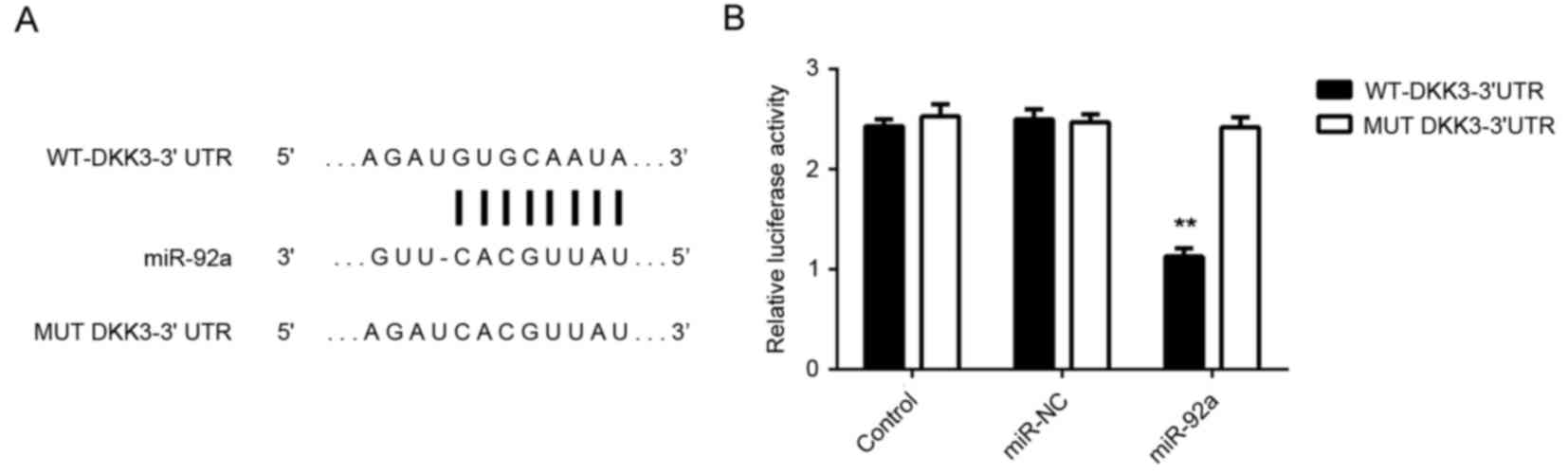
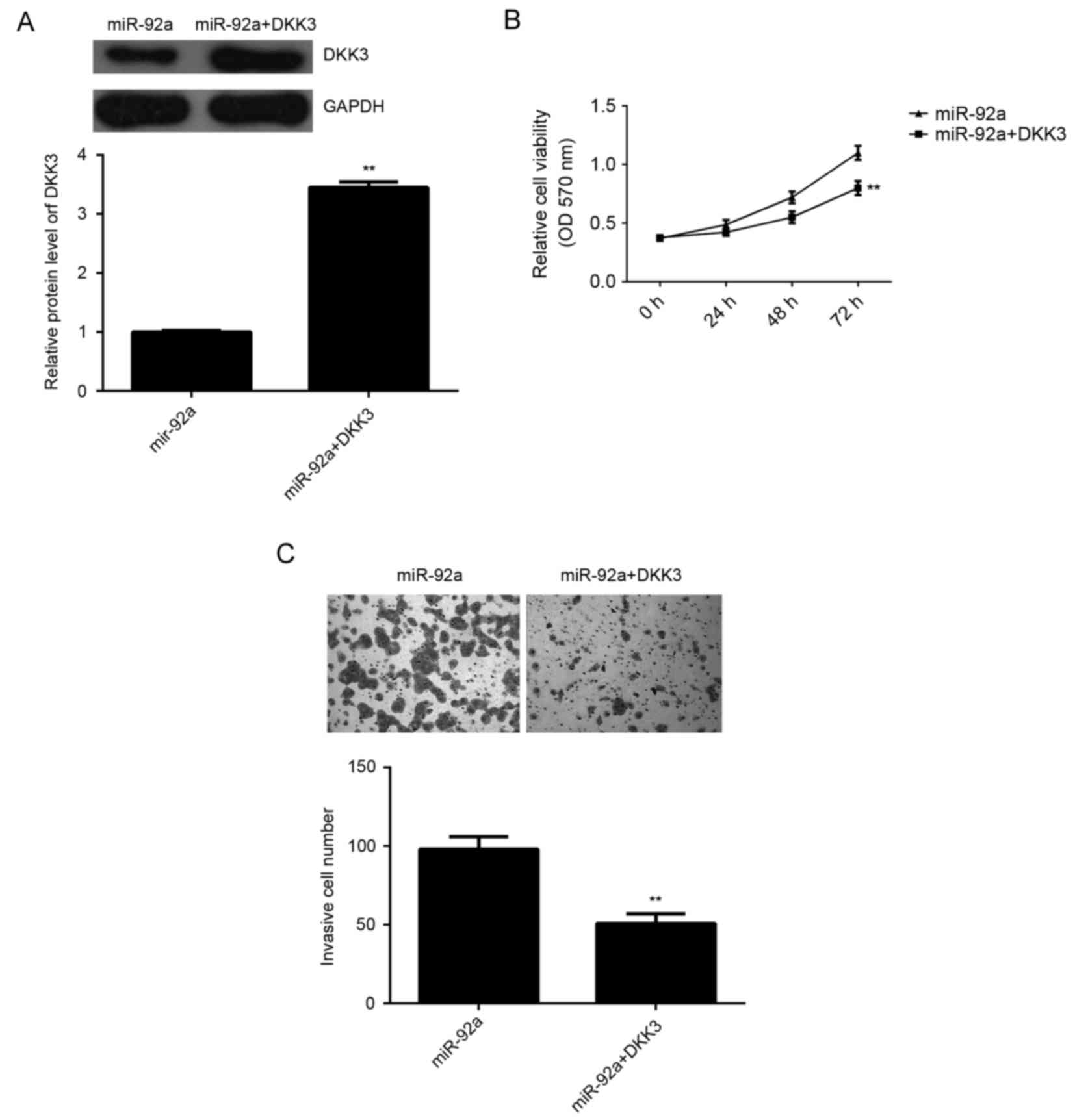
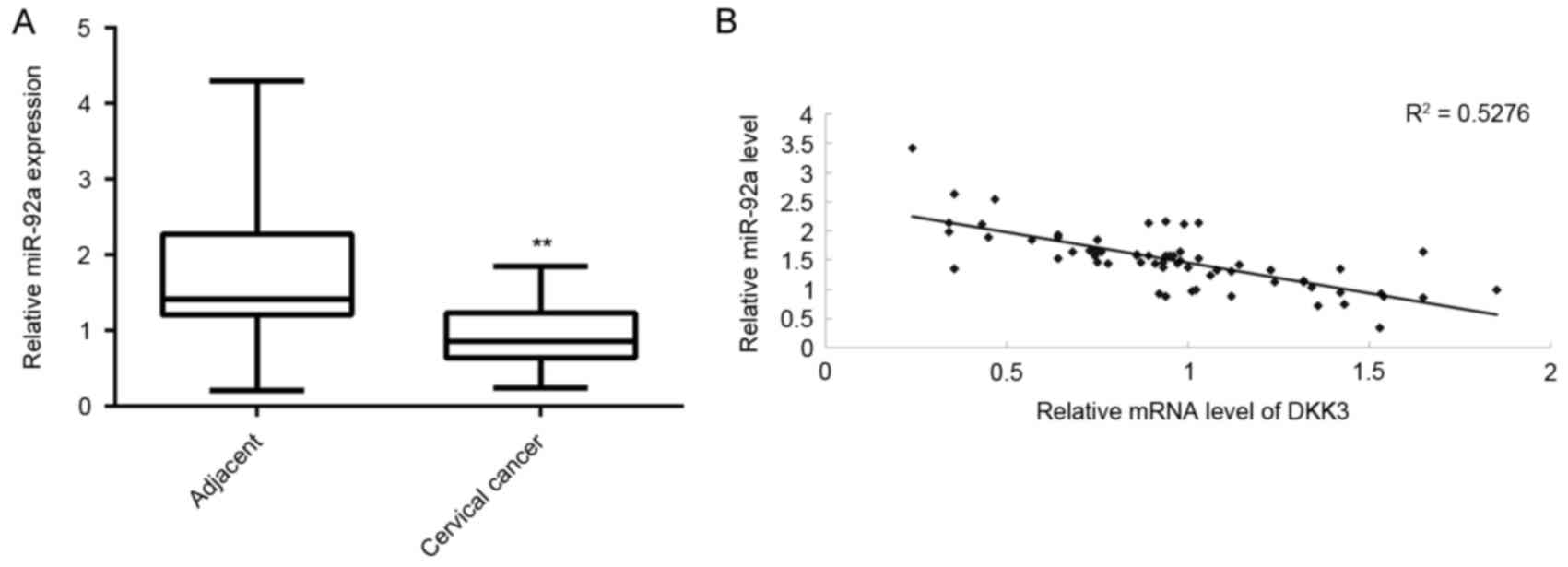
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wright JD, Huang Y, Ananth CV, Tergas AI,
Duffy C, Deutsch I, Burke WM, Hou JY, Neugut AI and Hershman DL:
Influence of treatment center and hospital volume on survival for
locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 139:506–512. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moss EG: MicroRNAs: Hidden in the genome.
Curr Biol. 12:R138–R140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ye JJ and Cao J: MicroRNAs in colorectal
cancer as markers and targets: Recent advances. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:4288–4299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao J, Deng B, Zheng L, Dou L, Guo Y and
Guo K: miR-27b is upregulated in cervical carcinogenesis and
promotes cell growth and invasion by regulating CDH11 and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep. 35:1645–1651.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ribeiro J, Marinho-Dias J, Monteiro P,
Loureiro J, Baldaque I, Medeiros R and Sousa H: miR-34a and
miR-125b expression in HPV infection and cervical cancer
development. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3045842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei Q, Li YX, Liu M, Li X and Tang H:
MiR-17-5p targets TP53INP1 and regulates cell proliferation and
apoptosis of cervical cancer cells. IUBMB Life. 64:697–704. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu L, Yu X, Guo X, Tian Z, Su M, Long Y,
Huang C, Zhou F, Liu M, Wu X and Wang X: miR-143 is downregulated
in cervical cancer and promotes apoptosis and inhibits tumor
formation by targeting Bcl-2. Mol Med Rep. 5:753–760.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang Z, Chen S, Luan X, Li Y, Liu M, Li X,
Liu T and Tang H: MicroRNA-214 is aberrantly expressed in cervical
cancers and inhibits the growth of HeLa cells. IUBMB Life.
61:1075–1082. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ke TW, Wei PL, Yeh KT, Chen WT and Cheng
YW: MiR-92a promotes cell metastasis of colorectal cancer through
PTEN-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:2649–2655. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin HY, Chiang CH and Hung WC: STAT3
upregulates miR-92a to inhibit RECK expression and to promote
invasiveness of lung cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 109:731–738. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jikuzono T, Kawamoto M, Yoshitake H,
Kikuchi K, Akasu H, Ishikawa H, Hirokawa M, Miyauchi A, Tsuchiya S,
Shimizu K and Takizawa T: The miR-221/222 cluster, miR-10b and
miR-92a are highly upregulated in metastatic minimally invasive
follicular thyroid carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:1858–1868.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He G, Zhang L, Li Q and Yang L:
miR-92a/DUSP10/JNK signalling axis promotes human pancreatic cancer
cells proliferation. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:25–30. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou C, Shen L, Mao L, Wang B, Li Y and Yu
H: miR-92a is upregulated in cervical cancer and promotes cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting FBXW7. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 458:63–69. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo Q and Qin W: DKK3 blocked
translocation of β-catenin/EMT induced by hypoxia and improved
gemcitabine therapeutic effect in pancreatic cancer Bxpc-3 cell. J
Cell Mol Med. 19:2832–2841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mohammadpour H, Pourfathollah AA, Zarif M
Nikougoftar and Khalili S: Key role of Dkk3 protein in inhibition
of cancer cell proliferation: An in silico identification. J Theor
Biol. 393:98–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cristóbal I, Torrejón B, Madoz-Gúrpide J,
Rojo F and Garcia-Foncillas J: Deregulation of miR-92a in locally
advanced rectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 55:6122016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ren C, Wang W, Han C, Chen H, Fu D, Luo Y,
Yao H, Wang D, Ma L, Zhou L, et al: Expression and prognostic value
of miR-92a in patients with gastric cancer. Tumour Biol.
37:9483–9491. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharifi M and Salehi R: Blockage of
miR-92a-3p with locked nucleic acid induces apoptosis and prevents
cell proliferation in human acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Cancer
Gene Ther. 23:29–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu S, Liu L, Chang EB, Wang JY and Raufman
JP: Butyrate inhibits pro-proliferative miR-92a by diminishing
c-Myc-induced miR-17-92a cluster transcription in human colon
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 14:1802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Wang HK, Li Y, Hafner M, Banerjee
NS, Tang S, Briskin D, Meyers C, Chow LT, Xie X, et al: microRNAs
are biomarkers of oncogenic human papillomavirus infections. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:pp. 4262–4267. 2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Niehrs C: Function and biological roles of
the Dickkopf family of Wnt modulators. Oncogene. 25:7469–7481.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fukusumi Y, Meier F, Götz S, Matheus F,
Irmler M, Beckervordersandforth R, Faus-Kessler T, Minina E, Rauser
B, Zhang J, et al: Dickkopf 3 promotes the differentiation of a
rostrolateral midbrain dopaminergic neuronal subset in vivo and
from pluripotent stem cells in vitro in the mouse. J Neurosci.
35:13385–13401. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Z, Lin L, Thomas DG, Nadal E, Chang
AC, Beer DG and Lin J: The role of Dickkopf-3 overexpression in
esophageal adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
150:377–385.e2. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ryu SW, Kim JH, Kim MK, Lee YJ, Park JS,
Park HM, Kim DH, Lee SH and Lee EJ: Reduced expression of DKK3 is
associated with adverse clinical outcomes of uterine cervical
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 23:134–140. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee EJ, Jo M, Rho SB, Park K, Yoo YN, Park
J, Chae M, Zhang W and Lee JH: Dkk3, downregulated in cervical
cancer, functions as a negative regulator of beta-catenin. Int J
Cancer. 124:287–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Haug BH, Henriksen JR, Buechner J, Geerts
D, Tømte E, Kogner P, Martinsson T, Flægstad T, Sveinbjørnsson B
and Einvik C: MYCN-regulated miRNA-92 inhibits secretion of the
tumor suppressor DICKKOPF-3 (DKK3) in neuroblastoma.
Carcinogenesis. 32:1005–1012. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|