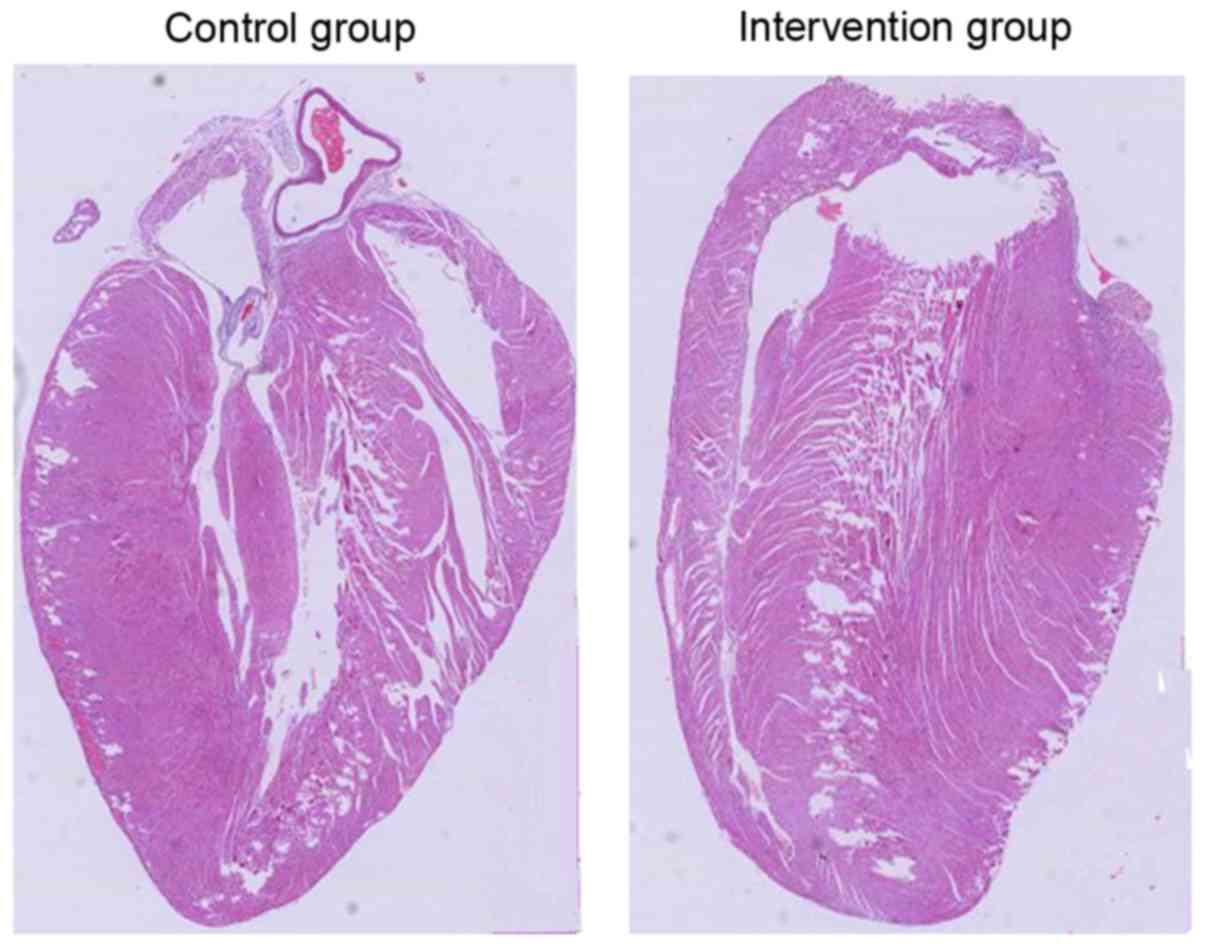
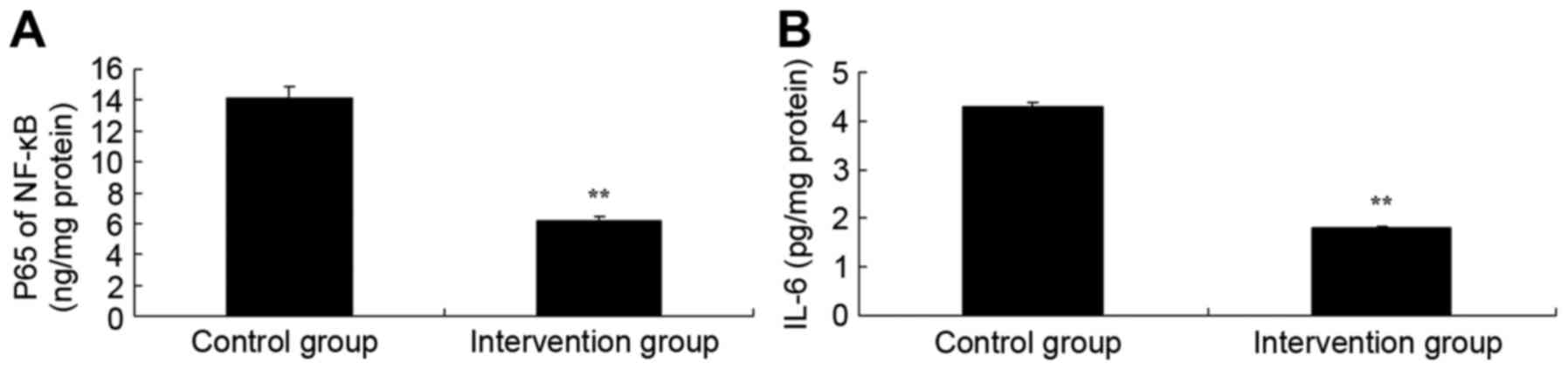
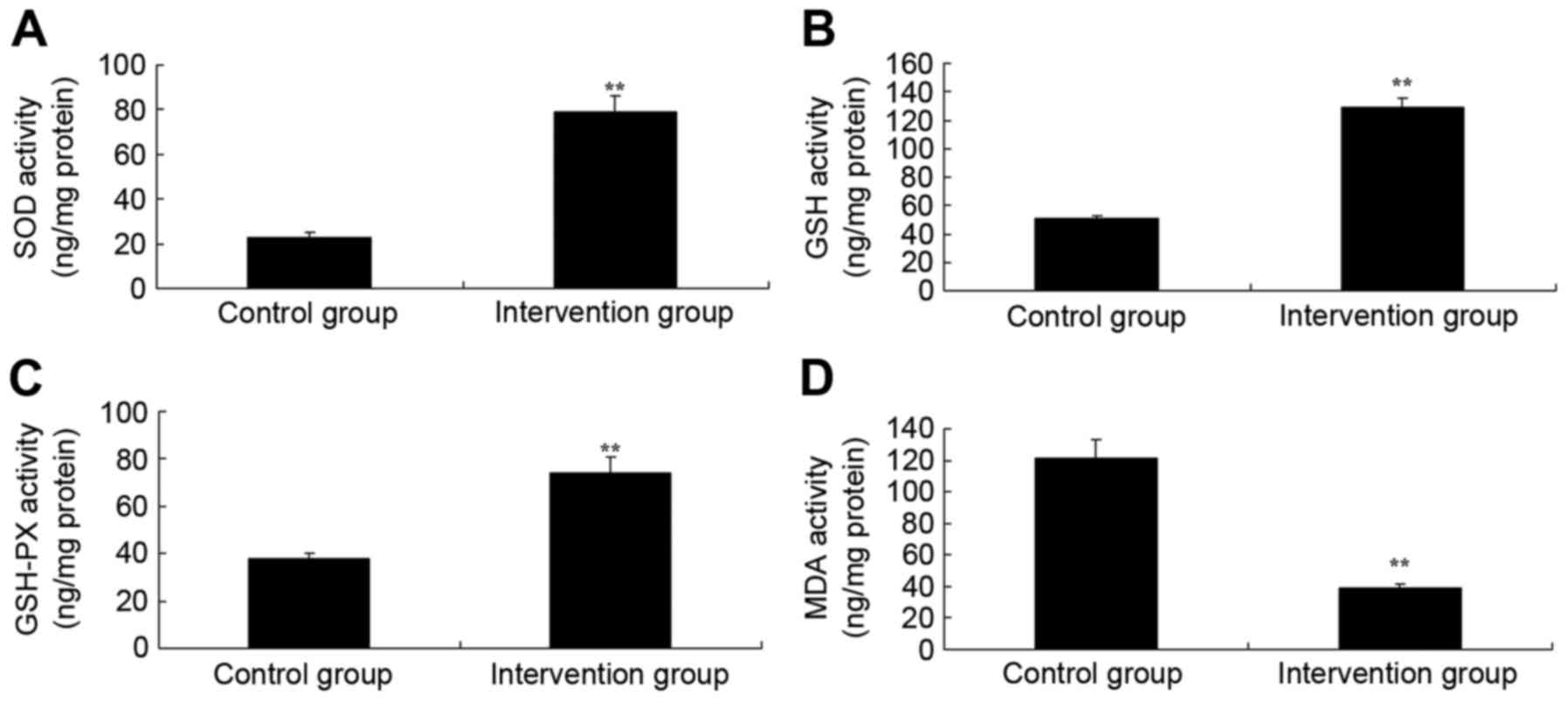
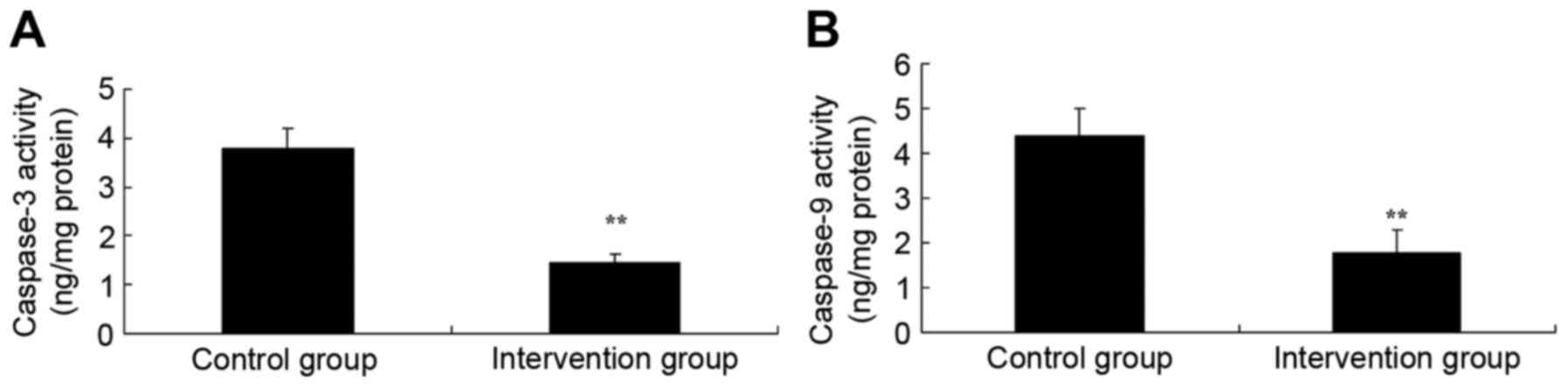
|
1
|
Bayir H, Kapralov AA, Jiang J, Huang Z,
Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Zhao Q, Belikova NA, Vlasova II, Maeda A, et
al: Peroxidase mechanism of lipid-dependent cross-linking of
synuclein with cytochrome C: Protection against apoptosis versus
delayed oxidative stress in Parkinson disease. J Biol Chem.
284:15951–15969. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huerta C, Sánchez-Ferrero E, Coto E,
Blázquez M, Ribacoba R, Guisasola LM, Salvador C and Alvarez V: No
association between Parkinson's disease and three polymorphisms in
the eNOS, nNOS, and iNOS genes. Neurosci Lett. 413:202–205. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Przedborski S, Jackson-Lewis V, Yokoyama
R, Shibata T, Dawson VL and Dawson TM: Role of neuronal nitric
oxide in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
(MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:4565–4571. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pontone GM, Palanci J, Williams JR and
Bassett SS: Screening for DSM-IV-TR cognitive disorder NOS in
Parkinson's disease using the Mattis Dementia Rating Scale. Int J
Geriatr Psychiatry. 28:364–371. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Manosroi A, Kitdamrongtham W, Ishii K,
Shinozaki T, Tachi Y, Takagi M, Ebina K, Zhang J, Manosroi J,
Akihisa R and Akihisa T: Limonoids from Azadirachta indica
var. Siamensis extracts and their cytotoxic and
melanogenesis-inhibitory activities. Chem Biodivers. 11:505–531.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martins VL, Caley MP, Moore K, Szentpetery
Z, Marsh ST, Murrell DF, Kim MH, Avari M, McGrath JA, Cerio R, et
al: Suppression of TGFβ and Angiogenesis by Type VII Collagen in
Cutaneous SCC. J Natl Cancer Inst. 108:pii: djv293. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lindholm EE, Aune E, Noren CB, Seljeflot
I, Hayes T, Otterstad JE and Kirkeboen KA: The anesthesia in
abdominal aortic surgery (ABSENT) study: A prospective, randomized,
controlled trial comparing troponin T release with
fentanyl-sevoflurane and propofol-remifentanil anesthesia in major
vascular surgery. Anesthesiology. 119:802–812. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Klein BY, Tamir H, Hirschberg DL, Ludwig
RJ, Glickstein SB, Myers MM and Welch MG: Oxytocin opposes effects
of bacterial endotoxin on ER-stress signaling in Caco2BB gut cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1860:402–411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoneshima E, Okamoto K, Sakai E,
Nishishita K, Yoshida N and Tsukuba T: The transcription factor EB
(TFEB) regulates osteoblast differentiation through
ATF4/CHOP-dependent pathway. J Cell Physiol. 23:1321–1333. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Restuccia A, Tian YF, Collier JH and
Hudalla GA: Self-assembled glycopeptide nanofibers as modulators of
galectin-1 bioactivity. Cell Mol Bioeng. 8:471–487. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deng LJ, Peng QL, Wang LH, Xu J, Liu JS,
Li YJ, Zhuo ZJ, Bai LL, Hu LP, Chen WM, et al: Arenobufagin
intercalates with DNA leading to G2 cell cycle arrest via ATM/ATR
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:34258–34275. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shrivastava P, Vaibhav K, Tabassum R, Khan
A, Ishrat T, Khan MM, Ahmad A and Islam F, Safhi MM and Islam F:
Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effect of Piperine on 6-OHDA
induced Parkinson's rat model. J Nutr Biochem. 24:680–687. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yasuda T, Hayakawa H, Nihira T, Ren YR,
Nakata Y, Nagai M, Hattori N, Miyake K, Takada M, Shimada T, et al:
Parkin-mediated protection of dopaminergic neurons in a chronic
MPTP-minipump mouse model of Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 70:686–697. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Y, Wang D, Xu T, Liu P, Cao Y, Wang
Y, Yang X, Xu X, Wang X and Niu H: Bladder cancer cells re-educate
TAMs through lactate shuttling in the microfluidic cancer
microenvironment. Oncotarget. 6:39196–39210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Soares DG, Godin AM, Menezes RR, Nogueira
RD, Brito AM, Melo IS, Coura GM, Souza DG, Amaral FA, Paulino TP,
et al: Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of
azadirachtin in mice. Planta Med. 80:630–636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim WH, Song HO, Jin CM, Hur JM, Lee HS,
Jin HY, Kim SY and Park H: The methanol extract of Azadirachta
indica A. Juss leaf protects mice against lethal endotoxemia
and sepsis. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 20:96–103. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Omobowale TO, Oyagbemi AA, Oyewunmi OA and
Adejumobi OA: Chemopreventive effect of methanolic extract of
Azadirachta indica on experimental Trypanosoma brucei
induced oxidative stress in dogs. Pharmacognosy Res. 7:249–258.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S, Moneim Abdel AE
and Delic D: Protective effect of Azadirachta indica extract
against Eimeria papillata-induced coccidiosis. Parasitol
Res. 112:101–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rodriguez DAO, de Lima RF, Campos MS,
Costa JR, Biancardi MF, Marques MR, Taboga SR and Santos FCA:
Intrauterine exposure to bisphenol A promotes different effects in
both neonatal and adult prostate of male and female gerbils
(Meriones unguiculatus). Environ Toxicol. 31:1740–1750.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yue K, Trujillo-de Santiago G, Alvarez MM,
Tamayol A, Annabi N and Khademhosseini A: Synthesis, properties and
biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels.
Biomaterials. 73:254–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan Y, Martin LM, Bosco DB, Bundy JL,
Nowakowski RS, Sang QX and Li Y: Differential effects of acellular
embryonic matrices on pluripotent stem cell expansion and neural
differentiation. Biomaterials. 73:231–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koyano-Nakagawa N, Shi X, Rasmussen TL,
Das S, Walter CA and Garry DJ: Feedback mechanisms regulate Ets
variant 2 (Etv2) gene expression and hematoendothelial lineages. J
Biol Chem. 290:28107–28119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Warsinske HC, Ashley SL, Linderman JJ,
Moore BB and Kirschner DE: Identifying mechanisms of homeostatic
signaling in fibroblast differentiation. Bull Math Biol.
77:1556–1582. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyamoto DT, Zheng Y, Wittner BS, Lee RJ,
Zhu H, Broderick KT, Desai R, Fox DB, Brannigan BW, Trautwein J, et
al: RNA-Seq of single prostate CTCs implicates noncanonical Wnt
signaling in antiandrogen resistance. Science. 349:1351–1356. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khoo NK, Cantu-Medellin N, St Croix C and
Kelley EE: In vivo immuno-spin trapping: Imaging the footprints of
oxidative stress. Curr Protoc Cytom. 74:12.42.1–11. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|