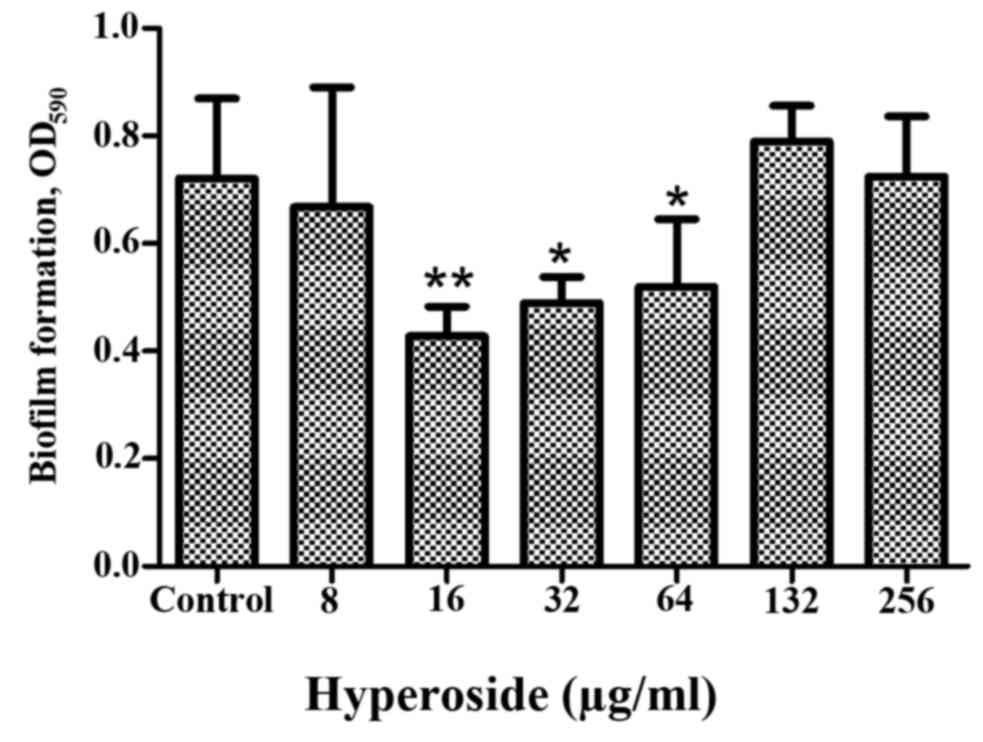
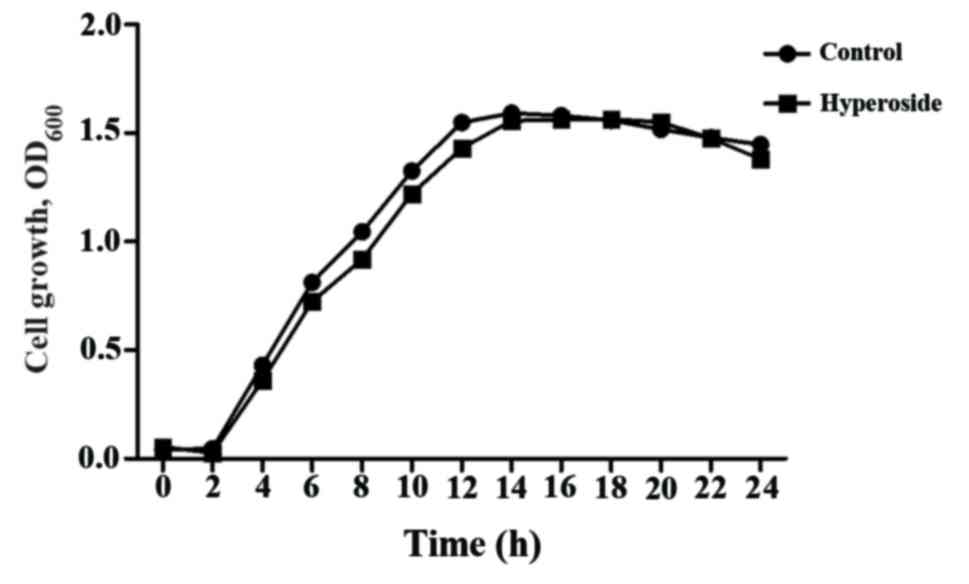
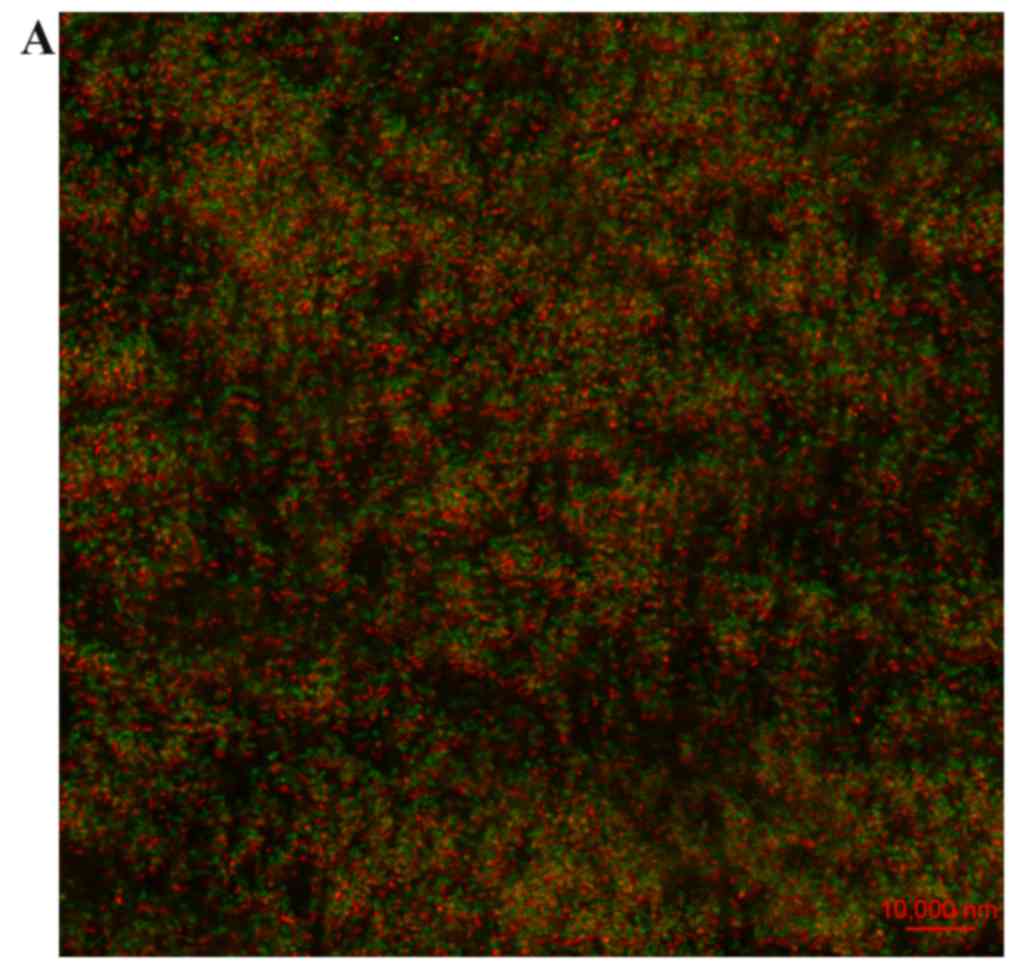
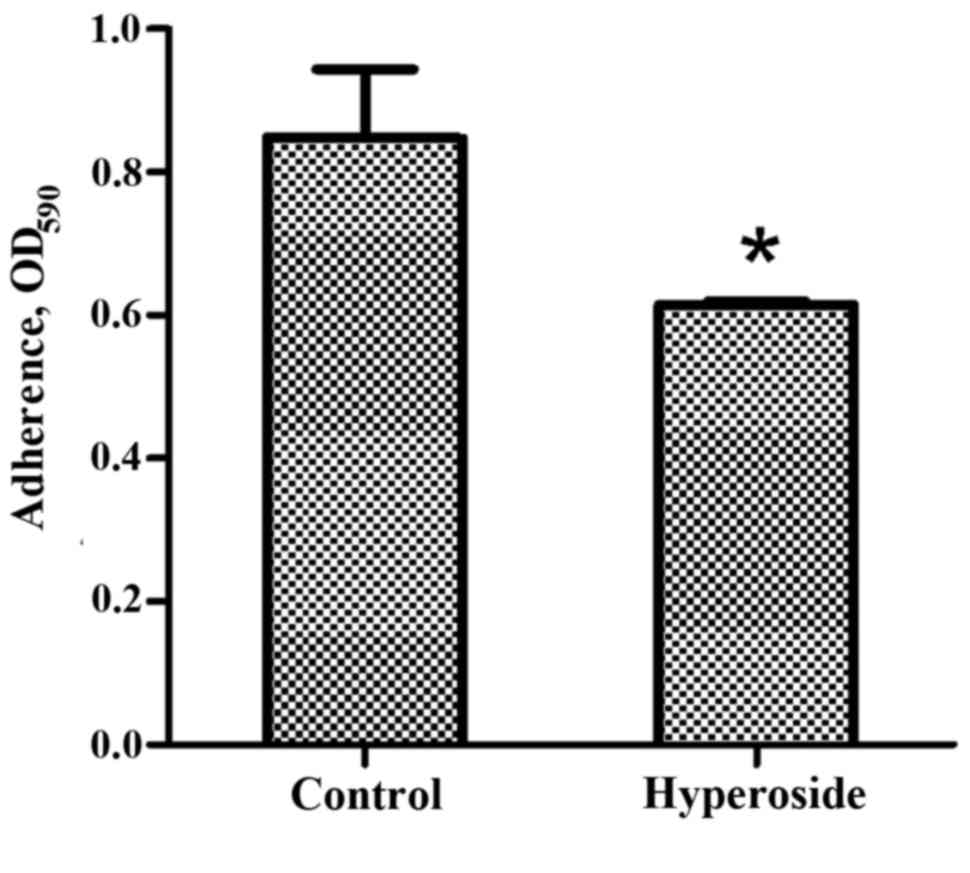
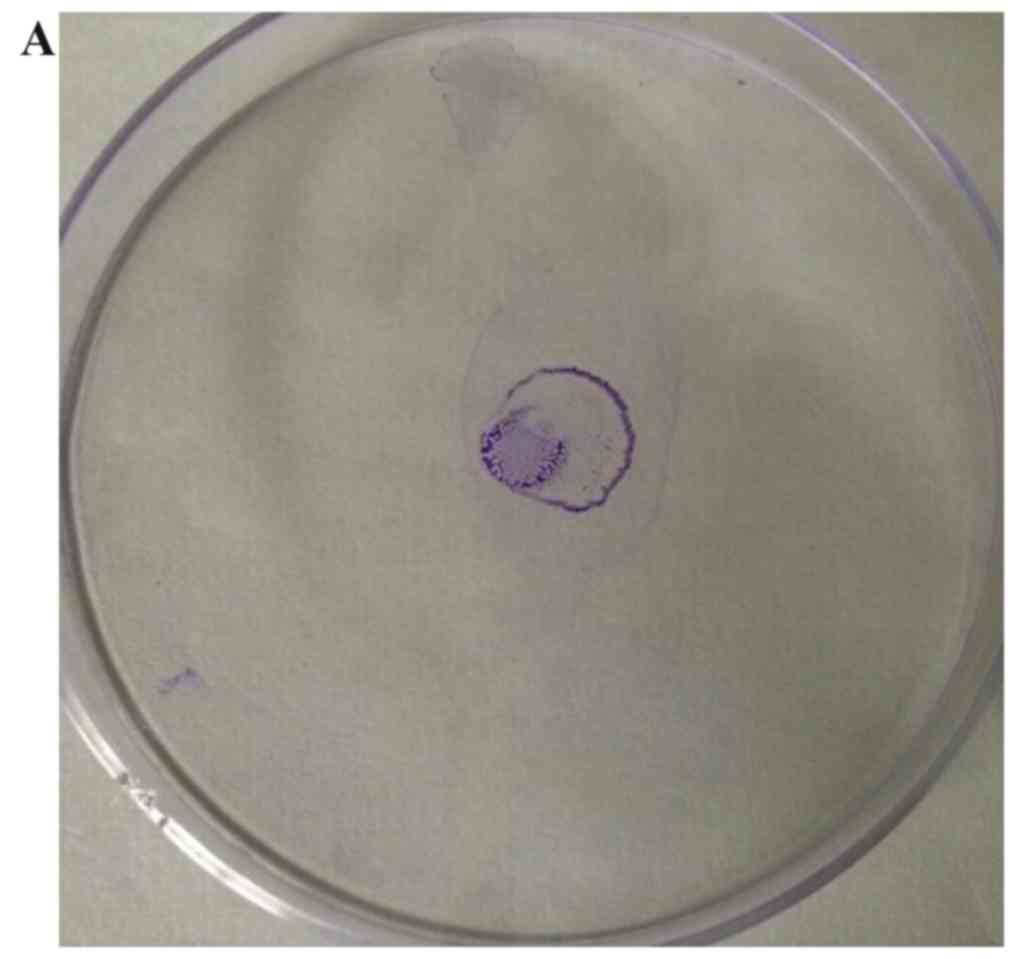
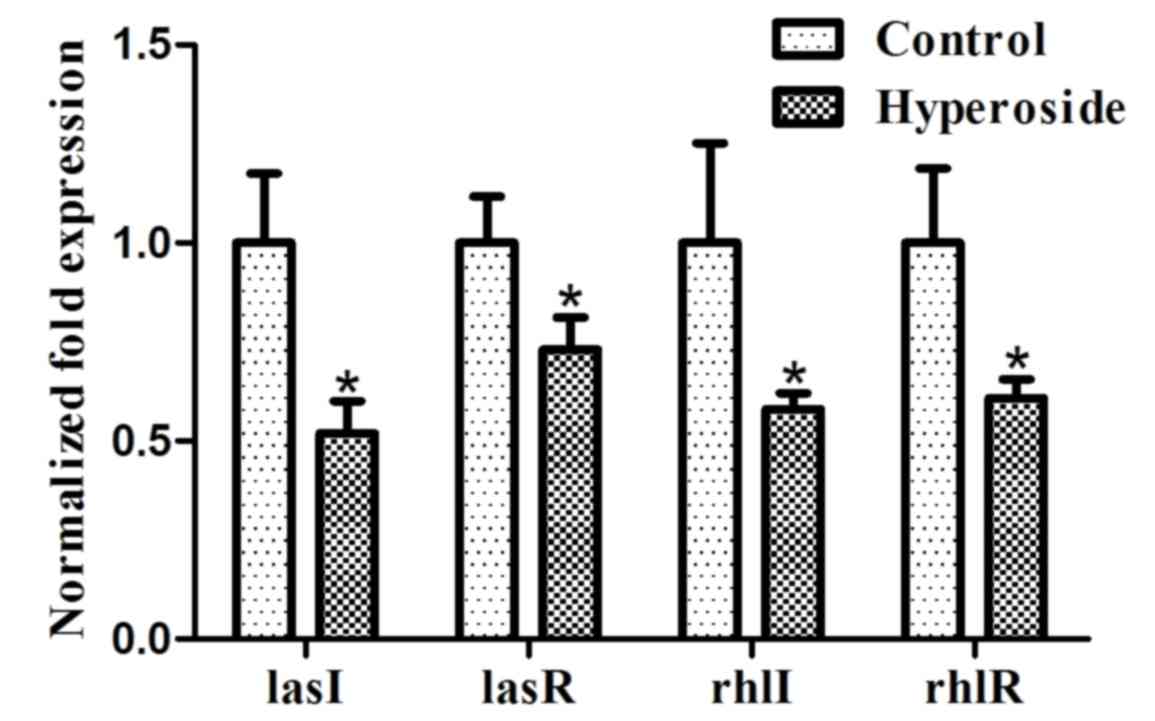
|
1
|
Gristina AG, Oga M, Webb LX and Hobgood
CD: Adherent bacterial colonization in the pathogenesis of
osteomyelitis. Science. 228:990–993. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goossens H: Susceptibility of
multi-drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care
units: Results from the European MYSTIC study group. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 9:980–983. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chatterjee M, Anju CP, Biswas L, Kumar V
Anil, Mohan C Gopi and Biswas R: Antibiotic resistance in
Pseudomonas aeruginosa and alternative therapeutic options. Int J
Med Microbiol. 306:48–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Musken M, Di Fiore S, Romling U and
Häussler S: A 96-well-plate-based optical method for the
quantitative and qualitative evaluation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
biofilm formation and its application to susceptibility testing.
Nat Protoc. 5:1460–1469. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Høiby N, Johansen H Krogh, Moser C, Song
Z, Ciofu O and Kharazmi A: Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the in vitro
and in vivo biofilm mode of growth. Microbes Infect. 3:23–35. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ceri H, Olson ME, Stremick C, Read RR,
Morck D and Buret A: The Calgary Biofilm Device: New technology for
rapid determination of antibiotic susceptibilities of bacterial
biofilms. J Clin Microbiol. 37:1771–1776. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anwar H and Costerton JW: Enhanced
activity of combination of tobramycin and piperacillin for
eradication of sessile biofilm cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 34:1666–1671. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Van Delden C and Iglewski BH: Cell-to-cell
signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg Infect Dis.
4:551–560. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Wang T, Hu J, Ren C, Lei H, Hou Y
and Brantner AH: Anti-biofilm activity of TanReQing, a Traditional
Chinese Medicine used for the treatment of acute pneumonia. J
Ethnopharmacol. 134:165–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Palombo EA: Traditional medicinal plant
extracts and natural products with activity against oral bacteria:
Potential application in the prevention and treatment of oral
diseases. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:6803542011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sayem SM, Manzo E, Ciavatta L, Tramice A,
Cordone A, Zanfardino A, De Felice M and Varcamonti M: Anti-biofilm
activity of an exopolysaccharide from a sponge-associated strain of
Bacillus licheniformis. Microb Cell Fact. 10:742011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X, Shang F, Meng Y, Li L, Cui Y,
Zhang M, Qi K and Xue T: Ethanol extract of Sanguisorba officinalis
L. inhibits biofilm formation of methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcusaureus in an ica-dependent manner. J Dairy Sci.
98:8486–8491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ren S, Wu M, Guo J, Zhang W, Liu X, Sun L,
Holyst R, Hou S, Fang Y and Feng X: Sterilization of
polydimethylsiloxane surface with Chinese herb extract: A new
antibiotic mechanism of chlorogenic acid. Sci Rep. 5:104642015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen ZW, Ma CG and Xu SY: Mechanism of
analgesic action of hyperin. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 24:326–330. 1989.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xin Q and Chen S: Advances in the study of
the protection of hyperin against ischemic injuries of tissues and
organs. Zhong Yao Cai. 26:213–215. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang WQ, Ma CG and Xu SY: Protective
effect of hyperin against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion
injury. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 17:341–344. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Verma N, Amresh G, Sahu PK, Mishra N, Rao
ChV and Singh AP: Pharmacological evaluation of hyperin for
antihyperglycemic activity and effect on lipid profile in diabetic
rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 51:65–72. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee S, Park HS, Notsu Y, Ban HS, Kim YP,
Ishihara K, Hirasawa N, Jung SH, Lee YS, Lim SS, et al: Effects of
hyperin, isoquercitrin and quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced
nitrite production in rat peritoneal macrophages. Phytother Res.
22:1552–1556. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Marčetić MD, Milenković MT, Lakušić DV and
Lakušić BS: Chemical Composition and antimicrobial activity of the
essential oil and methanol extract of Hypericum aegypticum subsp.
webbii (Spach) N. Robson. Chem Biodivers. 13:427–436. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee S, Shin DS, Oh KB and Shin KH:
Antibacterial compounds from the leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus.
Arch Pharm Res. 26:40–42. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang SS, Wang DM, Pu WJ and Li DW:
Phytochemical profiles, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of
three Potentilla species. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:3212013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Neidig A, Yeung AT, Rosay T, Tettmann B,
Strempel N, Rueger M, Lesouhaitier O and Overhage J: TypA is
involved in virulence, antimicrobial resistance and biofilm
formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 13:772013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bala A, Kumar R and Harjai K: Inhibition
of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by azithromycin and its
effectiveness in urinary tract infections. J Med Microbiol.
60:300–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xing HY, Liu Y, Chen JH, Sun FJ, Shi HQ
and Xia PY: Hyperoside attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced L02
cell damage via MAPK-dependent Keap-Nrf-ARE signaling pathway.
Biochem Biophys Commun. 410:759–765. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li W, Liu M, Xu YF, Feng Y, Che JP, Wang
GC and Zheng JH: Combination of quercetin and hyperoside has
anticancer effects on renal cancer cells through inhibition of
oncogenic microRNA-27a. Oncol Rep. 31:117–124. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ku SK, Kwak S, Kwon OJ and Bae JS:
Hyperoside inhibits high-glucose-induced vascular inflammation in
vitro and in vivo. Inflammation. 37:1389–1400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Abedini A, Roumy V, Mahieux S, Biabiany M,
Standaert-Vitse A, Rivière C, Sahpaz S, Bailleul F, Neut C and
Hennebelle T: Rosmarinic acid and its methyl ester as antimicrobial
components of the hydromethanolic extract of Hyptis atrorubens
poit. (Lamiaceae). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:6045362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsunaga T, Nakahara A, Minnatul KM,
Noiri Y, Ebisu S, Kato A and Azakami H: The inhibitory effects of
catechins on biofilm formation by the periodontopathogenic
bacterium, Eikenella corrodens. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
74:2445–2450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giltner CL, van Schaik EJ, Audette GF, Kao
D, Hodges RS, Hassett DJ and Irvin RT: The Pseudomonas aeruginosa
type IV pilin receptor binding domain functions as an adhesin for
both biotic and abiotic surfaces. Mol Microbiol. 59:1083–1096.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davies DG, Parsek MR, Pearson JP, Iglewski
BH, Costerton JW and Greenberg EP: The involvement of cell-to-cell
signals in the development of a bacterial biofilm. Science.
280:295–298. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morici LA, Carterson AJ, Wagner VE, Frisk
A, Schurr JR, Hönerzu Bentrup K, Hassett DJ, Iglewski BH, Sauer K
and Schurr MJ: Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgR represses the Rhl
quorum-sensing system in a biofilm-specific manner. J Bacteriol.
189:7752–7764. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
De Kievit TR, Gillis R, Marx S, Brown C
and Iglewski BH: Quorum-sensing genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
biofilms: Their role and expression patterns. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 67:1865–1873. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zeng Z, Qian L, Cao L, Tan H, Huang Y, Xue
X, Shen Y and Zhou S: Virtual screening for novel quorum sensing
inhibitors to eradicate biofilm formation of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 79:119–126. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vo GD, Brindle E and Heys J: An
experimentally validated immersed boundary model of fluid-biofilm
interaction. Water Sci Technol. 61:3033–3040. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cirioni O, Silvestri C, Ghiselli R, Kamysz
W, Minardi D, Castelli P, Orlando F, Kamysz E, Provinciali M,
Muzzonigro G, et al: In vitro and in vivo effects of sub-MICs of
pexiganan and imipenem of Pseudomonas aeruginosa adhesion and
biofilm development. Infez Med. 21:287–295. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao YL, Zhou YH, Chen JQ, Huang QY, Han
Q, Liu B, Cheng GD and Li YH: Quantitative proteomic analysis of
sub-MIC erythromycin inhibiting biofilm formation of S, suis in
vitro. J Proteomics. 116:1–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang C, Cheng H, Zhang X, Xu S, Guan Y, Yu
L and Yun Y: In vitro activity of baicalin against non-albicans
Candida biofilms. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 35:639–641. 2010.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Saleem M, Nazir M, Ali MS, Hussain H, Lee
YS, Riaz N and Jabbar A: Antimicrobial natural products: An update
on future antibiotic drug candidates. Nat Prod Rep. 27:238–254.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tolker-Nielsen T, Brinch UC, Ragas PC,
Andersen JB, Jacobsen CS and Molin S: Development and dynamics of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa sp. biofilms. J Bacteriol. 182:6482–6489.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton
JW and Davies DG: Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple
phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J Bacteriol.
184:1140–1154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Köhler T, Curty LK, Barja F, van Delden C
and Pechére JC: Swarming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is dependent on
cell-to-cell signaling and requires flagella and pili. J Bacteriol.
182:5990–5996. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Olson KM, Starks CM, Williams RB,
O'Neil-Johnson M, Huang Z, Ellis M, Reilly JE and Eldridge GR:
Novel pentadecenyl tetrazole enhances susceptibility of
methincillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm to gentamicin.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 55:3691–3695. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pettit RK, Weber CA, Lawrence SB, Pettit
GR, Kean MJ and Cage GD: In vivo activity of anprocide alone and in
vitro activity in combination with conventional antibiotics against
Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. J
Med Microbiol. 58:1203–1206. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
McConeghy KW and LaPlante KL: In vitro
activity of tigecycline in combination with gentamicin against
biofilm-forming Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.
68:1–6. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen YQ, Zuo XJ, Zhu LN, Song ZJ, Shi HZ,
Zuo P and Guo XH: In vitro effects of honeysuckle aqueous extracts
alone and in combination with ceftazidime on Pseudomonas aeruginosa
biofilms. Chin J Microbiol Immunol. 24:738–742. 2004.
|
|
47
|
Kong JL, Liu XL, Chen YQ, et al: In vitro
effect of Scutellaria aqueous extracts combination with
levofloxacin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Tianjin Med J.
36:331–333. 2008.
|
|
48
|
Huang XM, Huang LC, Fang ZH, et al:
Synergism of Sophora flavescens ait and ciprofloxacin on
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J Shaoguan Univ. 27:60–63.
2006.
|
|
49
|
Zhou Q, Deng CH, Zhang W, et al: In vitro
effects of aqueous extract of Sophora in combination with
ceftazidime on elimination of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J
New Chin Med. 40:98–99. 2008.
|
|
50
|
Jayaraman P, Sakharkar MK, Lim CS, Tang TH
and Sakharkar KR: Activity and interactions of antibiotic and
phytochemical combinations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in vitro.
Int J Biol Sci. 6:556–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Das MC, Sandhu P, Gupta P, Rudrapaul P, De
UC, Tribedi P, Akhter Y and Bhattacharjee S: Attenuation of
Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation by Vitexin: A
combinatorial study with azithromycin and gentamicin. Sci Rep.
6:233372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|