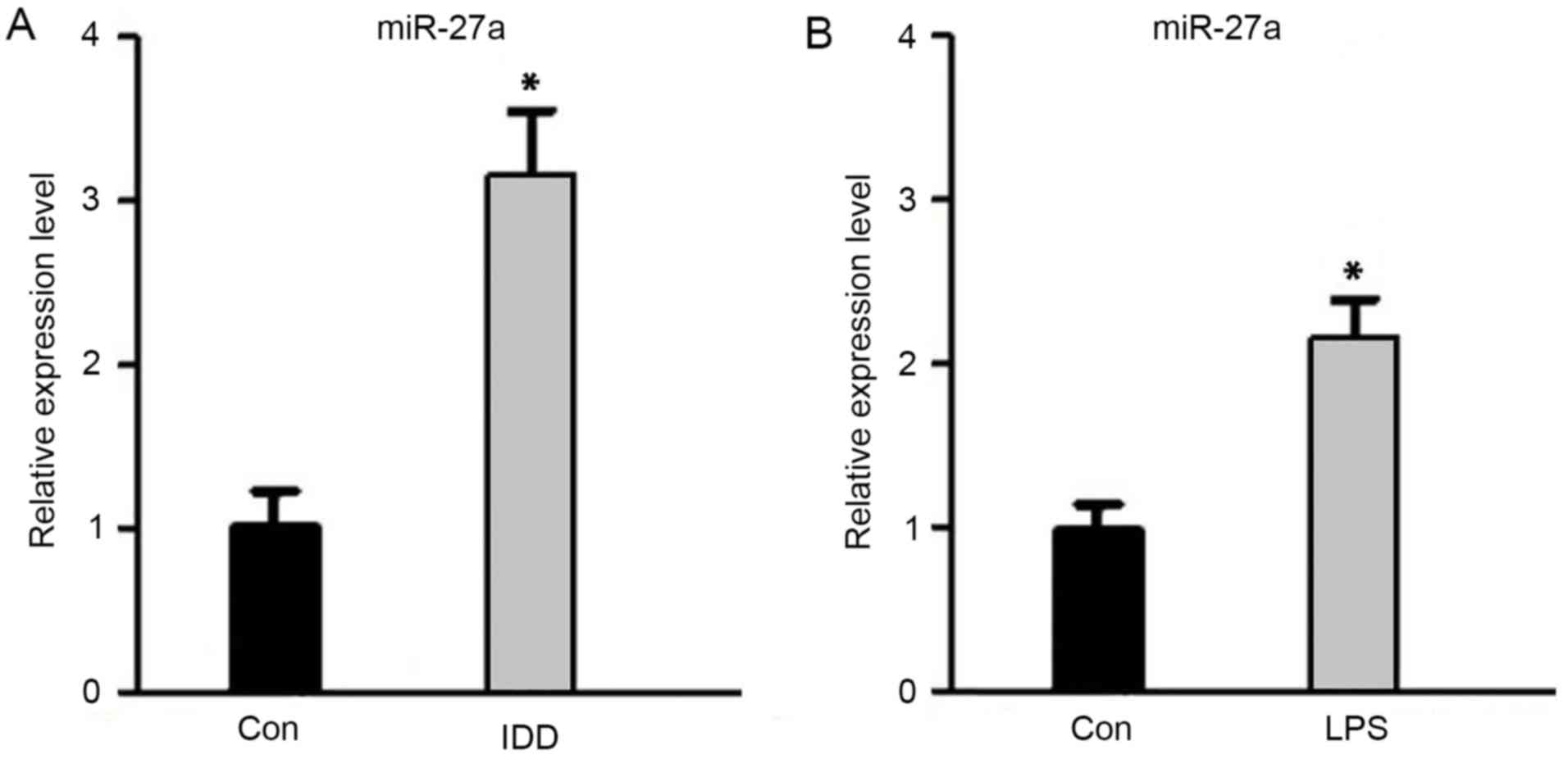
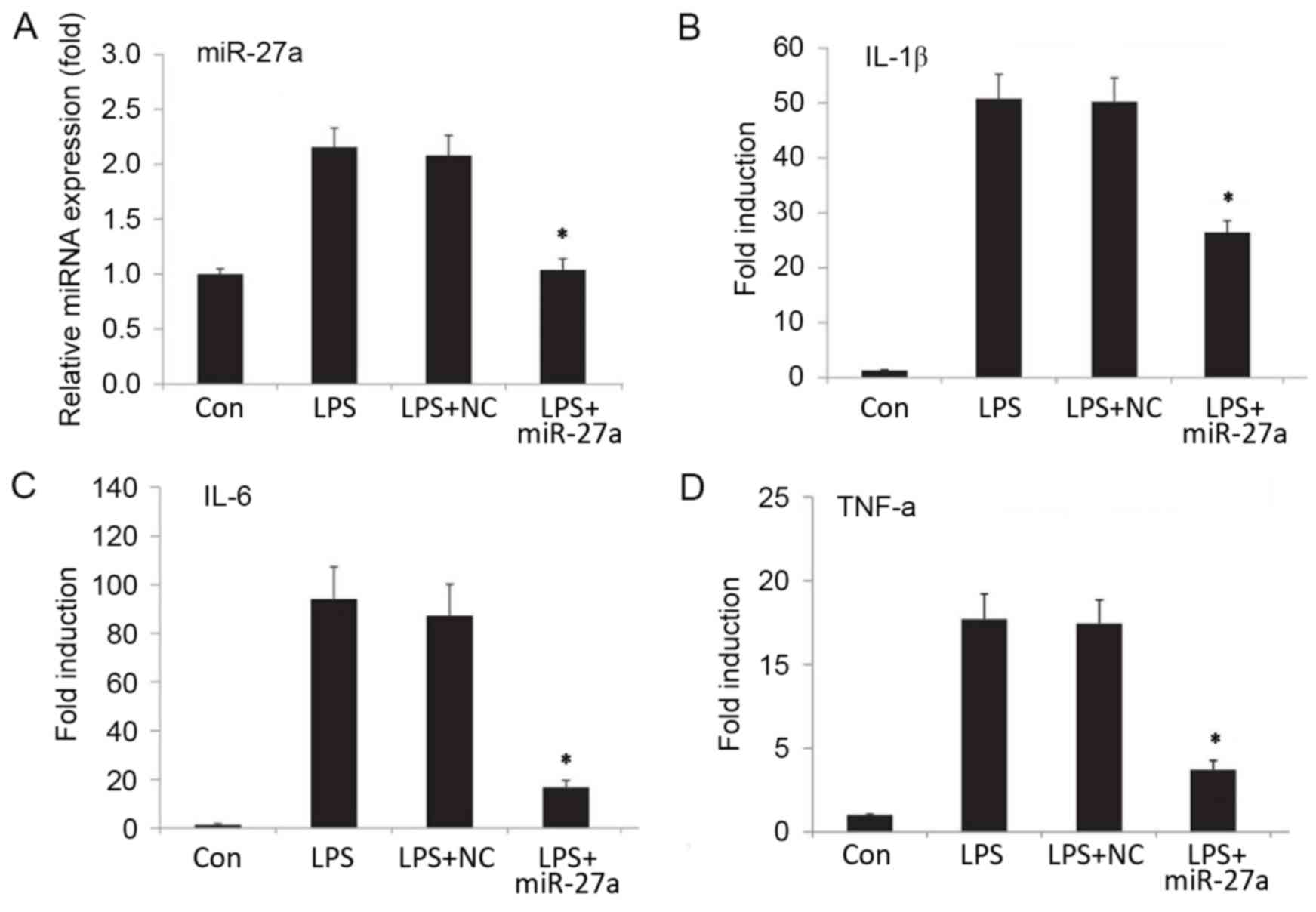
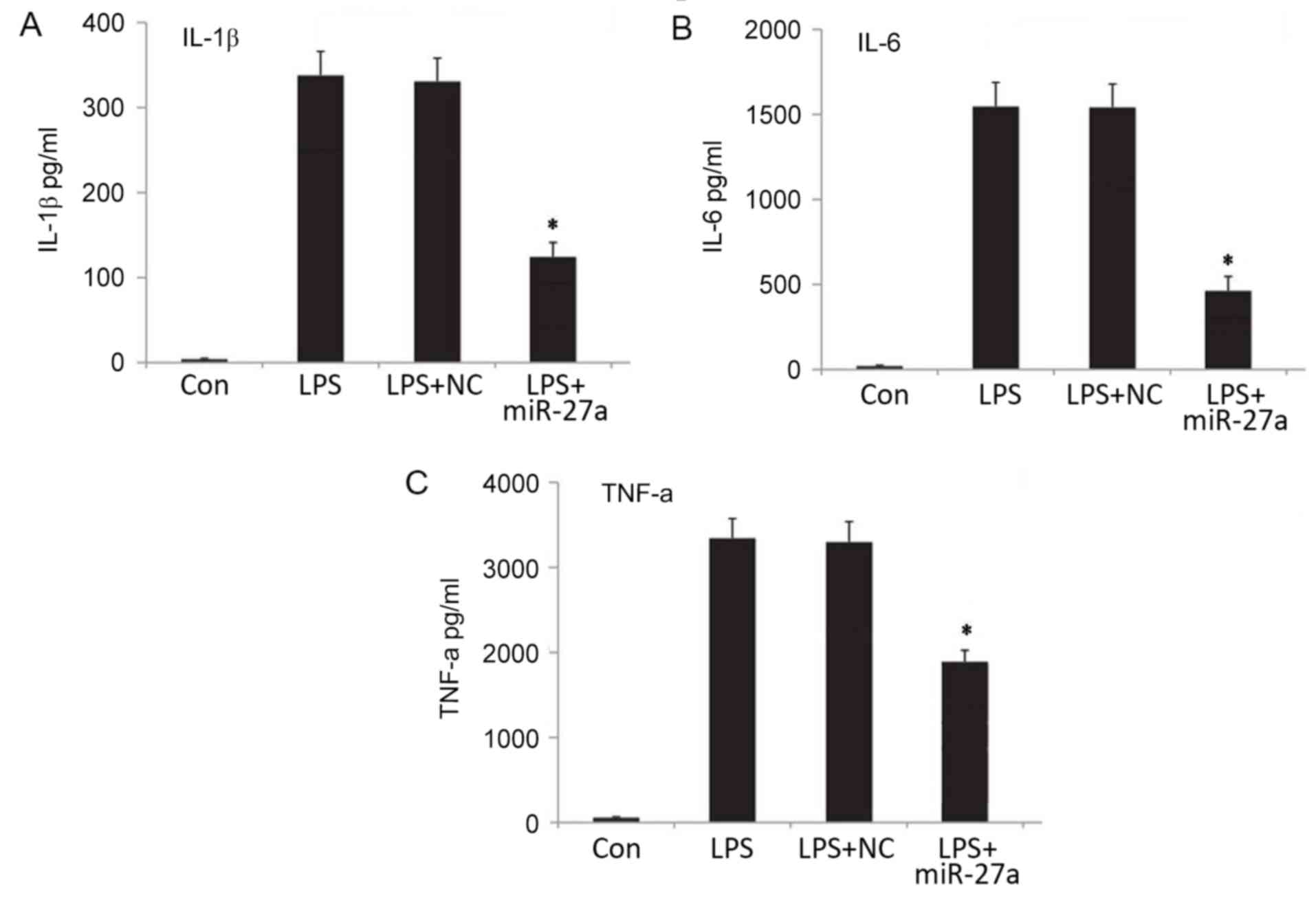
|
1
|
Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R,
Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V,
et al: Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289
diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the
Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 380:2163–2196. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gore M, Sadosky A, Stacey BR, Tai KS and
Leslie D: The burden of chronic low back pain: Clinical
comorbidities, treatment patterns, and health care costs in usual
care settings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:E668–E677. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Millecamps M, Tajerian M, Naso L, Sage EH
and Stone LS: Lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration associated
with axial and radiating low back pain in ageing SPARC-null mice.
Pain. 153:1167–1179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Adams MA and Roughley PJ: What is
intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 31:2151–2161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mayer JE, Iatridis JC, Chan D, Qureshi SA,
Gottesman O and Hecht AC: Genetic polymorphisms associated with
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 13:299–317. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Freemont AJ: The cellular pathobiology of
the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 48:5–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Z, Liang J, Wu WK, Yu X, Yu J, Weng X
and Shen J: Leptin activates RhoA/ROCK pathway to induce
cytoskeleton remodeling in nucleus pulposus cells. Int J Mol Sci.
15:1176–1188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Yu X, Liang J, Qiu G
and Liu J: The role of leptin on the organization and expression of
cytoskeleton elements in nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res.
31:847–857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ellman MB, Kim JS, An HS, Chen D, KC R, An
J, Dittakavi T, van Wijnen AJ, Cs-Szabo G, Li X, et al: Toll-like
receptor adaptor signaling molecule MyD88 on intervertebral disk
homeostasis: In vitro, ex vivo studies. Gene. 505:283–290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwata M, Ochi H, Asou Y, Haro H, Aikawa T,
Harada Y, Nezu Y, Yogo T, Tagawa M and Hara Y: Variations in gene
and protein expression in canine chondrodystrophic nucleus pulposus
cells following long-term three-dimensional culture. PLoS One.
8:e631202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
Elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Teague EM, Print CG and Hull ML: The role
of microRNAs in endometriosis and associated reproductive
conditions. Hum Reprod Update. 16:142–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang HQ, Yu XD, Liu ZH, Cheng X, Samartzis
D, Jia LT, Wu SX, Huang J, Chen J and Luo ZJ: Deregulated miR-155
promotes Fas-mediated apoptosis in human intervertebral disc
degeneration by targeting FADD and caspase-3. J Pathol.
225:232–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu X, Li Z, Shen J, Wu WK, Liang J, Weng X
and Qiu G: MicroRNA-10b promotes nucleus pulposus cell
proliferation through RhoC-Akt pathway by targeting HOXD10 in
intervetebral disc degeneration. PLoS One. 8:e830802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohrt-Nissen S, Dөssing KB, Rossing M,
Lajer C, Vikeså J, Nielsen FC, Friis-Hansen L and Dahl B:
Characterization of miRNA expression in human degenerative lumbar
disks. Connect Tissue Res. 54:197–203. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, Huang X, Liu X, Xiao S, Zhang Y,
Xiang T, Shen X, Wang G and Sheng B: miR-21 promotes human nucleus
pulposus cell proliferation through PTEN/AKT signaling. Int J Mol
Sci. 15:4007–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu G, Cao P, Chen H, Yuan W, Wang J and
Tang X: MiR-27a regulates apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells by
targeting PI3K. PLoS One. 8:e752512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji J, Zhang J, Huang G, Qian J, Wang X and
Mei S: Over-expressed microRNA-27a and 27b influence fat
accumulation and cell proliferation during rat hepatic stellate
cell activation. FEBS Lett. 583:759–766. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu T, Tang H, Lang Y, Liu M and Li X:
MicroRNA-27a functions as an oncogene in gastric adenocarcinoma by
targeting prohibitin. Cancer Lett. 273:233–242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma Y, Yu S, Zhao W, Lu Z and Chen J:
miR-27a regulates the growth, colony formation and migration of
pancreatic cancer cells by targeting Sprouty2. Cancer Lett.
298:150–158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao B, Yu Q, Li H, Guo X and He X:
Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in patients with
intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Med. 33:43–50. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M,
Hodler J and Boos N: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
26:1873–1878. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao L, Lu X and Cao Y: MicroRNA and
signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response. Cell
Signal. 25:1625–1634. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ell B and Kang Y: MicroRNAs as regulators
of bone homeostasis and bone metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 3:5492014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao X, Yang L and Hu J: Down-regulation
of miR-27a might inhibit proliferation and drug resistance of
gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Drayton RM, Dudziec E, Peter S, Bertz S,
Hartmann A, Bryant HE and Catto JW: Reduced expression of miRNA-27a
modulates cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by targeting the
cystine/glutamate exchanger SLC7A11. Clin Cancer Res. 20:1990–2000.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hezova R, Kovarikova A, Bienertova-Vasku
J, Sachlova M, Redova M, Vasku A, Svoboda M, Radova L, Kiss I,
Vyzula R and Slaby O: Evaluation of SNPs in miR-196-a2, miR-27a and
miR-146a as risk factors of colorectal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:2827–2831. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gruber HE, Norton HJ, Sun Y and Hanley EN
Jr: Crystal deposits in the human intervertebral disc: Implications
for disc degeneration. Spine J. 7:444–450. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wuertz K, Vo N, Kletsas D and Boos N:
Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: The
roles of NF-kB and MAP kinases. Eur Cell Mater. 23:103–120.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kokubo Y, Uchida K, Kobayashi S, Yayama T,
Sato R, Nakajima H, Takamura T, Mwaka E, Orwotho N, Bangirana A and
Baba H: Herniated and spondylotic intervertebral discs of the human
cervical spine: Histological and immunohistological findings in 500
en bloc surgical samples. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg
Spine. 9:285–295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvis W, So S, Chen
J, Jing L, Bullock R, Isaacs RE, Brown C and Richardson WJ:
Proinflammatory cytokine expression profile in degenerated and
herniated human intervertebral disc tissues. Arthritis Rheum.
62:1974–1982. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu C, Yang H, Gao F, Li X, An Y, Wang J
and Jin A: Resistin promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by
upregulation of ADAMTS-5 through p38MAPK signaling pathway. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 41:1414–1420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|