune
thyroiditis in the mouse. Curr Protoc Immunol. 15:Unit
15.72007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prassopoulos P, Daskalogiannaki M,
Raissaki M, Hatjidakis A and Gourtsoyiannis N: Determination of
normal splenic volume on computed tomography in relation to age,
gender and body habitus. Eru Radiol. 7:246–248. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-tie quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nagayama Y, Horie I, Saitoh O, Nakahara M
and Abiru N: CD4+ CD25+ naturally occurring regulatory T cells and
not lymphopenia play a role in the pathogenesis of iodide-induced
autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD-H2 h4 mice. J Autoimmun. 29:195–202.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Armengol MP, Juan M, Lucas-Martín A,
Fernández-Figueras MT, Jaraquemada D, Gallart T and Pujol-Borrell
R: Thyroid autoimmune disease: Demonstration of thyroid
antigen-specific B cells and recombination-activating gene
expression in chemokine-containing active intrathyroidal germinal
centers. Am J Pathol. 159:861–873. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Choi EW, Shin IS, Lee HW, Park SY, Park
JH, Nam MH, Kim JS, Woo SK, Yoon EJ, Kang SK, et al:
Transplantation of CTLA4Ig gene-transduced adipose tissue-derived
mesenchymal stem cells reduces inflammatory immune response and
improves Th1/Th2 balance in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. J
Gene Med. 13:3–16. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang SK, Shin IS, Ko MS, Jo JY and Ra JC:
Journey of mesenchymal stem cells for homing: Strategies to enhance
efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Int.
2012:3429682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H,
Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T and Nomura T: Foxp3+
CD25+ CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance
and autoimmune disease. Immunol rev. 212:8–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wing K and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T cells
exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat
Immunol. 11:7–13. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yudoh K, Matsuno H, Nakazawa F, Yonezawa T
and Kimura T: Reduced expression of the regulatory CD4+ T cell
subset is related to Th1/Th2 balance and disease severity in
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 43:617–627. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arbabi S and Maier RV: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases. Crit Care Med. 30 Suppl 1:S74–S79. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Schett G, Tohidast-Akrad M, Smolen JS,
Schmid BJ, Steiner CW, Bitzan P, Zenz P, Redlich K, Xu Q and
Steiner G: Activation, differential localization, and regulation of
the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular
signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 43:2501–2512. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao L, Liu X, Liang J, Han S, Wang Y, Yin
Y, Luo Y and Li J: Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK mediates hypoxic
preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemic
injury via mitochondria translocation of Bcl-xL in mice. Brain Res.
1503:78–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ren G, Zhao X, Zhang L, Zhang J,
L'Huillier A, Ling W, Roberts AI, Le AD, Shi S, Shao C and Shi Y:
Inflammatory cytokine-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in mesenchymal stem cells are
critical for immunosuppression. J immunol. 184:2321–2328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luz-Crawford P, Noël D, Fernandez X,
Khoury M, Figueroa F, Carrión F, Jorgensen C and Djouad F:
Mesenchymal stem cells repress Th17 molecular program through the
PD-1 pathway. PLoS One. 7:e452722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Deng J, Zou ZM, Zhou TL, Su YP, Ai GP,
Wang JP, Xu H and Dong SW: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can
be mobilized into peripheral blood by G-CSF in vivo and integrate
into traumatically injured cerebral tissue. Neurolo Sci.
32:641–651. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yen BL, Huang HI, Chien CC, Jui HY, Ko BS,
Yao M, Shun CT, Yen ML, Lee MC and Chen YC: Isolation of
multipotent cells from human term placenta. Stem Cells. 23:3–9.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|