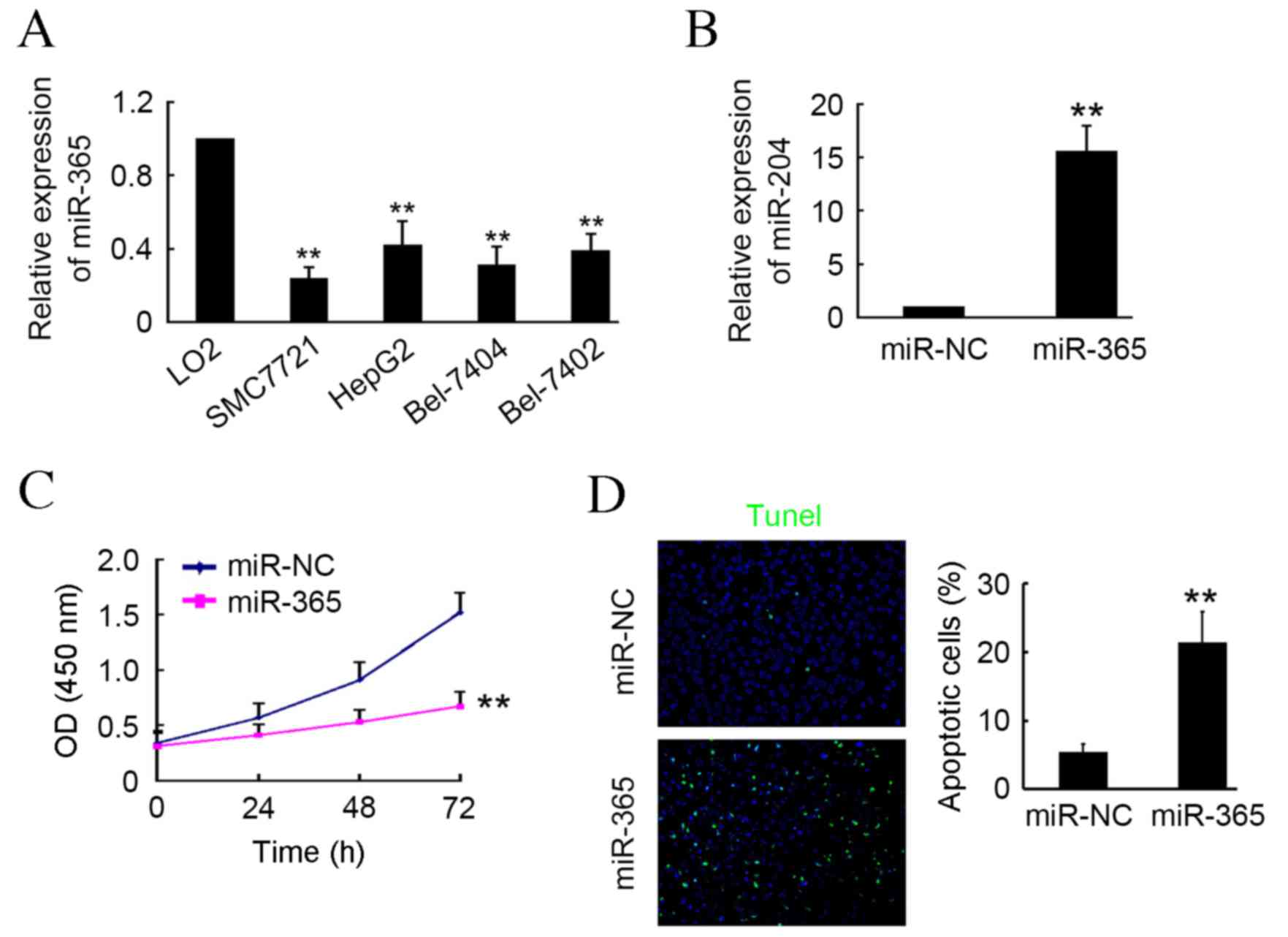
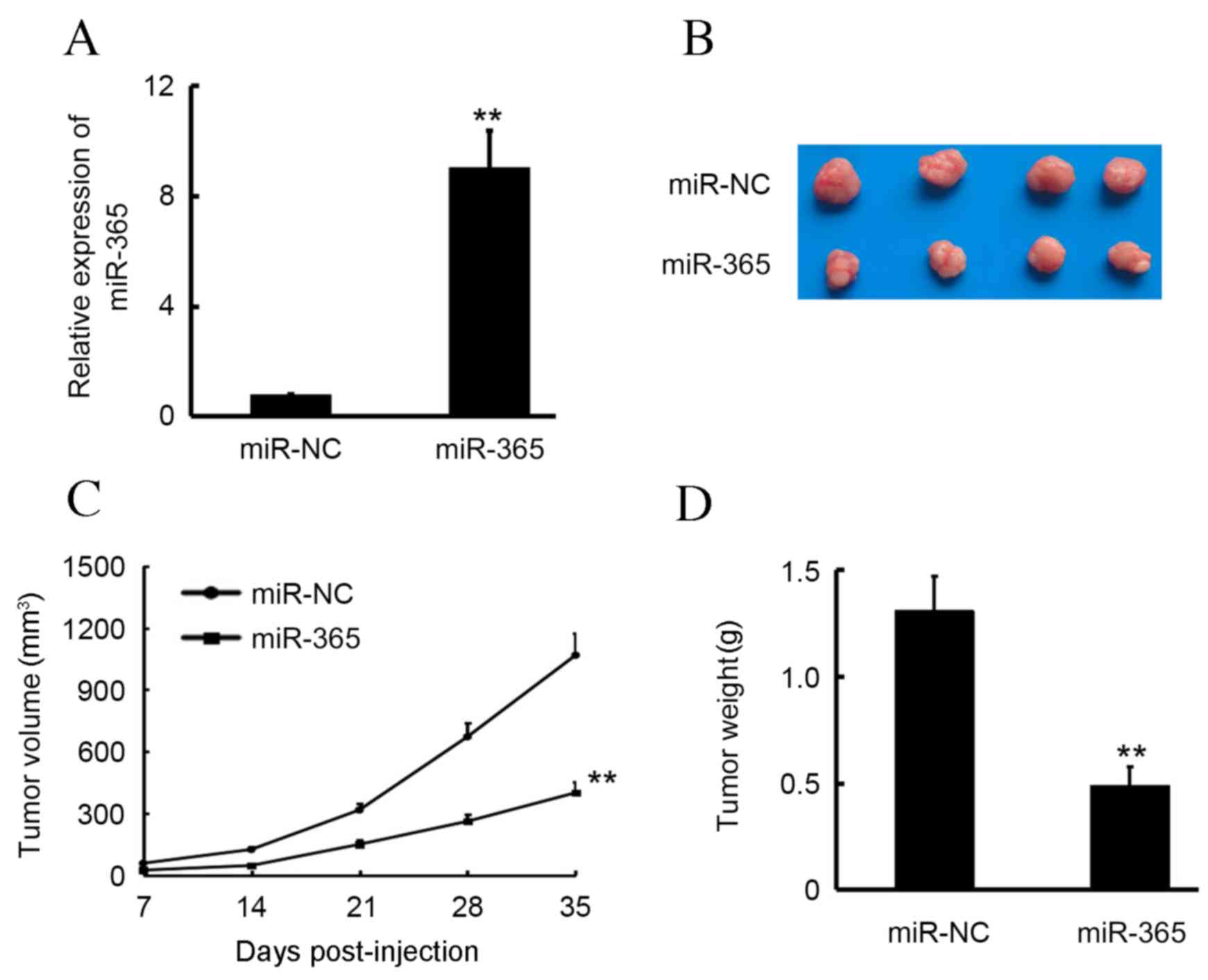
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ariff B, Lloyd CR, Khan S, Shariff M,
Thillainayagam AV, Bansi DS, Khan SA, Taylor-Robinson SD and Lim
AK: Imaging of liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1289–1300.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marrero JA, Feng Z, Wang Y, Nguyen MH,
Befeler AS, Roberts LR, Reddy KR, Harnois D, Llovet JM, Normolle D,
et al: Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma carboxyprothrombin, and
lectin-bound alpha-fetoprotein in early hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 137:110–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Borel F, Konstantinova P and Jansen PL:
Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of miRNA signatures in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:1371–1383.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruix J, Llovet JM, Castells A, Montañá X,
Brú C, Ayuso MC, Vilana R and Rodés J: Transarterial embolization
versus symptomatic treatment in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of a randomized, controlled trial
in a single institution. Hepatology. 27:1578–1583. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Anwar SL and Lehmann U: MicroRNAs:
Emerging novel clinical biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinomas. J
Clin Med. 4:1631–1650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He J, Zhao K, Zheng L, Xu Z, Gong W, Chen
S, Shen X, Huang G, Gao M, Zeng Y, et al: Upregulation of
microRNA-122 by farnesoid X receptor suppresses the growth of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 14:1632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giordano S and Columbano A: MicroRNAs: New
tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma? Hepatology. 57:840–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang XW, Heegaard NH and Orum H: MicroRNAs
in liver disease. Gastroenterology. 142:1431–1443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hamada S, Masamune A, Miura S, Satoh K and
Shimosegawa T: MiR-365 induces gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic
cancer cells by targeting the adaptor protein SHC1 and
pro-apoptotic regulator BAX. Cell Signal. 26:179–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nie J, Liu L, Zheng W, Chen L, Wu X, Xu Y,
Du X and Han W: microRNA-365, down-regulated in colon cancer,
inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis of colon
cancer cells by probably targeting Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2.
Carcinogenesis. 33:220–225. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Z, Huang Z, Ye Q, Ming Y, Zhang S,
Zhao Y, Liu L, Wang Q and Cheng K: Prognostic significance and
anti-proliferation effect of microRNA-365 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1705–1711. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai L, Cui X, Zhang X, Cheng L, Liu Y,
Yang Y, Fan P, Wang Q, Lin Y, Zhang J, et al: SARI inhibits
angiogenesis and tumour growth of human colon cancer through
directly targeting ceruloplasmin. Nat Commun. 7:119962016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ghidini M and Braconi C: Non-Coding RNAs
in primary liver cancer. Front Med (Lausanne). 2:362015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei R, Huang GL, Zhang MY, Li BK, Zhang
HZ, Shi M, Chen XQ, Huang L, Zhou QM, Jia WH, et al: Clinical
significance and prognostic value of microRNA expression signatures
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:4780–4791. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wong CM, Wong CC, Lee JM, Fan DN, Au SL
and Ng IO: Sequential alterations of microRNA expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma development and venous metastasis.
Hepatology. 55:1453–1461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C,
Bioulac-Sage P, Pelletier L, Rebouissou S and Zucman-Rossi J:
MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with
clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations.
Hepatology. 47:1955–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang S and He X: The role of microRNAs in
liver cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 104:235–240. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salvi A, Abeni E, Portolani N, Barlati S
and De Petro G: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell-specific miRNAs
reveal the differential expression of miR-24 and miR-27a in
cirrhotic/non-cirrhotic HCC. Int J Oncol. 42:391–402.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meng FL, Wang W and Jia WD: Diagnostic and
prognostic significance of serum miR-24-3p in HBV-related
hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:1772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma Y, She XG, Ming YZ and Wan QQ: miR-24
promotes the proliferation and invasion of HCC cells by targeting
SOX7. Tumour Biol. 35:10731–10736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lockshin RA and Williams CM: Programmed
cell death-i. Cytology of degeneration in the intersegmental
muscles of the pernyi silkmoth. J Insect Physiol. 11:123–133. 1965.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thomas S, Quinn BA, Das SK, Dash R, Emdad
L, Dasgupta S, Wang XY, Dent P, Reed JC, Pellecchia M, et al:
Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:61–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin B, Xiao B, Liang D, Xia J, Li Y and
Yang H: MicroRNAs expression in ox-LDL treated HUVECs: MiR-365
modulates apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 410:127–133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|