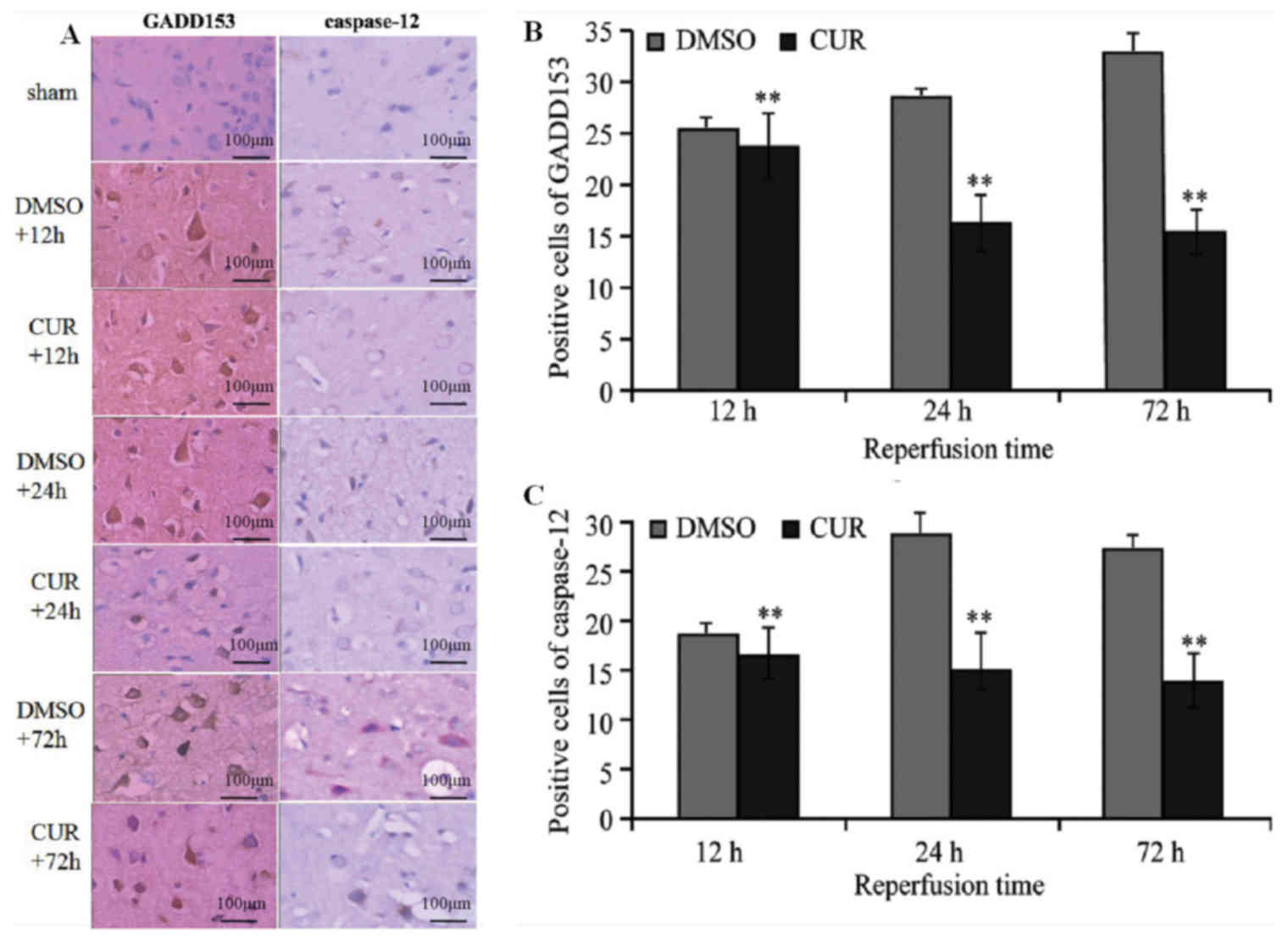
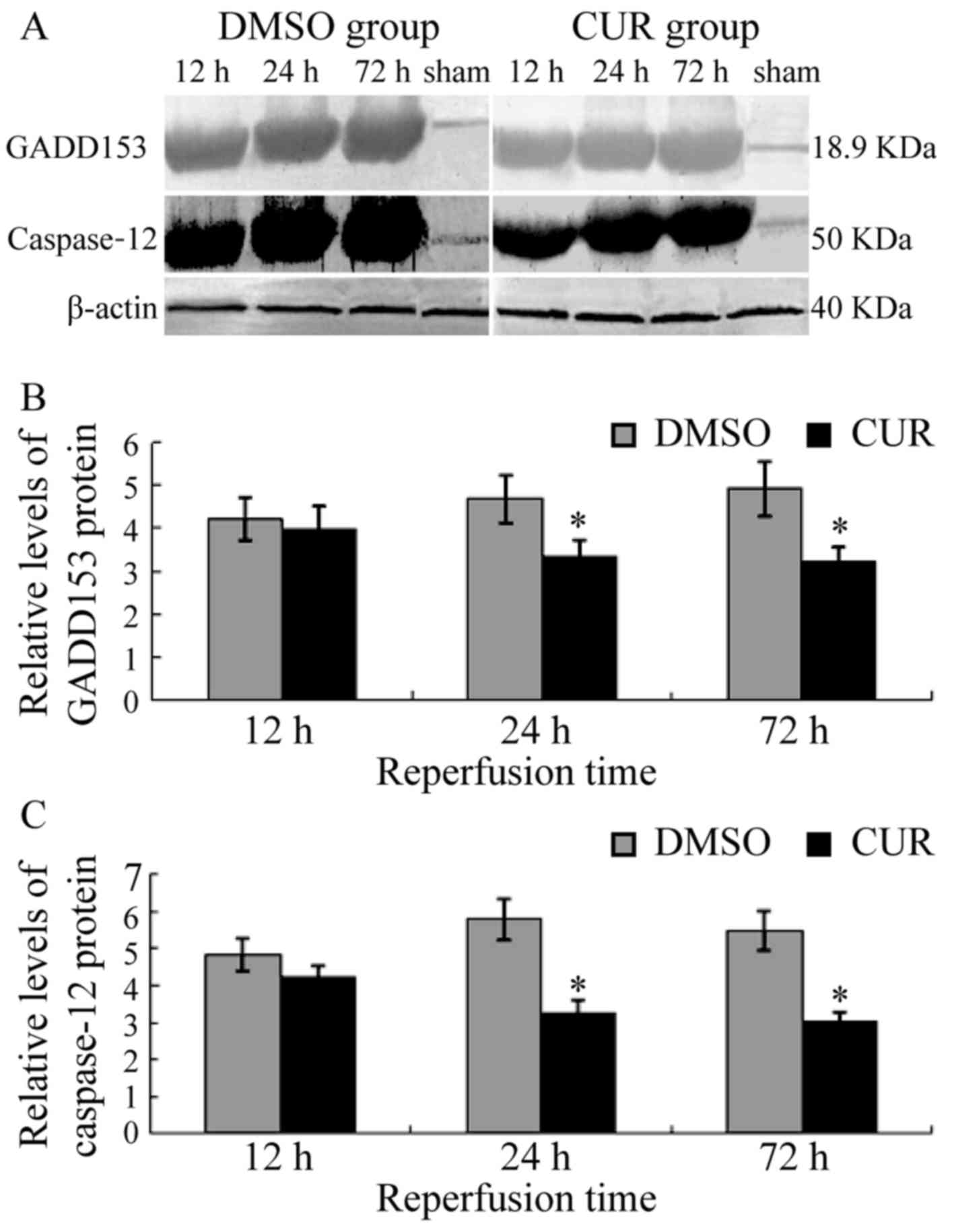
|
1
|
Verkhratsky A: Physiology and
pathophysiology of the calcium store in the endoplasmic reticulum
of neurons. Physiol Rev. 85:201–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boyce M and Yuan J: Cellular response to
endoplasmic reticulum stress: A matter of life or death. Cell Death
Differ. 13:363–373. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hetz C: The unfolded protein response:
Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 13:89–102. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu BR, Martone ME, Jones YZ and Liu CL:
Protein aggregation after transient cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci.
20:3191–3199. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ge P, Luo Y, Liu CL and Hu B: Protein
aggregation and proteasome dysfunction after brain ischemia.
Stroke. 38:3230–3236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kohno K, Higuchi T, Ohta S, Kohno K, Kumon
Y and Sakaki S: Neuroprotective nitric oxide synthase inhibitor
reduces intracellular calcium accumulation following transient
global ischemia in the gerbil. Neurosci Lett. 224:17–20. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roberts GG, Di Loreto MJ, Marshall M, Wang
J and DeGracia DJ: Hippocampal cellular stress responses after
global brain ischemia and reperfusion. Antioxid Redox Signal.
9:2265–2275. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakka VP, Gusain A and Raghubir R:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage
after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neurotox Res.
17:189–202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shibata M, Hattori H, Sasaki T, Gotoh J,
Hamada J and Fukuuchi Y: Activation of caspase-12 by endoplasmic
reticulum stress induced by transient middle cerebral artery
occlusion in mice. Neuroscience. 118:491–499. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tajiri S, Oyadomari S, Yano S, Morioka M,
Gotoh T, Hamada JI, Ushio Y and Mori M: Ischemic-induced neuronal
cell death is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway
involving CHOP. Cell Death Differ. 11:403–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou H, Beevers CS and Huang S: The
targets of curcumin. Curr Drug Targets. 12:332–347. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Onder A, Kapan M, Gümüş M, Yüksel H, Böyük
A, Alp H, Başarili MK and Firat U: The protective effects of
curcumin on intestine and remote organs against mesenteric
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Turk J Gastroenterol. 23:141–147.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang J, Wang W, Sun YJ, Hu M, Li F and
Zhu DY: Neuroprotective effect of curcumin on focal cerebral
ischemic rats by preventing blood-brain barrier damage. Eur J
Pharmacol. 561:54–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang TF, Zhang YJ, Zhou HY, Wang HM, Tian
LP, Liu J, Ding JQ and Chen SD: Curcumin ameliorates the
neurodegenerative pathology in A53T α-synuclein cell model of
Parkinson's disease through the downregulation of mTOR/p70S6K
signaling and the recovery of macroautophagy. J Neuroimmune
Pharmacol. 8:356–369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reddy PH, Manczak M, Yin X, Grady MC,
Mitchell A, Kandimalla R and Kuruva CS: Protective effects of a
natural product, curcumin, against amyloid β induced mitochondrial
and synaptic toxicities in Alzheimer's disease. J Investig Med.
64:1220–1234. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng HL, Dang HZ, Fan H, Chen XP, Rao YX,
Ren Y, Yang JD, Shi J, Wang PW and Tian JZ: Curcumin ameliorates
insulin signaling pathway in brain of Alzheimer's disease
transgenic mice. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 29:734–741. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pluta R, Bogucka-Kocka A, Ułamek-Kozioł M,
Furmaga-Jabłońska W, Januszewski S, Brzozowska J, Jabłoński M and
Kocki J: Neurogenesis and neuroprotection in postischemic brain
neurodegeneration with Alzheimer phenotype: Is there a role for
curcumin? Folia Neuropathol. 53:89–99. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animalsGuide for
the Care & Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th. Washington (DC):
National Academies Press (US); 2011, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao H, Gao J, Feng YB, Pang ZY and Chi ZF:
2R, 4R-APDC decreases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of
adult rats: The effect of 2R, 4R-APDC on cell proliferation.
Neuroreport. 18:1459–1462. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
DeGracia DJ and Montie HL: Cerebral
ischemia and the unfolded protein response. J Neurochem. 91:1–8.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boyce M, Bryant KF, Jousse C, Long K,
Harding HP, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Ma D, Coen DM, Ron D and Yuan
J: A selective inhibitor of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation protects
cells from ER stress. Science. 307:935–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee DY, Lee KS, Lee HJ, Kim DH, Noh YH, Yu
K, Jung HY, Lee SH, Lee JY, Youn YC, et al: Activation of PERK
signaling attenuates Abeta-mediated ER stress. PLoS One.
5:e104892010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lamkanfi M, Kalai M and Vandenabeele P:
Caspase-12: An overview. Cell Death Differ. 11:365–368. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li G, Mongillo M, Chin KT, Harding H, Ron
D, Marks AR and Tabas I: Role of ERO1-mediated stimulation of
inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor activity in endoplasmic
reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 186:783–792. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Timmins JM, Ozcan L, Seimon TA, Li G,
Malagelada C, Backs J, Backs T, Bassel-Duby R, Olson EN, Anderson
ME and Tabas I: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
links endoplasmic reticulum stress with Fas and mitochondrial
apoptosis pathways. J Clin Invest. 119:2925–2941. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McCullough KD, Martindale JL, Klotz LO, Aw
TY and Holbrook NJ: Gadd153 sensitizes cells to endoplasmic
reticulum stress by down-regulating Bcl-2 and perturbing the
cellular redox state. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1249–1259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ferri KF and Kroemer G: Organelle-specific
initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol. 3:E255–E263.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maheshwari RK, Singh AK, Gaddipati J and
Srimal RC: Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short
review. Life Sci. 78:2081–2087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Lei P and Safe
S: Inhibition of NFkappaB and pancreatic cancer cell and tumor
growth by curcumin is dependent on specificity protein
downregulation. J Biol Chem. 285:25332–25344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chhunchha B, Fatma N, Kubo E, Rai P, Singh
SP and Singh DP: Curcumin abates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress
based-ER stress-mediated cell death in mouse hippocampal cells
(HT22) by controlling Prdx6 and NF-κB regulation. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 304:C636–C655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun Q, Jia N, Wang W, Jin H, Xu J and Hu
H: Activation of SIRT1 by curcumin blocks the neurotoxicity of
amyloid-β25–35 in rat cortical neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
448:89–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang L, Zhang B, Huang F, Liu B and Xie Y:
Curcumin inhibits lipolysis via suppression of ER stress in adipose
tissue and prevents hepatic insulin resistance. J Lipid Res.
57:1243–1255. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|