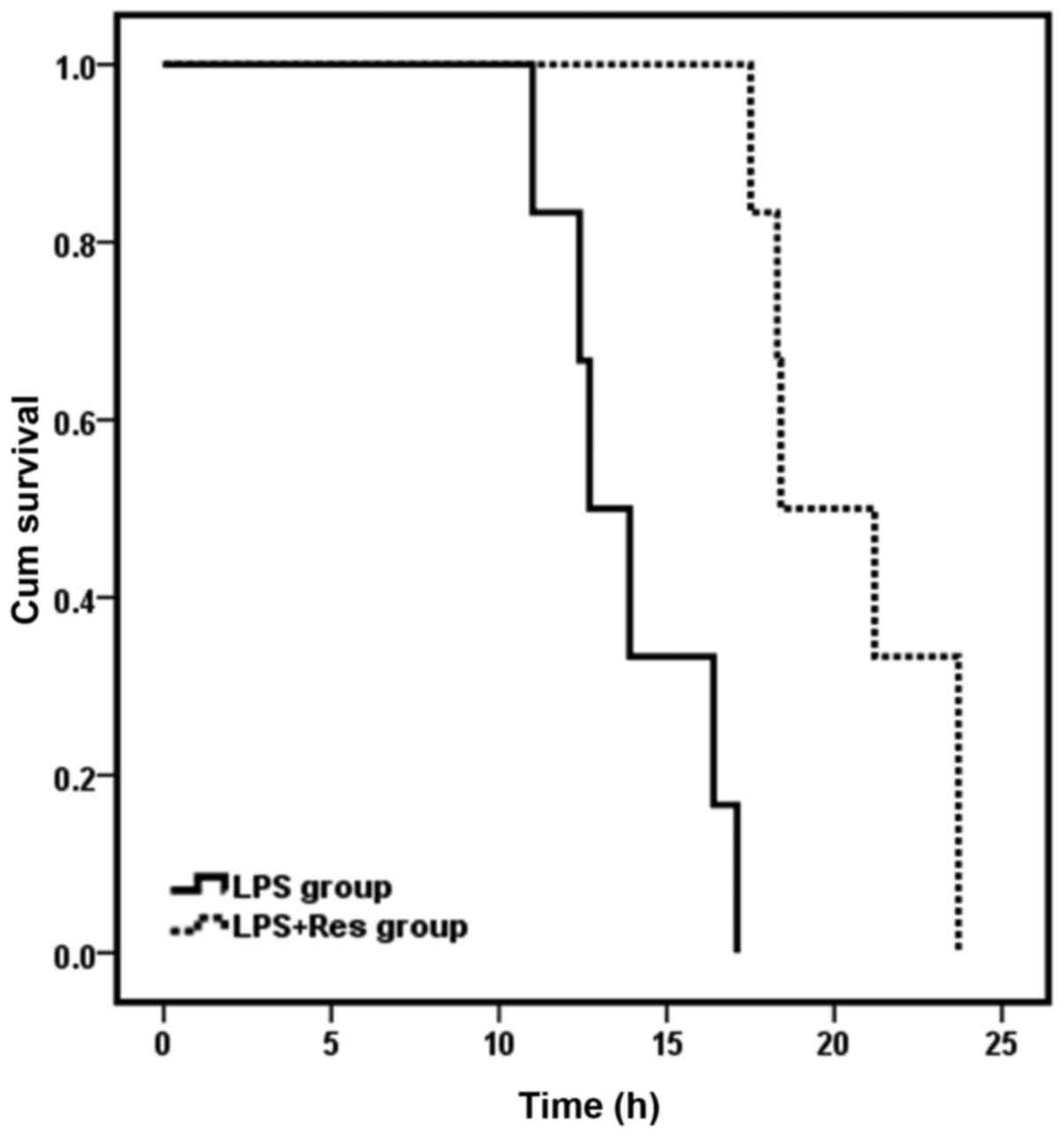
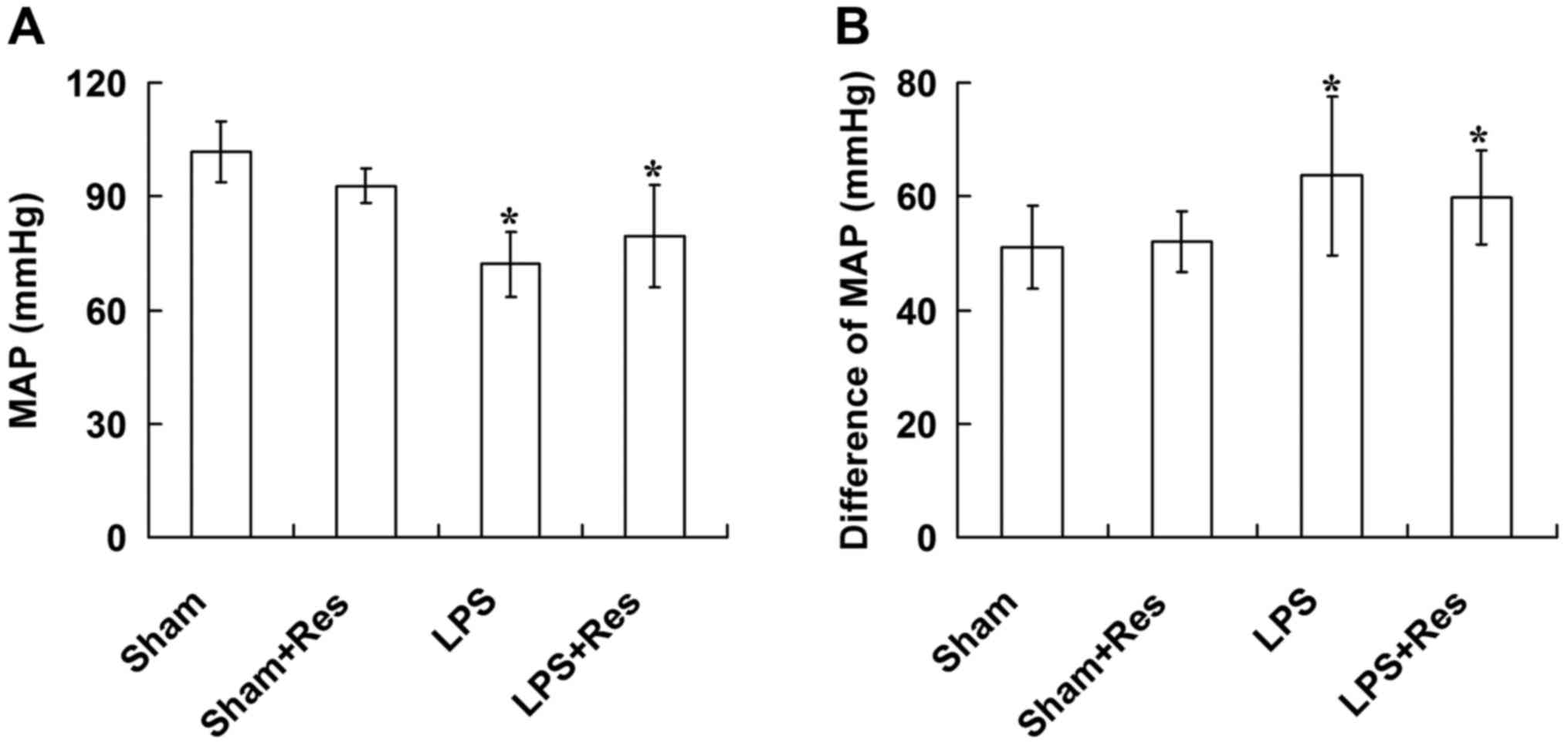
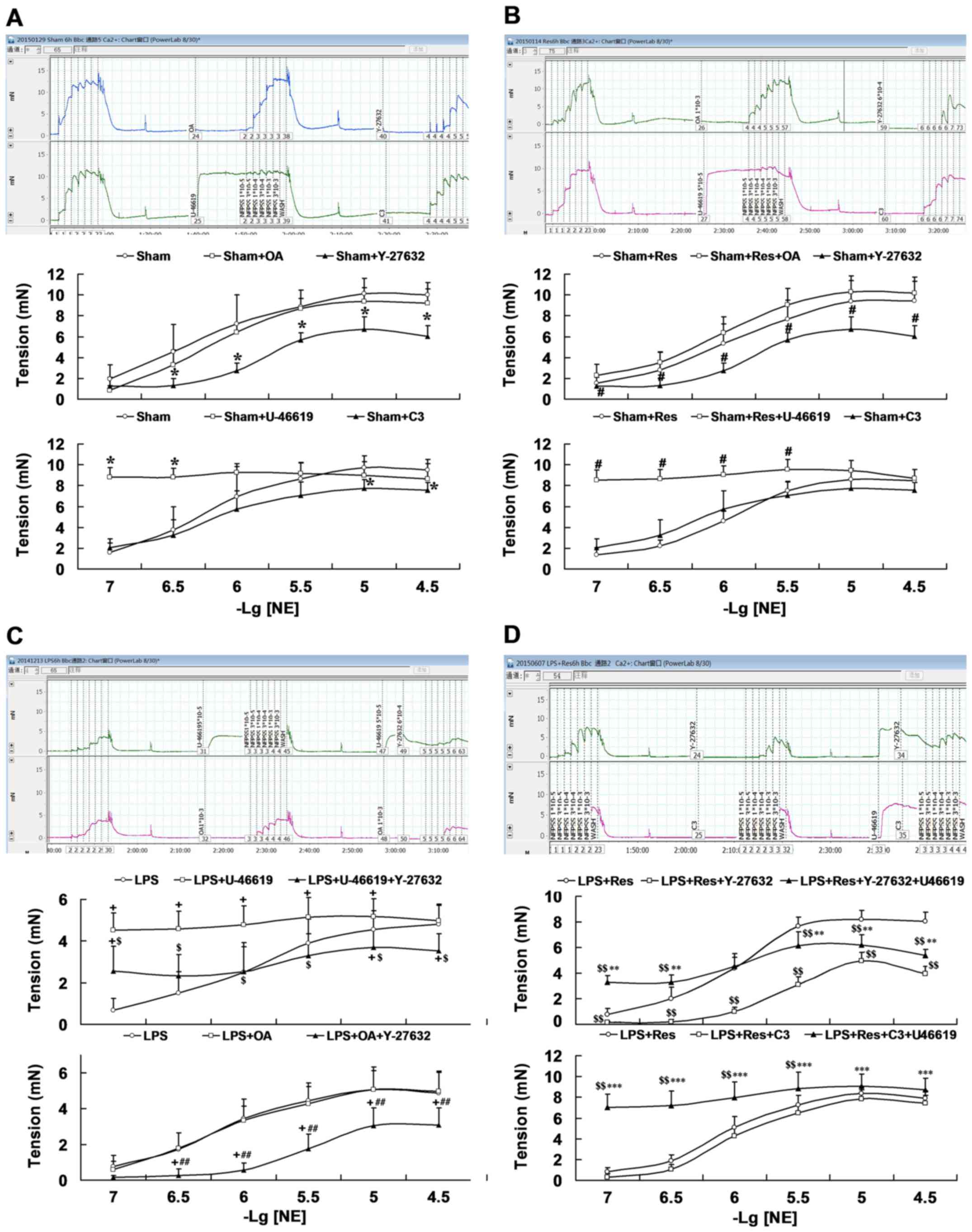
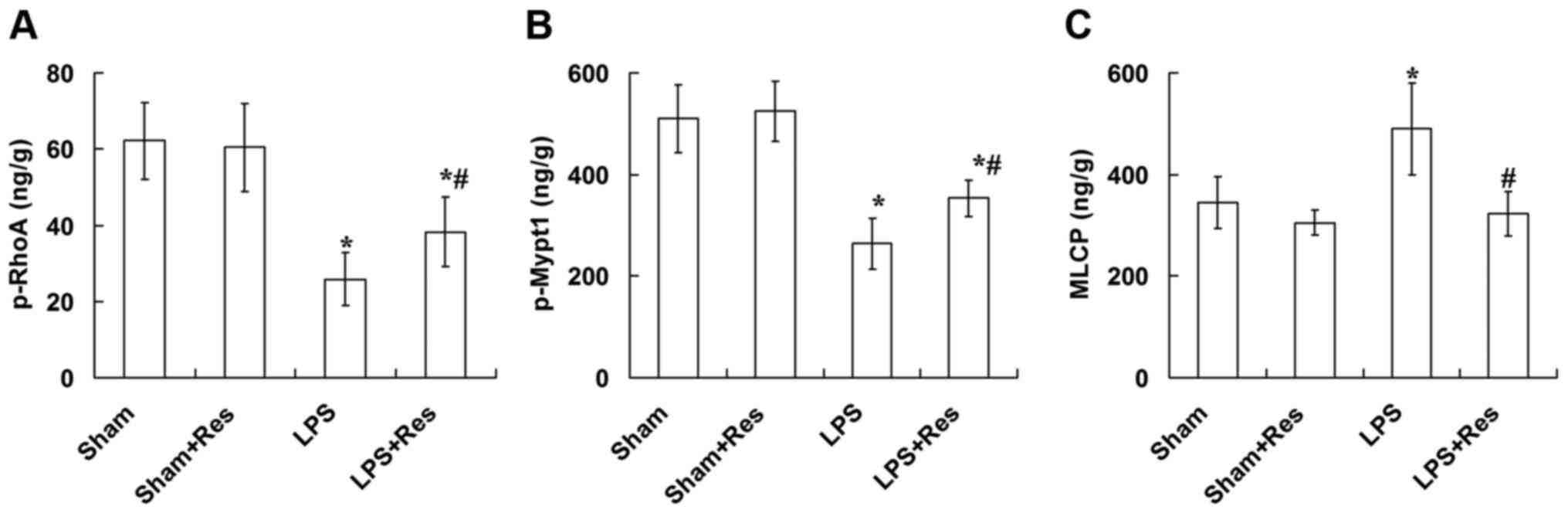
|
1
|
Maloney PJ: Sepsis and septic shock. Emerg
Med Clin North Am. 31:583–600. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Angus DC and van der Poll T: Severe sepsis
and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 369:840–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsao CM, Chen SJ, Tsou MY and Wu CC:
Effect of propofol on vascular reactivity in thoracic aortas from
rats with endotoxemia. J Chin Med Assoc. 75:262–268. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liang JL, Yang GM, Li T and Liu LM:
Interleukin 1β attenuates vascular α1 adrenergic receptors
expression following lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in
rabbits: Involvement of JAK2-STAT3 pathway. J Trauma Acute Care
Surg. 76:762–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piotrowska H, Kucinska M and Murias M:
Biological activity of piceatannol: Leaving the shadow of
resveratrol. Mutat Res. 750:60–82. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kuršvietienė L, Stanevičienė I,
Mongirdienė A and Bernatonienė J: Multiplicity of effects and
health benefits of resveratrol. Medicina (Kaunas). 52:148–155.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kolgazi M, Sener G, Cetinel S, Gedik N and
Alican I: Resveratrol reduces renal and lung injury caused by
sepsis in rats. J Surg Res. 134:315–321. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu W, Lu Y, Yao J, Li Z, Chen Z, Wang G,
Jing H, Zhang X, Li M, Peng J and Tian X: Novel role of
resveratrol: Suppression of high-mobility group protein box 1
nucleocytoplasmic translocation by the upregulation of sirtuin 1 in
sepsis-induced liver injury. Shock. 42:440–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang HX, Duan GL, Wang CN, Zhang YQ, Zhu
XY and Liu YJ: Protective effect of resveratrol against
endotoxemia-induced lung injury involves the reduction of
oxidative/nitrative stress. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 27:150–155. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sebai H, Sani M, Aouani E and
Ghanem-Boughanmi N: Cardioprotective effect of resveratrol on
lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in rat. Drug Chem
Toxicol. 34:146–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sebai H, Sani M, Yacoubi MT, Aouani E,
Ghanem-Boughanmi N and Ben-Attia M: Resveratrol, a red wine
polyphenol, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress
in rat liver. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 73:1078–1083. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao Q, Jing C, Tang X, Yin Y, Han X and Wu
W: Protective effect of resveratrol on acute lung injury induced by
lipopolysaccharide in mice. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 294:527–532. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Holthoff JH, Wang Z, Seely KA, Gokden N
and Mayeux PR: Resveratrol improves renal microcirculation,
protects the tubular epithelium, and prolongs survival in a mouse
model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Kidney Int.
81:370–378. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tseng TL, Chen MF, Liu CH, Pang CY, Hsu YH
and Lee TJ: Induction of endothelium-dependent constriction of
mesenteric arteries in endotoxemic hypotensive shock. Br J
Pharmacol. 173:1179–1195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liao MH, Shih CC, Tsao CM, Chen SJ and Wu
CC: RhoA/Rho-kinase and nitric oxide in vascular reactivity in rats
with endotoxaemia. PLoS One. 8:e563312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smeding L, Leong-Poi H, Hu P, Shan Y,
Haitsma JJ, Horvath E, Furmli S, Masoom H, Kuiper JW, Slutsky AS,
et al: Salutary effect of resveratrol on sepsis-induced myocardial
depression. Crit Care Med. 40:1896–1907. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai X, Pei Q, Song X, Zhou X, Yin Z, Jia
R, Zou Y, Li L, Yue G, Liang X, et al: The enhancement of immune
function and activation of NF-κB by resveratrol-treatment in
immunosuppressive mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 33:42–47. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu LM, Ward JA and Dubick MA:
Hemorrhage-induced vascular hyporeactivity to norepinephrine in
select vasculatures of rats and the roles of nitric oxide and
endothelin. Shock. 19:208–214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao ZG, Niu CY, Wei YL, Zhang YP, Si YH
and Zhang J: Mesenteric lymph return is an important contributor to
vascular hyporeactivity and calcium desensitization after
hemorrhagic shock. Shock. 38:186–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li A, Dong L, Duan ML, Sun K, Liu YY, Wang
MX, Deng JN, Fan JY, Wang BE and Han JY: Emodin improves
lipopolysaccharide-induced microcirculatory disturbance in rat
mesentery. Microcirculation. 20:617–628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Sun K, Liu YY, Zhang YP, Hu BH,
Chang X, Yan L, Pan CS, Li Q, Fan JY, et al: Ginsenoside Rb1
ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced albumin leakage from rat
mesenteric venules by intervening in both trans- and paracellular
pathway. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 306:G289–G300.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pei H, Zhang Y, Wu H, Ren L, Jia X, Zhang
Y and Chen M: Relationship between iNOS expression and apoptosis in
cerebral tissue, and the effect of sini injection in endotoxin
shock rats. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:486–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Liu B, Fukudome EY, Lu J, Chong W,
Jin G, Liu Z, Velmahos GC, Demoya M, King DR and Alam HB:
Identification of citrullinated histone H3 as a potential serum
protein biomarker in a lethal model of lipopolysaccharide-induced
shock. Surgery. 150:442–451. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu C, Zhang GF, Song SW, Cai GJ, Liu WH,
Miao CY and Su DE: Effects of ketanserin on endotoxic shock and
baroreflex function in rodents. J Infect Dis. 204:1605–1612. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Madonna R, Jiang J and Geng YJ: Attenuated
expression of gelsolin in association with induction of aquaporin-1
and nitric oxide synthase in dysfunctional hearts of aging mice
exposed to endotoxin. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 25:911–922.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Noworyta-Sokołowska K, Górska A and
Gołembiowska K: LPS-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory
reaction in the rat striatum. Pharmacol Rep. 65:863–869. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park EJ, Jang HJ, Tsoyi K, Kim YM, Park
SW, Kim HJ, Lee JH and Chang KC: The heme oxygenase-1 inducer
THI-56 negatively regulates iNOS expression and HMGB1 release in
LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells and CLP-induced septic mice. PLoS
One. 8:e762932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao T, Li Y, Liu B, Liu Z, Chong W, Duan
X, Deperalta DK, Velmahos GC and Alam HB: Novel pharmacologic
treatment attenuates septic shock and improves long-term survival.
Surgery. 154:206–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang K, Nan C, Fei D, Meng X, Liu W, Zhang
W, Jiang L and Zhao M, Pan S and Zhao M: Heme oxygenase 1 modulates
thrombomodulin and endothelial protein C receptor levels to
attenuate septic kidney injury. Shock. 40:136–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Olguner CG, Koca U, Altekin E, Ergür BU,
Duru S, Girgin P, Taşdöğen A, Gündüz K, Güzeldağ S, Akkuş M and
Micili SC: Ischemic preconditioning attenuates lipid peroxidation
and apoptosis in the cecal ligation and puncture model of sepsis.
Exp Ther Med. 5:1581–1588. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Buchholz BM, Chanthaphavong RS, Billiar TR
and Bauer AJ: Role of interleukin-6 in hemopoietic and
non-hemopoietic synergy mediating TLR4-triggered late murine ileus
and endotoxic shock. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 24:658–669, e294.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen L, Yang S, Zumbrun EE, Guan H,
Nagarkatti PS and Nagarkatti M: Resveratrol attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing
inflammation driven by macrophages. Mol Nutr Food Res. 59:853–864.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fatehi-Hassanabad Z, Muller B,
Andriantsitohaina R, Furman BL, Parratt JR and Stoclet JC:
Influence of indomethacin on the haemodynamic effects of
lipopolysaccharide in rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 10:258–263.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boffa JJ and Arendshorst WJ: Maintenance
of renal vascular reactivity contributes to acute renal failure
during endotoxemic shock. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:117–124. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shaikh WA, Patel M, Shah HD, Nimbalkar AS,
Patel N and Singh SK: Arterial blood pressure is inversely
associated with vascular sympathetic reactivity (isometric handgrip
exercise) in Gujarati Indian adolescents. Indian J Physiol
Pharmacol. 58:271–274. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bing RJ, Termin A, Conforto A, Dudek R and
Hoffmann MJ: Membrane function and vascular reactivity. Biosci Rep.
13:61–67. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ponnoth DS and Mustafa S Jamal: Adenosine
receptors and vascular inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1808:1429–1434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guzmán-Gutiérrez E, Arroyo P, Salsoso R,
Fuenzalida B, Sáez T, Leiva A, Pardo F and Sobrevia L: Role of
insulin and adenosine in the human placenta microvascular and
macrovascular endothelial cell dysfunction in gestational diabetes
mellitus. Microcirculation. 21:26–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liang JL, Yang GM, Li T and Liu LM:
Effects of interleukin-1β on vascular reactivity after
lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock in rabbits and its
relationship with PKC and Rho kinase. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
62:84–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Recoquillon S, Carusio N, Lagrue-Lakhal
AH, Tual-Chalot S, Filippelli A, Andriantsitohaina R and Martinez
MC: Interaction in endothelium of non-muscular myosin light-chain
kinase and the NF-κB pathway is critical to
lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular hyporeactivity. Clin Sci
(Lond). 129:687–698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu Y, Yang G, Xiao X, Liu L and Li T: Bkca
opener, NS1619 pretreatment protects against shock-induced vascular
hyporeactivity through PDZ-Rho GEF-RhoA-Rho kinase pathway in rats.
J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 76:394–401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao Z, Si Y, Zhang Y, Du S, Zhang L and
Niu C: Postshock mesenteric lymph drainage ameliorates vascular
reactivity and calcium sensitivity through RhoA. J Surg Res.
186:304–309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li T, Fang Y, Yang G, Xu J, Zhu Y and Liu
L: Effects of the balance in activity of RhoA and Rac1 on the
shock-induced biphasic change of vascular reactivity in rats. Ann
Surg. 253:185–193. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu Y, Li T, Tang XF, Chen K and Liu L:
Effects of ischemic preconditioning on vascular reactivity and
calcium sensitivity after hemorrhagic shock and their relationship
to the RhoA-Rho-kinase pathway in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
57:231–239. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Okumura N, Fujii K, Kagami T, Makiko N,
Kitahara M, Kinoshita S and Koizumi N: Activation of the Rho/Rho
kinase signaling pathway is involved in cell death of corneal
endothelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:6843–6851. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Akbar H, Duan X, Saleem S, Davis AK and
Zheng Y: RhoA and Rac1 GTPases differentially regulate
agonist-receptor mediated reactive oxygen species generation in
platelets. PLoS One. 11:e01632272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bang J, Jang M, Huh JH, Na JW, Shim M,
Carlson BA, Tobe R, Tsuji PA, Gladyshev VN, Hatfield DL and Lee BJ:
Deficiency of the 15-kDa selenoprotein led to cytoskeleton
remodeling and non-apoptotic membrane blebbing through a RhoA/ROCK
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 456:884–890. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lei Y, Peng X, Liu L, Dong Z and Li T:
Beneficial effect of cyclosporine A on traumatic hemorrhagic shock.
J Surg Res. 195:529–540. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fang Y, Li T, Fan X, Zhu Y and Liu L:
Beneficial effects of activation of PKC on hemorrhagic shock in
rats. J Trauma. 68:865–873. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang X, Song R, Bian HN, Brunk UT, Zhao M
and Zhao KS: Polydatin, a natural polyphenol, protects arterial
smooth muscle cells against mitochondrial dysfunction and lysosomal
destabilization following hemorrhagic shock. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 302:R805–R814. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang X, Song R, Chen Y, Zhao M and Zhao
KS: Polydatin - a new mitochondria protector for acute severe
hemorrhagic shock treatment. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
22:169–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|