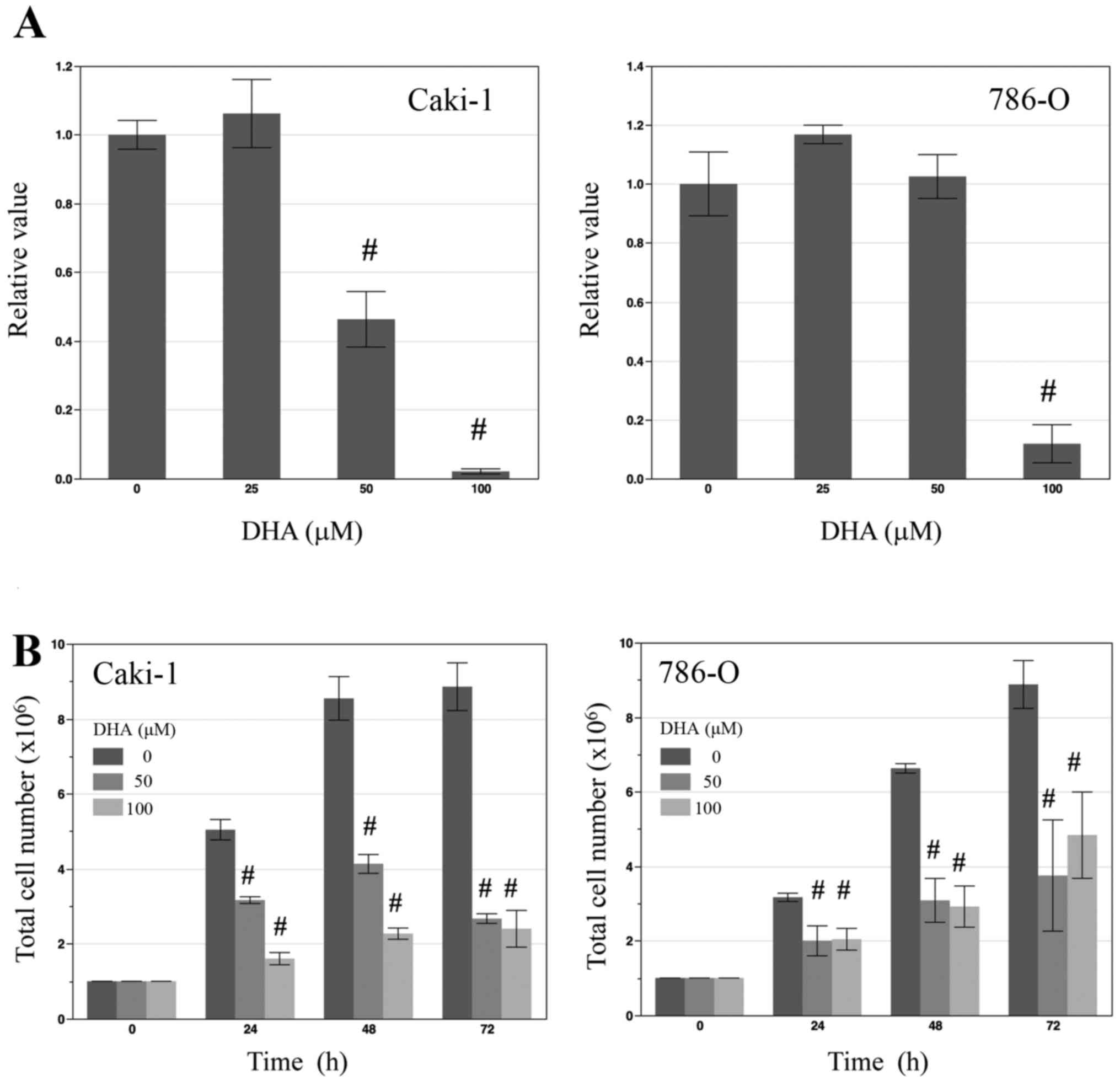
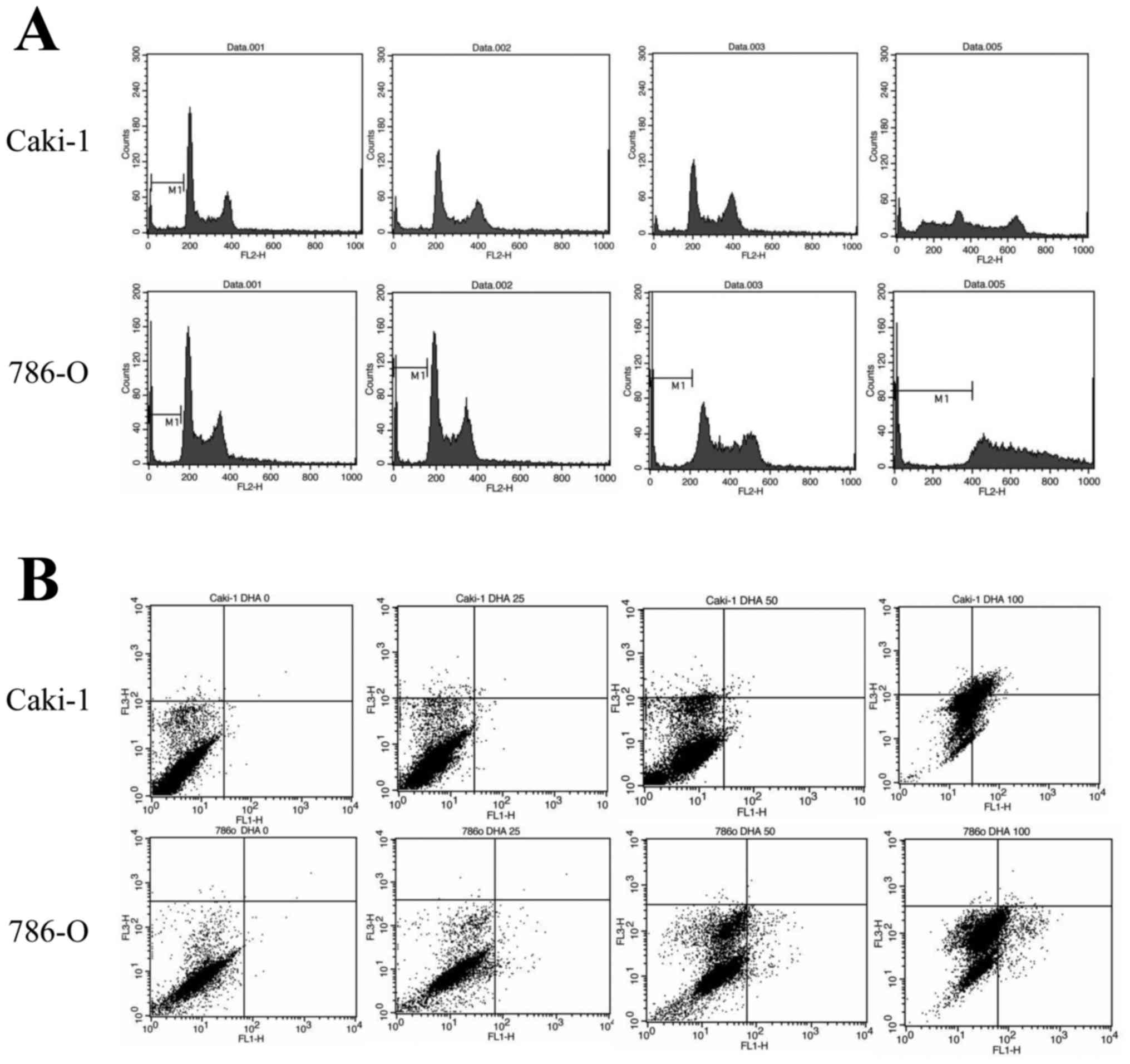
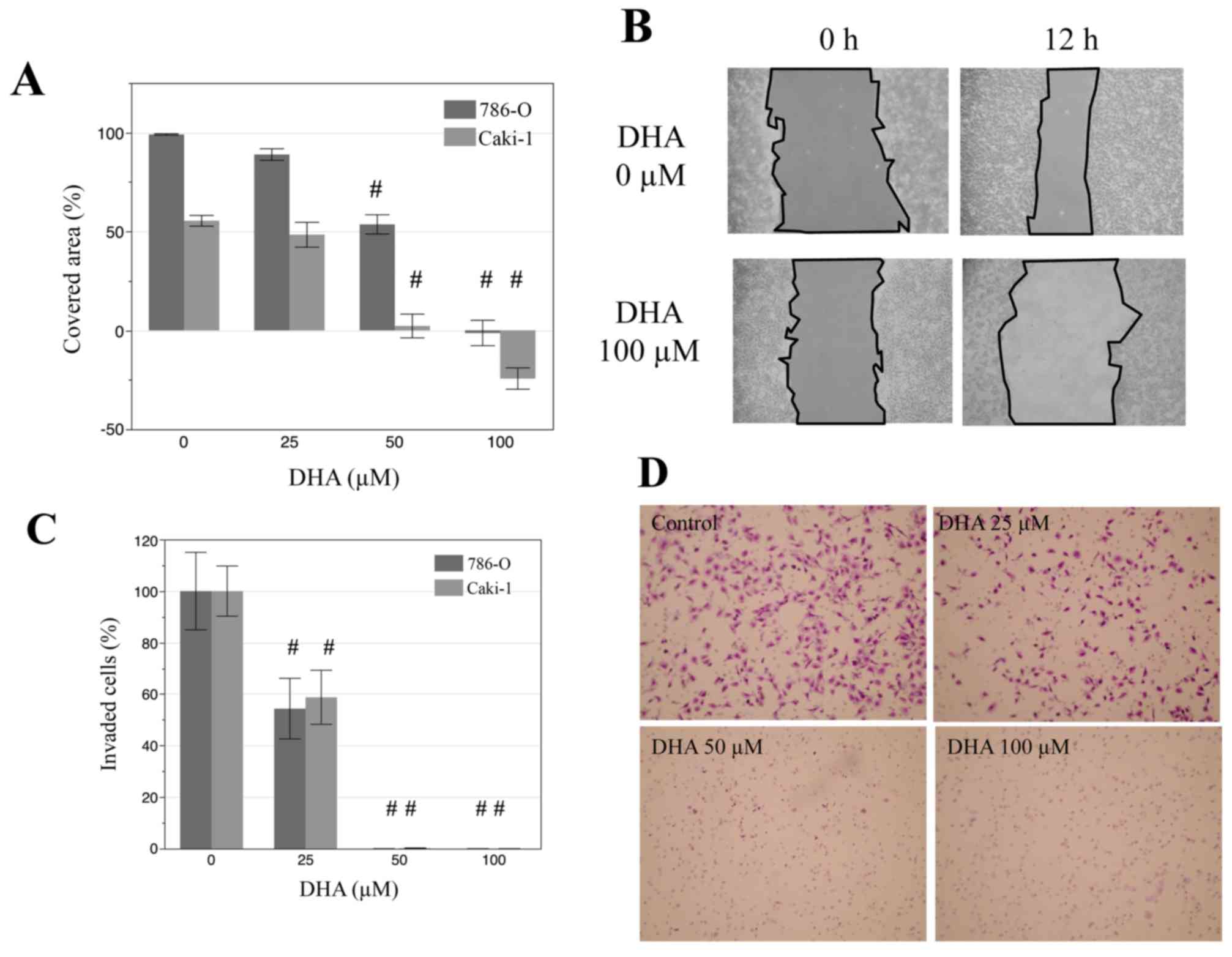
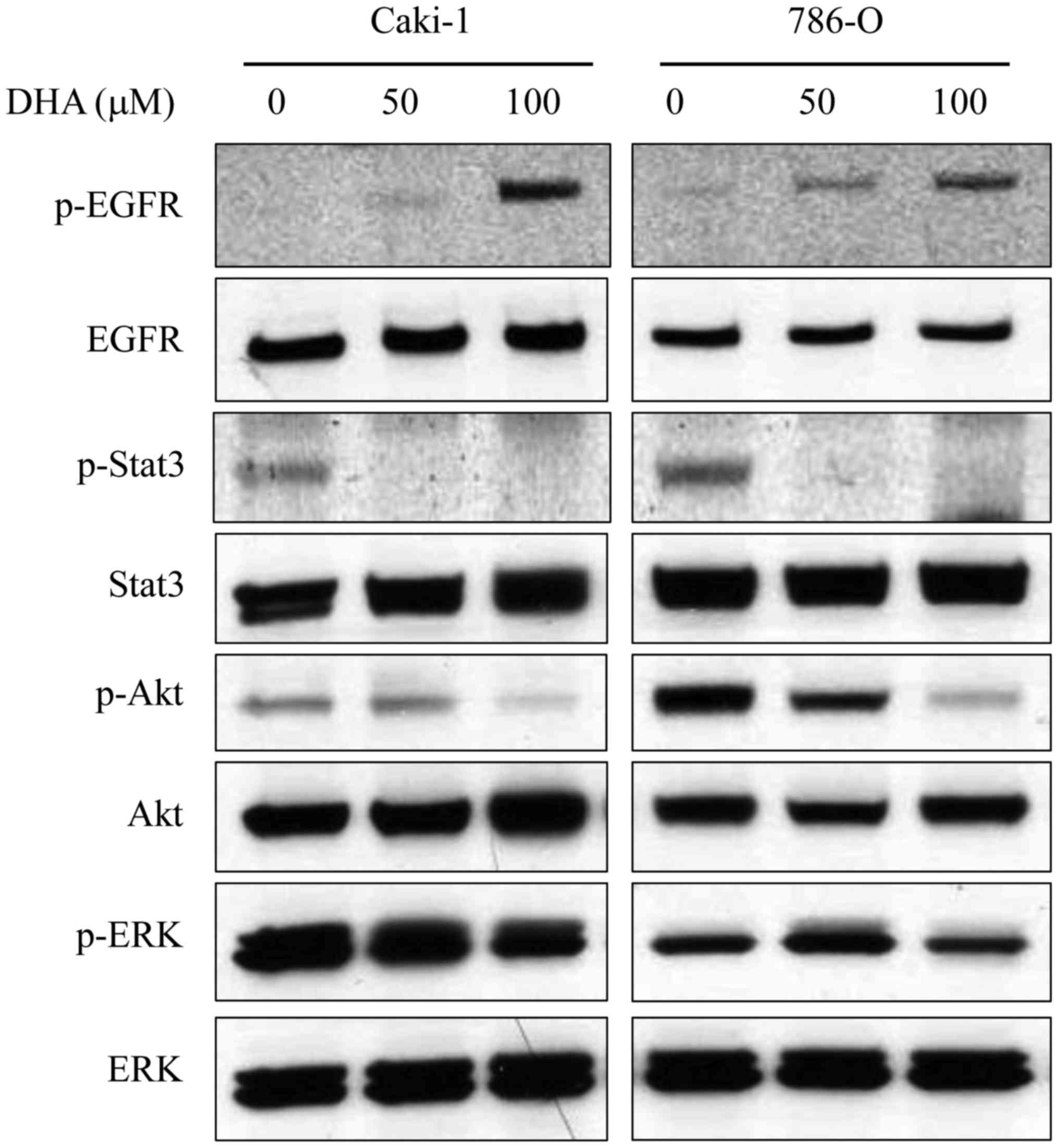
|
1
|
Larsson SC, Kumlin M, Ingelman-Sundberg M
and Wolk A: Dietary long-chain n-3 fatty acids for the prevention
of cancer: A review of potential mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr.
79:935–945. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sasazuki S, Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Sawada N,
Shimazu T, Yamaji T, Takachi R and Tsugane S; Japan Public Health
Center-Based Prospective Study Group, : Intake of n-3 and n-6
polyunsaturated fatty acids and development of colorectal cancer by
subsite: Japan public health center-based prospective study. Int J
Cancer. 129:1718–1729. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Terry PD, Rohan TE and Wolk A: Intakes of
fish and marine fatty acids and the risks of cancers of the breast
and prostate and of other hormone-related cancers: A review of the
epidemiologic evidence. Am J Clin Nutr. 77:532–543. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sonoda T, Nagata Y, Mori M, Miyanaga N,
Takashima N, Okumura K, Goto K, Naito S, Fujimoto K, Hirao Y, et
al: A case-control study of diet and prostate cancer in Japan:
Possible protective effect of traditional Japanese diet. Cancer
Sci. 95:238–242. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spencer L, Mann C, Metcalfe M, Webb M,
Pollard C, Spencer D, Berry D, Steward W and Dennison A: The effect
of omega-3 FAs on tumour angiogenesis and their therapeutic
potential. Eur J Cancer. 45:2077–2086. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Serini S, Trombino S, Oliva F, Piccioni E,
Monego G, Resci F, Boninsegna A, Picci N, Ranelletti FO and
Calviello G: Docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis in lung cancer
cells by increasing MKP-1 and down-regulating p-ERK1/2 and p-p38
expression. Apoptosis. 13:1172–1183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mandal CC, Ghosh-Choudhury T, Yoneda T,
Choudhury GG and Ghosh-Choudhury N: Fish oil prevents breast cancer
cell metastasis to bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:602–607.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang G, Panigrahy D, Mahakian LM, Yang J,
Liu JY, Lee KS Stephen, Wettersten HI, Ulu A, Hu X, Tam S, et al:
Epoxy metabolites of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) inhibit
angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:pp. 6530–6535. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rogers KR, Kikawa KD, Mouradian M,
Hernandez K, McKinnon KM, Ahwah SM and Pardini RS: Docosahexaenoic
acid alters epidermal growth factor receptor-related signaling by
disrupting its lipid raft association. Carcinogenesis.
31:1523–1530. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Patterson RE, Flatt SW, Newman VA,
Natarajan L, Rock CL, Thomson CA, Caan BJ, Parker BA and Pierce JP:
Marine fatty acid intake is associated with breast cancer
prognosis. J Nutr. 141:201–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaughan VC, Hassing MR and Lewandowski PA:
Marine polyunsaturated fatty acids and cancer therapy. Br J Cancer.
108:486–492. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bougnoux P, Hajjaji N, Ferrasson MN,
Giraudeau B, Couet C and Le Floch O: Improving outcome of
chemotherapy of metastatic breast cancer by docosahexaenoic acid: A
phase II trial. Br J Cancer. 101:1978–1985. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bukowski RM: Prognostic factors for
survival in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Update, 2008. Cancer.
115 10 Suppl:S2273–S2281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Linehan WM, Srinivasan R and Schmidt LS:
The genetic basis of kidney cancer: A metabolic disease. Nat Rev
Urol. 7:277–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sonpavde G and Choueiri TK: Biomarkers:
The next therapeutic hurdle in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Br
J Cancer. 107:1009–1016. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ghadimi R, Kuriki K, Tsuge S, Takeda E,
Imaeda N, Suzuki S, Sawai A, Takekuma K, Hosono A, Tokudome Y, et
al: Serum concentrations of fatty acids and colorectal adenoma
risk: A case-control study in Japan. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
9:111–118. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Horiguchi A, Asano T, Ito K, Sumitomo M
and Hayakawa M: Pharmacological inhibitor of fatty acid synthase
suppresses growth and invasiveness of renal cancer cells. J Urol.
180:729–736. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Calviello G, Resci F, Serini S, Piccioni
E, Toesca A, Boninsegna A, Monego G, Ranelletti FO and Palozza P:
Docosahexaenoic acid induces proteasome-dependent degradation of
beta-catenin, down-regulation of survivin and apoptosis in human
colorectal cancer cells not expressing COX-2. Carcinogenesis.
28:1202–1209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kang KS, Wang P, Yamabe N, Fukui M, Jay T
and Zhu BT: Docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells
in vitro and in vivo via reactive oxygen species formation and
caspase 8 activation. PLoS One. 5:e102962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu Y, Sun H, Owens RT, Gu Z, Wu J, Chen
YQ, O'Flaherty JT and Edwards IJ: Syndecan-1-dependent suppression
of PDK1/Akt/bad signaling by docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis
in prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 12:826–836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Minner S, Rump D, Tennstedt P, Simon R,
Burandt E, Terracciano L, Moch H, Wilczak W, Bokemeyer C, Fisch M,
et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor protein expression and
genomic alterations in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 118:1268–1275.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sawada N, Inoue M, Iwasaki M, Sasazuki S,
Shimazu T, Yamaji T, Takachi R, Tanaka Y, Mizokami M and Tsugane S;
Japan Public Health Center-Based Prospective Study Group, :
Consumption of n-3 fatty acids and fish reduces risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 142:1468–1475. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
El-Mesery M, Al-Gayyar M, Salem H,
Darweish M and El-Mowafy A: Chemopreventive and renal protective
effects for docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): Implications of CRP and
lipid peroxides. Cell Div. 4:62009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zuijdgeest-van Leeuwen SD, van der Heijden
MS, Rietveld T, Van den Berg JW, Tilanus HW, Burgers JA, Wilson JH
and Dagnelie PC: Fatty acid composition of plasma lipids in
patients with pancreatic, lung and oesophageal cancer in comparison
with healthy subjects. Clin Nutr. 21:225–230. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cvetković Z, Vucić V, Cvetković B,
Petrović M, Ristić-Medić D, Tepsić J and Glibetić M: Abnormal fatty
acid distribution of the serum phospholipids of patients with
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann Hematol. 89:775–782. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Macášek J, Vecka M, Žák A, Urbánek M,
Krechler T, Petruželka L, Staňková B and Zeman M: Plasma fatty acid
composition in patients with pancreatic cancer: Correlations to
clinical parameters. Nutr Cancer. 64:946–955. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pike LJ: Rafts defined: A report on the
keystone symposium on lipid rafts and cell function. J Lipid Res.
47:1597–1598. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kalyankrishna S and Grandis JR: Epidermal
growth factor receptor biology in head and neck cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 24:2666–2672. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Shimada T, Uchida A,
Marumo K and Murai M: Activation of signal transducer and activator
of transcription 3 in renal cell carcinoma: A study of incidence
and its association with pathological features and clinical
outcome. J Urol. 168:762–765. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horiguchi A, Oya M, Uchida A, Marumo K and
Murai M: Elevated Akt activation and its impact on
clinicopathological features of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
169:710–713. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuroda K, Horiguchi A, Sumitomo M and
Asano T, Ito K, Hayakawa M and Asano T: Activated Akt prevents
antitumor activity of gefitinib in renal cancer cells. Urology.
74:209–215. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|