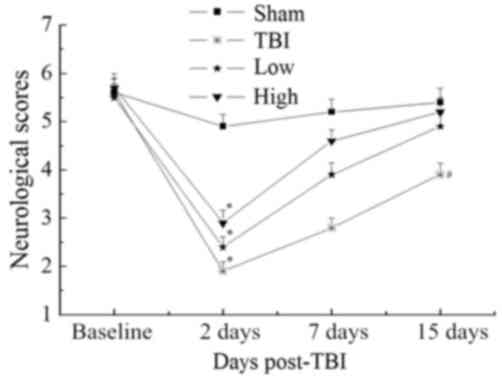
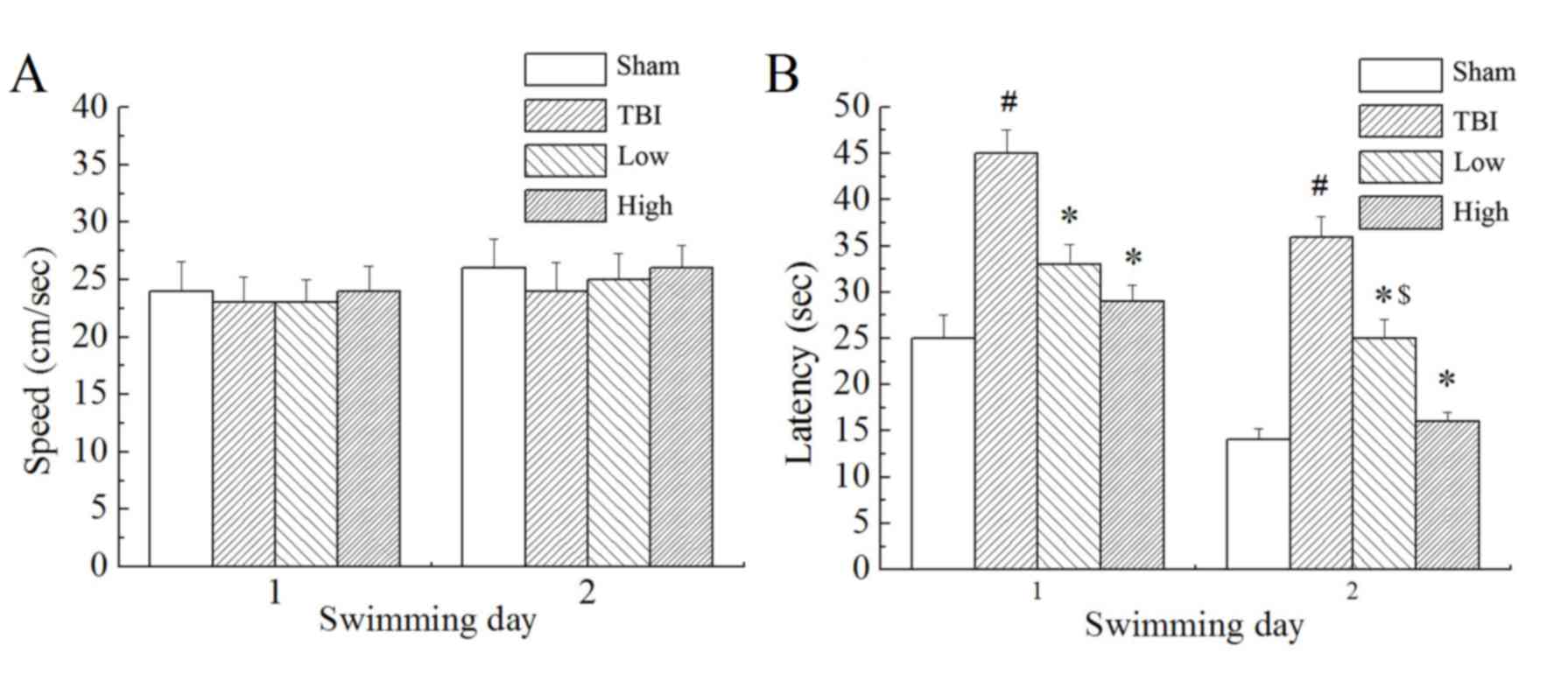
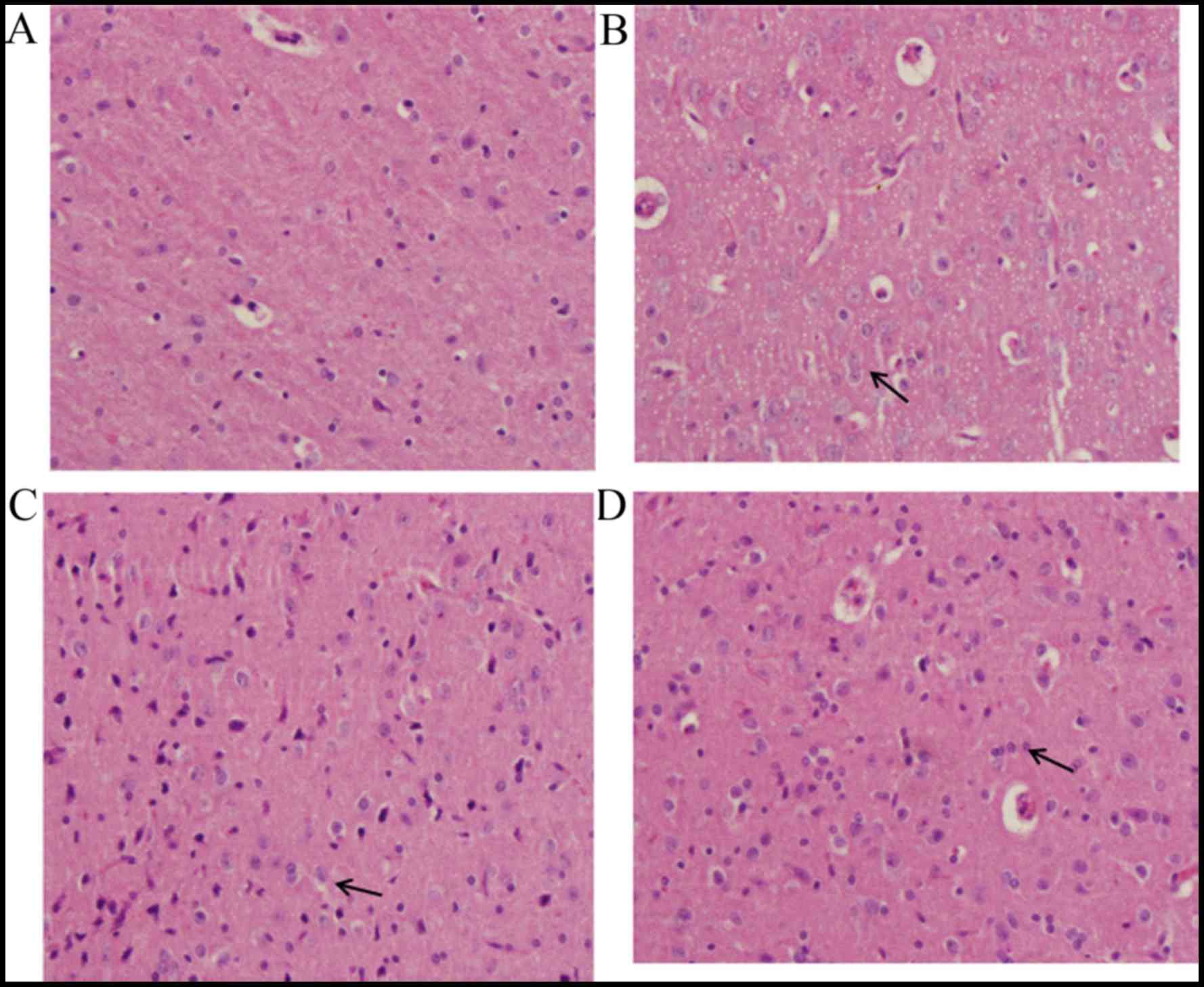
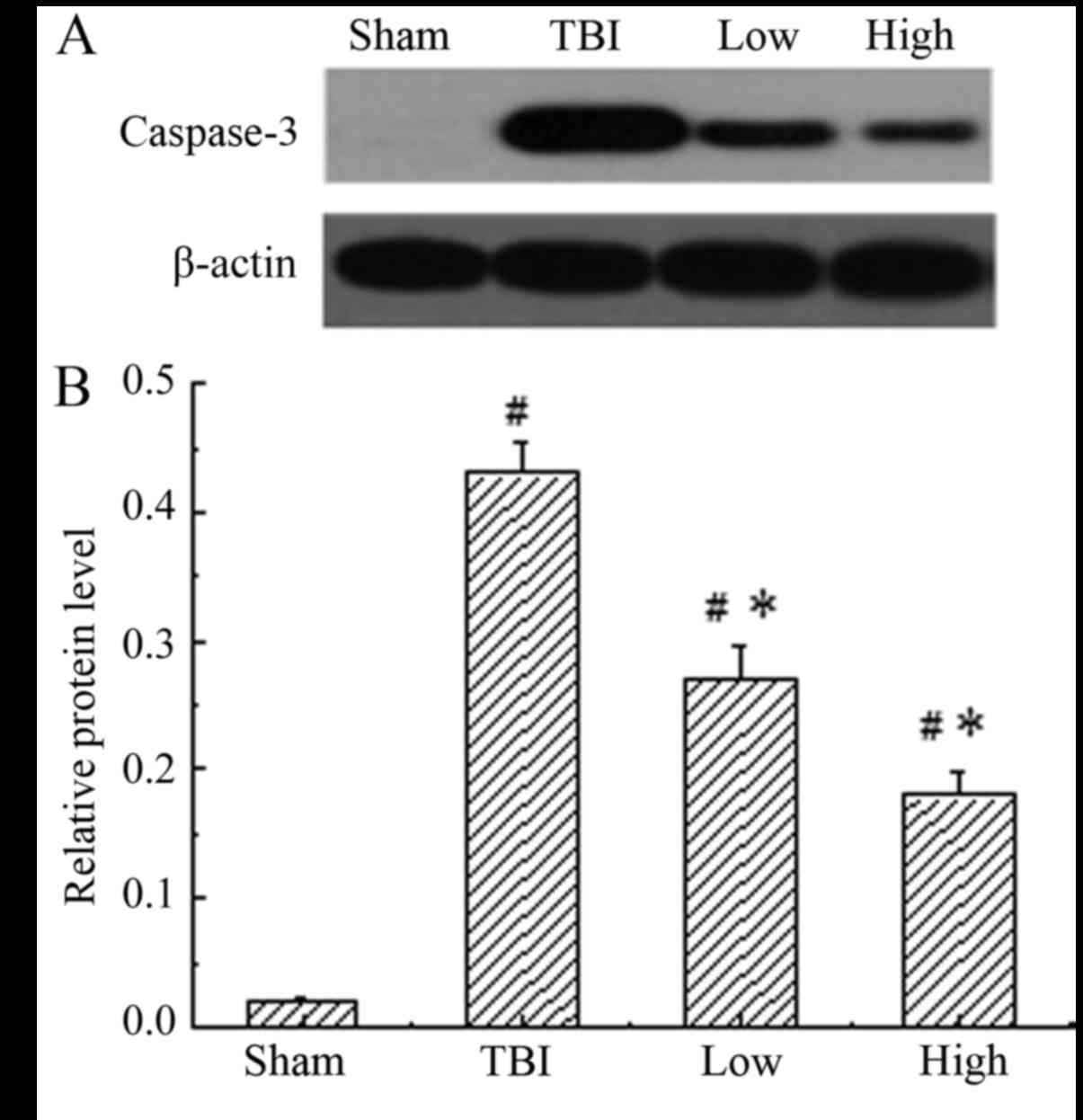
|
1
|
Maas AI, Stocchetti N and Bullock R:
Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet
Neurol. 7:728–741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lauterbach MD, Notarangelo PL, Nichols SJ,
Lane KS and Koliatsos VE: Diagnostic and treatment challenges in
traumatic brain injury patients with severe neuropsychiatric
symptoms: Insights into psychiatric practice. Neuropsychiatr Dis
Treat. 11:1601–1607. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McIntosh TK: Neurochemical sequelae of
traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic implication. Cerebrovasc Brain
Metabol Rev. 6:109–162. 1994.
|
|
4
|
Park E, Bell JD and Baker AJ: Traumatic
brain injury: Can the consequences be stopped. CMAJ. 178:1163–1170.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raghupathi R, Conti AC, Graham DI,
Krajewski S, Reed JC, Grady MS, Trojanowski JQ and McIntosh TK:
Mild traumatic brain injury induces apoptotic cell death in the
cortex that is preceded by decreased in cellular Bcl-2
immunoreactivity. Neuroscience. 110:605–616. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McHugh GS, Engel DC, Butcher I, Steyerberg
EW, Lu J, Mushkudiani N, Hernández AV, Marmarou A, Maas AI and
Murray GD: Prognostic value of secondary insults in traumatic brain
injury: Results from the IMPACT study. J Neurotrauma. 24:287–293.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
King JT Jr, Carlier PM and Marion DW:
Early glasgow outcome scale scores predict long-term functional
outcome in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J
Neurotrauma. 22:947–954. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fork M, Bartels C, Ebert AD, Grubich C,
Synowitz H and Wallesch CW: Neuropsychological sequelae of diffuse
traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 19:101–108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bao HJ, Wang T, Zhang MY, Liu R, Dai DK,
Wang YQ, Wang L, Zhang L, Gao YZ, Qin ZH, et al: Poloxamer-188
attenuates TBI-induced blood-brain barrier damage leading to
decreased brain edema and reduced cellular death. Neurochem Res.
37:2856–2867. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lenzlinger PM, Morganti-Kossmann MC,
Laurer HL and McIntosh TK: The duality of the inflammatory response
to traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol. 24:169–181. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liou AK, Clark RS, Henshall DC, Yin XM and
Chen J: To die or not to die for neurons in ischemia, traumatic
brain injury and epilepsy: A review on the stress-activated
signaling pathways and apoptotic pathways. Prog Neurobiol.
69:103–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu A, Ying Z and Gomez-Pinilla F: The
salutary effects of DHA dietary supplementation on cognition,
neuroplasticity and membrane homeostasis after brain trauma. J
Neurotrauma. 28:2113–2122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cole GM, Ma QL and Frautschy SA: Dietary
fatty acids and the aging brain. Nutr Rev. 68:S102–111. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bousquet M, Calon F and Cicchetti F:
Impact of ω-3 fatty acids in Parkinson's disease. Ageing Res Rev.
10:453–463. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalmijn S, Feskens EJ, Launer LJ and
Kromhout D: Polyunsaturated fatty acids, antioxidants and cognitive
function in very old men. Am J Epidemiol. 145:33–41. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dyall SC: Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids
and the brain: A review of the independent and shared effects of
EPA, DPA and DHA. Front Aging Neurosci. 7:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu A, Ying Z and Gomez-Pinilla F: Omega-3
fatty acids supplementation restores mechanisms that maintain brain
homeostasis in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 24:1587–1595.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang PK, Khatchadourian A, McKinney RA
and Maysinger D: Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): A modulator of
microglia activity and dendritic spine morphology. J
Neuroinflammation. 12:342015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pusceddu MM, Kelly P, Stanton C, Cryan JF
and Dinan TG: N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids through the lifespan:
Implication for psychopathology. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.
19:pyw0782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen W, Esselman WJ, Jump DB and Busik JV:
Anti-inflam-matory effect of docosahexaenoic acid on
cytokine-induced adhesion molecule expression in human retinal
vascular endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
46:4342–4347. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Florent S, Malaplate-Armand C, Youssef I,
Kriem B, Koziel V, Escanyé MC, Fifre A, Sponne I, Leininger-Muller
B, Olivier JL, et al: Docosahexaenoic acid prevents neuronal
apoptosis induced by soluble amyloid-beta oligomers. J Neurochem.
96:385–395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gyoneva S and Ransohoff RM: Inflammatory
reaction after traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic potential of
targeting cell-cell communication by chemokines. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 36:471–480. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McIntosh TK, Vink R, Noble L, Yamakami I,
Fernvak S, Soares H and Faden AL: Traumatic brain injury in the
rat: Characterization of a lateral fluid-percussion model.
Neuroscience. 28:233–244. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohlsson AL and Johansson BB: Environment
influences functional outcome of cerebral infarction in rats.
Stroke. 26:644–649. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gasparovic C, Yeo R, Mannell M, Ling J,
Elgie R, Phillips J, Doezema D and Mayer AR: Neurometabolite
concentrations in gray and white matter in mild traumatic brain
injury: An 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Neurotrauma.
26:1635–1643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nguemeni C, Delplanque B, Rovère C,
Simon-Rousseau N, Gandin C, Agnani G, Nahon JL, Heurteaux C and
Blondeau N: Dietary supplementation of alpha-linolenic acid in an
enriched rapeseed oil diet protects from stroke. Pharmacol Res.
61:226–233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Martín A, Boisgard R, Kassiou M, Dollé F
and Tavitian B: Reduced PBR/TSPO expression after minocycline
treatment in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia: A PET study
using (18)F]DPA-714. Mol Imaging Biol. 13:10–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bailes JE and Mills JD: Docosahexaenoic
acid reduces traumatic axonal injury in a rodent head injury model.
J Neurotrauma. 27:1617–1624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC, Chen M,
Dixon CE, Seidberg NA, Melick J, Loeffert JE, Nathaniel PD, Jin KL
and Graham SH: Caspase-3 mediated neuronal death after traumatic
brain injury in rats. J Neurochem. 74:740–753. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salakou S, Kardamakis D, Tsamandas AC,
Zolota V, Apostolakis E, Tzelepi V, Papathanasopoulos P, Bonikos
DS, Papapetropoulos T, Petsas T and Dougenis D: Increased Bax/Bcl-2
ratio up-regulates caspase-3 and increases apoptosis in the thymus
of patients with myasthenia gravis. In Vivo. 21:123–132.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Solaroglu I, Tsubokawa T, Cahill J and
Zhang JH: Anti-apoptotic effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating
factor after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience.
143:965–974. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hara A, Hirose Y, Wang A, Yoshimi N,
Tanaka T and Mori H: Localization of Bax and Bcl-2 proteins,
regulators of programmed cell death, in the human central nervous
system. Virchows Arch. 429:249–253. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiao D and Zhang L: Upregulation of Bax
and Bcl-2 following prenatal cocaine exposure induces apoptosis in
fetal rat brain. Int J Med Sci. 5:295–302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kao TK, Ou YC, Kuo JS, Chen WY, Liao SL,
Wu CW, Chen CJ, Ling NN, Zhang YH and Peng WH: Neuroprotection by
tetramethylpyrazine against ischemic brain injury in rats.
Neurochem Int. 48:166–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wei L, Cui L, Snider BJ, Rivkin M, Yu SS,
Lee CS, Adams LD, Gottlieb DI, Johnson EM Jr, Yu SP and Choi DW:
Transplantation of embryonic stem cells overexpressing Bcl-2
promotes functional recovery after transient cerebral ischemia.
Neurobiol Dis. 19:183–193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|