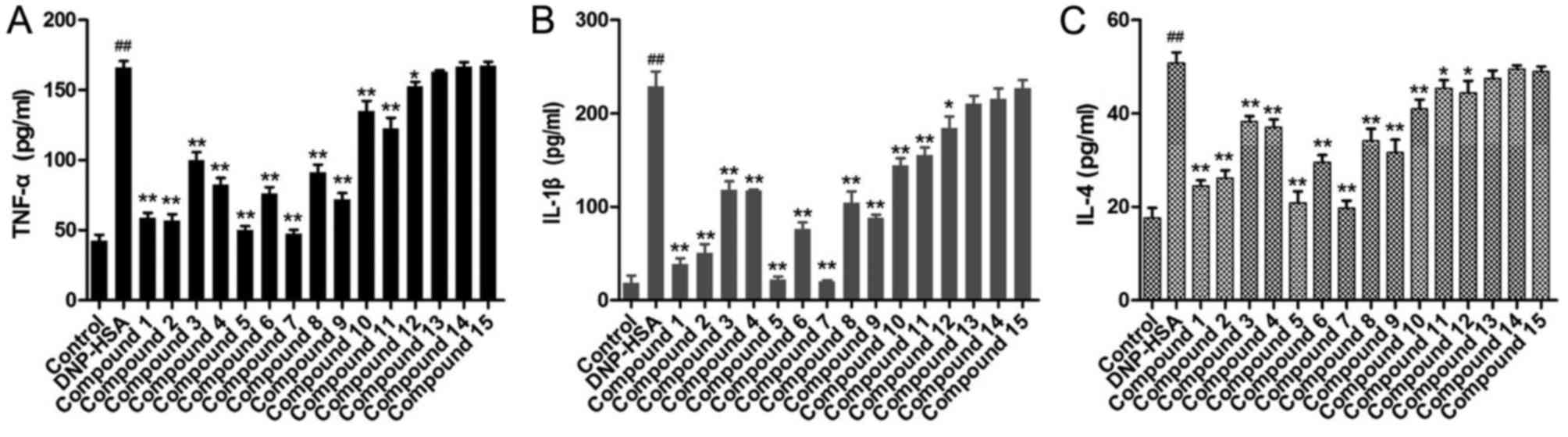
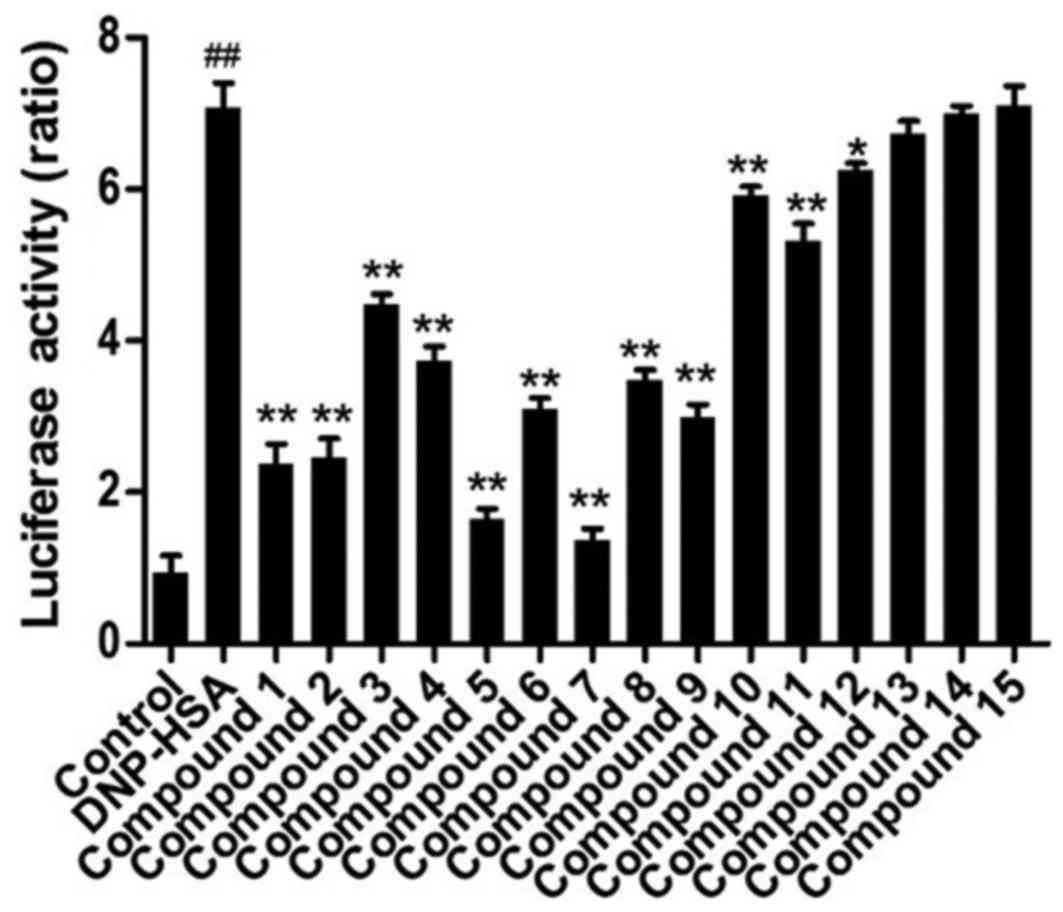
|
1
|
Erb KJ: Can helminths or helminth-derived
products be used in humans to prevent or treat allergic diseases?
Trends Immunol. 30:75–82. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kraft S and Kinet JP: New developments in
FcepsilonRI regulation, function and inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol.
7:365–378. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Galli SJ and Tsai M: IgE and mast cells in
allergic disease. Nat Med. 18:693–704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Castle JD, Guo Z and Liu L: Function of
the t-SNARE SNAP-23 and secretory carrier membrane proteins
(SCAMPs) in exocytosis in mast cells. Mol Immunol. 38:1337–1340.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galli SJ, Kalesnikoff J, Grimbaldeston MA,
Piliponsky AM, Williams CM and Tsai M: Mast cells as ‘tunable’
effector and immunoregulatory cells: Recent advances. Annu Rev
Immunol. 23:749–786. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kay AB: Allergy and allergic diseases.
First of two parts. New Eng J Med. 344:30–37. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB in
immunobiology. Cell Res. 21:223–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bae Y, Lee S and Kim SH: Chrysin
suppresses mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation: Involvement of
calcium, caspase-1 and nuclear factor-κB. Toxicol Appl Pharm.
254:56–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Je IG, Kim DS, Kim SW, Lee S, Lee HS, Park
EK, Khang D and Kim SH: Tyrosol suppresses allergic inflammation by
inhibiting the activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in mast
cells. PLoS One. 10:e01298292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kwon YS, Kobayashi A, Kajiyama SI, Kawazu
K, Kanzaki H and Kim CM: Antimicrobial constituents of Angelica
dahurica roots. Phytochemistry. 44:887–889. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Oh H, Lee HS, Kim T, Chai KY, Chung HT,
Kwon TO, Jun JY, Jeong OS, Kim YC and Yun YG: Furocoumarins from
Angelica dahurica with heptaprotective activity on tacrine-induced
cytotoxicity in Hep G2 cells. Planta Med. 68:463–464. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao Y, Zhang Y, Wang N and He L:
Antioxidant effect of imperatorin from Angelica dahurica in
hypertension via inhibiting NADPH oxidase activation and MAPK
pathway. J Am Soc Hypertens. 8:527–536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seo WD, Kim JY, Ryu HW, Kim JH, Han SI, Ra
JE, Seo KH, Jang KC and Lee JH: Identification and characterisation
of coumarins from the roots of Angelica dahurica and their
inhibitory effects against cholinesterase. J Funct Foods.
5:1421–1431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim HS, Shin BR, Lee HK, Park YS, Liu Q,
Kim SY, Lee MK, Hong JT, Kim Y and Han SB: Dendritic cell
activation by polysaccharide isolated from Angelica dahurica. Food
Chem Toxicol. 55:241–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kimura Y, Ohminami H, Arichi H, Okuda H,
Baba K, Kozawa M and Arichi S: Effects of various coumarins from
roots of Angelica dahurica on actions of adrenaline, ACTH and
insulin in fat cells. Planta Med. 45:183–187. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ban HS, Lim SS, Suzuki K, Jung SH, Lee S,
Lee YS, Shin KH and Ohuchi K: Inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins
isolated from the roots of Angelica dahurica on prostaglandin E2
production. Planta Med. 69:408–412. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deng GG, Wei W, Yang XW, Zhang YB, Xu W,
Gong NB, Lü Y and Wang FF: New coumarins from the roots of Angelica
dahurica var. formosana cv. Chuanbaizhi and their inhibition on NO
production in LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells. Fitoterapia.
101:194–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang WQ, Song YL, Zhu ZX, Su C, Zhang X,
Wang J, Shi SP and Tu PF: Anti-inflammatory dimeric furanocoumarins
from the roots of Angelica dahurica. Fitoterapia. 105:187–193.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kimura Y and Okuda H: Histamine-release
effectors from Angelica dahurica var. Dahurica root. J Nat Prod.
60:249–251. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee MY, Lee JA, Seo CS, Ha H, Lee H, Son
JK and Shin HK: Anti-inflammatory activity of Angelica dahurica
ethanolic extract on RAW264.7 cells via upregulation of heme
oxygenase-1. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:1047–1055. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee MY, Seo CS, Lee JA, Lee NH, Kim JH, Ha
H, Zheng MS, Son JK and Shin HK: Anti-asthmatic effects of Angelica
dahurica against ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation via
upregulation of heme oxygenase-1. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:829–837.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qiao SY, Yao XS and Wang ZY: Coumarins of
the roots of Angelica dahurica. Planta Med. 62:5841996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang J, Zhou L, Sun J, Han J and Guo DA:
Chromatographic fingerprint analysis and characterization of
furocoumarins in the roots of Angelica dahurica by HPLC/DAD/ESI-MSn
technique. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 47:778–785. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao XZ, Feng X, Jia XD, Dong YF and Wang
M: Neolignan glycoside from Angelica dahurica. Chin Chem Lett.
18:168–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lechner D, Stavri M, Oluwatuyi M,
Pereda-Miranda R and Gibbons S: The anti-staphylococcal activity of
Angelica dahurica (Bai Zhi). Phytochemistry. 65:331–335. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao XR, Huo XK, Dong PP, Wang C, Huang
SS, Zhang BJ, Zhang HL, Deng S, Liu KX and Ma XC: Inhibitory
effects of highly oxygenated lanostane derivatives from the fungus
Ganoderma lucidum on P-glycoprotein and α-glucosidase. J Nat Prod.
78:1868–1876. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Damu GL, Cui SF, Peng XM, Wen QM, Cai GX
and Zhou CH: Synthesis and bioactive evaluation of a novel series
of coumarinazoles. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 24:3605–3608. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang B, Xu L, Zou Z and Yang S: Chemical
constituents isolated from Angelica dahurica var. formosana. Chin
Trad Herb Drugs. 36:1132–1137. 2005.
|
|
30
|
Hata K, Kozawa M, Yen K and Kimura Y:
Pharmacognostical studies on umbelliferous plants. XX. Studies on
Chinese drug ‘bvaku-shi’. 5. On the coumarins of the roots of
Angelica formosana Boiss. and A. anomala Lall. Yakugaku Zasshi.
83:611–614. 1963.(In Japanese).
|
|
31
|
Wang MY, Jia MR, Ma YY, Tang SW, Jiang GH
and Li XB: Studies on analgestic components of RadixAngelicae
dahuricae. Chin Pharm J. 40:583–587. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Sun X, Zhang C, Li J, Feng J, Zhou H, Fu S
and Chen W: Chemical constituents from Peucedanum decursivum. Chin
Trad Herb Drugs. 44:2044–2047. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Jin MH, Moon TC, Hong TG, Park KM, Son JK
and Chang HW:
5-Methoxy-8-(2-hydroxy-3-buthoxy-3-methylbutyloxy)-psoralen
isolated from Angelica dahurica inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 and
5-lipoxygenase in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells. Arch Pharm
Res. 31:617–621. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moon TC, Jin MH, Son JK and Chang HW: The
effects of isoimperatorin isolated from Angelicae dahuricae on
cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase in mouse bone marrow-derived
mast cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:210–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|