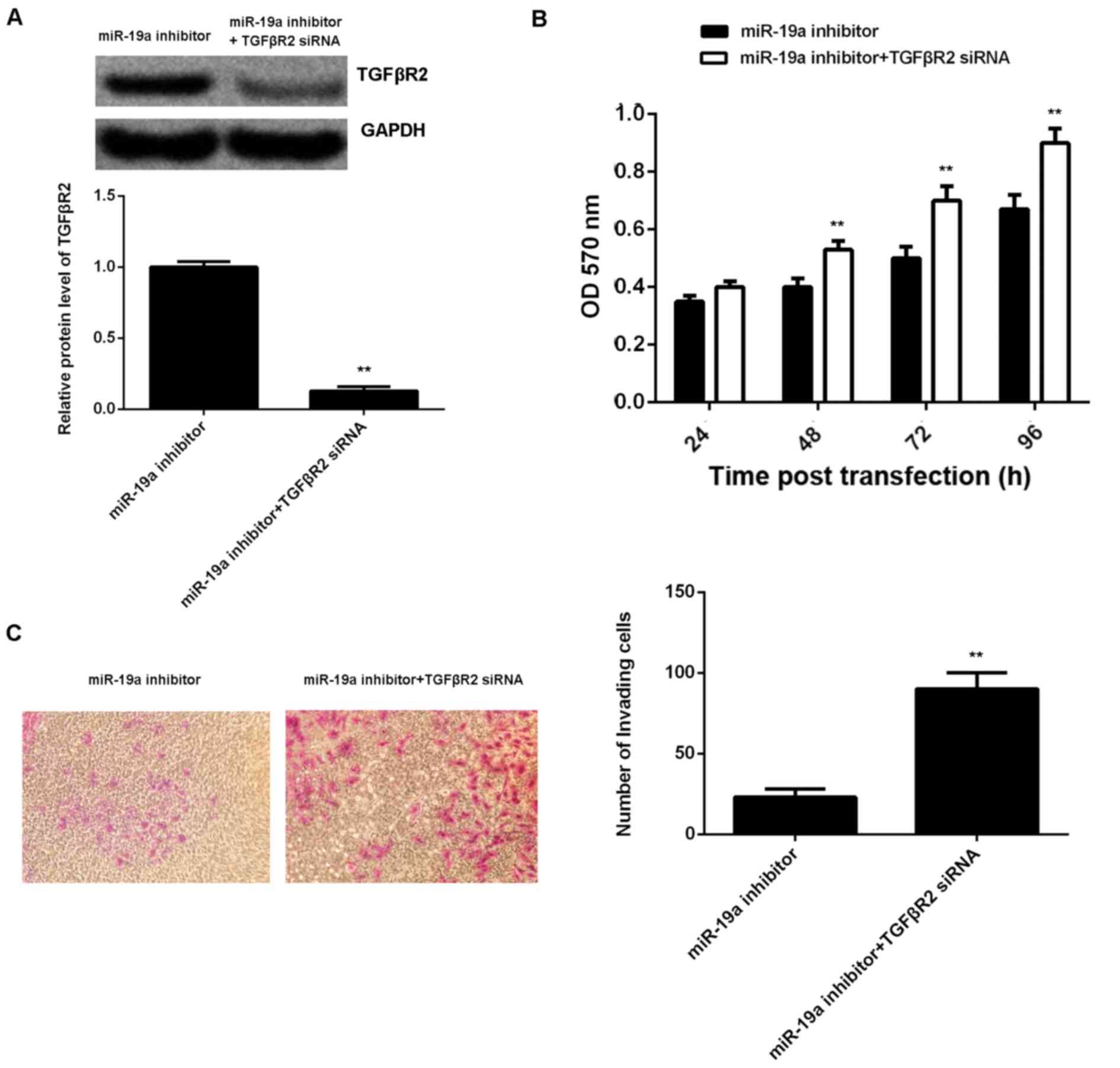
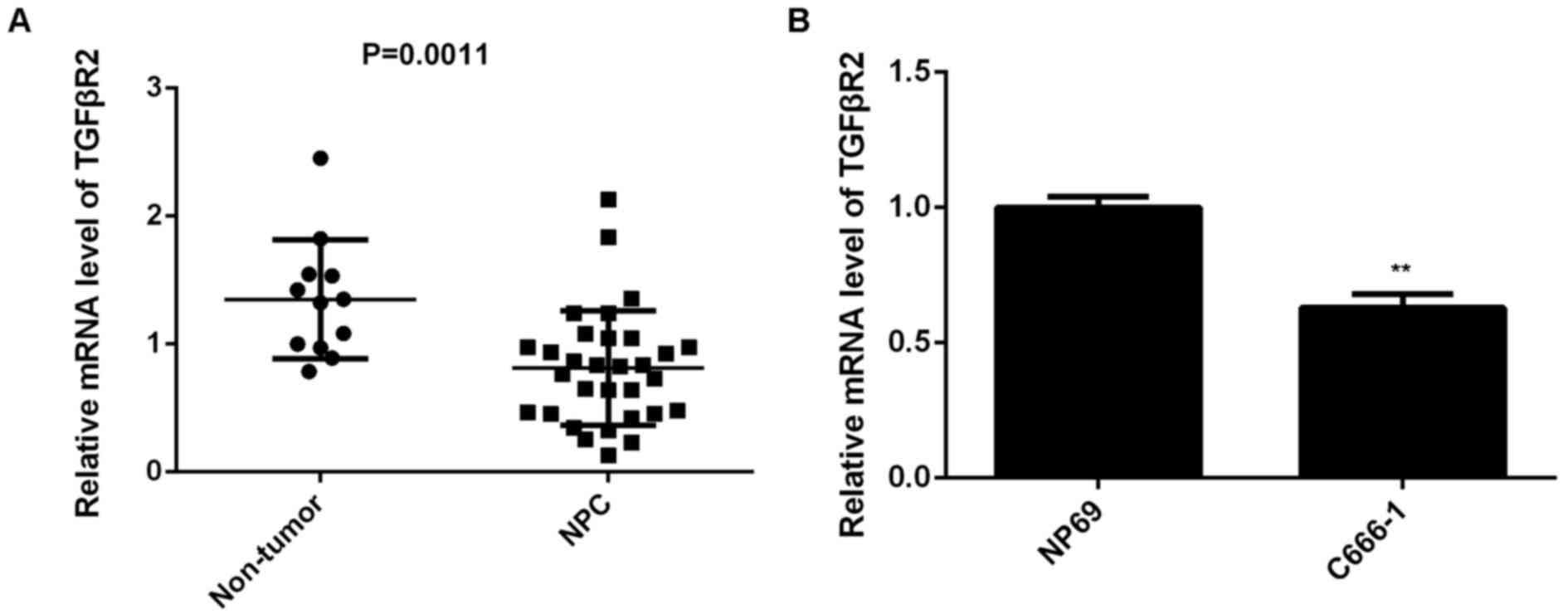
|
1
|
Wei WI and Sham JS: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Lancet. 365:2041–2054. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bei JX, Li Y, Jia WH, Feng BJ, Zhou G,
Chen LZ, Feng QS, Low HQ, Zhang H, He F, et al: A genome-wide
association study of nasopharyngeal carcinoma identifies three new
susceptibility loci. Nat Genet. 42:599–603. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raab-Traub N: Epstein-Barr virus in the
pathogenesis of NPC. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:431–441. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deng M, Ye Q, Qin Z, Zheng Y, He W, Tang
H, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Zhou M, Li X, et al: miR-214 promotes
tumorigenesis by targeting lactotransferrin in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:1793–1800. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun Q, Liu T, Zhang T, Du S, Xie GX, Lin
X, Chen L and Yuan Y: miR-101 sensitizes human nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells to radiation by targeting stathmin 1. Mol Med Rep.
11:3330–3336. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yamamoto K, Ito S, Hanafusa H, Shimizu K
and Ouchida M: Uncovering direct targets of miR-19a involved in
lung cancer progression. PLoS One. 10:e01378872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Q, Liu M, Ma F, Luo Y, Cai R, Wang L,
Xu N and Xu B: Correction: Circulating miR-19a and miR-205 in serum
may predict the sensitivity of luminal a subtype of breast cancer
patients to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with epirubicin plus
paclitaxel. PLoS One. 10:e01368262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang L, Wang X, Wen C, Yang X, Song M,
Chen J, Wang C, Zhang B, Wang L, Iwamoto A, et al: Hsa-miR-19a is
associated with lymph metastasis and mediates the TNF-α induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep.
5:133502015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiao W, Gao Z, Duan Y, Yuan W and Ke Y:
Downregulation of miR-19a exhibits inhibitory effects on metastatic
renal cell carcinoma by targeting PIK3CA and inactivating Notch
signaling in vitro. Oncol Rep. 34:739–746. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan Y, Yin H, Zhang H, Fang J, Zheng W, Li
ID, Li Y, Cao W, Sun C, Liang Y, et al: Sp1-driven up-regulation of
miR-19a decreases RHOB and promotes pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget.
6:17391–17403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu WD, Zuo Y, Xu Z and Zhang M: MiR-19a
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through PI3K/AKT pathway
in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 21:4564–4573.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu TY, Zhang TH, Qu LM, Feng JP, Tian LL,
Zhang BH, Li DD, Sun YN and Liu M: MiR-19a is correlated with
prognosis and apoptosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by
regulating TIMP-2 expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:56–63.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng Y, Liu J, Kang Y, He Y, Liang B, Yang
P and Yu Z: miR-19a acts as an oncogenic microRNA and is
up-regulated in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:672014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pezzini A, Del Zotto E, Giossi A, Volonghi
I, Costa P and Padovani A: Transforming growth factor β signaling
perturbation in the Loeys-Dietz syndrome. Curr Med Chem.
19:454–460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang YS, Zhong Y, Yu L and Wang L:
Association between the TGFBR2 G-875A polymorphism and cancer risk:
Evidence from a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:8705–8708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de Miranda NF, van Dinther M, Van den
Akker BE, van Wezel T, ten Dijke P and Morreau H: Transforming
growth factor β signaling in colorectal cancer cells with
microsatellite instability despite biallelic mutations in TGFBR2.
Gastroenterology. 148:1427–1437.e8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang W, Zeng Z, Fan S, Wang J, Yang J,
Zhou Y, Li X, Huang D, Liang F, Wu M, et al: Evaluation of the
prognostic value of TGF-β superfamily type I receptor and TGF-β
type II receptor expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using
high-throughput tissue microarrays. J Mol Histol. 43:297–306. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang G, Nishimoto K, Zhou Z, Hughes D and
Kleinerman ES: miR-20a encoded by the miR-17-92 cluster increases
the metastatic potential of osteosarcoma cells by regulating Fas
expression. Cancer Res. 72:908–916. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li H, Bian C, Liao L, Li J and Zhao RC:
miR-17-5p promotes human breast cancer cell migration and invasion
through suppression of HBP1. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:565–575.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen HC, Chen GH, Chen YH, Liao WL, Liu
CY, Chang KP, Chang YS and Chen SJ: MicroRNA deregulation and
pathway alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer.
100:1002–1011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo Z, Dai Y, Zhang L, Jiang C, Li Z, Yang
J, McCarthy JB, She X, Zhang W, Ma J, et al: miR-18a promotes
malignant progression by impairing microRNA biogenesis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 34:415–425. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hao M, Zang M, Wendlandt E, Xu Y, An G,
Gong D, Li F, Qi F, Zhang Y, Yang Y, et al: Low serum miR-19a
expression as a novel poor prognostic indicator in multiple
myeloma. Int J Cancer. 136:1835–1844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu G, Li H, Wang X, Wu T, Zhu J, Huang S,
Wan Y and Tang J: MicroRNA-19a targets tissue factor to inhibit
colon cancer cells migration and invasion. Mol Cell Biochem.
380:239–247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang Z, Yin J, Fu W, Mo Y, Pan Y, Dai L,
Huang H, Li S and Zhao J: MiRNA 17 family regulates
cisplatin-resistant and metastasis by targeting TGFbetaR2 in NSCLC.
PLoS One. 9:e946392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma ZL, Hou PP, Li YL, Wang DT, Yuan TW,
Wei JL, Zhao BT, Lou JT, Zhao XT, Jin Y and Jin YX: MicroRNA-34a
inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of non-small
cell lung cancer H1299 cell line by targeting TGFβR2. Tumour Biol.
36:2481–2490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xiong W, Zeng ZY, Xia JH, Xia K, Shen SR,
Li XL, Hu DX, Tan C, Xiang JJ, Zhou J, et al: A susceptibility
locus at chromosome 3p21 linked to familial nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 64:1972–1974. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lyu X, Fang W, Cai L, Zheng H, Ye Y, Zhang
L, Li J, Peng H, Cho WC, Wang E, et al: TGFβR2 is a major target of
miR-93 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma aggressiveness. Mol Cancer.
13:512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|