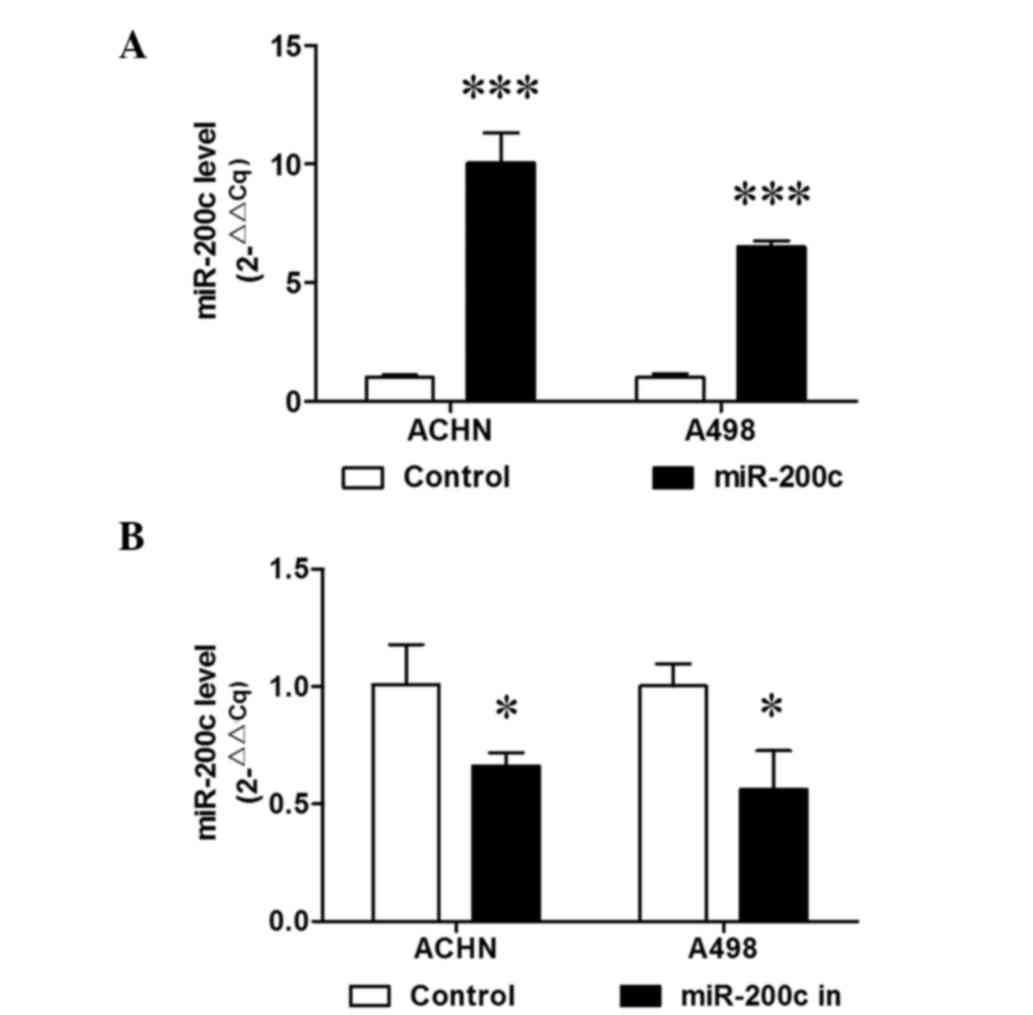
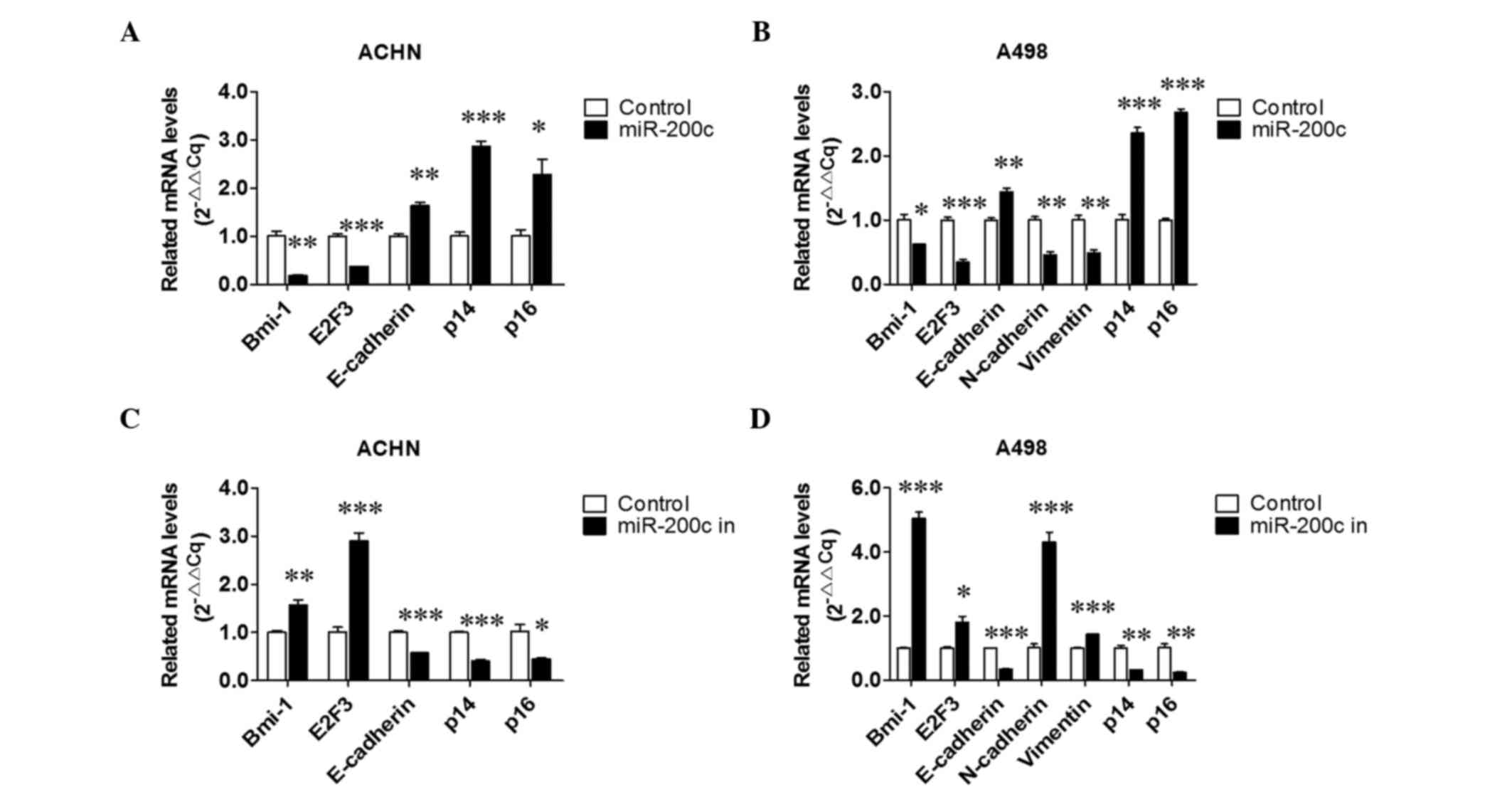
|
1
|
Brown M, Suryawanshi H, Hafner M, Farazi
TA and Tuschl T: Mammalian miRNA curation through next-generation
sequencing. Front Genet. 4:1452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pavelic S Kraljevic, Sedic M, Bosnjak H,
Spaventi S and Pavelic K: Metastasis: New perspectives on an old
problem. Mol Cancer. 10:222011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang L, Li J and Song L: Bmi-1, stem
cells and cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 41:527–534.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Olsson AY, Feber A, Edwards S, Te Poele R,
Giddings I, Merson S and Cooper CS: Role of E2F3 expression in
modulating cellular proliferation rate in human bladder and
prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 26:1028–1037. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, Feng Y, Yu CP, Hu
LJ, Kong QL, Xu LH, Zhang X, Liu WL, et al: The polycomb group
protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN and induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3626–3636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim JH, Yoon SY, Kim CN, Joo JH, Moon SK,
Choe IS, Choe YK and Kim JW: The Bmi-1 oncoprotein is overexpressed
in human colorectal cancer and correlates with the reduced
p16INK4a/p14ARF proteins. Cancer Lett. 203:217–224. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Silva J, Garcia JM, Peña C, García V,
Domínguez G, Suárez D, Camacho FI, Espinosa R, Provencio M, España
P and Bonilla F: Implication of polycomb members Bmi-1, Mel-18 and
Hpc-2 in the regulation of p16INK4a, p14ARF, h-TERT, and c-Myc
expression in primary breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res.
12:6929–6936. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Feng X, Wang Z, Fillmore R and Xi Y:
MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett.
344:166–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mongroo PS and Rustgi AK: The role of the
miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol
Ther. 10:219–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Korpal M and Kang Y: The emerging role of
miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol. 5:115–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park SM, Gaur AB, Lengyel E and Peter ME:
The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer
cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes
Dev. 22:894–907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Chen X, Wang R, Xiao P, Xu Z, Chen
L, Hang W, Ruan A, Yang H and Zhang X: MicroRNA-200c modulates the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human renal cell carcinoma
metastasis. Oncol Rep. 30:643–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stadler WM: Maturing of renal cancer
therapeutics. J Clin Oncol. 32:722–724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang H, Fang F, Chang R and Yang L:
MicroRNA-140-5p suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
transforming growth factor β receptor 1 and fibroblast growth
factor 9 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 58:205–217. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wiklund ED, Bramsen JB, Hulf T, Dyrskjøt
L, Ramanathan R, Hansen TB, Villadsen SB, Gao S, Ostenfeld MS,
Borre M, et al: Coordinated epigenetic repression of the miR-200
family and miR-205 in invasive bladder cancer. Int J Cancer.
128:1327–1334. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Castro-Vega LJ, Jouravleva K, Liu WY,
Martinez C, Gestraud P, Hupé P, Servant N, Albaud B, Gentien D, Gad
S, et al: Telomere crisis in kidney epithelial cells promotes the
acquisition of a microRNA signature retrieved in aggressive renal
cell carcinomas. Carcinogenesis. 34:1173–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakada C, Matsuura K, Tsukamoto Y,
Tanigawa M, Yoshimoto T, Narimatsu T, Nguyen LT, Hijiya N, Uchida
T, Sato F, et al: Genome-wide microRNA expression profiling in
renal cell carcinoma: Significant down-regulation of miR-141 and
miR-200c. J Pathol. 216:418–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kong D, Li Y, Wang Z, Banerjee S, Ahmad A,
Kim HR and Sarkar FH: MiR-200 regulates PDGFDmediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion, and invasion of
prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells. 27:1712–1721. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Li Y, Wang Z,
Sethi S and Sarkar FH: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is
mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer
cells. PloS One. 5:e124452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu J, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Sato N,
Kayashima T, Fujita H, Nakata K and Tanaka M: MicroRNA,
hsa-miR-200c, is an independent prognostic factor in pancreatic
cancer and its upregulation inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion but
increases cell proliferation. Mol Cancer. 9:1692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, Lobo N,
Dalerba P, Qian D, Diehn M, Liu H, Panula SP, Chiao E, et al:
Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with
normal stem cells. Cell. 138:592–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu X, Jiang X, Li H, Guo L, Jiang W and Lu
SH: MiR-203 inhibits the proliferation and self-renewal of
esophageal cancer stem-like cells by suppressing stem renewal
factor Bmi-1. Stem Cells Dev. 23:576–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feber A, Clark J, Goodwin G, Dodson AR,
Smith PH, Fletcher A, Edwards S, Flohr P, Falconer A, Roe T, et al:
Amplification and overexpression of E2F3 in human bladder cancer.
Oncogene. 23:1627–1630. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Foster CS, Falconer A, Dodson AR, Norman
AR, Dennis N, Fletcher A, Southgate C, Dowe A, Dearnaley D, Jhavar
S, et al: Transcription factor E2F3 overexpressed in prostate
cancer independently predicts clinical outcome. Oncogene.
23:5871–5879. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lukas J, Parry D, Aagaard L, Mann DJ,
Bartkova J, Strauss M, Peters G and Bartek J:
Retinoblastoma-protein-dependent cell-cycle inhibition by the
tumour suppressor p16. Nature. 375:503–536. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Molofsky AV, He S, Bydon M, Morrison SJ
and Pardal R: Bmi-1 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal and
neural development but not mouse growth and survival by repressing
the p16Ink4a and p19Arf senescence pathways. Genes Dev.
19:1432–1437. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y, Xiong Y and Yarbrough WG: ARF
promotes MDM2 degradation and stabilizes p53: ARF-INK4a locus
deletion impairs both the Rb and p53 tumor suppression pathways.
Cell. 92:725–734. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nilsson K and Landberg G: Subcellular
localization, modification and protein complex formation of the
cdk-inhibitor p16 in Rb-functional and Rb-inactivated tumor cells.
Int J Cancer. 118:1120–1125. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|