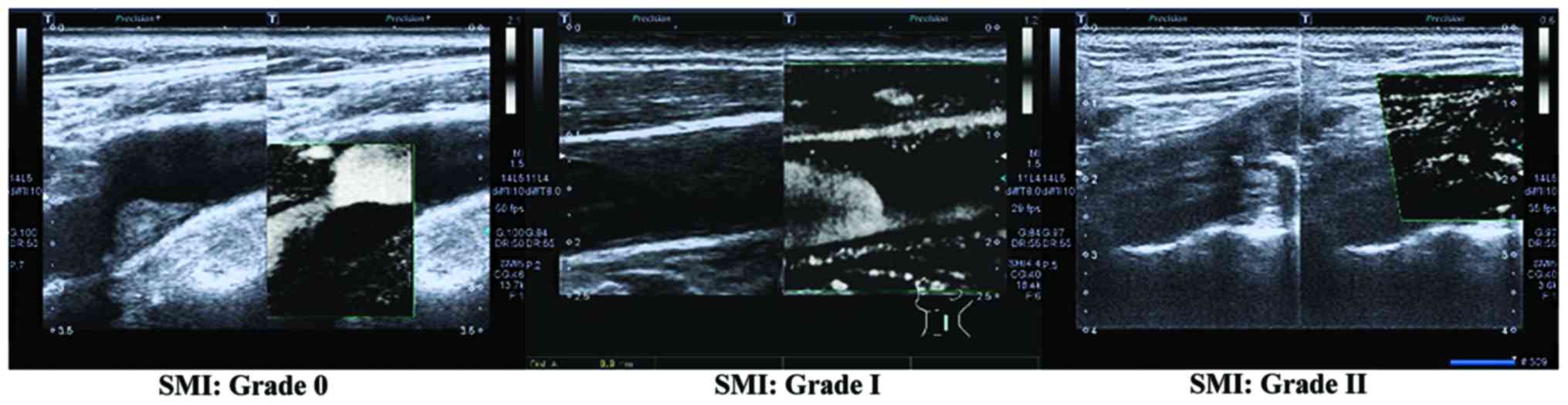
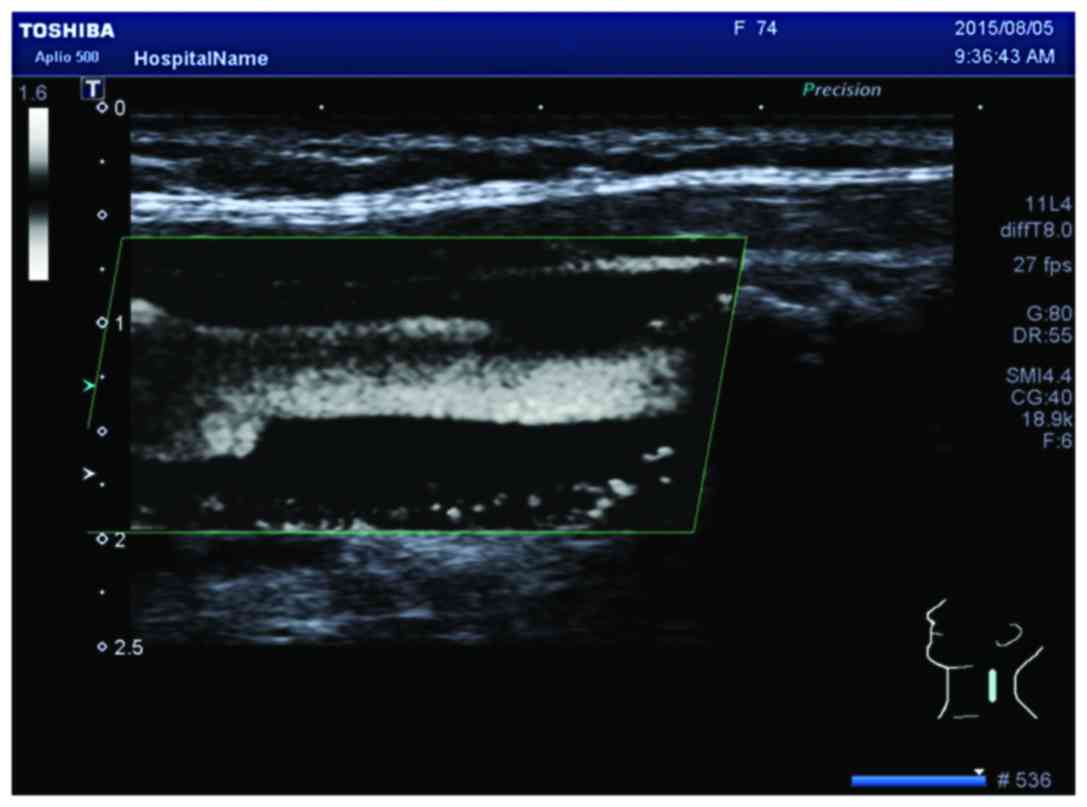
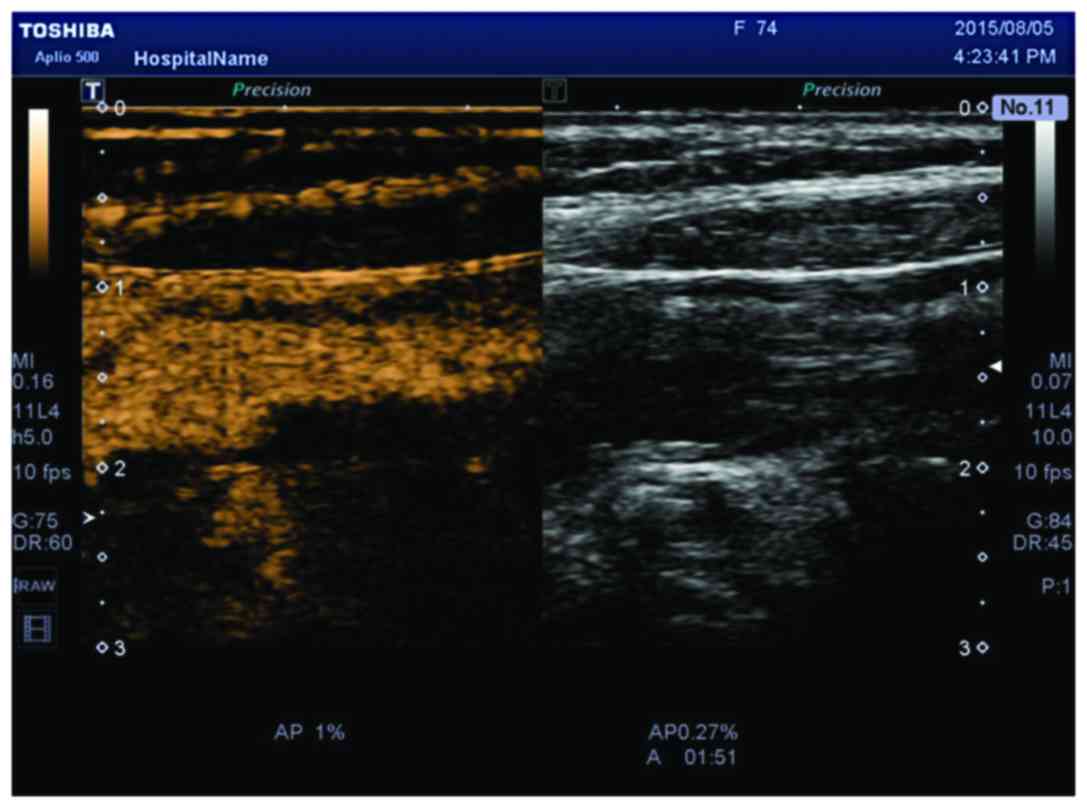
|
1
|
Gray-Weale AC, Graham JC, Burnett JR,
Byrne K and Lusby RJ: Carotid artery atheroma: comparison of
preoperative B-mode ultrasound appearance with carotid
endarterectomy specimen pathology. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino).
29:676–681. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, Casscells SW,
Litovsky S, Rumberger J, Badimon JJ, Stefanadis C, Moreno P,
Pasterkamp G, et al: From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient:
a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: part I.
Circulation. 108:1664–1672. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hellings WE, Peeters W, Moll FL, Piers SR,
van Setten J, van der Spek PJ, De Vries JP, Seldenrijk KA, De Bruin
PC, Vink A, et al: Composition of carotid atherosclerotic plaque is
associated with cardiovascular outcome: a prognostic study.
Circulation. 121:1941–1950. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hingwala D, Kesavadas C, Sylaja PN, Thomas
B and Kapilamoorthy TR: Multimodality imaging of carotid
atherosclerotic plaque: going beyond stenosis. Indian J Radiol
Imaging. 23:26–34. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fleiner M, Kummer M, Mirlacher M, Sauter
G, Cathomas G, Krapf R and Biedermann BC: Arterial
neovascularization and inflammation in vulnerable patients: early
and late signs of symptomatic atherosclerosis. Circulation.
110:2843–2850. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shah F, Balan P, Weinberg M, Reddy V,
Neems R, Feinstein M, Dainauskas J, Meyer P, Goldin M and Feinstein
SB: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of atherosclerotic carotid
plaque neovascularization: a new surrogate marker of
atherosclerosis? Vasc Med. 12:291–297. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV,
Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP and Narula J: Atherosclerotic plaque
progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source
of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:2054–2061. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Staub D, Partovi S, Schinkel AF, Coll B,
Uthoff H, Aschwanden M, Jaeger KA and Feinstein SB: Correlation of
carotid artery atherosclerotic lesion echogenicity and severity at
standard US with intraplaque neovascularization detected at
contrast-enhanced US. Radiology. 258:618–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Russell DA, Wijeyaratne SM and Gough MJ:
Changes in carotid plaque echomorphology with time since a
neurologic event. J Vasc Surg. 45:367–372. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sztajzel R, Momjian S, Momjian-Mayor I,
Murith N, Djebaili K, Boissard G, Comelli M and Pizolatto G:
Stratified gray-scale median analysis and color mapping of the
carotid plaque: correlation with endarterectomy specimen histology
of 28 patients. Stroke. 36:741–745. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakamura J, Nakamura T, Deyama J, Fujioka
D, Kawabata K, Obata JE, Watanabe K, Watanabe Y and Kugiyama K:
Assessment of carotid plaque neovascularization using quantitative
analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging is useful for risk
stratification in patients with coronary artery disease. Int J
Cardiol. 195:113–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fisher M, Paganini-Hill A, Martin A,
Cosgrove M, Toole JF, Barnett HJ and Norris J: Carotid plaque
pathology: thrombosis, ulceration, and stroke pathogenesis. Stroke.
36:253–257. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
ten Kate GL, van Dijk AC, van den Oord SC,
Hussain B, Verhagen HJ, Sijbrands EJ, van der Steen AF, van der
Lugt A and Schinkel AF: Usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasound
for detection of carotid plaque ulceration in patients with
symptomatic carotid atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 112:292–298.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vicenzini E, Giannoni MF, Sirimarco G,
Ricciardi MC, Toscano M, Lenzi GL and Di Piero V: Imaging of plaque
perfusion using contrast-enhanced ultrasound - clinical
significance. Perspect Med. 1:44–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hoogi A, Adam D, Hoffman A, Kerner H,
Reisner S and Gaitini D: Carotid plaque vulnerability:
quantification of neovascularization on contrast-enhanced
ultrasound with histopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
196:431–436. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nandalur KR, Baskurt E, Hagspiel KD,
Phillips CD and Kramer CM: Calcified carotid atherosclerotic plaque
is associated less with ischemic symptoms than is noncalcified
plaque on MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 184:295–298. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seo Y, Watanabe S, Ishizu T, Moriyama N,
Takeyasu N, Maeda H, Ishimitsu T, Aonuma K and Yamaguchi I:
Echolucent carotid plaques as a feature in patients with acute
coronary syndrome. Circ J. 70:1629–1634. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grønholdt ML, Nordestgaard BG, Schroeder
TV, Vorstrup S and Sillesen H: Ultrasonic echolucent carotid
plaques predict future strokes. Circulation. 104:68–73. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
de Blois J, Stranden E, Jogestrand T,
Henareh L and Agewall S: Echogenicity of the carotid intima-media
complex and cardiovascular risk factors. Clin Physiol Funct
Imaging. 32:400–403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shalhoub J, Owen DR, Gauthier T, Monaco C,
Leen EL and Davies AH: The use of contrast enhanced ultrasound in
carotid arterial disease. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 39:381–387.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ogata T, Yasaka M, Wakugawa Y, Kitazono T
and Okada Y: Morphological classification of mobile plaques and
their association with early recurrence of stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis.
30:606–611. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Higashida T, Kanno H, Nakano M, Funakoshi
K and Yamamoto I: Expression of hypoxia-inducible angiogenic
proteins (hypoxia- inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial
growth factor, and E26 transformation-specific-1) and plaque
hemorrhage in human carotid atherosclerosis. J Neurosurg.
109:83–91. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee SH, Lee JH, Yoo SY, Hur J, Kim HS and
Kwon SM: Hypoxia inhibits cellular senescence to restore the
therapeutic potential of old human endothelial progenitor cells via
the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-TWIST-p21 axis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 33:2407–2414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim HS, Woo JS, Kim BY, Jang HH, Hwang SJ,
Kwon SJ, Choi EY, Kim JB, Cheng X, Jin E, et al: Biochemical and
clinical correlation of intraplaque neovascularization using
contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the carotid artery.
Atherosclerosis. 233:579–583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sluimer JC, Gasc JM, van Wanroij JL,
Kisters N, Groeneweg M, Gelpke MD Sollewijn, Cleutjens JP, van den
Akker LH, Corvol P, Wouters BG, et al: Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible
transcription factor, and macrophages in human atherosclerotic
plaques are correlated with intraplaque angiogenesis. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 51:1258–1265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao X, Kong J, Zhao Y, Wang X, Bu P,
Zhang C and Zhang Y: Gene silencing of TACE enhances plaque
stability and improves vascular remodeling in a rabbit model of
atherosclerosis. Sci Rep. 5:179392015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang YH, Zheng QC, Yuan GX and Ren JH: The
application of ultrasound B-flow imaging in detection of carotid
atherosclerotic micro-vessel with ischemic cerebrovascular disease.
Saudi Med J. 33:1080–1086. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lind L, Andersson J, Rönn M, Gustavsson T,
Holdfelt P, Hulthe J, Elmgren A, Zilmer K and Zilmer M: Brachial
artery intima-media thickness and echogenicity in relation to
lipids and markers of oxidative stress in elderly subjects: the
prospective investigation of the vasculature in Uppsala Seniors
(PIVUS) Study. Lipids. 43:133–141. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schulte-Altedorneburg G, Droste DW, Haas
N, Kemény V, Nabavi DG, Füzesi L and Ringelstein EB: Preoperative
B-mode ultrasound plaque appearance compared with carotid
endarterectomy specimen histology. Acta Neurol Scand. 101:188–194.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ostling G, Hedblad B, Berglund G and
Gonçalves I: Increased echolucency of carotid plaques in patients
with type 2 diabetes. Stroke. 38:2074–2078. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sabetai MM, Tegos TJ, Nicolaides AN,
Dhanjil S, Pare GJ and Stevens JM: Reproducibility of
computer-quantified carotid plaque echogenicity: can we overcome
the subjectivity? Stroke. 31:2189–2196. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kyriacou EC, Petroudi S, Pattichis CS,
Pattichis MS, Griffin M, Kakkos S and Nicolaides A: Prediction of
high-risk asymptomatic carotid plaques based on ultrasonic image
features. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 16:966–973. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Östling G, Persson M, Hedblad B and
Gonçalves I: Comparison of grey scale median (GSM) measurement in
ultrasound images of human carotid plaques using two different
softwares. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 33:431–435. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mathiesen EB, Bønaa KH and Joakimsen O:
Echolucent plaques are associated with high risk of ischemic
cerebrovascular events in carotid stenosis: the tromsø study.
Circulation. 103:2171–2175. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ariyoshi K, Okuya S, Kunitsugu I,
Matsunaga K, Nagao Y, Nomiyama R, Takeda K and Tanizawa Y:
Ultrasound analysis of gray-scale median value of carotid plaques
is a useful reference index for cerebro-cardiovascular events in
patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Investig. 6:91–97. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|