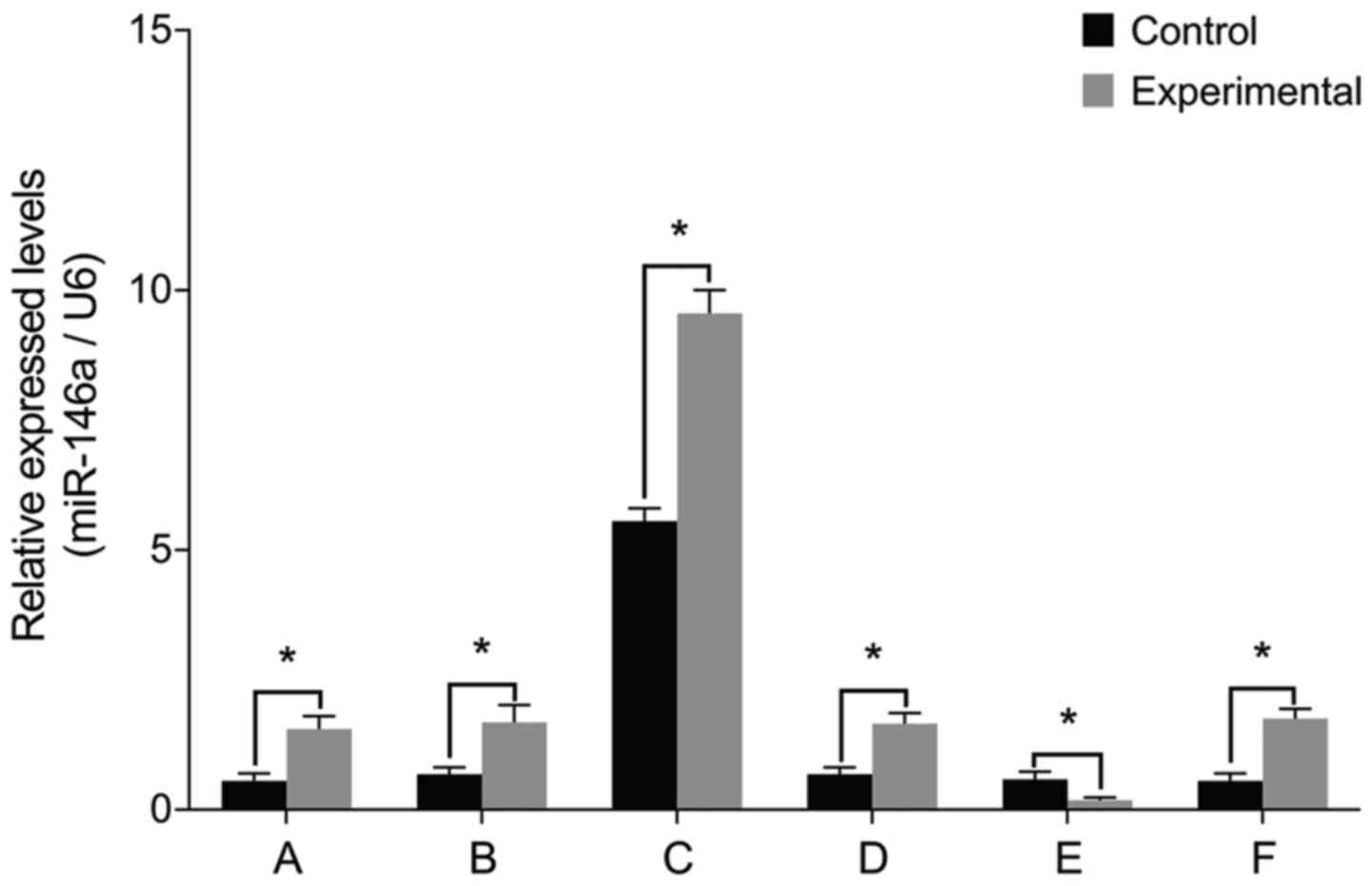
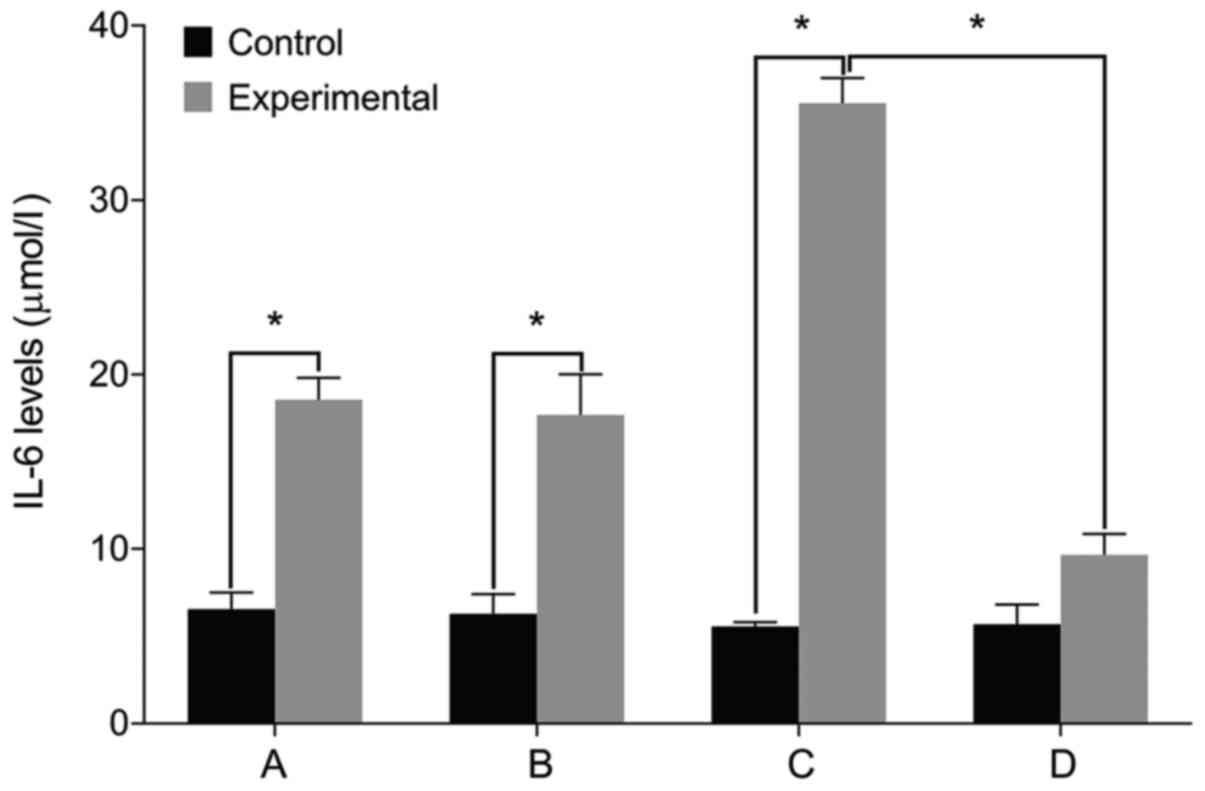
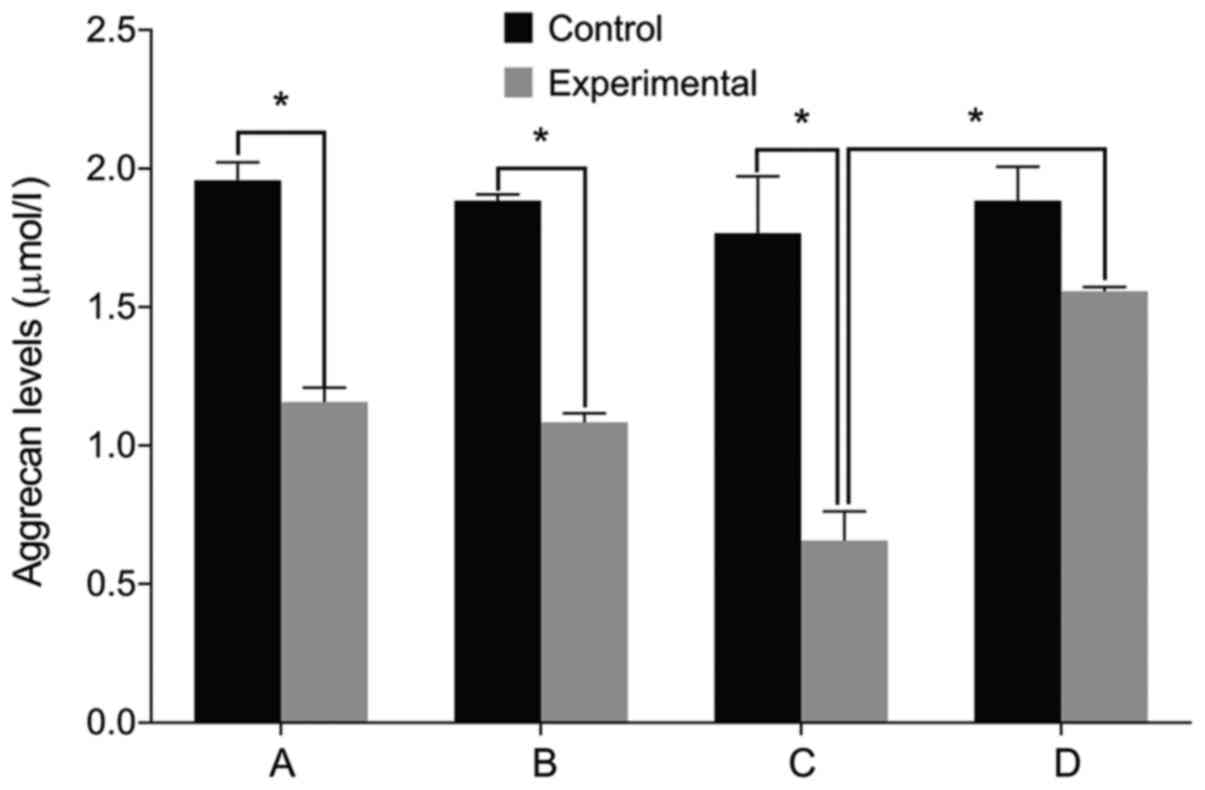
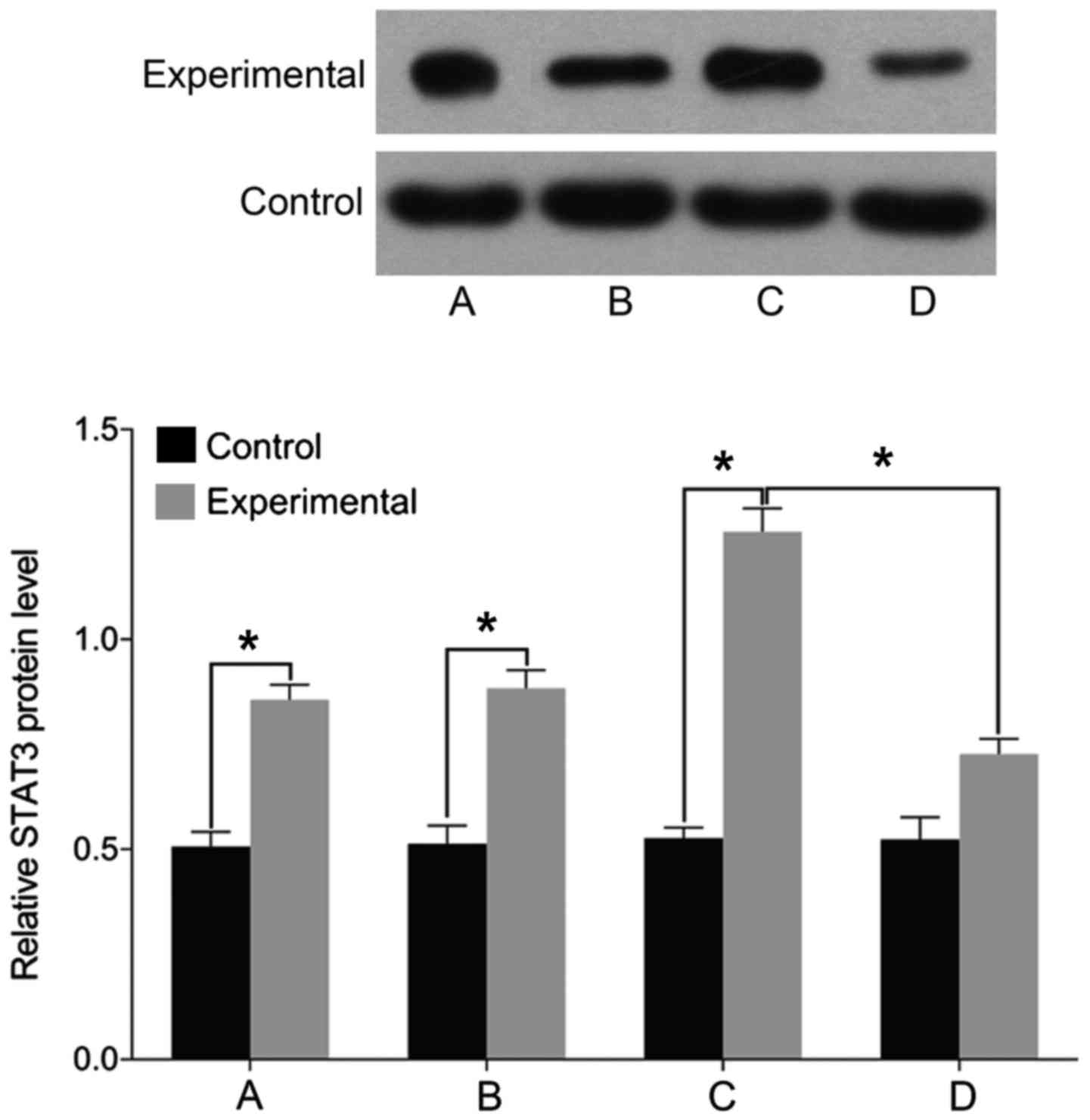
|
1
|
Ma T, Guo CJ, Zhao X, Wu L, Sun SX and Jin
QH: The effect of curcumin on NF-κB expression in rat with lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
19:1305–1314. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang X, Wang H, Yang H, Li J, Cai Q,
Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: Tumor necrosis factor-α- and
interleukin-1β-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in
nucleus pulposus cells requires cooperative signaling via syndecan
4 and mitogen-activated protein kinase-NF-κB axis: Implications in
inflammatory disc disease. Am J Pathol. 184:2560–2572. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun Z, Yin Z, Liu C, Liang H, Jiang M and
Tian J: IL-1β promotes ADAMTS enzyme-mediated aggrecan degradation
through NF-κB in human intervertebral disc. J Orthop Surg.
10:1592015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu C, Fei HD, Sun ZY and Tian JW:
Bioinformatic analysis of the microarray gene expression profile in
degenerative intervertebral disc cells exposed to TNF-α. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:3332–3339. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang SY, Zhao QF, Fang NN and Yu JG:
Betulin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines expression through
activation STAT3 signaling pathway in human cardiac cells. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:455–460. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu X, Luo F, Liu Y, Zhang A, Li J, Wang B,
Xu W, Shi L, Liu X, Lu L, et al: The IL-6/STAT3 pathway via miR-21
is involved in the neoplastic and metastatic properties of
arsenite-transformed human keratinocytes. Toxicol Lett.
237:191–199. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ye EA and Steinle JJ: miR-146a attenuates
inflammatory pathways mediated by TLR4/NF-κB and TNFα to protect
primary human retinal microvascular endothelial cells grown in high
glucose. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:39584532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao B, Yu Q, Li H, Guo X and He X:
Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in patients with
intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Med. 33:43–50.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gu SX, Li X, Hamilton JL, Chee A, Kc R,
Chen D, An HS, Kim JS, Oh CD, Ma YZ, et al: MicroRNA-146a reduces
IL-1 dependent inflammatory responses in the intervertebral disc.
Gene. 555:80–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu P, Feng B, Wang G, Ning B and Jia T:
Microarray based analysis of gene regulation by microRNA in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep. 12:4925–4930.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Risbud MV and Shapiro IM: Role of
cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc
content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:44–56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deng X, Zhao F, Kang B and Zhang X:
Elevated interleukin-6 expression levels are associated with
intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Ther Med. 11:1425–1432.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Molinos M, Almeida CR, Caldeira J, Cunha
C, Gonçalves RM and Barbosa MA: Inflammation in intervertebral disc
degeneration and regeneration. J R Soc Interface. 12:201411912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burke JG, Watson RWG, McCormack D, Dowling
FE, Walsh MG and Fitzpatrick JM: Intervertebral discs which cause
low back pain secrete high levels of proinflammatory mediators. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 84:196–201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson ZI, Schoepflin ZR, Choi H, Shapiro
IM and Risbud MV: Disc in flames: Roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 30:104–116;
discussion 116–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miao D and Zhang L: Leptin modulates the
expression of catabolic genes in rat nucleus pulposus cells through
the mitogen-activated protein kinase and Janus kinase 2/signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathways. Mol Med Rep.
12:1761–1768. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang XH, Zhu L, Hong X, Wang YT, Wang F,
Bao JP, Xie XH, Liu L and Wu XT: Resveratrol attenuated
TNF-α-induced MMP-3 expression in human nucleus pulposus cells by
activating autophagy via AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 241:848–853. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tian Y, Yuan W, Fujita N, Wang J, Wang H,
Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: Inflammatory cytokines associated with
degenerative disc disease control aggrecanase-1 (ADAMTS-4)
expression in nucleus pulposus cells through MAPK and NF-κB. Am J
Pathol. 182:2310–2321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|