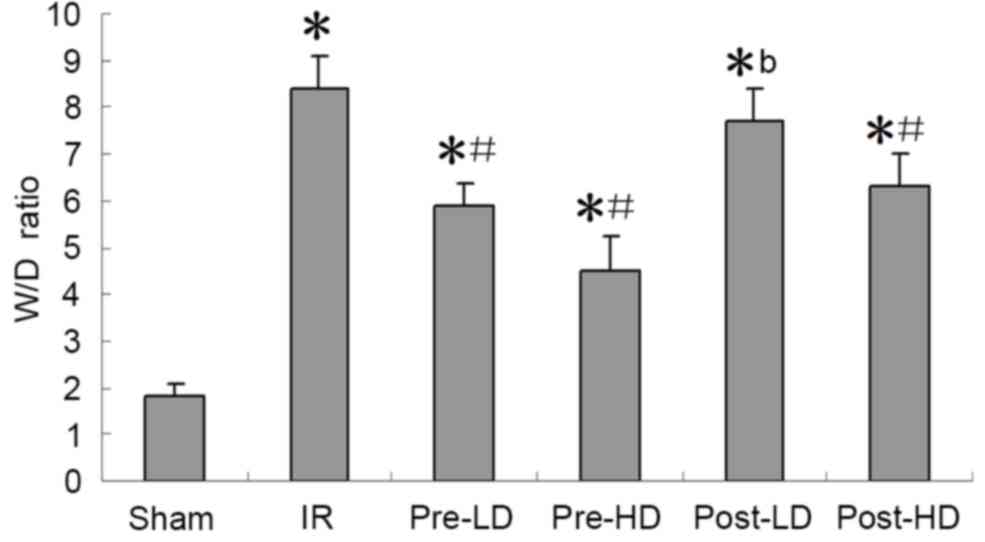
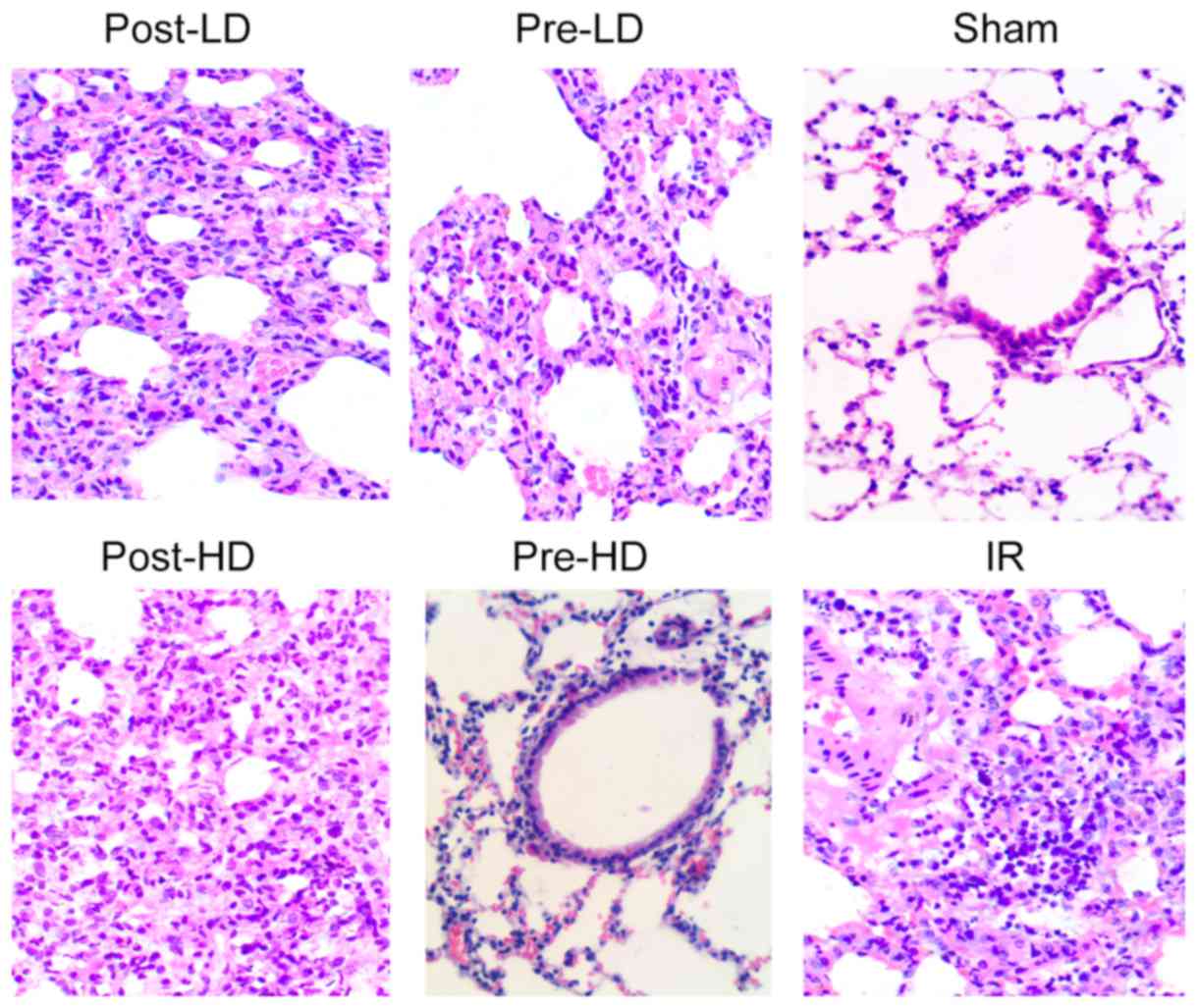
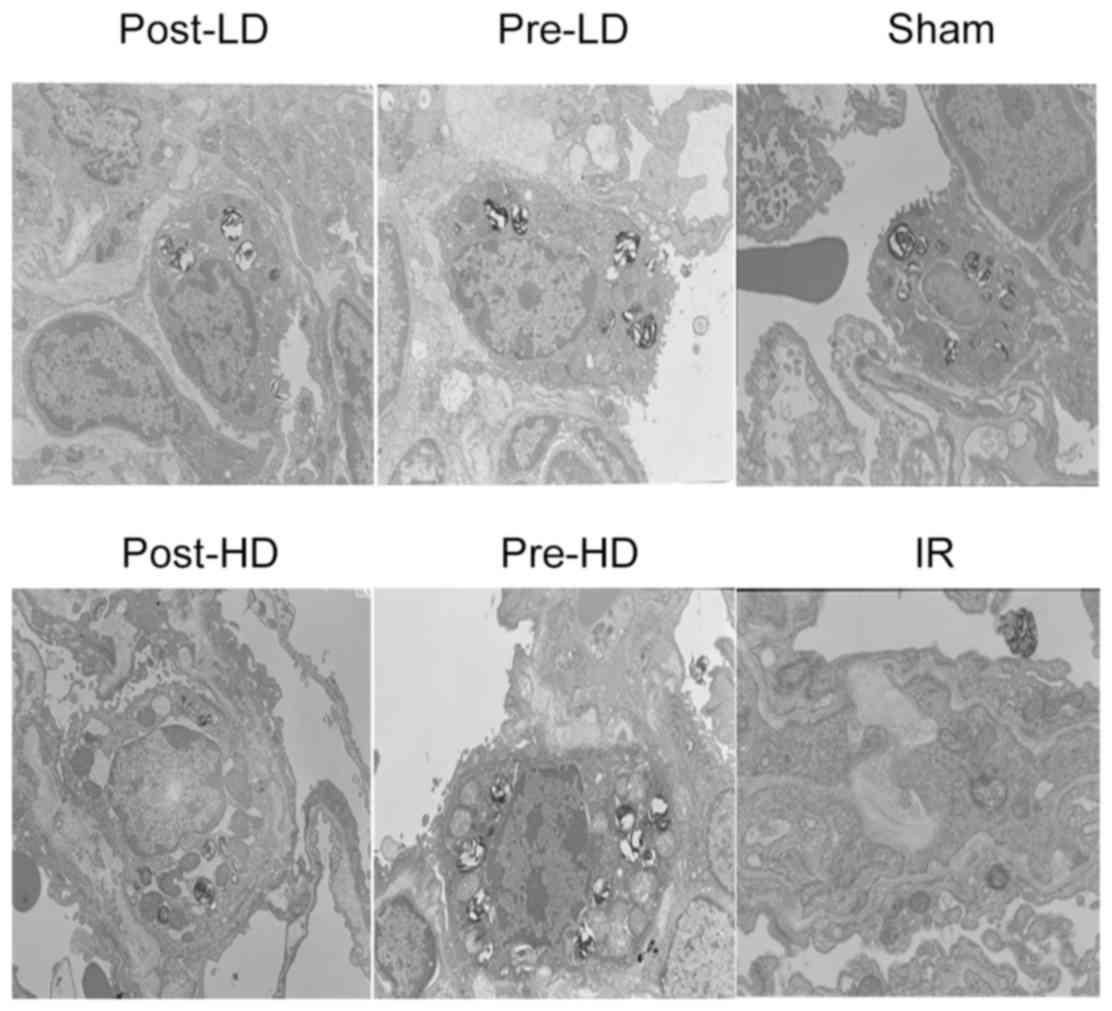
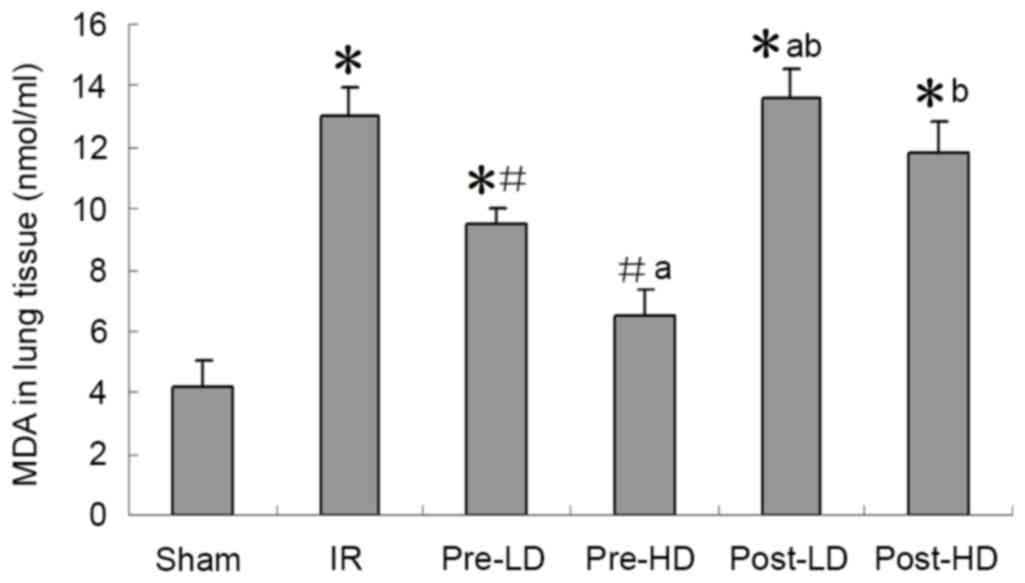
|
1
|
Christie JD, Carby M, Bag R, Corris P,
Hertz M and Weill D; ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung Graft
Dysfunction, : Report of the ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung
Graft Dysfunction part II: Definition. A consensus statement of the
International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart
Lung Transplant. 24:1454–1459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ng CS, Wan S, Yim AP and Arifi AA:
Pulmonary dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Chest. 121:1269–1277.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shimamoto A, Pohlman TH, Shomura S,
Tarukawa T, Takao M and Shimpo H: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates
lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ann Thorac Surg. 82:2017–2023.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambrosio G and Tritto I: Reperfusion
injury: Experimental evidence and clinical implications. Am Heart
J. 138:S69–S75. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reino DC, Pisarenko V, Palange D, Doucet
D, Bonitz RP, Lu Q, Colorado I, Sheth SU, Chandler B, Kannan KB, et
al: Trauma Hemorrhagic Shock-Induced Lung Injury Involves a
Gut-Lymph-Induced TLR4 Pathway in Mice. PLoS One. 6:e148292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang L, Li L, Shen J, Qi Z and Guo L:
Effect of dexmedetomidine on lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol
Med Rep. 9:419–426. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen J and Fu G, Jiang L, Xu J, Li L and
Fu G: Effect of dexmedetomidine pretreatment on lung injury
following intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Exp Ther Med.
6:1359–1364. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ogata M, Hino S, Saito A, Morikawa K,
Kondo S, Kanemoto S, Murakami T, Taniguchi M, Tanii I, Yoshinaga K,
et al: Autophagy is activated for cell survival after endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol. 26:9220–9231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tra T, Gong L, Kao LP, Li XL, Grandela C,
Devenish RJ, Wolvetang E and Prescott M: Autophagy in human
embryonic stem cells. PLoS One. 6:e274852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kuma A, Hatano M, Matsui M, Yamamoto A,
Nakaya H, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y, Tokuhisa T and Mizushima N: The
role of autophagy during the early neonatal starvation period.
Nature. 432:1032–1036. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Ueno T, Iwata J,
Murata S, Tanida I, Ezaki J, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, Uchiyama Y, et
al: Impairment of starvation-induced and constitutive autophagy in
Atg7-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 169:425–434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Suzuki C, Isaka Y, Takabatake Y, Tanaka H,
Koike M, Shibata M, Uchiyama Y, Takahara S and Imai E:
Participation of autophagy in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 368:100–106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang M, Liu K, Luo J and Dong Z:
Autophagy is a renoprotective mechanism during in vitro hypoxia and
in vivo ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol. 176:1181–1192.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gump JM, Staskiewicz L, Morgan MJ, Bamberg
A, Riches DW and Thorburn A: Autophagy variation within a cell
population determines cell fate through selective degradationof
Fap-1. Nat Cell Biol. 16:47–54. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang D, Li C, Zhou J, Song Y, Fang X, Ou
J, Li J and Bai C: Autophagy protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury through alleviating
blood-air barrier damage. J Heart Lung Transplant. 34:746–755.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Wang JS, Zheng ZK, Tang J, Fan K,
Guo H and Wang JJ: Participation of autophagy in lung
ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo. J Surg Res. 182:e79–e87. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luce JM: Acute lung injury and the acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 26:369–376. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang XY, Liu ZM, Wen SH, Li YS, Li Y, Yao
X, Huang WQ and Liu KX: Dexmedetomidine administration before, but
not after, ischemia attenuates intestinal injury induced by
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Anesthesiology.
116:1035–1046. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lempiäinen J, Finchenberg P, Mervaala EE,
Storvik M, Kaivola J, Lindstedt K, Levijoki J and Mervaala EM:
Dexmedetomidine preconditioning ameliorates kidney
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2:e000452014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de Perrot M, Liu M, Waddell TK and
Keshavjee S: Ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung injury. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 167:490–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zimmerman BJ and Granger DN: Mechanisms of
reperfusion injury. Am J Med Sci. 307:284–292. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Greef KE, Ysebaert DK, Ghielli M,
Vercauteren S, Nouwen EJ, Eyskens EJ and De Broe ME: Neutrophilsand
acute ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Nephrol. 11:110–122.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oredsson S, Plate G and Qvarfordt P:
Experimental evaluation of oxygen free radical scavengers in the
prevention of reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. Eur J Surg.
160:97–103. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deby C and Goutier R: New perspectives on
the biochemistry of superoxide anion and the efficiency of
superoxide dismutases. Biochem Pharmacol. 39:399–405. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feinman R, Deitch EA, Watkins AC, Abungu
B, Colorado I, Kannan KB, Sheth SU, Caputo FJ, Lu Q, Ramanathan M,
et al: HIF-1 mediates pathogenic inflammatory responses to
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 299:G833–G843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao X, Jin Y, Li H, Wang Z, Zhang W and
Feng C: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha contributes to pulmonary
vascular dysfunction in lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3081–3088. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer
H, Gil L and Elazar Z: Reactive oxygen species are essential for
autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBOJ.
26:1749–1760. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Høyer-Hansen M, Bastholm L, Szyniarowski
P, Campanella M, Szabadkai G, Farkas T, Bianchi K, Fehrenbacher N,
Elling F, Rizzuto R, et al: Control of macroautophagy by calcium,
calmodulin-dependent kinase kinase-beta, and Bcl-2. Mol Cell.
25:193–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang J, Wang JS, Zheng ZK, Tang J, Fan K,
Guo H and Wang JJ: Participation of autophagy in lung
ischemia-reperfusion injury in vivo. J Surg Res. 182:e79–e87. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsui Y, Kyoi S, Takagi H, Hsu CP,
Hariharan N, Ago T, Vatner SF and Sadoshima J: Molecular mechanisms
and physiological significance of autophagy during myocardial
ischemia and reperfusion. Autophagy. 4:409–415. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang D, Li C, Zhou J, Song Y, Fang X, Ou
J, Li J and Bai C: Autophagy protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced lung injury through alleviating
blood-air barrier damage. J Heart Lung Transplant. 34:746–755.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Selfeating and self-killing: Crosstalk between autophagy
and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ and Jin S: The
coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 8204–8209. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim SY, Song X, Zhang L, Bartlett DL and
Lee YJ: Role of Bcl-xL/Beclin-1 in interplay between apoptosis and
autophagy in oxaliplatin and bortezomib-induced cell death. Biochem
Pharmacol. 88:178–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Brady NR, Logue SE,
Sayen MR, Jinno M, Kirshenbaum LA, Gottlieb RA and Gustafsson AB:
Response to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury involves Bnip3
and autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 14:146–157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tracy K, Dibling BC, Spike BT, Knabb JR,
Schumacker P and Macleod KF: BNIP3 is an RB/E2F target gene
required for hypoxia-induced autophagy. Mol Cell Biol.
27:6229–6242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Azad MB, Chen Y, Henson ES, Cizeau J,
McMillan-Ward E, Israels SJ and Gibson SB: Hypoxia induces
autophagic cell death in apoptosis-competent cells through a
mechanism involving BNIP3. Autophagy. 4:195–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang H, Bosch-Marcc M, Shimoda LA, Tan
YS, Baek JH, Wesley JB, Gonzalez FJ and Semenza GL: Mitochondrial
autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic response to
hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 283:10892–10903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Novak I, Kirkin V, McEwan DG, Zhang J,
Wild P, Rozenknop A, Rogov V, Löhr F, Popovic D, Occhipinti A, et
al: Nix is selective autophagy receptor for mitochondrial
clearance. EMBO Rep. 11:45–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Band M, Joel A, Hernandez A and Avivi A:
Hypoxia-induced BNIP3 expression and mitophagy: In vivo comparision
of the rat and the hypoxia-tolerant mole, Spalax ehrenbergi. FASEB
J. 23:2327–2335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bellot G, Garcia-Medina R, Gounon P,
Chiche J, Roux D, Pouysségur J and Mazure NM: Hypoxia-induced
autophagy is mediated through hypoxia-inducible factor induction of
BNIP3 and BNIP3L via their BH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol.
29:2570–2581. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|