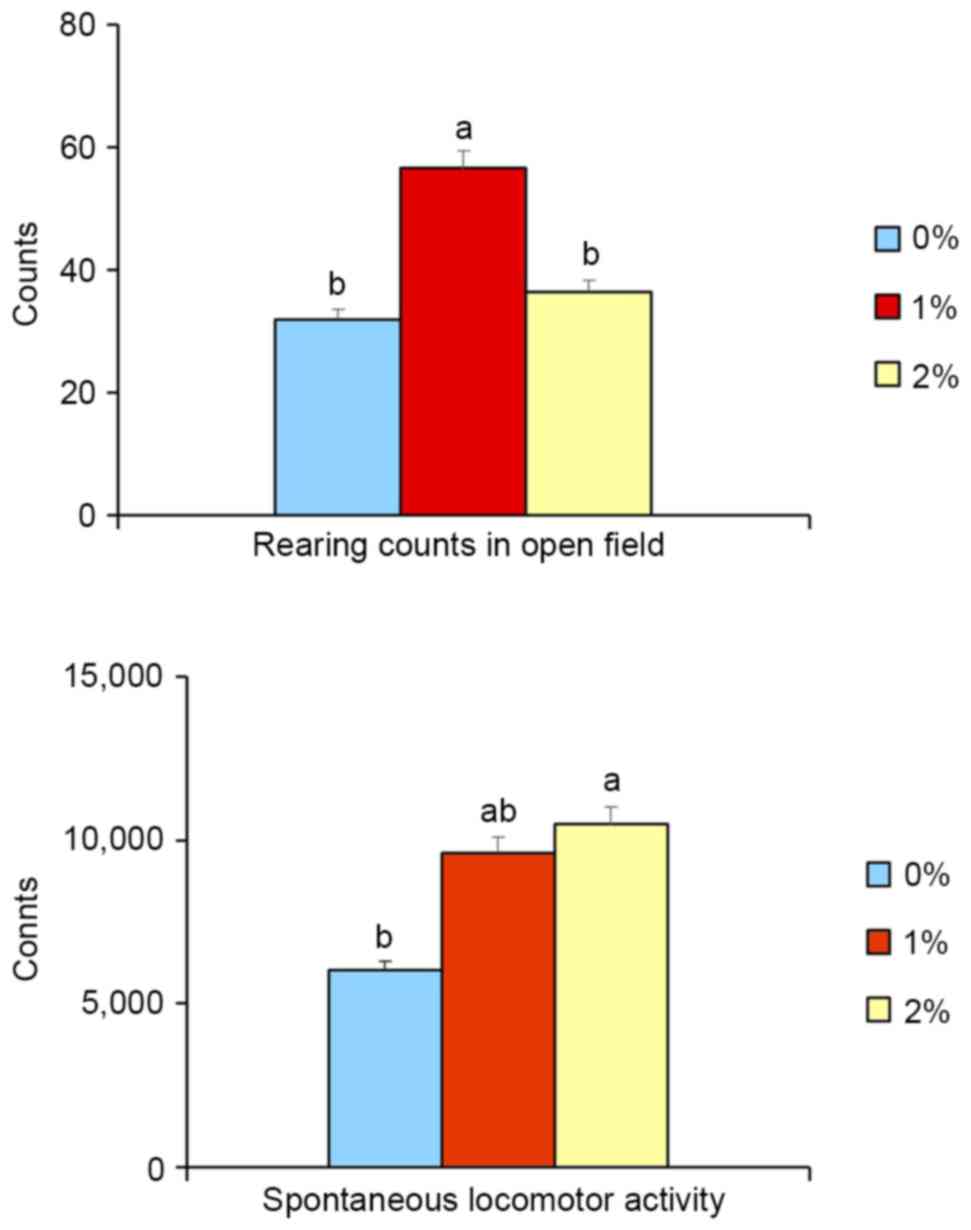
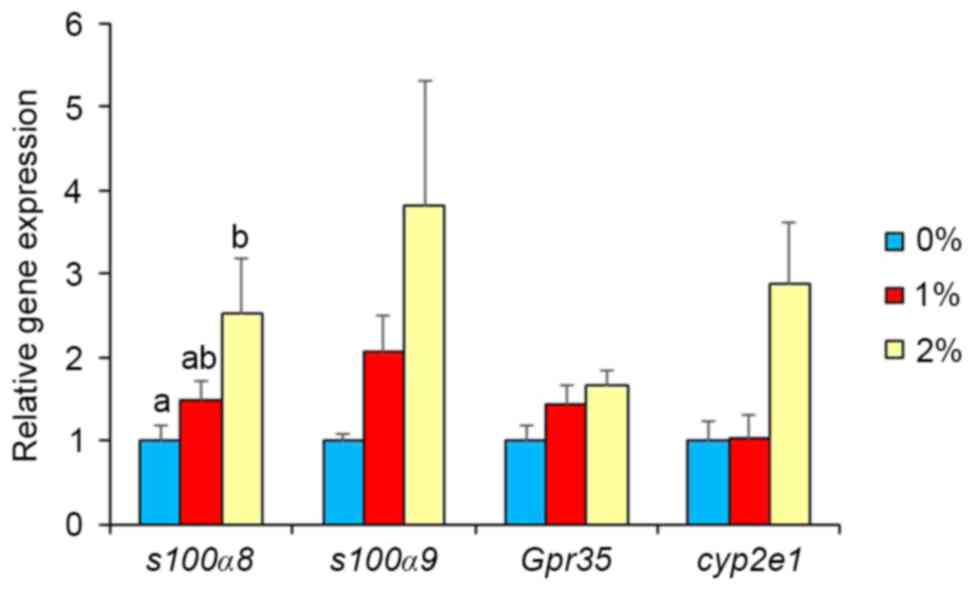
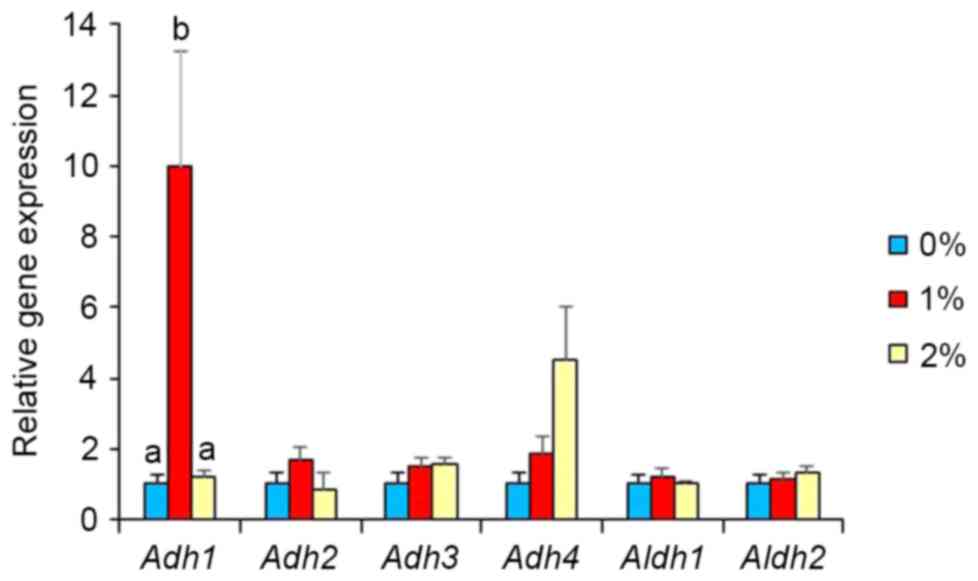
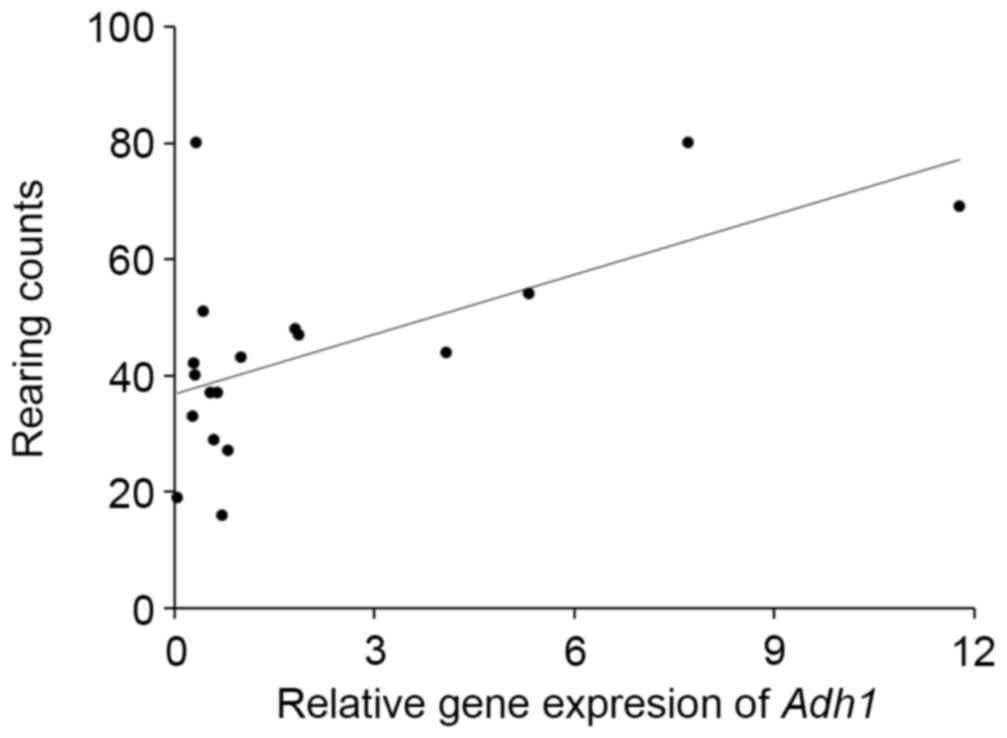
|
1
|
Marmot MG, Rose G, Shipley MJ and Thomas
BJ: Alcohol and mortality: A U-shaped curve. Lancet. 1:580–583.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Di Castelnuovo A, Costanzo S, Bagnardi V,
Donati MB, Iacoviello L and de Gaetano G: Alcohol dosing and total
mortality in men and women: An updated meta-analysis of 34
prospective studies. Arch Intern Med. 166:2437–2445. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nova E, Baccan GC, Veses A, Zapatera B and
Marcos A: Potential health benefits of moderate alcohol
consumption: Current perspectives in research. Proc Nutr Soc.
71:pp. 307–315. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mukamal KJ, Kuller LH, Fitzpatrick AL,
Longstreth WT Jr, Mittleman MA and Siscovick DS: Prospective study
of alcohol consumption and risk of dementia in older adults. JAMA.
289:1405–1413. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peters R, Peters J, Warner J, Beckett N
and Bulpitt C: Alcohol, dementia and cognitive decline in the
elderly: A systematic review. Age Ageing. 37:505–512. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fagrell B, De Faire U, Bondy S, Criqui M,
Gaziano M, Gronbaek M, Jackson R, Klatsky A, Salonen J and Shaper
AG: The effects of light to moderate drinking on cardiovascular
diseases. J Intern Med. 246:331–340. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McCann SE, Sempos C, Freudenheim JL, Muti
P, Russell M, Nochajski TH, Ram M, Hovey K and Trevisan M:
Alcoholic beverage preference and characteristics of drinkers and
nondrinkers in western New York (United States). Nutr Metab
Cardiovasc Dis. 13:2–11. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lieber CS and DeCarli LM: Liquid diet
technique of ethanol administration: 1989 update. Alcohol Alcohol.
24:197–211. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Izu H, Shobayashi M, Manabe Y, Goto K and
Iefuji H: S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)-accumulating sake yeast
suppresses acute alcohol-induced live injury in mice. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 70:2982–2989. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Collins MA, Neafsey EJ, Mukamal KJ, Gray
MO, Parks DA, Das DK and Korthuis RJ: Alcohol in moderation,
cardioprotection and neuroprotection: Epidemiological
considerations and mechanistic studies. Alcohol Clin Exp Res.
33:206–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ilomaki J, Jokanovic N, Tan EC and
Lonnroos E: Alcohol consumption, dementia and cognitive decline: An
overview of systematic reviews. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 10:204–212.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Godfrey J, Jeanguenin L, Castro N, Olney
JJ, Dudley J, Pipkin J, Walls SM, Wang W, Herr DR, Harris GL and
Brasser SM: Chronic voluntary ethanol consumption induces favorable
ceramide profiles in selectively bred alcohol-preferring (P) rats.
PLoS One. 10:e01390122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Osaki A, Okazaki Y, Kimoto A, Izu H and
Kato N: Beneficial effect of low dose of ethanol on liver function
and serum urate in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol
(Tokyo). 60:408–412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hosokawa M, Kasai R, Higuchi K, Takeshita
S, Shimizu K, Hamamoto H, Honma A, Irino M, Toda K, Matsumura A, et
al: Grading score system: A method for evaluation of the degree of
senescence in senescence accelerated mouse (SAM). Mech Ageing Dev.
26:91–102. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takeda T: Senescence-accelerated mouse
(SAM) with special references to neurodegeneration models, SAMP8
and SAMP10 mice. Neurochem Res. 34:639–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Lian K, Han B, Wang Y, Kuo SH,
Geng Y, Qiang J, Sun M and Wang M: Age-related alterations in the
metabolic profile in the hippocampus of the senescence-accelerated
mouse prone 8: A spontaneous Alzheimer's disease mouse model. J
Alzheimers Dis. 39:841–848. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shinozaki M, Takahashi Y, Mukaino M, Saito
N, Toyama Y, Okano H and Nakamura M: Novel concept of motor
functional analysis for spinal cord injury in adult mice. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2011:1574582011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lamming DW: Diminished mTOR signaling: A
common mode of action for endocrine longevity factors.
Springerplus. 3:7352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Easton A, Arbuzova J and Turek FW: The
circadian Clock mutation increases exploratory activity and
escape-seeking behavior. Genes Brain Behav. 2:11–19. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pardo M, López-Cruz L, Valverde O, Ledent
C, Baqi Y, Müller CE, Salamone JD and Correa M: Effect of
subtype-selective adenosine receptor antagonists on basal or
haloperidol-regulated striatal function: Studies of exploratory
locomotion and c-Fos immunoreactivity in outbred and A(2A)R KO
mice. Behav Brain Res. 247:217–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ikegami S, Shumiya S and Kawamura H:
Age-related changes in radial-arm maze learning and basal forebrain
cholinergic systems in senescence accelerated mice (SAM). Behav
Brain Res. 51:15–22. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lalonde R and Strazielle C: Exploratory
activity and motor coordination in old versus middle-aged C57BL/6 J
mice. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 49:39–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aoyama Y, Kim TY, Yoshimoto T, Niimi K,
Takahashi E and Itakura C: Impaired motor function in
senescence-accelerated mouse prone 1 (SAMP1). Brain Res.
1515:48–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arizzi MN, Correa M, Betz AJ, Wisniecki A
and Salamone JD: Behavioral effects of intraventricular injections
of low doses of ethanol, acetaldehyde and acetate in rats: Studies
with low and high rate operant schedules. Behav Brain Res.
147:203–210. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gebhardt C, Németh J, Angel P and Hess J:
S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1622–1631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Divorty N, Mackenzie AE, Nicklin SA and
Milligan G: G protein-coupled receptor 35: An emerging target in
inflammatory and cardiovascular disease. Front Pharmacol. 6:412015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Seitz HK and Wang XD: The role of
cytochrome P450 2E1 in ethanol-mediated carcinogenesis. Subcell
Biochem. 67:131–143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boleda MD, Saubi N, Farrés J and Parés X:
Physiological substrates for rat alcohol dehydrogenase classes:
Aldehydes of lipid peroxidation, omega-hydroxyfatty acids and
retinoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 307:85–90. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Buervenich S, Sydow O, Carmine A, Zhang Z,
Anvret M and Olson L: Alcohol dehydrogenase alleles in Parkinson's
disease. Mov Disord. 15:813–818. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Anvret A, Ran C, Westerlund M, Gellhaar S,
Lindqvist E, Pernold K, Lundströmer K, Duester G, Felder MR, Galter
D and Belin AC: Adh1 and Adh1/4 knockout mice as possible rodent
models for presymptomatic parkinson's disease. Behav Brain Res.
227:252–257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duester G: Alcohol dehydrogenase as a
critical mediator of retinoic acid synthesis from vitamin A in the
mouse embryo. J Nutr. 128 2 Suppl:459S–462S. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Molotkov A, Deltour L, Foglio MH, Cuenca
AE and Duester G: Distinct retinoid metabolic functions for alcohol
dehydrogenase genes Adh1 and Adh4 in protection against vitamin A
toxicity or deficiency revealed in double null mutant mice. J Biol
Chem. 277:13804–13811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sodhi RK and Singh N: Retinoids as
potential targets for Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.
120:117–123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu YY, Ni DF and Xu CM: Gene expression
profiles in the olfactory bulb from a rat model of Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 18:581–593. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Emeson EE, Manaves V, Singer T and Tabesh
T: Chronic alcohol feeding inhibits atherogenesis in C57BL/6
hyperlipidemic mice. Am J Pathol. 147:1749–1758. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|