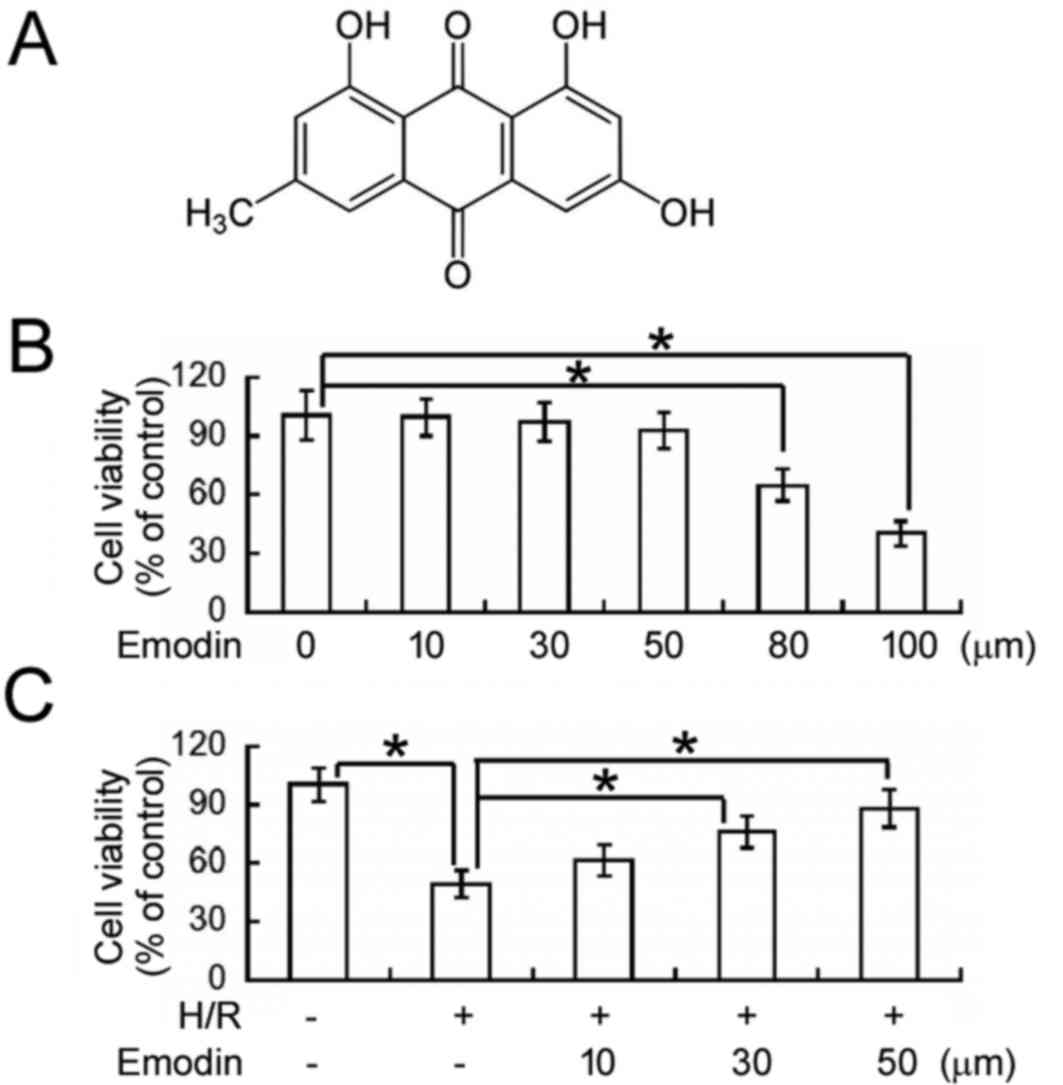
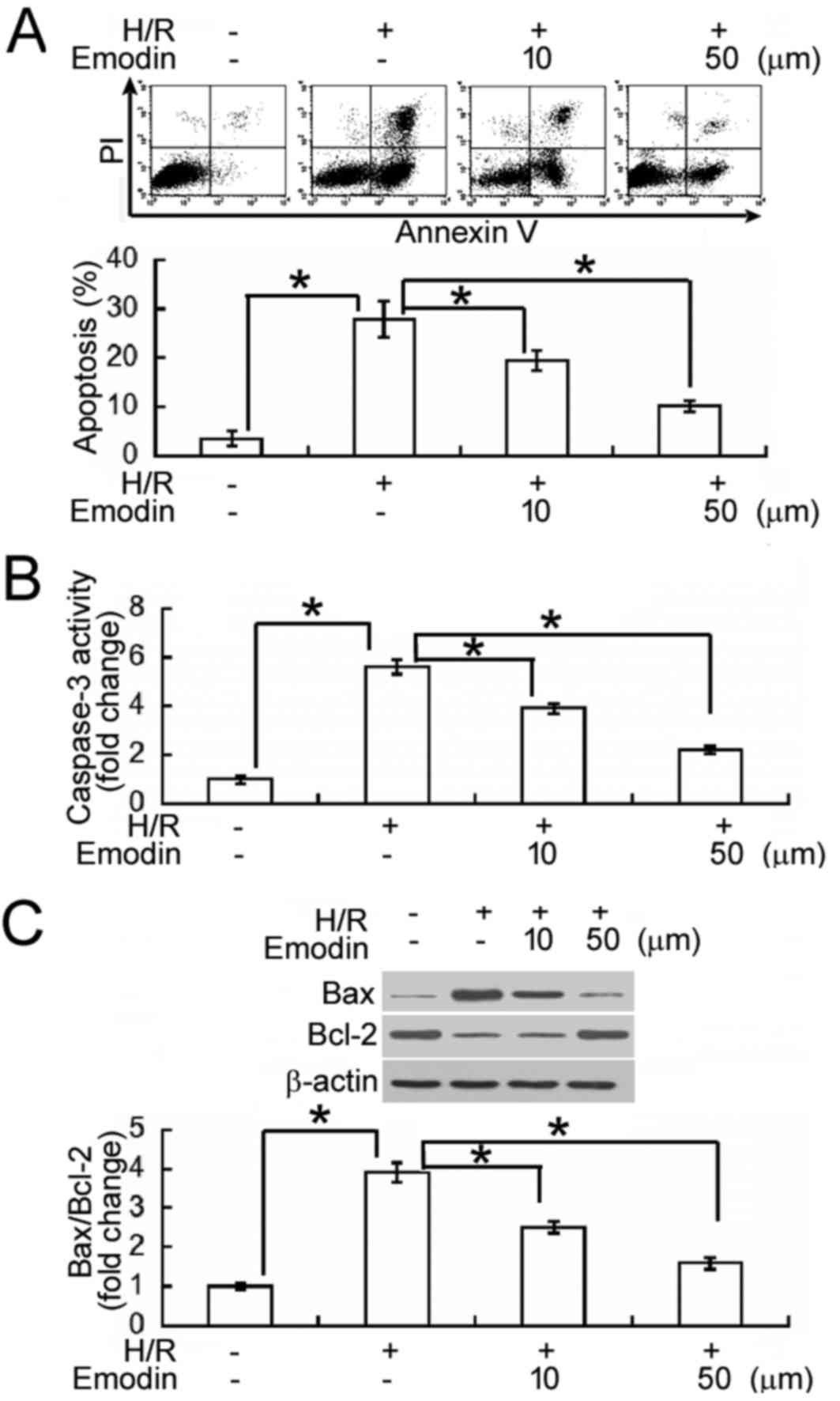
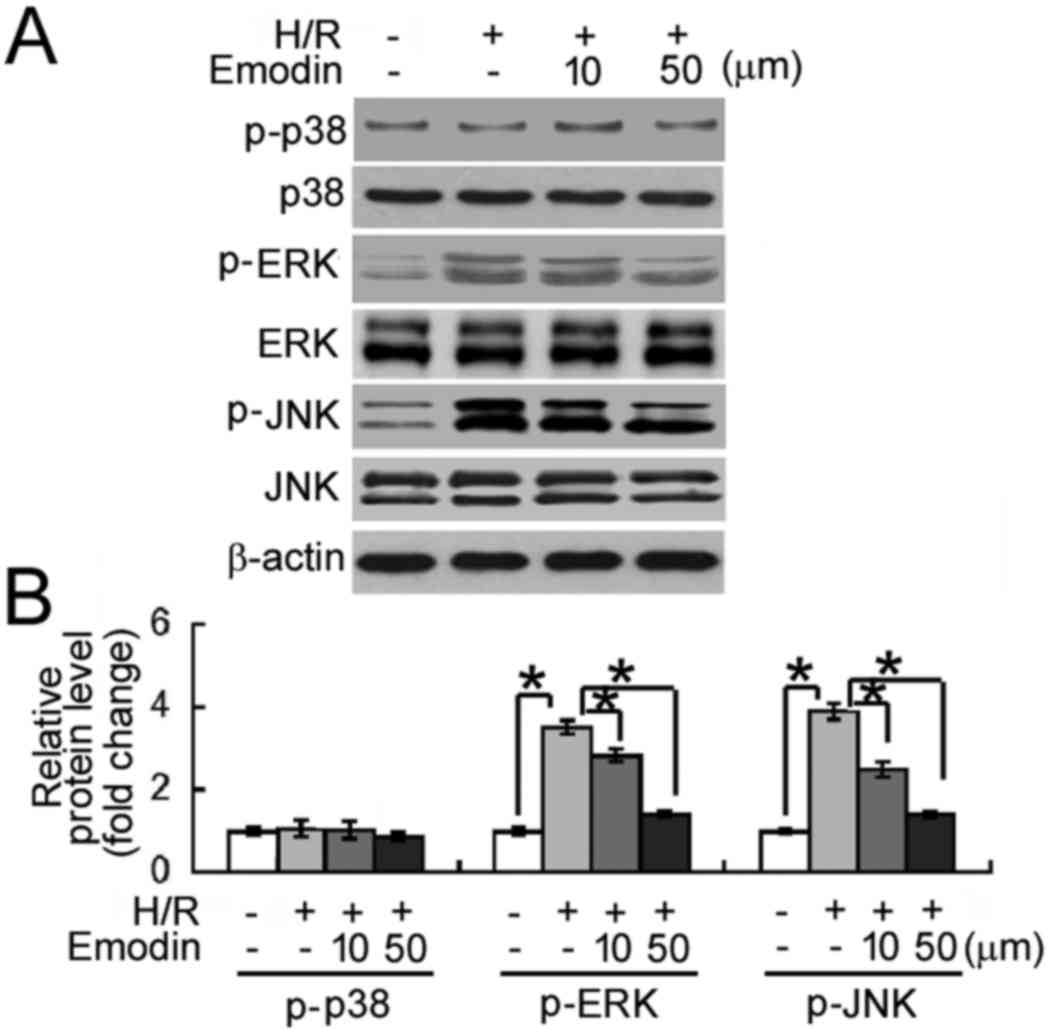
|
1
|
Lee D, Park S, Bae S, Jeong D, Park M,
Kang C, Yoo W, Samad MA, Ke Q, Khang G and Kang PM: Hydrogen
peroxide-activatable antioxidant prodrug as a targeted therapeutic
agent for ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. 5:165922015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y, Liao H, Zhong S, Gao F, Chen Y,
Huang Z, Lu S, Sun T, Wang B, Li W, et al: Effect of N-n-butyl
haloperidol iodide on ROS/JNK/Egr-1 signaling in H9c2 cells after
hypoxia/reoxygenation. Sci Rep. 5:118092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang
DG and Pae HO: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive
oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal
Transduct. 2011.792–639. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Kunduzova OR, Bianchi P, Pizzinat N,
Escourrou G, Seguelas MH, Parini A and Cambon C: Regulation of
JNK/ERK activation, cell apoptosis, and tissue regeneration by
monoamine oxidases after renal ischemia-reperfusion. FASEB J.
16:1129–1131. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aichner D and Ganzera M: Analysis of
anthraquinones in rhubarb (Rheum palmatumRheum officinale) by
supercritical fluid chromatography. Talanta. 144:1239–1244. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen R, Zhang J, Hu Y, Wang S, Chen M and
Wang Y: Potential antineoplastic effects of Aloe-emodin: A
comprehensive review. Am J Chin Med. 42:275–288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Y, Tu X, Lin G, Xia H, Huang H, Wan J,
Cheng Z, Liu M, Chen G, Zhang H, et al: Emodin-mediated protection
from acute myocardial infarction via inhibition of inflammation and
apoptosis in local ischemic myocardium. Life Sci. 81:1332–1338.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du Y and Ko KM: Effects of emodin
treatment on mitochondrial ATP generation capacity and antioxidant
components as well as susceptibility to ischemia-reperfusion injury
in rat hearts: Single versus multiple doses and gender difference.
Life Sci. 77:2770–2782. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guan X, Qian Y, Shen Y, Zhang L, Du Y, Dai
H, Qian J and Yan Y: Autophagy protects renal tubular cells against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in a time-dependent manner. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:285–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou T, Chuang CC and Zuo L: Molecular
characterization of reactive oxygen species in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Res Int. 2015:8649462015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duan J, Guan Y, Mu F, Guo C, Zhang E, Yin
Y, Wei G, Zhu Y, Cui J, Cao J, et al: Protective effect of butin
against ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in diabetic
mice: Involvement of the AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Sci
Rep. 7:414912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai Q, Ma T, Li C, Tian Y and Li H:
Catalpol protects pre-myelinating oligodendrocytes against
ischemia-induced oxidative injury through ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Int J Biol Sci. 12:1415–1426. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zu G, Guo J, Che N, Zhou T and Zhang X:
Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 on intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis
via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 6:384802016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xue WH, Shi XQ, Liang SH, Zhou L, Liu KF
and Zhao J: Emodin attenuates cigarette smoke induced lung injury
in a mouse model via suppression of reactive oxygen species
production. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 29:526–532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nemmar A, Al-Salam S, Yuvaraju P, Beegam S
and Ali BH: Emodin mitigates diesel exhaust particles-induced
increase in airway resistance, inflammation and oxidative stress in
mice. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 215:51–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki C, Isaka Y, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y,
Takabatake Y, Ito T, Takahara S and Imai E: Bcl-2 protects tubular
epithelial cells from ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting
apoptosis. Cell Transplant. 17:223–229. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kvansakul M and Hinds MG: The Bcl-2
family: Structures, interactions and targets for drug discovery.
Apoptosis. 20:136–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bae EH, Cho S, Joo SY, Ma SK, Kim SH, Lee
J and Kim SW: 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal-induced apoptosis in human renal
proximal tubular epithelial cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
26:3866–3873. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park SY, Jin ML, Ko MJ, Park G and Choi
YW: Anti-neuroinflammatory effect of emodin in LPS-stimulated
microglia: Involvement of AMPK/Nrf2 activation. Neurochem Res.
41:2981–2992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin JT, Wan B, Liu DD, Wan SX, Fu HY, Wan
Y, Zhang H and Chen Y: Emodin alleviates lung injury in rats with
sepsis. J Surg Res. 202:308–314. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|