|
1
|
Yee M, Buczynski BW and O'Reilly MA:
Neonatal hyperoxia stimulates the expansion of alveolar epithelial
type II cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:757–766. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Steer JH, Mann TS, Lo SZ, Inglis JJ, Yap
HS, Henry PJ and Joyce DA: Early induction of uncoupling protein-2
in pulmonary macrophages in hyperoxia-associated lung injury. Inhal
Toxicol. 25:544–552. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hong Y, Sun LI, Sun R, Chen H, Yu Y and
Xie K: Combination therapy of molecular hydrogen and hyperoxia
improves survival rate and organ damage in a zymosan-induced
generalized inflammation model. Exp Ther Med. 11:2590–2596. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chowdhury Roy S, Sengupta S, Biswas S,
Sinha TK, Sen R, Basak RK, Adhikari B and Bhattacharyya A:
Bacterial fucose-rich polysaccharide stabilizes MAPK-mediated
Nrf2/Keap1 signaling by directly scavenging reactive oxygen species
during hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis of human lung fibroblast
cells. PLoS One. 9:e1136632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giorgio M, Trinei M, Migliaccio E and
Pelicci PG: Hydrogen peroxide: A metabolic by-product or a common
mediator of ageing signals? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:722–728. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carnesecchi S, Deffert C, Pagano A,
Garrido-Urbani S, Métrailler-Ruchonnet I, Schäppi M, Donati Y,
Matthay MA, Krause KH and Argiroffo Barazzone C: NADPH oxidase-1
plays a crucial role in hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury in
mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 180:972–981. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Crane DD, Bauler TJ, Wehrly TD and Bosio
CM: Mitochondrial ROS potentiates indirect activation of the AIM2
inflammasome. Front Microbiol. 5:4382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oparka M, Walczak J, Malinska D, van Oppen
LM, Szczepanowska J, Koopman WJ and Wieckowski MR: Quantifying ROS
levels using CM-H2DCFDA and HyPer. Methods. 109:3–11. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ishibashi T: Molecular hydrogen: New
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapy for rheumatoid arthritis
and related diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 19:6375–6381. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai X, Chen X, Wang X, Xu C, Guo Q, Zhu L,
Zhu S and Xu J: Pre-protective effect of lipoic acid on injury
induced by H2O2 in IPEC-J2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 378:73–81.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rhee SG: Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary
evil for cell signaling. Science. 312:1882–1883. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Z, Choo-Wing R, Sun H, Sureshbabu A,
Sakurai R, Rehan VK and Bhandari V: A potential role of the JNK
pathway in hyperoxia-induced cell death, myofibroblast
transdifferentiation and TGF-β1-mediated injury in the developing
murine lung. BMC Cell Biol. 12:542011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mikami Y, Iwase T, Komiyama Y, Matsumoto
N, Oki H and Komiyama K: Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor
inhibits expression of polymeric immunoglobulin receptor via the
NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Immunol. 67:568–574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
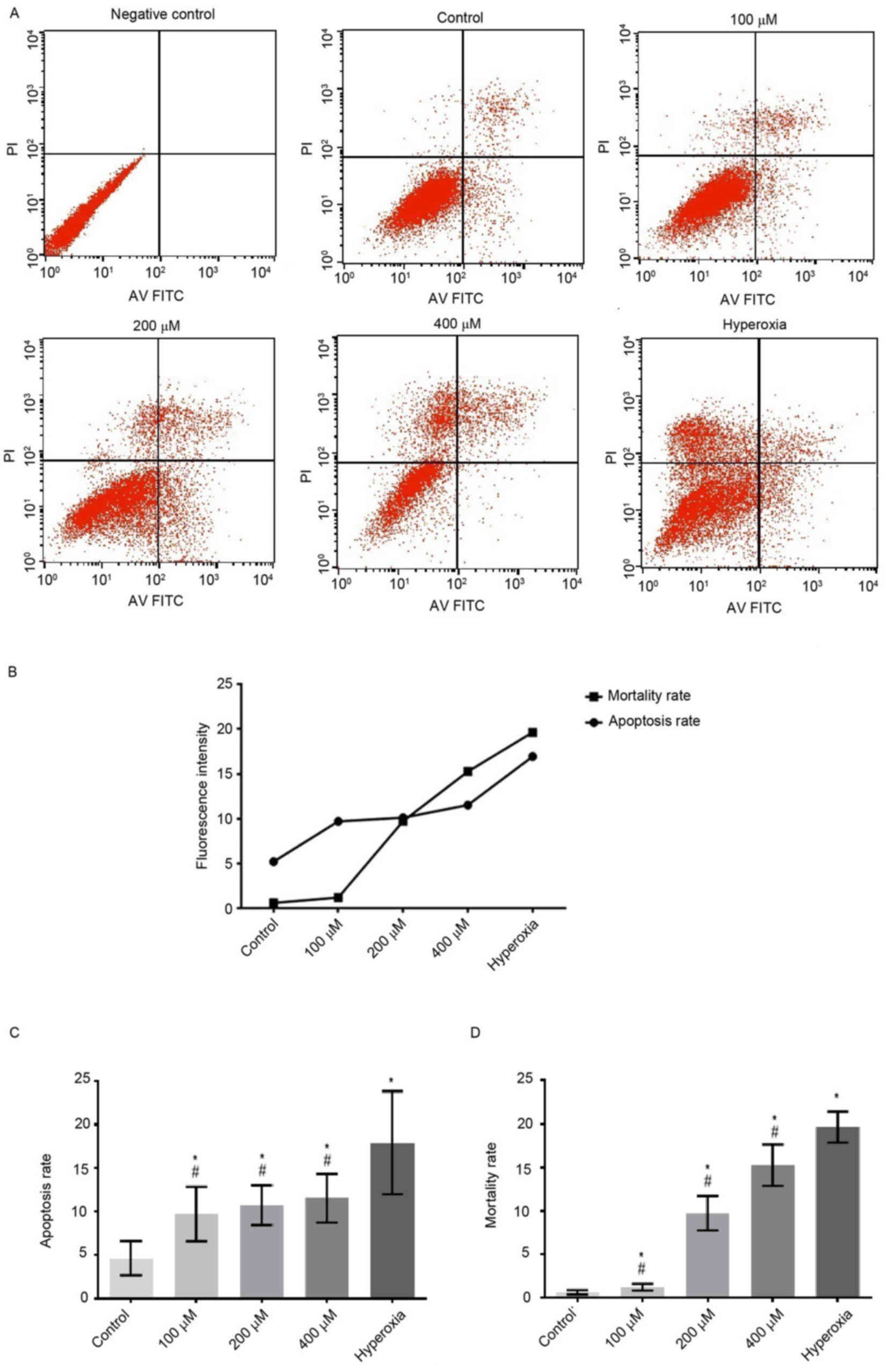
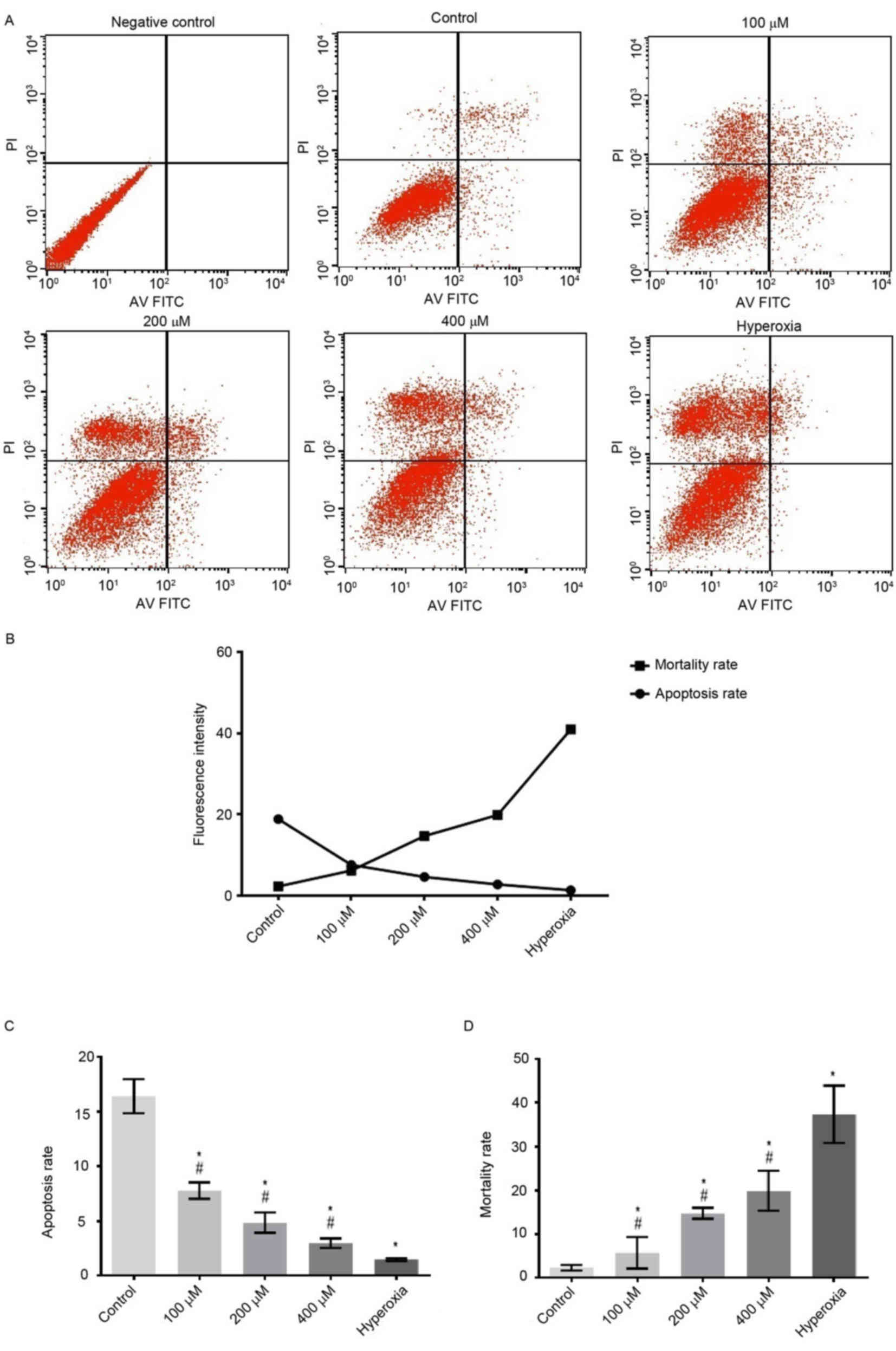
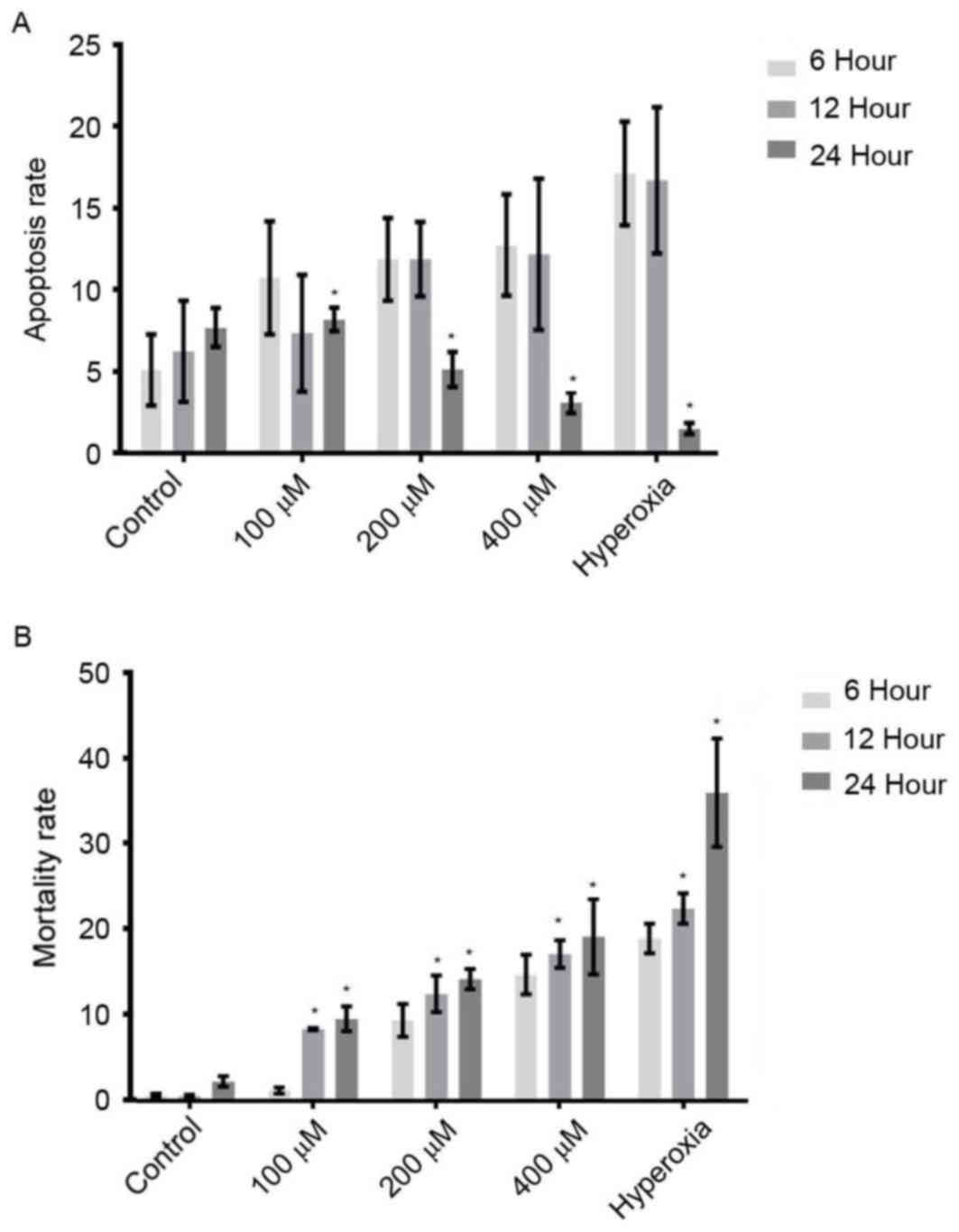
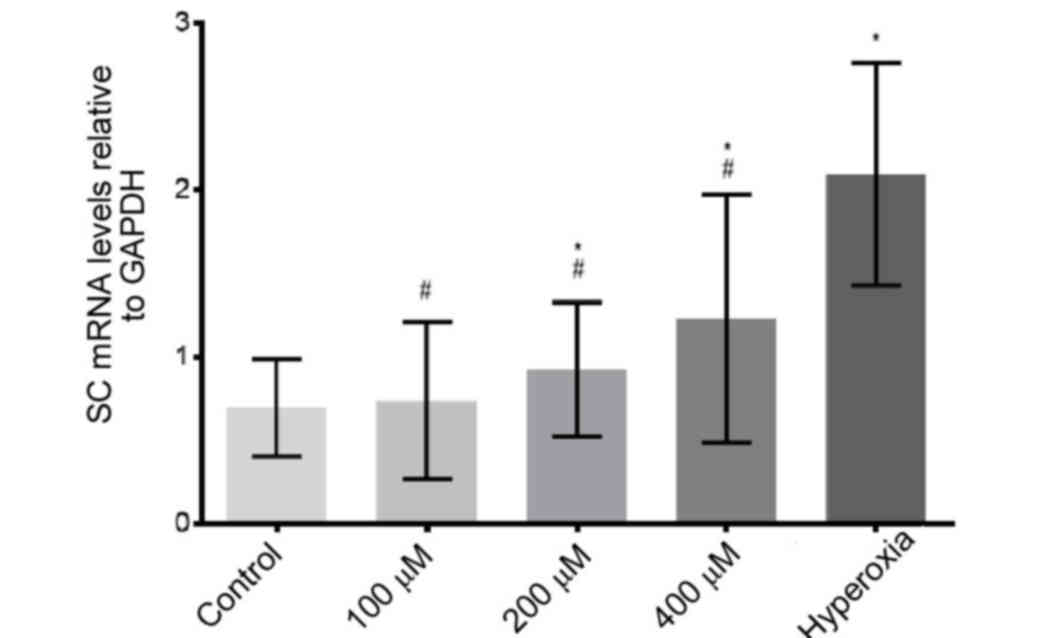
Liu DY, Jiang T, Wang S and Cao X: Effect
of hyperoxia on pulmonary SIgA and its components, IgA and SC. J
Clin Immunol. 33:1009–1017. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Macpherson AJ, McCoy KD, Johansen FE and
Brandtzaeg P: The immune geography of IgA induction and function.
Mucosal Immunol. 1:11–22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mostov KE and Deitcher DL: Polymeric
immunoglobulin receptor expressed in MDCK cells transcytoses IgA.
Cell. 46:613–621. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johansen FE and Kaetzel CS: Regulation of
the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor and IgA transport: New
advances in environmental factors that stimulate pIgR expression
and its role in mucosal immunity. Mucosal Immunol. 4:598–602. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bruno ME, Frantz AL, Rogier EW, Johansen
FE and Kaetzel CS: Regulation of the polymeric immunoglobulin
receptor by the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways in
intestinal epithelial cells. Mucosal Immunol. 4:468–478. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Davids BJ, Palm JE, Housley MP, Smith JR,
Andersen YS, Martin MG, Hendrickson BA, Johansen FE, Svärd SG,
Gillin FD and Eckmann L: Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in
intestinal immune defense against the lumen-dwelling protozoan
parasite Giardia. J Immunol. 177:6281–6290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Perrier C, Sprenger N and Corthesy B:
Glycans on secretory component participate in innate protection
against mucosal pathogens. J Biol Chem. 281:14280–14287. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaetzel CS: The polymeric immunoglobulin
receptor: Bridging innate and adaptive immune responses at mucosal
surfaces. Immunol Rev. 206:83–99. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baylor AE, Diebel LN, Liberati DM,
Dulchavsky SA, Diglio CA and Brown WJ: The effects of varying
oxygen conditions and immunoglobulin A on barrier defense to
bacterial invasion. Am Surg. 69:231–237. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diebel LN, Liberati DM, Brown WJ,
Dulchavsky SA, Painter TM, Diglio CA and Montgomery PC: Secretory
immunoglobulin A blocks hypoxia-augmented bacterial passage across
Madin-Darby canine kidney cell monolayers. J Trauma. 43:759–763.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Torbati D, Tan GH, Smith S, Frazier KS,
Gelvez J, Fakioglu H and Totapally BR: Multiple-organ effect of
normobaric hyperoxia in neonatal rats. J Crit Care. 21:85–94. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu DY and Li JJ: Effect of hyperoxia on
the intestinal IgA secretory component in neonatal rats and on
intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res.
43:1034–1041. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Corthesy B: Role of secretory
immunoglobulin A and secretory component in the protection of
mucosal surfaces. Future Microbiol. 5:817–829. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu B, Tan X, Liang J, Wu S, Liu J, Zhang
Q and Zhu R: A reduction in reactive oxygen species contributes to
dihydromyricetin-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 4:70412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thannickal VJ and Fanburg BL: Reactive
oxygen species in cell signaling. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 279:L1005–L1028. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Matsuzawa A and Ichijo H: Redox control of
cell fate by MAP kinase: Physiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase
pathway in stress signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1780:1325–1336.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Woolley JF, Stanicka J and Cotter TG:
Recent advances in reactive oxygen species measurement in
biological systems. Trends Biochem Sci. 38:556–565. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kang KA, Lee HC, Lee JJ, Hong MN, Park MJ,
Lee YS, Choi HD, Kim N, Ko YG and Lee JS: Effects of combined
radiofrequency radiation exposure on levels of reactive oxygen
species in neuronal cells. J Radiat Res. 55:265–276. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shen HM and Liu ZG: JNK signaling pathway
is a key modulator in cell death mediated by reactive oxygen and
nitrogen species. Free Radical Biol Med. 40:928–939. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kajino-Sakamoto R, Omori E, Nighot PK,
Blikslager AT, Matsumoto K and Ninomiya-Tsuji J: TGF-beta-activated
kinase 1 signaling maintains intestinal integrity by preventing
accumulation of reactive oxygen species in the intestinal
epithelium. J Immunol. 185:4729–4737. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fujisawa T, Takeda K and Ichijo H: ASK
family proteins in stress response and disease. Mol Biotechnol.
37:13–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xiao J, Deng J, Lv L, Kang Q, Ma P, Yan F,
Song X, Gao B, Zhang Y and Xu J: Hydrogen peroxide induce human
cytomegalovirus replication through the activation of p38-MAPK
signaling pathway. Viruses. 7:2816–2833. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma Z, Moruzzi N, Catrina SB, Grill V and
Björklund A: Hyperoxia inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion
and mitochondrial metabolism in rat pancreatic islets. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 443:223–228. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jin S, Ray RM and Johnson LR:
TNF-alpha/cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in intestinal epithelial
cells requires Rac1-regulated reactive oxygen species. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G928–G937. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee MK, Lu Y, Di LQ and Xu HQ: Protection
of Tong-Sai-Mai Decoction against Apoptosis Induced by H2O2 in PC12
Cells: Mechanisms via Bcl-2-Mitochondria-ROS-INOS Pathway. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:3714192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kina S, Nakasone T, Takemoto H, Matayoshi
A, Makishi S, Sunagawa N, Liang F, Phonaphonh T and Sunakawa H:
Regulation of chemokine production via oxidative pathway in HeLa
cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2009:1837602009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|